Paramesonephric duct
Appearance
| Paramesonephric duct | |
|---|---|
 Urogenital sinus of female human embryo of eight and a half to nine weeks old. | |
 Tail end of human embryo, from eight and a half to nine weeks old. | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 17 |
| Precursor | Intermediate mesoderm |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | d. paramesonephricus |
| MeSH | D009095 |
| TE | duct_by_E5.7.2.3.0.0.3 E5.7.2.3.0.0.3 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The Müllerian ducts (or paramesonephric ducts) are paired ducts of the embryo which run down the lateral sides of the urogenital ridge and terminate at the [mullerian tubercle| mullerian eminence] in the primitive urogenital sinus. In the female, it will develop to form the fallopian tubes, uterus, and the upper portion of the vagina. It is tissue of mesodermal origin.
Regulation of development
The development of the Müllerian ducts is controlled by the presence or absence of "AMH", or Anti-müllerian hormone (also known as "MIF" for "Müllerian inhibiting factor", or "MIH" for "Müllerian inhibiting hormone").
| male embryogenesis | The testes produce AMH and as a result the development of the Müllerian ducts is inhibited. | Disturbances can lead to persistent müllerian duct syndrome. | The ducts disappear except for the vestigial vagina masculina and the appendix testis. |
| female embryogenesis | The absence of AMH results in the development of female reproductive organs, as noted above. | Disturbance in the development may result in uterine absence (Mullerian agenesis) or uterine malformations. | The ducts develop into the upper vagina, cervix, uterus and oviducts. |
Eponym
They are named after Johannes Peter Müller, a physiologist who described these ducts in his text "Bildungsgeschichte der Genitalien" in 1830.
Additional images
-
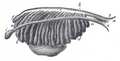
Enlarged view from the front of the left Wolffian body before the establishment of the distinction of sex.
-
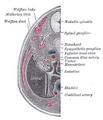
Transverse section of human embryo eight and a half to nine weeks old.
See also
- Defeminization
- prostatic utricle
- List of homologues of the human reproductive system
- Sexual differentiation
- Wolffian duct
External links
- genital-010—Embryo Images at University of North Carolina