Ann Arbor, Michigan
- For the railroad company, see Ann Arbor Railroad.
- For the automobile company, see Ann Arbor (automobile).
Ann Arbor, Michigan | |
|---|---|
| File:Annarborskyline.JPG | |
| Nickname(s): A-squared, Ace Deuce, A-2, Tree-town | |
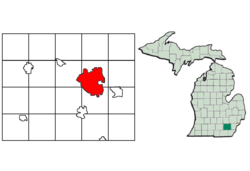 Location of Ann Arbor within Washtenaw County, Michigan. | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Michigan |
| County | Washtenaw |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | John Hieftje |
| Elevation | 840 ft (260 m) |
| Population (2000) | |
• City | 114,024 |
| • Urban | 283,904 |
| • Metro | 341,847 |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| Website | www.ci.ann-arbor.mi.us |
Ann Arbor is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of Washtenaw County. It is the state's seventh largest city with a population of 114,024 as of the 2000 census, of which 36,892 (32%) are college or graduate students.[1] Supposedly named for the spouses of the city's founders and for the stands of trees in the area, Ann Arbor is best known as the location of the main campus of the University of Michigan, which moved from Detroit in 1837.
The city's economy, which was once noted for production of agricultural implements, carriages, furniture, pianos, organs, pottery, and flour, is now dominated by education, high tech, and biotechnology. Average home prices and property taxes are well above the state and national medians. The city is also known for its political liberalism and its large number of restaurants and performance venues.
History
Ann Arbor was founded in January 1824 by John Allen and Elisha Rumsey, both of whom were land speculators. There are various accounts concerning the origin of the settlement's name; one states that Allen and Rumsey decided to name it "Annsarbour" for their spouses, both named Ann, and for the stands of burr oak in the 640 acres (260 ha) of land they had purchased for $800 from the federal government.[2] The regional Native Americans named the settlement Kaw-goosh-kaw-nick, after the sound of Allen's grist mill.

Ann Arbor became the seat of Washtenaw County in 1827, and was incorporated as a village in 1833. The town set aside 40 acres (16 ha) of undeveloped land and offered it to the State of Michigan as the site of the state capital, but it lost the bid to Lansing in 1836. In 1837, the unused land was given to the University of Michigan, forever linking Ann Arbor and its history with the university.[3] The town became a regional transportation hub in 1839 with the arrival of the Michigan Central Railroad, and in 1851 Ann Arbor was chartered as a city.
During World War II, Ford Motor Company's nearby Willow Run plant turned out B-24 Liberator bombers. The population of Ann Arbor exploded with an influx of military personnel, war workers, and their families.
During the 1960s and 1970s, the city gained a reputation as an important center for liberal politics. Presidential candidate John F. Kennedy unveiled his Peace Corps proposal in 1960 at the University of Michigan, and President Lyndon B. Johnson first called for a "Great Society at the university in 1964."[4] The city also became a locus for left-wing activism, and served as a hub for the civil-rights movement and anti-Vietnam War movement, as well as the student movement. The first major meetings of the national left-wing campus group Students for a Democratic Society took place in Ann Arbor in 1960; in 1965, the city was home to the first U.S. teach-in against the Vietnam War.[5] During the ensuing fifteen years, many countercultural and New Left enterprises sprang up and developed strong constituencies within the city.

These influences washed into municipal politics during the early and mid-1970s when three members of the local, progressive Human Rights Party (HRP) won city-council seats on the strength of the student vote. During their time on the council, HRP representatives fought for measures including pioneering antidiscrimination ordinances, measures decriminalizing marijuana possession, and a rent-control ordinance;[6] many of these remain in effect in modified form.
Alongside these liberal and left-wing efforts, a small group of conservative institutions were born in Ann Arbor. These include Word of God (established in 1967), a charismatic inter-denominational movement of national scope;[5] and the Thomas More Law Center (established in 1999), a leading religious-conservative advocacy group.
The economy of Ann Arbor underwent a gradual shift from a manufacturing base to a service and technology base during the 20th century, which accelerated in the 1970s and 1980s. At the same time, the downtown transformed from one dominated by retail establishments dealing in staple goods to one composed mainly of eateries, cafés, bars, clubs, and specialty shops. Over the past several decades, Ann Arbor has increasingly found itself grappling with the effects of sharply rising land values and gentrification, as well as urban sprawl stretching far into the outlying countryside. On November 2, 2004, voters approved a greenbelt plan under which the city government would buy development rights to pieces of land adjacent to Ann Arbor to preserve them from sprawling development.[7] Since then, a vociferous local debate has hinged on whether, and how, to accommodate and guide development within city limits.
