Ghana
Republic of Ghana | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Freedom and Justice" | |
| Anthem: God Bless Our Homeland Ghana [1] | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Accra |
| Official languages | English |
| Demonym(s) | Ghanaian |
| Government | Constitutional republic |
| John Agyekum Kufuor | |
| Alhaji Aliu Mahama | |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
• Declared | 6 March 1957 |
• Republic | 1 July 1960 |
• Constitution | 28 April 1992 |
| Area | |
• Total | 238,534 km2 (92,098 sq mi) (91st) |
• Water (%) | 3.5 |
| Population | |
• 2007 estimate | 23,000,000[2] (48th) |
• Density | 93/km2 (240.9/sq mi) (103rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2007[3] estimate |
• Total | $60 billion (55th) |
• Per capita | $2,750 (136th) |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (135th) |
| Currency | Ghanaian cedi (GHS) |
| Time zone | UTC0 (GMT) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC0 (GMT) |
| Calling code | 233 |
| ISO 3166 code | GH |
| Internet TLD | .gh |
The Republic of Ghana is a country in West Africa. It borders Côte d'Ivoire (also known as Ivory Coast) to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, Togo to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south. The word "Ghana" means "Warrior King",[4] and was the source of the name "Guinea" (via French Guinoye) used to refer to the West African coast (as in Gulf of Guinea).
Ghana was inhabited in pre-colonial times by a number of ancient kingdoms, including the Ga Adangbes on the eastern coast, inland Empire of Ashanti and various Fante states along the coast and inland. Trade with European states flourished after contact with the Portuguese in the 15th century, and the British established a crown colony, Gold Coast, in 1874.[5]
Upon achieving independence from the United Kingdom in 1957,[6] the name Ghana was chosen for the new nation to reflect the ancient Empire of Ghana that once extended throughout much of western Africa. In the Ashanti language it is spelled Gaana.
History
Medieval Ghana (4th - 13th Century):The Republic of Ghana is named after the medieval Ghana Empire of West Africa. The actual name of the Empire was Wagadugu. Ghana was the title of the kings who ruled the kingdom. It was controlled by Sundiata in 1240 AD, and absorbed into the larger Mali Empire. (Mali Empire reached its peak of success under Mansa Musa around 1307.)
Geographically, the old Ghana was approximately 500 miles north of the present Ghana, and occupied the area between Rivers Senegal and Niger.
Some inhabitants of present Ghana have ancestors linked with the medieval Ghana. This can be traced down to the Mande and Voltaic people of Northern Ghana--Mamprussi, Dagomba and the Gonja.
Anecdotal evidence connected the Akans to this Empire. The evidence lies in names like Danso shared by the Akans of present Ghana and Mandikas of Senegal/Gambia who have strong links with the Empire.
Ghana was also the site of the Empire of Ashanti which was perhaps the most advanced black state in sub-Sahara Africa. It is said that at its peak, the King of Ashanti could field 500,000 troops.
Up until March 1957, Ghana was known to much of the world as the Gold Coast. The Portuguese who came to Ghana in the 15th Century found so much gold between the rivers Ankobra and the Volta that they named the place Mina - meaning Mine. The Gold Coast was later adopted by English colonists. Similarly, the French, equally impressed by the trinkets worn by the coastal people, named the area to the west "Cote d'Ivoire," or Ivory Coast.
In 1481, King John II of Portugal commissioned Diogo d'Azambuja to build Elmina Castle, which was completed the next year. Their aim was to trade in gold, ivory and slaves, consolidating their burgeoning power in the region.
By 1598 the Dutch had joined them, and built forts at Komenda and Kormantsi. In 1637 they captured Elmina Castle from the Portuguese and Axim in 1642 (Fort St Anthony). Other European traders joined in by the mid 17th century, largely English, Danes and Swedes. The coastline was dotted by more than 30 forts and castles built by Dutch, British and Danish merchants. The Gold Coast became the highest concentration of European military architecture outside of Europe. By the latter part of 19th century the Dutch and the British were the only traders left and after the Dutch withdrew in 1874, Britain made the Gold Coast a protectorate.
