User:EthanL13/sandbox/Road signs in Morocco
| This is not a Wikipedia article: It is an individual user's work-in-progress page, and may be incomplete and/or unreliable. For guidance on developing this draft, see Wikipedia:So you made a userspace draft. Find sources: Google (books · news · scholar · free images · WP refs) · FENS · JSTOR · TWL |

Road signs in Morocco are regulated under the joint decree n° 2805-14 in the Official Bulletin of the Kingdom of Morocco.[1] A further joint decree in 2019, n° 3106-19, strengthened the legal system in relation to road signs.[2][3] They are also laid out in the General Instruction on Road Signage (IGSR, French: Instruction Générale sur la Signalisation Routière). Morocco is a signatory of the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. They are broadly similar to those formerly and currently used in France.
Design

Directional signage bears some similarity to former French Michelin signage and subsequently 1940s signage. Other signage, such as warning and regulatory, is quite similar to those used in France today, in particular the symbols used on these signs.
In 2019, following the joint decree, the colour of symbols and text on white backgrounds was changed from dark blue to black, following the practice of that in Europe and the rest of the Maghreb.[2]
Road signs in Morocco generally appear in Arabic and French, and are generally bilingual. Tamazight is also used, particularly on motorway signage. Bilingual signs in Arabic and Tamazight began being installed on motorways in 2015, where it replaced French.[4] In some cases signs containing all three languages can be seen.
Arabic text uses the ASV Codar typeface, Latin text uses the Caractères typeface and Tifinagh text uses the Tifinaghe-Izuren IRCAM typeface, according to a document published by the Ministry of Equipment and Water in 2019.[5] However, Latin text on signage manufactured before this document used a narrower font, as well as a serif font for italic text, akin to those used on the aforementioned former French signage.
Additional panels
- Category panels
-
80.01
Refers to vehicles or combinations of vehicles with a maximum GVW or maximum authorised rolling weight of less than 3.5 tonnes. -
80.02
Public transport vehicles -
80.03
Motorcycles and mopeds (>50cc) -
80.04
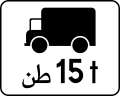
All vehicles carrying goods -
80.05
Vehicles carrying goods with a GVW and permissible total rolling weight exceeding the number indicated -
80.06
Agricultural motor vehicles -
80.07
Cycles -
80.08
Pedestrians -
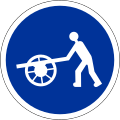
80.09
Hand carts -
80.10
Animal drawn vehicles -
80.11
Vehicles with a GVW which exceeds the number indicated -
80.12
Vehicles with a width greater than the number indicated -
80.13
Vehicles with a height greater than the number indicated -
80.14
Vehicles with a length greater than the number indicated -
80.15
Vehicles weighing more than the specified number per axle -
80.16
Vehicles carrying more than a certain quantity of flammable or explosive material and marked as such -
80.17
Vehicles carrying more than a certain quantity of material likely to pollute water and marked as such -
80.18
Vehicles equipped with snow chains -
80.19
Facilities for the physically disabled -
80.20
Vehicles towing a caravan or trailer weighing more than 250 kg and whose total rolling weight, vehicle plus trailer, does not exceed 3.5 tonnes -
80.21
Mopeds (<50cc) -
80.22
Vehicles carrying dangerous goods
- Additional panels for parking and stopping signs
-
81.01
Indicates that parking is unilateral and alternates on a semi-monthly basis -
81.03
Gives details of the prohibition -
81.04
Concerns paid parking without a parking meter -
81.05
Indicates that parking is paid with a parking meter -
81.06
Indicates that parking is reserved for vehicles used by the physically disabled with reduced mobility -
81.08
Indicates that parking and/or stopping causes an obstruction. It complements the 328.1 and 328.2 signs. The vehicle may be impounded.