Geography and cityscape

According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has an area of 27.7 square miles (71.7 km²); 27.0 square miles (70.0 km²) is land and 0.7 square miles (1.7 km²) or 2.42% is water, much of which is part of the Huron River. Ann Arbor is approximately 40 miles (64 km) west of Detroit. Ann Arbor Charter Township is adjacent, on the city's north and east sides. Ann Arbor is situated on the Huron River, in a productive agricultural and fruit-growing region. The landscape of Ann Arbor consists of hills and valleys, with the terrain becoming steeper near the Huron River. The elevation ranges from about 750 feet (230 m) along the Huron River to about 900 feet (275 m) above sea level in southern and northeastern Ann Arbor.[8] The elevation is about 839 feet (256 m) at Ann Arbor Municipal Airport, which is at 42°13.38′N 83°44.74′W / 42.22300°N 83.74567°W.[9]
Ann Arbor's "Tree Town" nickname stems from the dense forestation of its parks and residential areas. The city holds more than 50,000 trees sited along city streets and an equal number in city parks.[10] In recent years, the emerald ash borer has destroyed many of the city's approximately 10,500 ash trees. The city contains 147 municipal parks, ranging from small neighborhood parks to large recreation areas, with several large city parks and a university park bordering sections of the Huron River.[11] The largest are Argo Park, Riverside Park, County Farm Park, and Gallup Park (near the Huron Parkway),[12] while Fuller Recreation Area, near the University Hospital complex, contains sports fields, pedestrian and bike paths, and swimming pools. Nichols Arboretum, which is owned jointly by the City of Ann Arbor and the University of Michigan (and known locally as "The Arboretum" or simply "The Arb"), is a 123-acre (50 ha) preserve containing hundreds of plant and tree species on the east side of the city near the university's central campus.
The Kerrytown Shops, Main Street Business District, the State Street Business District, and the South University Business District are commercial areas in downtown. Three commercial areas south of downtown include the areas near I-94 and Ann Arbor-Saline Road, Briarwood Mall, and the South Industrial area. Other commercial areas include the Arborland/Washtenaw Avenue and Packard Road merchants on the east side, the Plymouth Road area in the northeast, and the Westgate/West Stadium areas on the west side. The downtown contains a mix of 19th and early 20th century structures and modern-style buildings, as well as a farmers' market in the Kerrytown district.[13] The city's commercial districts are composed mostly of two to four-story structures, although the downtown and the area near Briarwood Mall contain a small number of high-rise buildings.
Ann Arbor's residential neighborhoods contain a range of architectural styles, from classic 19th and early 20th century designs to ranch-style houses. Contemporary-style houses are farther from the downtown district. Surrounding the University of Michigan campus are houses and apartment complexes occupied primarily by student renters. The 19th century buildings and streetscape of the Old West Side neighborhood have been preserved virtually intact; in 1972, the district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places, and it is further protected by city ordinances and a nonprofit preservation group.[14]
Climate
Ann Arbor has a typically Midwestern humid continental seasonal climate, which is influenced by the Great Lakes. There are four seasons, with winters being cold with moderate snowfall while summers can be warm and humid. The area experiences lake effect, primarily in the form of increased cloudiness during late fall and early winter.[15] The highest average temperature is in July at 83 °F (28 °C) while the lowest average temperature is in January at 16 °F (−9 °C). However, summer temperatures can top 90 °F (32 °C), and winter temperatures can drop below 0 °F (−17 °C). Average monthly precipitation ranges from 2 to 4 inches (44 to 92 mm), with the heaviest occurring during the summer months. Snowfall, which normally occurs from November to April, ranges from 1 to 10 inches (3 to 25 cm) per month.[16] The highest recorded temperature was 105 °F (40.6 °C) on July 24, 1934, while the lowest recorded temperature was −22.0 °F (−30 °C) on January 19, 1994.[17]
| Climate data for Ann Arbor, Michigan | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Source: Weatherbase[18] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1860 | 5,097 | — | |
| 1870 | 7,363 | 44.5% | |
| 1880 | 8,061 | 9.5% | |
| 1890 | 9,431 | 17.0% | |
