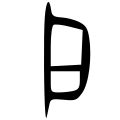
Radical 63
| 戶 | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| 戶 (U+6236) "door, house" | ||
| Pronunciations | ||
| Pinyin: | hù | |
| Bopomofo: | ㄏㄨˋ | |
| Wade–Giles: | hu4 | |
| Cantonese Yale: | wuh | |
| Jyutping: | wu6 | |
| Pe̍h-ōe-jī: | hō͘ | |
| Japanese Kana: | コ ko (on'yomi) と to (kun'yomi) | |
| Sino-Korean: | 호 ho | |
| Names | ||
| Chinese name(s): | 戶字頭/户字头 hùzìtóu | |
| Japanese name(s): | 扉の戸 tobiranoto | |
| Hangul: | 지게 jige | |
| Stroke order animation | ||
 | ||
Radical 63 or radical door (戶部) meaning "door" is one of the 34 Kangxi radicals (214 radicals in total) composed of 4 strokes.
In the Kangxi Dictionary, there are 44 characters (out of 49,030) to be found under this radical.
户, the xin zixing (new character form) of 戶, is the 97th indexing component in the Table of Indexing Chinese Character Components predominantly adopted by Simplified Chinese dictionaries published in mainland China. Since the difference between 户 and 戶 is defined as a typeface difference rather than variant forms, no associated indexing component is listed under 户. 户 is also the standard form in Hong Kong Traditional Chinese.
In Japanese jōyō kanji (commonly used kanji), the radical 戶 is replaced with the shinjitai (new) form 戸, while the kyujitai (old) form as a component is used in hyōgai kanji.
Evolution
[edit]-
Oracle bone script character
-
Bronze script character
-
Large seal script character
-
Small seal script character
Derived characters
[edit]| Strokes | Characters |
|---|---|
| +0 | 戶Kangxi/TW 户SC/HK 戸JP |
| +1 | 戹SC/戹TC |
| +3 | 戺SC/戺TC 戻JP (=戾) 戼 (=卯 -> 卩) |
| +4 | 戽SC/戽TC 戾SC/戾TC 房SC/房TC/房JP 所SC/TC/KO/所JP |
| +5 | 扁SC/扁TC/JP 扂SC/扂TC/JP 扃SC/扃TC/JP |
| +6 | 扄 扅SC/扅TC 扆SC/扆TC/JP 扇SC/扇TC/扇JP |
| +7 | 扈SC/扈TC/扈JP |
| +8 | 扉SC/扉TC/扉JP 扊SC/扊TC |
Variant forms
[edit]

This radical takes different forms in different languages or characters.
Traditionally, both 戶 and 戸 were widely used in printing, while 户 was used only as a writing form. In the Kangxi Dictionary, 戶 was chosen as the standard form, which was then inherited by Taiwan Traditional Chinese and Korean hanja.
In mainland China, after the adoption of simplified Chinese characters and xin zixing (new character forms), 户, which used to be a handwriting form, became the standard xin zixing printing form. This change also applies to China's Guo Biao (national standard) Traditional Chinese which is used chiefly in printing Chinese classics. 户 is also the standard form in Hong Kong's List of Graphemes of Commonly-Used Chinese Characters, a non-mandatory standard of Hong Kong Traditional Chinese, though 戶 appears more frequently in daily use. Note that in both mainland China and Hong Kong, the left component of 所 remains to be 戶.
In Japan, the radical 戶 in jōyō kanji (commonly used kanji, including 所) are replaced with its shinjitai form 戸, while in hyōgai kanji (characters from outside the jōyō kanji table), the radical remains to be 戶, causing an inconsistency. Both 戶部 and 戸部 could be used as the radical's names in Japanese dictionaries' indexes.
| Kangxi Dictionary Taiwan Trad. Chinese Japanese hyōgai kanji Korean |
Simplified Chinese Hong Kong Trad. Chinese Guo Biao Trad. Chinese |
Japanese jōyō kanji |
|---|---|---|
| 戶 | 户 | 戸 |
Sinogram
[edit]The radical is also used as an independent Chinese character. It is one of the kyōiku kanji or kanji taught in elementary school in Japan.[1] It is a second grade kanji.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "The Kyoiku Kanji (教育漢字) - Kanshudo". www.kanshudo.com. Archived from the original on March 24, 2022. Retrieved 2023-05-06.
Literature
[edit]- Fazzioli, Edoardo (1987). Chinese calligraphy : from pictograph to ideogram : the history of 214 essential Chinese/Japanese characters. calligraphy by Rebecca Hon Ko. New York: Abbeville Press. ISBN 0-89659-774-1.
- Lunde, Ken (Jan 5, 2009). "Appendix J: Japanese Character Sets" (PDF). CJKV Information Processing: Chinese, Japanese, Korean & Vietnamese Computing (Second ed.). Sebastopol, Calif.: O'Reilly Media. ISBN 978-0-596-51447-1.