- Distance panels and length panels
-
Distance panel 82
Indicates the length of the section between the sign and the start of the dangerous passage or the zone to which the regulations apply or the point which is the subject of the indication -
Length panel 83
Indicates the length of the section that is dangerous or subject to regulation or covered by the indication
- Stop and priority panels
-
Stop panel 84.01
Indicates the distance between the sign and the point where the driver must stop and give way -
Give way panel 84.02
Indicates to the driver to give way
- Position or direction panels
-
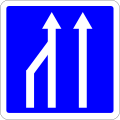
85.01
Indicates the position of the lane affected by the sign it accompanies -
85.02
Indicates the direction to follow, and where applicable the distance, to reach the service indicated by the sign -
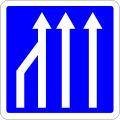
85.03
Indicates that the sign it accompanies relates to the lane above which it is placed
- Panels to enforce parking and stopping regulations (signs indicating that parking and stopping restrictions apply)
-
86.01
Indicates that the section to which the requirement applies extends after the sign (this is the beginning of the section) -
86.02
Indicates that the section to which the requirement applies extends before the sign (this is the end of the section) -
86.03
Indicates that the section to which the requirement applies extends on either side of the sign (this is a reminder) -
86.04
Indicates that the section to which the regulation applies extends in the direction(s) indicated by the arrow(s) -
86.05
Indicates that the section to which the regulation applies extends in the direction(s) indicated by the arrow(s) -
86.06
Indicates that the section to which the regulation applies extends in the direction(s) indicated by the arrow(s)
- Panels with various indications
-
87.01
Provides various indications (in writing form) -
87.07
Indicates that the emergency stop location is equipped with an emergency call station -
87.08
Indicates that the emergency stop location is equipped with an emergency call station and a fire extinguisher -
87.09
Indicates that the sign with which it is associated relates to an air danger area -
87.10
Indicates that the pedestrian crossing is raised -
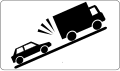
87.11
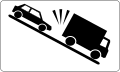
Indicates the risk of colliding with slow vehicles on a descent -
87.12
Indicates the risk of colliding with slow vehicles on an ascent
- Scheme panels
-
88
A diagram shows the approaching intersection and a broad line indicates the priority branches.
Warning signs
-
101.1
Curve to right -
101.2
Curve to left -
101.3
Succession of curves, first to right -
101.4
Succession of curves, first to left -
102.1
Dangerous descent -
102.2.
Steep ascent -
103.1
Road narrows -
103.2
Road narrows on right -
103.3
Road narrows on left -
104
Narrow bridge -
105
Opening bridge -
106
Quayside or river bank -
107.1
Potholes or speed bumps -
107.2
Speed hump -
108
Slippery surface -
109
Submersible surface -
110
Loose chippings -
111
Risk of rockfall -
112
Pedestrian crossing -
113
Place frequented by children -
114
Cyclists or mopeds -
115.1
Domestic animals crossing (cows) -
115.2
Domestic animals crossing (sheep) -
115.3
Domestic animals crossing (camels) -
116
Wild animals crossing -
117
Horseriders crossing -
118
Traffic lights ahead -
119
Crossing an air danger zone -
120
Sidewinds -
121
Two-way traffic -
122
Other dangers -
123
Level crossing with manually operated barriers for passing trains -
124
Level crossing without barriers or half barriers -
125
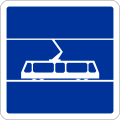
Tramway track crossing -
126
Farm machinery crossing -
127
Animal-drawn vehicles crossing
Intersection and priority signs
-
201
Stop (Arabic) -
201
Stop (Latin) -
202.1
Yield at intersection - position signal -
202.2
Yield at intersection - signal in advance of 202.1 -
202.3
Yield at intersection - sign in advance of stop sign -
203
Intersection of roads to which the general priority to the right rule applies -
204
Intersection of a priority road with a minor road -
205
Roundabout -
206
Indication that a road has priority status -
207
End of a road's priority status
Regulatory signs
Prohibition signs
-
301
No entry -
302
No motor vehicles -
303.1
No motor vehicles except motorcycles and mopeds -
303.2
No public transport vehicles -
304
No bicycles -
305
No mopeds -
306
No motorcycles -
307
No goods vehicles -
308
No pedestrians -
309
No animal-drawn vehicles -
310
No handcarts -
311
No farm vehicles -
312
No motor vehicles except mopeds -
313
No vehicles transporting explosive or inflammable materials -
314.1
No vehicles carrying water pollutants -
314.2
No vehicles carrying dangerous goods -