| 1900 | 14,509 | 53.8% | |
| 1910 | 14,817 | 2.1% | |
| 1920 | 19,516 | 31.7% | |
| 1930 | 26,944 | 38.1% | |
| 1940 | 29,815 | 10.7% | |
| 1950 | 48,251 | 61.8% | |
| 1960 | 67,340 | 39.6% | |
| 1970 | 100,035 | 48.6% | |
| 1980 | 107,969 | 7.9% | |
| 1990 | 109,592 | 1.5% | |
| 2000 | 114,024 | 4.0% | |
| 2005 (est.) | 113,271 |
As of the 2000 census,[19] there were 114,024 people, 45,693 households, and 21,704 families residing in the city. The population density was 4,221.1 people per square mile (1,629.9/km²). There were 47,218 housing units at an average density of 1,748.0 per square mile (675.0/km²), making it less dense than inner-ring Detroit suburbs like Oak Park and Ferndale (and than Detroit proper), but denser than outer-ring suburbs like Livonia. The racial makeup of the city was 74.68% White, 8.83% Black or African American, 0.29% Native American, 11.90% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 1.21% from other races, and 3.05% from two or more races. 3.34% of the population were Hispanic American or Latino. Because of the pull of the university, the city has one of the highest foreign-born population percentages in the state sitting at 16.6%.
Out of the 45,693 households, 23.0% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 37.8% were married couples living together, 7.5% had a female householder with no husband present, and 52.5% were nonfamilies. 35.5% of households were made up of individuals and 6.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.22 and the average family size was 2.90.
In the city, the population age was spread out; 16.8% were under 18, 26.8% from 18 to 24, 31.2% from 25 to 44, 17.3% from 45 to 64, and 7.9% were 65 or older. The median age was 28 years. For every 100 females there were 97.7 males; while for every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.4 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $46,299, and the median income for a family was $71,293. Males had a median income of $48,880 versus $36,561 for females. The per capita income for the city was $26,419. Approximately 4.6% of families and 16.6% of the population were below the poverty line, including 7.3% of those under age 18 and 5.1% of those age 65 or over.
Ann Arbor's crime rate was below the national average in 2000. The violent crime rate was much further below the national average than the property crime rate; they were 48% and 11% less than the national average, respectively.[20][21]
Law and government

Ann Arbor has a Council-manager form of government. The mayor, who is elected every even-numbered year, is the presiding officer of the City Council and has the power to appoint all Council committee members as well as board and commission members, with the approval of the City Council. The mayor of Ann Arbor is John Hieftje (Democrat), who has served in that capacity since the 2000 election. The city council has ten members, two from each of the city's five wards, with the mayor wielding the tie-breaking vote. Council members serve two-year terms; half the council is elected in annual elections.[22] City operations are managed by the City Administrator, who is chosen by the city council.
Ann Arbor is in the 15th Congressional district, and is represented by Representative John Dingell (Democrat). On the state level, the city is in the 18th district in the Michigan Senate. In the Michigan State House of Representatives, the city of Ann Arbor is in the 53rd district, while northeastern Ann Arbor and Ann Arbor Township are in the 52nd district.[23] As the seat of Washtenaw County, the city is the location of the county's trial, civil, and criminal courts. Ann Arbor is the site of a United States district court, whose downtown building also houses a post office.
Left-wing politics have been particularly strong in municipal government since the 1960s – an orientation evident in the passage of strong antidiscrimination ordinances. Voters also approved charter amendments that have lessened the penalties for possession of marijuana (1974), and that aim to protect access to abortion in the city should it ever become illegal in the State of Michigan (1990). In 1974, Kathy Kozachenko's victory in an Ann Arbor city-council race made her the country's first openly homosexual candidate to win public office.[24] In 1975, Ann Arbor became the first U.S. city to use instant-runoff voting for a mayoral race. Adopted through a ballot initiative sponsored by the local Human Rights Party, which feared a splintering of the liberal vote, the process was repealed in 1976 after use in only one election.[25] As of December 2006, Democrats hold the mayorship and all council seats.