For most of central sub-Saharan Africa, agricultural expansion marked the period before 500. Farming began earliest on the southern tips of the Sahara, eventually giving rise to village settlements. Toward the end of the classical era, larger regional kingdoms had formed in West Africa, one of which was the Kingdom of Ghana, north of what is today the nation of Ghana. After its fall at the beginning of the 13th century, Akan migrants moved southward then founded several nation-states including the first great Akan empire of the Bono which is now known as the Brong Ahafo region in Ghana. Later Akan groups such as the Ashanti federation and Fante states are thought to possibly have roots in the original Bono settlement at Bono manso. Much of the area was united under the Empire of Ashanti by the 16th century. The Ashanti government operated first as a loose network and eventually as a centralized kingdom with an advanced, highly-specialized bureaucracy centered in Kumasi.
The first contact between the Ghanaian peoples, the Fantes on the coastal area and Europeans occurred in 1482. The Portuguese first landed at Elmina, a coastal city inhabited by the Fanti nation-state in 1482. During the next few centuries parts of the area were controlled by British, Portuguese, and Scandinavian powers, with the British ultimately prevailing. These nation-states maintained varying alliances with the colonial powers and each other, which resulted in the 1806 Ashanti-Fante War, as well as an ongoing struggle by the Empire of Ashanti against the British. Moves toward regional de-colonization began in 1946, and the area's first constitution was promulgated in 1951.
Formed from the merger of the British colony Gold Coast, The Empire of Ashanti and the British Togoland trust territory by a UN sponsored plebiscite, Ghana became the first democratic sub-Sahara country in colonial Africa to gain its independence in 1957. Kwame Nkrumah, founder and first president of the modern Ghanaian state, was not only an African anti-colonial leader but also one with a dream of a united Africa which would not drift into neo-colonialism. He was the first African head of state to espouse Pan-Africanism, an idea he came into contact with during his studies at Lincoln University in Pennsylvania (United States), at the time when Marcus Garvey was becoming famous for his "Back to Africa Movement." He merged the dreams of both Marcus Garvey and the celebrated African-American scholar W.E.B. Du Bois into the formation of the modern day Ghana. Ghana's principles of freedom and justice, equity and free education for all, irrespective of ethnic background, religion or creed borrow from Osagyefo Dr Kwame Nkrumah's implementation of Pan-Africanism.
Nkrumah was overthrown by a military coup in 1966. It has been argued that this was supported by the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency[7][8], although that assertion remains generally unproven. A series of subsequent coups ended with the ascension to power of Flight Lieutenant Jerry Rawlings in 1981. These changes resulted in the suspension of the constitution in 1981 and the banning of political parties. A new constitution, restoring multi-party politics, was promulgated in 1992, and Rawlings was elected as president in the free and fair elections of that year and again won the elections 1996 to serve his second term. The constitution prohibited him from running for a third term. John Kufuor, the current president, is now serving his second term, which ends in 2008 where another election will be held to elect a new president. The year 2007 marks Ghana's Golden Jubilee celebration of its 50-year anniversary, which was on March 6th, 1957.
Economy
Well endowed with natural resources, Ghana has twice the per capita output of the poorer countries in West Africa. Even so, Ghana remains heavily dependent on international financial and technical assistance as well as the activities of the extensive Ghanaian diaspora, despite evidence of widespread corruption (see attached article). Gold, timber, cocoa, diamond, bauxite, and manganese exports are major sources of foreign exchange.[9] An oilfield which is reported to contain up to 3 billion barrels of light oil was discovered in 2007.[10]
The domestic economy continues to revolve around subsistence agriculture, which accounts for 50% of GDP and employs 85% of the work force,[11] mainly small landholders. Ghana made progress under a three-year structural adjustment programme in cooperation with the IMF.[neutrality is disputed] On the negative side, public sector wage increases and regional peacekeeping commitments have led to continued inflationary deficit financing, depreciation of the Cedi, and rising public discontent with Ghana's austerity measures. Even so, Ghana remains one of the more economically sound countries in all of Africa.
The country has since July, 2007, embarked on a currency re-denomination exercise, from Cedi (¢) to the new currency, the Ghana Cedi (GH¢). The transfer rate is 1 Ghana Cedi for every 10,000 Cedis. The Bank of Ghana has embarked upon an aggressive media campaign to educate the public about what re-denomination entails. The new Ghana Cedi is now exchanging at a rate of $1 USD =Gh¢ 0.93
Value Added Tax is a consumption tax administered in Ghana. The tax regime which started in 1998 had a single rate but since September 2007 entered into a multiple rate regime. In 1998, the rate of tax was 10% and amended in 2000 to 12.5%. However with the passage of Act 734 of 2007, a 3% VAT Flat Rate Scheme (VFRS) begun to operate for the retail distribution sector. This allows retailers of taxable goods under Act 546 to charge a marginal 3% on their sales and account on same to the VAT Service. It is aimed at simplifying the tax system and increasing compliance. It is the hope of government that if properly monitored, it would ultimately increase tax revenue in the country.