315
Width limit -
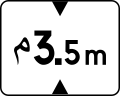
316
Height limit -
317
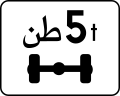
Weight limit -
318
Axle weight limit -
319
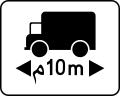
Length limit -
320
Minimum distance between vehicles -
321.1
No left turn -
321.2
No right turn -
321.3
No U-turn -
322.1
No overtaking -
322.2
No overtaking by heavy goods vehicles -
322.3
Give way to oncoming vehicles -
323
Speed limit -
324
No honking -
325.1
Stop - customs -
325.2
Stop - police -
325.3
Stop - gendarmerie -
325.4
Stop - traffic control -
326
Stop - snow barrier -
327
Stop - toll -
328.1
No parking -
328.2
No stopping -
328.3
Half-monthly parking -
328.4
Half monthly parking -
329
No motor vehicles -
330
No vehicles pulling caravans -
331
Other restrictions (example: closed to cattle)
End of prohibition signs
-
333
End of all previously signed restrictions -
334
End of speed limit -
329
End of no overtaking -
329
End of no overtaking by heavy goods vehicles -
329
End of no honking -
329
End of any other restrictions (example: End of prohibition to skiers)
Mandatory signs
-
340.1
Turn right -
340.2
Turn left -
341.1
Keep left -
342.2
Keep right -
342
Ahead only -
343.1
Turn right ahead -
343.2
Turn left ahead -
344.1
Go straight or turn right -
344.2
Go ahead or turn left -
345
Turn left or right -
346
Roundabout -
347
Cycle track -
348
Animal-drawn vehicle track -
349
Handcart track -
350
Animal track -
351
Horse-riding path -
352
Keep to the right (multi-lane road) -
353
Pedestrian path -
354
Minimum speed limit -
356
Public transport vehicles lane -
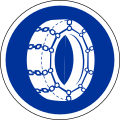
357
Snow chains mandatory -
358
Headlights mandatory -
359.1
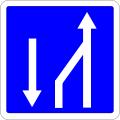
Tram lane -
359.2
Slow vehicle lane
End of mandatory signs
-
360
End of minimum speed limit -
361
End of cycle track -
362
End of pedestrian path -
363
End of horse-riding path -
364
End of public transport vehicle lane -
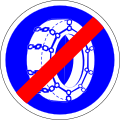
365
End of mandatory snow chains -
366
End of mandatory headlights -
367
End of tram lane -
368
End of slow vehicle lane
Zoning and end of zoning signs
-
370.1
No parking zone -
370.2
Semi-monthly alternating one-sided parking zone -
370.3
End of semi-monthly alternating one-sided parking zone control -
370.4
End of paid parking zone -
370.5
Semi-monthly alternating one-sided parking zone with disc control -
371
30 km/h speed limit zone -
372.1
End of no parking zone -
372.2
End of semi-monthly alternating one-sided parking zone -
372.3
End of time-limited parking zone with disc control -
372.4
End of paid parking zone -
372.5
End of semi-monthly alternating one-sided parking zone with disc control -
373
End of 30 km/h speed limit zone
Informatory signs
Indication signs
-
401.1
-
401.2
-
401.3
-
401.4
-
401.5
-
401.6
-
401.7
-
401.8
-
402
-
403
-
404
-
405
-
406
-
407
-
408
-
408
-
409.1
-
409.1
-
409.2
-
409.3
-
410.1
-
410.2
-
411
-
412.1
-
412.2
-
413
-
414
-
415
-
416
-
417
-
418
-
419
-
420
-
421
-
422
-
423.1
-
423.2
-
424
-
425
-
426
-
427
-
428
-
429
-
430
-
430
-
430
-
431
-
432
-
433
-
434
-
435
-
436
-
437
-
438
Service signs
-
440
-
442
-
443
-
444
-
444.1
-
445
-
446
-
447
-
448
-
449
-
450
-
451.1
-
451.2
-
451.3
-
451.4
-
451.5
-
452
-
453
-
454
-
455
-
456
-
457
-
458
-
459
-
460
-
461
-
462
-
463
-
464
-
465.1
-
465.2
-
470
-
471
-
472
Information and road safety signs
-
480
-
481.1
-
481.2
-
481.3
Direction and location signs
Direction signs
Location and identification signs
Milestones and distance markers
Tourist and local interest signs
Road markers
Temporary signs
-
900
-
901
-
901.1
-
901.2
-
902
-
903
-
904
-
905
-
906
-
907
-
908
-
910
-
911
Unoffical signs

See also
- Ministry of Equipment, Transport and Logistics
- Transport in Morocco
- Autoroutes of Morocco
- Road signs in France
References
- ^ "Bulletin Officiel n° 6332" (PDF). sgg.gov.ma (in French). Secrétariat Général du Gouvernement. 5 February 2015. Retrieved 15 July 2023.
- ^ a b "Communiqué sur la publication de l'arrêté conjoint du Ministre de l'Equipement, du Transport, de la Logistique et de l'Eau et du Ministre de l'Intérieur relatif à la signalisation routière". equipement.gov.ma (in French). Ministère de l'équipement et de l'eau. 5 December 2019. Retrieved 16 July 2023.
- ^ "Bulletin Officiel n° 6832" (PDF). sgg.gov.ma (in French). Secrétariat Général du Gouvernement. 21 November 2019. Retrieved 16 July 2023.
- ^ "Morocco: Amazigh Language Replaces French in Road Signalization". Morocco World News. 12 July 2015. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ "Instruction générale sur la signalisation routière - Partie 1 : Généralités". equipement.gov.ma. Ministère de l'équipement et de l'eau. Retrieved 15 July 2023.
External links