Ann Arbor has seven sister cities:
 - Tübingen, Germany, since 1965
- Tübingen, Germany, since 1965 - Belize City, Belize, since 1967
- Belize City, Belize, since 1967 - Hikone, Japan, since 1969
- Hikone, Japan, since 1969 - Peterborough, Ontario since 1983
- Peterborough, Ontario since 1983 - Juigalpa, Nicaragua, since 1986
- Juigalpa, Nicaragua, since 1986 - Dakar, Senegal, since 1997
- Dakar, Senegal, since 1997 - Remedios, Cuba, since 2003
- Remedios, Cuba, since 2003
Economy
The University of Michigan shapes Ann Arbor's economy significantly. It employs approximately 30,000 workers, including about 7,500 in the medical center.[26] Other employers are drawn to the area by the university's research and development money, and by its graduates. High tech, health services and biotechnology are other major components of the city's economy; numerous medical offices, laboratories, and associated companies are located in the city. Automobile manufacturers, such as General Motors and Ford, also employ residents.

Many high-tech companies are located in the city. During the 1980s, Ann Arbor Terminals manufactured a video-display terminal called the Ann Arbor Ambassador.[27] Other high-tech companies in the area include Arbor Networks (provider of Internet traffic engineering and security systems), Arbortext (provider of XML-based publishing software), JSTOR (the digital scholarly journal archive), MediaSpan Media Software (provider of newspaper publishing software and ASP services), and ProQuest, which includes UMI.
Websites and online media companies in the city include All Media Guide, Everything2, and the Weather Underground. Ann Arbor is also the site of the Michigan Information Technology Center (MITC), whose offices house Internet2 and the Merit Network, a nonprofit research and education computer network.[28] On July 11, 2006, Google announced plans to open a 1000-employee Ann Arbor office for its AdWords program later in the year.[29]
Pfizer, the city's second largest employer, operates a large pharmaceutical research facility on the northeast side of Ann Arbor. On January 22, 2007, Pfizer announced it would close operations in Ann Arbor by the end of 2008.[30] The facility was previously operated by Warner-Lambert and, before that, Parke-Davis. The city is the home of other research and engineering centers, including those of General Dynamics and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Other research centers sited in the city are the Environmental Protection Agency's National Vehicle and Fuel Emissions Laboratory[31] and the Toyota Technical Center.[32]
Several major companies are headquartered in Ann Arbor. The original Borders Books was opened on Ann Arbor's State Street in 1971 by brothers Tom and Louis Borders, and began operating other outlets around the region in 1985. The Borders chain is still based in the city, as is its flagship store (although not in its original location). Dogs are allowed inside the flagship store, and the cashiers have a stock of treats for such visitors.[33] Domino's Pizza's headquarters is near Ann Arbor on Domino's Farms, a 271-acre (109 hectare) Frank Lloyd Wright-inspired complex just northeast of the city.[34] Flint Ink Corp., another Ann Arbor-based company, was until recently the world's largest privately held ink manufacturer (in October 2005, it was acquired by Stuttgart-based XSYS Print Solutions).[35] Another Ann Arbor-based company is Zingerman's Delicatessen, which serves sandwiches and Jewish foods, and has developed businesses under a variety of brand names. Zingerman's has grown into a very large family of companies which offers a variety of products (bake shop, mail order, creamery) and services (business education).
Many cooperative enterprises were founded in the city during the 1960s and 1970s; among those that remain are the People's Food Co-op and the Inter-Cooperative Council at the University of Michigan, a student-housing cooperative. The North American Students of Cooperation (NASCO) is an association of cooperatives headquartered in Ann Arbor. There are also three cohousing communities — Sunward, Great Oak, and Touchstone — located immediately to the west of the city limits.[36]
Education
Higher education

The University of Michigan is the dominant institution of higher learning in Ann Arbor, providing the city with a distinctly college-town atmosphere.[37] Much of the campus is adjacent to and intermixed with the city's downtown district. Because the campus and the city expanded side-by-side, there is often no firm divide between the two, with university buildings scattered through much of the city center.