Regions and districts

Ghana is a divided into 10 regions, subdivided into a total of 138 districts. The regions are:
Column-generating template families
The templates listed here are not interchangeable. For example, using {{col-float}} with {{col-end}} instead of {{col-float-end}} would leave a <div>...</div> open, potentially harming any subsequent formatting.
| Type | Family | Handles wiki
table code?† |
Responsive/ mobile suited |
Start template | Column divider | End template |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float | "col-float" | Yes | Yes | {{col-float}} | {{col-float-break}} | {{col-float-end}} |
| "columns-start" | Yes | Yes | {{columns-start}} | {{column}} | {{columns-end}} | |
| Columns | "div col" | Yes | Yes | {{div col}} | – | {{div col end}} |
| "columns-list" | No | Yes | {{columns-list}} (wraps div col) | – | – | |
| Flexbox | "flex columns" | No | Yes | {{flex columns}} | – | – |
| Table | "col" | Yes | No | {{col-begin}}, {{col-begin-fixed}} or {{col-begin-small}} |
{{col-break}} or {{col-2}} .. {{col-5}} |
{{col-end}} |
† Can template handle the basic wiki markup {| | || |- |} used to create tables? If not, special templates that produce these elements (such as {{(!}}, {{!}}, {{!!}}, {{!-}}, {{!)}})—or HTML tags (<table>...</table>, <tr>...</tr>, etc.)—need to be used instead.
Population of major cities
| City | Population | |
|---|---|---|
| Accra | 2,096,653 | |
| Kumasi | 1,604,909 | |
| Tamale | 390,730 | |
| Sekondi-Takoradi | 260,651 | |
| Tema | 229,106 | |
| Teshie | 154,513 | |
| Cape Coast | 154,204 | |
| Obuasi | 147,613 |
Geography

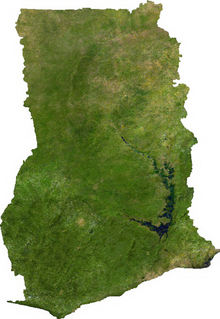
Ghana is a country located on the Gulf of Guinea, only a few degrees north of the Equator, therefore giving it a warm climate. The Greenwich Meridian also passes through Ghana, specifically through the industrial city of Ghana-Tema; so it is said that Ghana is geographically closer to the "center" of the world than any other country. La Cote d'Ivoire is located to the west of Ghana while Burkina Faso and Togo are located to its north and east respectively. The coastline is mostly a low, sandy shore backed by plains and scrub and intersected by several rivers and streams. A tropical rain forest belt, broken by heavily forested hills and many streams and rivers, extends northward from the shore. North of this belt, the land is covered by low bush, park-like savannah, and grassy plains.
The climate is tropical. The eastern coastal belt is warm and comparatively dry (see Dahomey Gap); the southwest corner, hot and humid; and the north, hot and dry. Lake Volta, the world's largest artificial lake, extends through large portions of eastern Ghana.
Demographics
Major Ethnic groups: Akan 49%, Moshi-Dagomba 16%, Ewe 13%, Ga 8%. European and other: 0.2%
Religions: Christian 63%, African beliefs 21%, Muslim 16%,[12] though more recent estimates indicate that Muslims make up 30% of the population.[13]
Languages
More than 100 languages and dialects are spoken in Ghana. English is the country's official language and predominates government and business affairs. It is also the standard language used for educational instruction. Native Ghanaian languages are divided into two linguistic subfamilies of the Niger-Congo language family. Languages belonging to the Kwa subfamily are found predominantly to the south of the Volta River, while those belonging to the Gur subfamily are found predominantly to the north. The Kwa group, which is spoken by about 75% of the country's population, includes the Akan, Ga-Dangme, and Ewe languages. The Gur group includes the Gurma, Grusi, and Dagbani languages.[14]
Nine languages have the status of government-sponsored languages: Akan, Dagaare/Wale, Dagbani, Dangme, Ewe, Ga, Gonja, Kasem, and Nzema. Though not an official language, Hausa is the lingua-franca spoken among Ghana's Muslims, who comprise about 14% of the population.
