Aspartame
| Aspartame[1] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
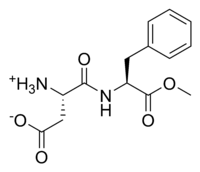
| Chemical name | N-(L-α-Aspartyl)-L-phenylalanine, 1-methyl ester | ||||
| Other names | NutraSweet Canderel Equal | ||||
| Chemical formula | C14H18N2O5 | ||||
| Molecular mass | 294.301 g/mol | ||||
| CAS number | [22839-47-0] | ||||
| Melting point | 246-247 °C | ||||
| Boiling point | decomposes | ||||
| SMILES | [NH3+] [C@@H](CC([O-])=O)C(N[C@@H] (CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(OC)=O)=O | ||||
| NFPA 704 |
| ||||
| Disclaimer and references | |||||
Aspartame (IPA: /ˈæ.spɚˌteɪm/ or /əˈspɑɹˌteɪm/) is the name for an artificial, non-carbohydrate sweetener, aspartyl-phenylalanine-1-methyl ester; i.e., the methyl ester of the dipeptide of the amino acid aspartic acid and the essential amino acid phenylalanine.
This sweetener is marketed under a number of trademark names, such as Equal, NutraSweet, Canderel, and NatraTaste and is an ingredient of approximately 6,000 consumer foods and beverages sold worldwide. It is commonly used in diet soft drinks, and is often provided as a table condiment. It is also used in some brands of chewable vitamin supplements and common in many sugar-free chewing gums. However, aspartame is not always suitable for baking because it often breaks down when heated and loses much of its sweetness. In the European Union, it is also known under the E number (additive code) E951. Aspartame is also one of the sugar substitutes used by diabetics.
Aspartame is a subject of vigorous public controversy due to perceived health risks (see aspartame controversy). It has lost ground in the market in recent years to sucralose.
Chemistry
Aspartame is the methyl ester of the dipeptide of the natural amino acids L-aspartic acid and L-phenylalanine. Under strongly acidic or alkaline conditions, aspartame first generates methanol by hydrolysis. Under more severe conditions, the peptide bonds are also hydrolyzed, resulting in the free amino acids. It is a nonpolar molecule.[2]
Properties and use
Aspartame is an attractive sweetener because it is approximately 200 times sweeter than sugar in typical concentrations, without the high energy value of sugar. While aspartame, like other peptides, has a caloric value of 4 kilocalories (17 kilojoules) per gram, the quantity of aspartame needed to produce a sweet taste is so small that its caloric contribution is negligible, which makes it a popular sweetener for those trying to avoid calories from sugar. The taste of aspartame is not identical to that of sugar: the sweetness of aspartame has a slower onset and longer duration than that of sugar, and some consumers find it unappealing. Blends of aspartame with acesulfame potassium are purported to have a more sugar-like taste, and to be more potent than either sweetener used alone.
Like many other peptides, aspartame may hydrolyze (break down) into its constituent amino acids under conditions of elevated temperature or high pH. This makes aspartame undesirable as a baking sweetener, and prone to degradation in products hosting a high-pH, as required for a long shelf life. The stability of aspartame under heating can be improved to some extent by encasing it in fats or in maltodextrin. The stability when dissolved in water depends markedly on pH. At room temperature, it is most stable at pH 4.3, where its half-life is nearly 300 days. At pH 7, however, its half-life is only a few days. Most soft-drinks have a pH between 3 and 5, where aspartame is reasonably stable. In products that may require a longer shelf life, such as syrups for fountain beverages, aspartame is sometimes blended with a more stable sweetener, such as saccharin. [1]
In products such as powdered beverages, the amine in aspartame can undergo a Maillard reaction with the aldehyde groups present in certain aroma compounds. The ensuing loss of both flavor and sweetness can be prevented by protecting the aldehyde as an acetal.
Discovery and approval
Aspartame was discovered in 1965 by James M. Schlatter, a chemist working for G.D. Searle & Company. Schlatter had synthesized aspartame in the course of producing an anti-ulcer drug candidate. He discovered its sweet taste serendipitously when he licked his finger, which had accidentally become contaminated with aspartame.[3]
Following initial safety testing, there was debate as to whether these tests had indicated that aspartame may cause cancer in rats; as a result, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) did not approve its use as a food additive in the United States for many years. In 1980, the FDA convened a Public Board of Inquiry (PBOI) consisting of independent advisors charged with examining the purported relationship between aspartame and brain cancer. The PBOI concluded that aspartame does not cause brain damage, but it recommended against approving aspartame at that time, citing unanswered questions about cancer in laboratory rats. In 1981, whilst Donald Rumsfeld was CEO of Searle, U.S. President Ronald Reagan appointed Arthur Hull Hayes as FDA commissioner. Citing data from a Japanese study that had not been available to the members of the PBOI, Hayes approved aspartame for use in dry goods.[4] In 1983 FDA further approved aspartame for use in carbonated beverages, and for use in other beverages, baked goods, and confections in 1993. In 1996, the FDA removed all restrictions from aspartame allowing it to be used in all foods.
