Andromeda (constellation)
| Constellation | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | And |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Andromedae |
| Right ascension | 1 |
| Declination | +40 |
| Area | 722 sq. deg. (19th) |
| Main stars | 4, 18 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 63 |
| Stars with planets | 2 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 3 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 5 |
| Brightest star | α And (Alpheratz) (2.1m) |
| Messier objects | 3 |
| Meteor showers | Andromedids (Bielids) |
| Bordering constellations | Perseus Cassiopeia Lacerta Pegasus Pisces Triangulum |
| Visible at latitudes between +90° and −40°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of November. | |
Andromeda (IPA: /ˌanˈdrɒmədə/) is a constellation named for the princess Andromeda (which is Greek for Ruler over men), a character in Greek mythology. The constellation is in the northern sky near the constellation Pegasus. It is most notable for containing the Andromeda Galaxy. It is sometimes called "The Chained Maiden" in English.
Corresponding Chinese constellations in Andromeda are Flying serpent (螣蛇), Celestial stable (天廄), Wall (壁), Legs (奎), Southern military gate (南軍門) and Great general of the heaven (天大将軍).
Notable features
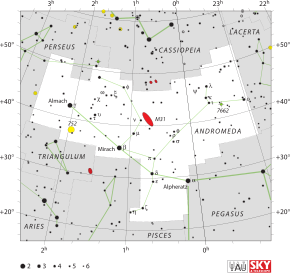
The brightest star in the constellation is Alpheratz (Sirrah in the image), which marks her head, Bayer designation Alpha Andromedae. Formerly considered common to Andromeda and Pegasus, as confirmed by its name, "navel of the horse", it was also designated δ Pegasi. With α, β, and γ Pegasi it forms an asterism called the Great Square of Pegasus.
β Andromedae is called Mirach, the girdle. It is 200 light years distant and of magnitude 2.1.
γ Andromedae, or Almach, is found at the tip of the southern leg of the big "A". It is a beautiful multiple star with contrasting colours.
υ Andromedae has a planetary system with three confirmed planets, 0.71 times, 2.11 times, and 4.61 times the mass of Jupiter.
Notable deep sky objects
The most famous deep sky object in Andromeda is M31, the Andromeda Galaxy, one of the most distant objects visible to the naked eye (M33 is slightly farther). It is an enormous spiral galaxy much like ours. To find the galaxy, draw a line between β and μ Andromedae, and extend the line approximately the same distance again from μ.
Mythology
If fainter stars, visible to the naked eye, in the constellation are considered, then the constellation takes the form of a stick-figure woman, with a prominent belt (as has the constellation Orion), where one arm has something long attached to it, giving the appearance of a female warrior holding a sword. This, together with other stars in the zodiac sign of Aries (part of Pisces, and the Pleiades), may be the origin of the myth of the girdle of Hippolyte, which forms part of The Twelve Labours of Herakles.
However, by including still fainter stars, the attachment extends in a different direction, giving the appearance of a maiden held by a chain.[1] Together with other constellations nearby (Cassiopeia, Cepheus, Cetus, Pegasus, and Perseus), this may be the source of the myth of the Boast of Cassiopeia, with which it is usually identified.
References
- H. A. Rey, The Stars — A New Way To See Them. Enlarged World-Wide Edition. Houghton Mifflin, Boston, 1997. ISBN 0-395-24830-2.
External links
- The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Andromeda
- NightSkyInfo.com: Constellation Andromeda
- Traditional astrological talisman of Andromeda
- WIKISKY.ORG: Andromeda
