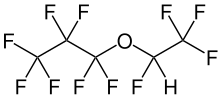
Fluoroether E-1
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
heptafluoropropyl 1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl ether, secondary hydrogen endcap
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.196.998 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5HF11O | |
| Molar mass | 286.044 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.538/cm³ (at 20 °C) |
| Boiling point | 40–42 °C (104–108 °F; 313–315 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H314, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P264+P265, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P319, P321, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Fluoroether E-1 (known chemically as heptafluoropropyl 1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl ether, is a chemical compound that is among the class of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). This synthetic fluorochemical is used in the GenX process, and may arise from the degradation of GenX chemicals including FRD-903.[2][3]
Production
[edit]The main production of Fluoroether E-1 is within the GenX process where FRD-903 (2,3,3,3-tetrafluoro-2-(heptafluoropropoxy)propanoic acid) is used to generate (FRD-902) ammonium 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoro-2-(heptafluoropropoxy)propanoate, and Fluoroether E-1 (heptafluoropropyl 1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl ether).[4]
Properties
[edit]Fluoroether E-1 is a colorless liquid that is practically insoluble in water. It is volatile and has a low boiling point.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ "Heptafluoropropyl 1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl ether". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ Zhang, Chuhui; McElroy, Amie C.; Liberatore, Hannah K.; Alexander, Nancy Lee M.; Knappe, Detlef R.U. (2022-05-17). "Stability of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Solvents Relevant to Environmental and Toxicological Analysis". Environmental Science & Technology. 56 (10): 6103–6112. doi:10.1021/acs.est.1c03979. ISSN 0013-936X. PMC 9065217. PMID 34734715.
- ^ Wickersham, Lindsay (10 March 2023). "Characterization of PFAS air emissions from thermal application of fluoropolymer dispersions on fabrics". Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association. 73 (7): 533–552. doi:10.1080/10962247.2023.2192009. PMC 10628852. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- ^ "Antwoord van Gedeputeerde Staten op vragen van W.A. Minderhout (PvdA)" [Answer from the Provincial Executive to questions from W.A. Minderhout (PvdA)] (PDF). Provincie Holland Zuid (in Dutch). 2015-09-15. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-02-08. Retrieved 2023-09-15.
- ^ "Heptafluoropropyl 1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl ether" (PDF). Apollo Scientific. 2023-10-07. Retrieved 2023-09-15.