In 1985, G.D. Searle was purchased by Monsanto. In this acquisition, Searle’s aspartame business became a separate Monsanto subsidiary, the NutraSweet Company. Monsanto subsequently sold the NutraSweet company to J.W. Childs Equity Partners II L.P. on May 25 2000.[5] The U.S. patent on aspartame expired in 1992, and the aspartame market is now hotly contested between the NutraSweet Company and other manufacturers such as Ajinomoto, Merisant and the Holland Sweetener Company — the latter of which left the business in 2006 due to a "persistently unprofitable business position" because "global aspartame markets are facing structural oversupply, which has caused worldwide strong price erosion over the last 5 years."[6]
Metabolism
Upon ingestion, aspartame breaks down into several residual chemicals, including aspartic acid, phenylalanine, methanol, and further breakdown products including formaldehyde[7] and formic acid. There is some controversy surrounding the rate of breakdown into these various products and the effects that they have on those that consume aspartame-sweetened foods (see Aspartame Controversy, below).
The naturally-occurring essential amino acid phenylalanine is a health hazard to those born with phenylketonuria (PKU), a rare inherited disease that prevents the essential amino acid phenylalanine from being properly converted into Tyrosine and eventually being metabolized. Since individuals with PKU must consider aspartame as an additional source of phenylalanine, aspartame-containing foods sold in the United States must state "Phenylketonurics: Contains Phenylalanine" on their product labels.
Aspartame controversy
Aspartame has been the subject of controversy regarding its safety and the circumstances of its approval by the American FDA and European FSA. Some studies have also recommended further investigation into connections between aspartame and negative effects such as headaches, brain tumors, brain lesions, and lymphoma.[8][9][10] These findings, combined with possible conflicts of interest in the approval process, have engendered vocal activism regarding the possible risks of aspartame.[11][12] The 2004 documentary Sweet Misery: A Poisoned World voices these same concerns.
On 14 December 2005, a member of the British House of Commons called on the British government to "ban the use and sale of aspartame" due to health concerns relating to this product.[13]
EU research confirms Carcinogenic effects of Aspartame on rats
The European Foundation of Oncology and Environmental Sciences has conducted two separate studies to conclude now in confirmed results that aspartame is a multi potential carcinogenic agent in rodents.
The first 2005 research publication:
Aspartame Induces Lymphomas and Leukaemias in Rats
And then follow up research resulted in the publication entitled First Experimental Demonstration of the Multipotential Carcinogenic Effects of Aspartame Administered in the Feed to Sprague-Dawley Rats2006.
Results of the study demonstrate that aspartame, administered at varying levels in feed, causes a statistically significant, dose-related increase of lymphomas-leukemias and malignant tumors of the renal pelvis in female rats and malignant tumors of peripheral nerves in male rats. These results demonstrate for the first time that aspartame is a carcinogenic agent, capable of inducing malignancies at dose levels lower than the current acceptable daily intake for humans (40 mg/kg of body weight in the EU, 50 mg/kg of body weight in the US).
The initial research publications where followed up by a second publication entitled “Results of Long-Term Carcinogenicity Bioassay on Sprague-Dawley Rats Exposed to Aspartame Administered in Feed”.
This publication and research confirmed the initial results and thus the current reserch and original research has confirmed the Carcinogenic Effects of Aspartame on rodents.
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 861.
- ^
David J. Ager, David P. Pantaleone, Scott A. Henderson, Alan R. Katritzky, Indra Prakash, D. Eric Walters (1998). "Commercial, Synthetic Nonnutritive Sweeteners". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 37 (13–24): 1802–1817. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980803)37:13/14%3C1802::AID-ANIE1802%3E3.0.CO;2-9.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ How Products Are Made: Aspartame
- ^ http://archive.gao.gov/d28t5/133460.pdf
- ^ http://www.findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0EUY/is_22_6/ai_62920821
- ^ http://www.marketwire.com/mw/release html b1?release id=115447
- ^ Trocho, C.; Pardo, R.; Rafecas, I.; Virgili, J.; Remesar, X.; Fernandez-Lopez, J.A.; Alemany, M. Formaldehyde derived from dietary aspartame binds to tissue components in vivo., Life Sci., 1998, 63(5), 337-349; Abstract
- ^ Olney, J.W., N.B. Farber, E. Spitznagel, L.N. Robins, 1996. "Increasing Brain Tumor Rates: Is There a Link to Aspartame?" Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, Volume 55, pages 1115-1123.
- ^ Soffritti, Morando, et al., "First Experimental Demonstration of the Multipotential Carcinogenic Effects of Aspartame Administered in the Feed to Sprague-Dawley Rats," Environmental Health Perspectives, Volume 114(3):379-385, 2006. http://www.ehponline.org/members/2005/8711/8711.pdf
- ^ Roberts, H.J., "Does Aspartame Cause Human Brain Cancer," Journal of Advancement in Medicine, Volume 4(4):231-241, 1991.
- ^ GAO 1986. "Six Former HHS Employees' Involvement in Aspartame's Approval," United States General Accounting Office, GAO/HRD-86-109BR, July 1986. http://archive.gao.gov/d4t4/130780.pdf
- ^ Gordon, Gregory, United Press International Investigation, "NutraSweet: Questions Swirl," 1987. http://www.dorway.com/upipaper.txt
- ^ "Commons Hansard". 14 Dec 2005 : Column 491WH : Artificial Sweeteners. House of Commons, United Kingdom Parliament. 2005-12-14. Retrieved 2007-03-05.