Other local colleges and universities are Cleary University, a private business school; Concordia University, a Lutheran liberal-arts institution; and Washtenaw Community College. Ave Maria School of Law, a Catholic institution established by Domino's Pizza cofounder Tom Monaghan, opened near northeastern Ann Arbor in 2000. There were plans to establish Ave Maria University on land occupied by Domino's Farms. However, due to conflicts with local zoning authorities, the new campus is under construction near Naples, Florida.[38] In February 2007, it was announced that Ave Maria School of Law will move to southwest Florida in 2009.[39]
Primary and secondary schools
Ann Arbor is home to more than 20 private schools,[40] including Clonlara School and Greenhills School, a prestigious prep school near Concordia University. The Ann Arbor Public School District handles local public education. The system – which enrolls 16,974 students (2005/2006 September head count) – consists of twenty-one elementary schools, five middle schools, and five high schools (two traditional, Pioneer and Huron, as well as three alternative schools: Community High, Stone School, and Roberto Clemente).[41] Due to overcrowding problems at the two traditional high schools, a third traditional high school, Skyline High School, is under construction and is slated to open in September 2008. The district also operates a K-8 open school program,[42] Ann Arbor Open, out of the former Mack School. This program is open to all families who live within the district. Ann Arbor Public Schools also operates a preschool and family center, with programs starting as early as birth for at-risk infants and other programs for at-risk children before kindergarten. The district has constructed a new preschool center to open in September 2006, with both free and tuition-based programs for preschoolers in the district.
Culture
Many Ann Arbor cultural attractions and events are sponsored by the University of Michigan. Several performing arts groups and facilities are on the university's campus, as are museums dedicated to art, archaeology, and natural history and sciences (see Museums at the University of Michigan). Regional and local performing arts groups not associated with the university include the Ann Arbor Civic Theatre; the Arbor Opera Theater; the Ann Arbor Symphony Orchestra; the Ann Arbor Ballet Theater; the Ann Arbor Civic Ballet (established in 1954 as Michigan's first chartered ballet company[43]); and Performance Network, which operates a downtown theater frequently offering new or nontraditional plays.
The Ann Arbor Hands-On Museum, located in a renovated and expanded historic downtown fire station, contains more than 250 interactive exhibits featuring science and technology. Multiple art galleries exist in the city, notably in the downtown area and around the University of Michigan campus. Aside from a large restaurant scene in the Main Street, South State Street, and South University Avenue areas, Ann Arbor ranks first among U.S. cities in the number of booksellers and books sold per capita.[44] The Ann Arbor District Library maintains four branch outlets in addition to its main downtown building; in 2008 a new branch building is set to replace the branch located in Plymouth Mall. The city is also home to the Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library.
Several annual events – many of them centered on performing and visual arts – draw visitors to Ann Arbor. One such event is the Ann Arbor Art Fairs, a set of four concurrent juried fairs held on downtown streets, which began in 1960. Scheduled on Wednesday through Saturday in the third week of July, the fairs draw upward of half a million visitors.[45] One event that is not related to visual and performing arts is Hash Bash, held on the first Saturday of April in support of the reform of marijuana laws. It has been celebrated since 1971. The Naked Mile, which features students running naked through the streets in late April to celebrate the end of the winter semester, has occurred since 1986. Beginning in 2000, however, a crackdown by university and city police, citing safety concerns, has reduced the size of the run.[46]
Ann Arbor has a major scene for college sports, notably at the University of Michigan, a member of the Big Ten Conference. Several well-known college sports facilities exist in the city, including Michigan Stadium, the largest American football stadium in the world with a 107,501 seating capacity.[47] The stadium is colloquially known as "The Big House." Crisler Arena and Yost Ice Arena play host to the school's basketball and ice hockey teams, respectively. Concordia University, a member of the NAIA, also fields sports teams.
A person from Ann Arbor is called an "Ann Arborite," and many long-time residents call themselves "townies." The city itself is often called A² ("A-squared") or A2 ("A two"), and, less commonly, Tree Town. Recently, some youths have taken to calling Ann Arbor Ace Deuce or simply The Deuce. With tongue-in-cheek reference to the city's liberal political leanings, some occasionally refer to Ann Arbor as The People's Republic of Ann Arbor[48] or 25 square miles surrounded by reality,[49] the latter phrase being adapted from Wisconsin Governor Lee Dreyfus's description of Madison, Wisconsin.
