Kabachnik–Fields reaction
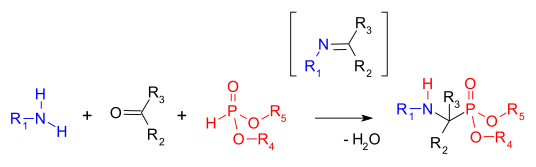
In organophosphorus chemistry, the Kabachnik–Fields reaction is a three-component organic reaction forming α-aminomethylphosphonates from an amine, a carbonyl compound, and a dialkyl phosphonate, (RO)2P(O)H (that are also called dialkylphosphites).[1] Aminophosphonates are synthetic targets of some importance as phosphorus analogues of α-amino acids (a bioisostere). This multicomponent reaction was independently discovered by Martin Kabachnik[2][3] and Ellis K. Fields[4] in 1952. The reaction is very similar to the two-component Pudovik reaction, which involves condensation of the phosphite and a preformed imine.
The first step in this reaction is the formation of an imine, followed by a hydrophosphonylation step where the phosphonate P-H bond across the C=N double bond.[5] The starting carbonyl component is usually an aldehyde and sometimes a ketone. The reaction can be accelerated with a combination of dehydrating reagent and Lewis acid.
Enantioselective variants of the Kabachnik-Fields reaction have been developed, for example employing α-methylbenzylamine provides a chiral, non-racemic α-aminophosphonate.[6]
References
- ^ Keglevich, Gyorgy; Balint, Erika (2012). "The Kabachnik-Fields reaction: mechanism and synthetic use". Molecules. 17 (11): 12821–12835. doi:10.3390/molecules171112821. PMC 6268146. PMID 23117425.
- ^ Kabachnik, Martin I.; Medved, T. Ya. (1953). "New method for the synthesis of 1-aminoalkylphosphonic acids Communication 1". Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Division of Chemical Science. 2 (5): 769–777. doi:10.1007/BF01178856.
- ^ Medved, T. Ya.; Kabachnik, Martin I. (1954). "New method for the synthesis of amino-phosphonic acids. Communication 2. Reaction of ketones with dialkyl phosphites and ammonia". Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Division of Chemical Science. 3 (2): 255–261. doi:10.1007/BF01177621.
- ^ Fields, Ellis K. (1952). "The synthesis of esters of substituted amino phosphonic acids". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 74 (6): 1528–1531. doi:10.1021/ja01126a054.
- ^ Zefirov, Nikolay S.; Elena D. Matveeva (2008-01-18). "Catalytic Kabachnik-Fields reaction: New horizons for old reaction" (PDF). Arkivoc. 2008 (i): 1–17. doi:10.3998/ark.5550190.0009.101. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
- ^ Gilmore, F.; McBride, A. (1972). "Synthesis of an optically active -aminophosphonic acid". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 94 (12): 4361. doi:10.1021/ja00767a065. PMID 5036657.