Leopold's maneuvers
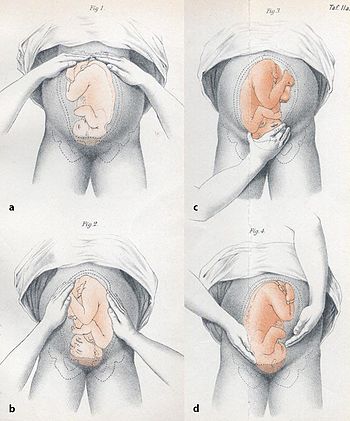
In obstetrics, Leopold maneuvers are a common and systematic way to determine the position of a fetus inside the woman's uterus. They are named after the gynecologist Christian Gerhard Leopold. They are also used to estimate term fetal weight.[1]
The maneuvers consist of four distinct actions, each helping to determine the position of the fetus. The maneuvers are important because they help determine the position and lie of the fetus, which in conjunction with correct assessment of the shape of the maternal pelvis can indicate whether the delivery is going to be complicated, or whether a caesarean section is necessary.
The examiner's skill and practice in performing the maneuvers are the primary factor in whether the fetal lie is correctly ascertained. Alternately, position can be determined by ultrasound performed by a sonographer or physician.
Performing the maneuvers
[edit]Leopold maneuvers are difficult to perform on obese women and women who have polyhydramnios. The palpation can sometimes be uncomfortable for the woman if care is not taken to ensure she is relaxed and adequately positioned. To aid in this, the health care provider should first ensure that the woman has recently emptied her bladder. If she has not, she may need to have a straight urinary catheter inserted to empty it if she is unable to micturate herself. The woman should lie on her back with her shoulders raised slightly on a pillow and her knees drawn up a little. Her abdomen should be uncovered, and most women appreciate it if the individual performing the maneuver warms their hands prior to palpation.
First maneuver: fundal grip
[edit]While facing the woman, palpate the woman's upper abdomen with both hands. An obstetrician can often determine the size, consistency, shape, and mobility of the form that is felt. The fetal head is hard, round, and moves independently of the trunk while the buttocks feel softer, are symmetric, and the shoulders and limbs have small bony processes; unlike the head, they move with the trunk.
Second maneuver: lateral grip
[edit]After the upper abdomen has been palpated and the form that is found is identified, the individual performing the maneuver attempts to determine the location of the fetal back. Still facing the woman, the health care provider palpates the abdomen with gentle but also deep pressure using the palm of the hands. First the right hand remains steady on one side of the abdomen while the left hand explores the right side of the woman's uterus. This is then repeated using the opposite side and hands. The fetal back will feel firm and smooth while fetal extremities (arms, legs, etc.) should feel like small irregularities and protrusions. The fetal back, once determined, should connect with the form found in the upper abdomen and also a mass in the maternal inlet, lower abdomen.
Third maneuver: second pelvic grip or Pawlik's grip
[edit]In the third maneuver the health care provider attempts to determine what fetal part is lying above the inlet, or lower abdomen.[2] The individual performing the maneuver first grasps the lower portion of the abdomen just above the pubic symphysis with the thumb and fingers of the right hand. This maneuver should yield the opposite information and validate the findings of the first maneuver. If the woman enters labor, this is the part which will most likely come first in a vaginal birth. If it is the head and is not actively engaged in the birthing process, it may be gently pushed back and forth.
Fourth maneuver: Leopold's first pelvic grip
[edit]The last maneuver requires that the health care provider face the woman's feet, as he or she will attempt to locate the fetus' brow. The fingers of both hands are moved gently down the sides of the uterus toward the pubis. The side where there is resistance to the descent of the fingers toward the pubis is greatest is where the brow is located. If the head of the fetus is well-flexed, it should be on the opposite side from the fetal back. If the fetal head is extended though, the occiput is instead felt and is located on the same side as the back.
Cautions
[edit]Leopold's maneuvers are intended to be performed by health care professionals: obstetricians and other physicians, certified nurse midwives, certified nurse practitioners and registered professional nurses, as they have received the training and instruction in how to perform them. If performed at home as an informational exercise, the examiner should take care to not roughly or excessively disturb the fetus. All findings are not truly diagnostic, and as such ultrasound may be required to conclusively determine the fetal position.
References
[edit]- ^ Nahum GG (April 2002). "Predicting fetal weight. Are Leopold's maneuvers still worth teaching to medical students and house staff?". J Reprod Med. 47 (4): 271–8. PMID 12012878.
- ^ "Pregnancy – antenatal checks of your baby". Better Health Channel. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009.