Media

The Ann Arbor News, owned by the Michigan-based Booth Newspapers chain, is the major daily newspaper serving Ann Arbor. Other established publications in the city include the Ann Arbor Observer, a monthly magazine with features covering local culture, politics, family life, business and history, as well as a comprehensive calendar of events; Current, an entertainment guide; and Ann Arbor Paper, a free monthly with columns, fiction, humor, reviews, and profiles.[51] The University of Michigan campus area is served by many student publications, including the independent Michigan Daily. The Ann Arbor Business Review covers local business in the area. Car and Driver magazine and Automobile Magazine are also based in Ann Arbor.
The three major AM radio stations based in Ann Arbor are WAAM 1600, a news and talk station; WLBY 1290, an Air America Radio affiliate; and WTKA 1050, which is primarily a sports station.[52] The city's FM stations include NPR affiliate WUOM 91.7; country station WWWW 102.9; adult-alternative station WQKL 107.1; and WCBN 88.3, a noncommercial, student-run station with eclectic music and public-affairs programming.[52] The city is also served by public and commercial radio broadcasters in Ypsilanti, the Lansing/Jackson area, Detroit, Windsor, and Toledo.
WPXD channel 31, an affiliate of the ION Television network, is licensed to the city. Community Television Network (CTN) is a city-provided cable television channel with production facilities open to city residents and nonprofit organizations.[53] Detroit and Toledo-area radio and television stations also serve Ann Arbor, and stations from Lansing and Windsor, Ontario, can be heard in parts of the area.
Health and utilities
The University of Michigan Medical Center, the preeminent health facility in the city, took the #12 slot in the 2006 U.S. News and World Report for hospitals.[54] The University of Michigan Health System (UMHS) includes University Hospital, C.S. Mott Children's Hospital and Women's Hospital in its core complex. UMHS also operates out-patient clinics and facilities throughout the city. The area's other major medical centers include a large facility operated by the Department of Veterans Affairs in Ann Arbor, and Saint Joseph Mercy Hospital in nearby Superior Township.
The city provides sewage disposal and water supply services, with water coming from the Huron River and groundwater sources. There are two water-treatment plants, one main and three outlying reservoirs, four pump stations, and two elevated tanks. These facilities serve the city, which is divided into five water districts. The city's water department also operates four dams along the Huron River, two of which provide hydroelectric power.[55] The city also offers waste management services, with Recycle Ann Arbor's handling recycling service. Other utilities are provided by private entities. Electrical power and gas are provided by DTE Energy. AT&T, the successor to Michigan Bell, Ameritech, and SBC Communications, is the primary wired telephone service provider for the area. Phone service is also available from various national wireless companies. Cable service is primarily provided by Comcast.
Transportation
The city is belted by three highways: I-94, which runs along the southern portion of the city; US 23, which primarily runs along the eastern edge of Ann Arbor; and M-14, which runs along the northern edge of the city. The streets in downtown Ann Arbor conform to a grid pattern, though this pattern is less common in the surrounding areas. Major roads branch out from the downtown district like spokes on a wheel to the highways surrounding the city. Several of the major surface arteries lead to the I-94/M-14 juncture in the west, US 23 in the east, and the city's southern areas. A large network of bike paths crisscrosses the city, as well.[56]

The Ann Arbor Transportation Authority (AATA), which brands itself as "The Ride," operates public bus services throughout Ann Arbor and nearby Ypsilanti. A separate zero-fare bus service operates within the University of Michigan campuses. A downtown bus depot served by Greyhound Lines provides out-of-town bus service, and is the city's only remaining example of the Streamline Moderne architectural style.[57] Megabus has three-times daily direct service to Chicago, Illinois, while a bus service provided by Amtrak connects to East Lansing and Toledo, Ohio, though only for rail passengers making connections.
Ann Arbor Municipal Airport is a small general aviation facility located south of I-94. Detroit Metropolitan Airport, the area's large international airport, is approximately 28 miles (45 km) east of the city, in Romulus. Willow Run Airport in nearby Ypsilanti serves freight, corporate, and general aviation clients.
The city was a major rail hub, notably for freight traffic between Toledo and ports north of Chicago, Illinois, from 1878 to 1982; however, the Ann Arbor Railroad also sold 1.1 million passenger tickets in 1913.[58] The city was also served by the Michigan Central Railroad starting in 1837. Amtrak provides service to Ann Arbor, operating its Wolverine three times daily in each direction between Chicago and Pontiac, via Detroit. Rail service is provided at the Ann Arbor Train Station; the present-day station neighbors the city's old Michigan Central Depot, which was renovated as a restaurant in 1969. There have been plans to build a commuter rail link between Ann Arbor and Detroit, with the U.S. federal government providing $100 million to enable its development.[59]
See also
Notes
- ^ "Ann Arbor city, Michigan - DP-2. Profile of Selected Social Characteristics: 2000". US Census Bureau. 2000. Retrieved 2007-02-12.
- ^ "1824–1859: Ann Arbor/Annarbour - the Naming of Ann Arbor. Pictorial History of Ann Arbor: 1824–1974". Ann Arbor District Library. 2003. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
- ^ Marwil, Jonathan (June 15, 1991). A History of Ann Arbor. University of Michigan Press. p. 13. ISBN 0-472-06463-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ "1940–1974: Progress and Preservation. Pictorial History of Ann Arbor: 1824–1974". Ann Arbor District Library. 2003. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
- ^ a b "1940–1974: From Protest to Outer Space. Pictorial History of Ann Arbor: 1824–1974". Ann Arbor District Library. 2003. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
- ^ Restivo, Terrence R. (March 22 2006). "The Building of a New Left Conglomerate in the City of Ann Arbor: VOICE, Action Movement and the Human Rights Party (1965–1975)" (pdf). McAnulty College and Graduate School of Liberal Arts, Duquesne University. Retrieved 2007-05-08.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Ann Arbor Parks and Greenbelt Proposal". Friends of Ann Arbor Open Space. March 2 2004. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Ann Arbor, USGS Ann Arbor East (MI) Topo Map". TopoZone. 2005. Retrieved 2005-06-15.
- ^ "KARB — Ann Arbor Municipal Airport". March 15 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-08.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|pubisher=ignored (|publisher=suggested) (help) - ^ "Fun Facts". Ann Arbor Area Convention and Visitor's Bureau. 2005. Retrieved 2005-09-06.
- ^ "Parks". Ann Arbor City Government. 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ "Ann Arbor Park Listings and Features". Ann Arbor City Government. 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ "Ann Arbor Farmers' Market". Ann Arbor City Government. 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ "Neighborhood Association". Old West Side Association. 2007. Retrieved 2006-06-04.
- ^ "Ann Arbor". MichiganVacations.com. 2005. Retrieved 2005-08-18.
- ^ "Average High/Low Temperatures for KYIP". Weather Underground (wunderground.com). 2005. Retrieved 2005-08-17.
- ^ "Records and Averages — Ann Arbor". Ann Arbor Weather Forecasts on Yahoo! Weather. 2005. Retrieved 2005-08-31.
- ^ "Weatherbase: Historical Weather for Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States of America". Weatherbase. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-04.
- ^ Geographic references - U.S. Census 2000
- ^ "Ann Arbor city, Michigan - MapStats". FedStats. October 24, 2006. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ "Reported crime in United States-Total". U.S. Department of Justice Office of Justice Programs -
Bureau of Justice Statistics. December 13, 2006. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
{{cite web}}: line feed character in|publisher=at position 56 (help)CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ "Government". Ann Arbor City Council. 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ "Ann Arbor Government Guide". Arborweb.com. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
- ^ Cohen-Vrignaud, Gerard (February 12 1999). "Gay and Proud". The Michigan Daily. Retrieved 2007-05-05.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Walter, Benjamin (August 26 2001). "Instant Runoff Voting (IRV) — History of Use in Ann Arbor". Green Party of Michigan. Retrieved 2007-05-05.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Ann Arbor: Economy". city-data.com. 2006. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
- ^ Williams, Paul (2006). "Ann Arbor Terminals, Inc". vt100.net. Retrieved 2007-05-05.
- ^ "MITC: A Vision Comes to Fruition". Michigan Information Technology Center. 2006. Retrieved 2006-06-04.
- ^ Goodman, David N. (July 11 2006). "Google Plans to Open Facility in Michigan". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2006-07-12.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help)CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ Jenny Rode and Stefanie Murray (January 22 2007). "Pfizer to close Ann Arbor campus". Ann Arbor News. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "National Vehicle and Fuel Emissions Laboratory". United States Environmental Protection Agency. April 3, 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ "About Toyota — Toyota Technical Center, USA, Inc". Toyota Motor Sales, U.S.A. 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ Blakeley, Pam (2005–2006). "Doggin' Around Ann Arbor". Ann Arbor Guide 2005–6.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); External link in|title= - ^ "Distinction and Visibility". Domino's Farms Office Park. 2006. Retrieved 2006-06-04.
- ^ "Flint Ink and XSYS Print Solutions Agree to Merge". Flint Group. July 20 2005. Retrieved 2007-05-08.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Our Communities". Cohousing Development Company L.L.C. 2006. Retrieved 2007-05-08.
- ^ Cochran, Jason (October 2002). "Ann Arbor, Michigan". Budget Travel Online.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); External link in|title= - ^ Hansen, Susan (July 31 2006). "Portrait of a tycoon as a driven benefactor". International Herald Tribune (The New York Times). Retrieved 2007-05-08.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Brannock, Jennifer (February 25 2007). "Florida vs. Michigan: Ave Maria law school not a game to them". Naples Daily News. Retrieved 2007-05-08.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Ann Arbor private schools". Schools K-12. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
- ^ "About AAPS: Demographics Data - Headcount by Grade and School". Ann Arbor Public Schools. 2005. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
- ^ "Ann Arbor Open School". Ann Arbor Public Schools. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
- ^ "City Guide — Dance". ArborWeb.com. 2005. Retrieved 2005-08-18.
- ^ "Ann Arbor Guide 2003–4". Ecurrent.com. 2003–2004. Retrieved 2005-08-17.
- ^ "About - Mission & History". Ann Arbor Street Art Fair. 2006. Retrieved 2007-02-20.
- ^ "Naked Mile Data Page". goodspeedupdate.com. April 2001. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ "List of 100,000+ Capacity Stadiums". WorldStadiums.com. 2006. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ^ Bakopoulos, Dean (April 17, 1997). "Places I'll remember: A farewell to Ann Arbor". The Michigan Daily.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); External link in|title= - ^ "Welcome to Ann Arbor". Booth Newspapers - The Ann Arbor News. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-20.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Fire Up Downtown". University of Michigan - Arts at Michigan. 2004. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
- ^ "Ann Arbor Publications". Arborweb.com. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
- ^ a b "Radio Broadcasting Stations - Ann Arbor MI". RadioStationWorld. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
- ^ "Community Television Network". Ann Arbor City Government. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
- ^ "America's Best Hospitals 2006: Honor Roll". US News and World Reports. 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-18.
- ^ "Water Treatment". City of Ann Arbor. 2005. Retrieved 2005-09-07.
- ^ "City of Ann Arbor Bikeway System" (PDF). City of Ann Arbor and Washtenaw County. 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ Brandt, Karen L. (Fall 2005/Winter 2006). "Ann Arbor Bus Depot". The Modern. 18 (2). Retrieved 2007-05-05.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Michigan's Ann Arbor Railroads — Building the Ann Arbor". Central Michigan University — Clarke Historical Library. December 8, 2005. Retrieved 2005-09-01.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ Mulcahy, John (August 28, 2005). "Is commuter rail finally on fast track? Federal grant gets Ann Arbor-Detroit link moving". Ann Arbor News. Retrieved 2005-09-01.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: year (link)
References
- Encyclopedia of Michigan. St. Clair Shores, MI: Somerset Publishers. 1999.
- Michigan Gazetteer. Wilmington, DE: American Historical Publications. 1991.
- Fisher, Dale (1996). Ann Arbor: Visions of the Eagle. Grass Lake, MI: Eyry of the Eagle Publishing. ISBN 096156234X.
- Marwil, Jonathan (1990). A History of Ann Arbor. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
- Schmittroth, Linda (Ed.) (1994). Cities of the United States (4th edition ed.). Detroit: Gale Group.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - "Social Characteristics of Ann Arbor". US Census Bureau. 2000.
- "Pictorial History of Ann Arbor". Ann Arbor District Library. 2003.
- Winling, LaDale C. (2007). "Student Housing, City Politics, and the University of Michigan, 1920–1980" (pdf). University of Michigan.
External links
- City's official website
- Ann Arbor Area Convention and Visitor's Bureau
- ArborUpdate.com—Ann Arbor community news
- ArborWiki—A wiki for Ann Arbor
- UmichCrime—Interactive map of incidents reported to the University of Michigan's Department of Public Safety
- Template:Wikitravel
Template:Geolinks-US-cityscale