Education
Presently, Ghana has 18,530 primary schools, 8,850 junior secondary schools, 900 senior secondary schools, 28 training colleges, 20 technical institutions, 4 diploma-awarding institutions, 6 public universities and over 10 private universities. That means that most Ghanaians have relatively easy access to primary and secondary education. These numbers can be contrasted with the single university and handful of secondary and primary schools that existed at the time of independence in 1957. Ghana's spending on education has varied between 28 and 40 percent of its annual budget in the past decade. All teaching is done in English, Ghana's official language.
Ghana has a 6-year primary education system beginning at the age of six and, under the educational reforms implemented in 1987, they pass on to a 3-year junior secondary school (JSS) program. At the end of the 3rd year of JSS, there is a Basic Education Certificate Examination (BECE). Those continuing must complete the 3-year senior secondary school (SSS) program and take an admission exam to enter university. School enrollment totals over 2 million: 1.3 million primary; 550,000 middle; 300,000 secondary; 84,280 technical; 18,000 teacher training, and 89,000 in university.
The shortage of places in post-secondary education is acute; only one out of nine senior secondary graduates finds a place in a technical, teacher-training, or four-year university program.
International rankings
| Organization | Survey | Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Heritage Foundation/The Wall Street Journal | Index of Economic Freedom | 91 out of 157[15] |
| Reporters Without Borders | Worldwide Press Freedom Index | 29 out of 168[16] |
| Transparency International | Corruption Perception Index | 69 out of 179[17] |
| United Nations Development Programme | Human Development Index | 135 out of 177[18] |
| Vision of Humanity | Global Peace Index | 40 out of 121[19] |
| World Economic Forum | Global Competitiveness Report | not ranked[20] |
See also
- Transport in Ghana
- List of Ghana-related topics
- List of Ghanaian companies
- Corruption in Ghana
- Communications in Ghana
- Military of Ghana
- Ghana Film Industry
- Empire of Ashanti
- List of Ghanaians
- Ghana Telecom University College
References
- ^ [1]
- ^ The World Factbook
- ^ The World Factbook
- ^ Jackson, John G. Introduction to African Civilizations, 2001. Page 201.
- ^ MacLean, Iain. Rational Choice and British Politics: An Analysis of Rhetoric and Manipulation from Peel to Blair, 2001. Page 76.
- ^ Peter N. Stearns and William Leonard Langer. The Encyclopedia of World History: Ancient, Medieval, and Modern, Chronologically Arranged, 2001. Page 1050.
- ^ Interview with John Stockwell in Pandora's Box: Black Power (Adam Curtis, BBC Two, 22 June 1992)
- ^ http://www.state.gov/www/about_state/history/vol_xxiv/s.html, http://www.state.gov/www/about_state/history/vol_xxiv/s.html, http://www.ghanaweb.com/GhanaHomePage/history/cia_nkrumah.php, http://www.ghanaweb.com/GhanaHomePage/features/artikel.php?ID=75990, On Nkrumah assassination by CIA: Gaines, Kevin (2006) American Africans in Ghana, Black expatriates and the Civil Rights Era, The University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill.
- ^ The World Factbook
- ^ [2]
- ^ The World Factbook
- ^ Facts on People of Ghana, accessed July 13, 2006
- ^ Historical Dictionary Of Women In Sub-Saharan Africa By Kathleen E. Sheldon, pg. 109
- ^ LaVerle Berry, ed. (1995). Ghana: A Country Study. Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 81–82. ISBN 0844408352.
- ^ "Heritage Foundation - 2007 Index of Economic Freedom". Official Website for the Index. The Wall Street Journal and The Heritage Foundation. Retrieved 2007-02-24.
The highest form of economic freedom provides an absolute right of property ownership, fully realised freedoms of movement for labour, capital, and goods, and an absolute absence of coercion or constraint of economic liberty beyond the extent necessary for citizens to protect and maintain liberty itself. In other words, individuals are free to work, produce, consume, and invest in any way they please, and that freedom is both protected by the state and unconstrained by the state.
- ^ "Reporters Without Borders - Worldwide Press Freedom Index 2006". Annual Worldwide Press Freedom Index. Reporters sans frontières. Retrieved 2007-02-24.
- ^ "Corruption Perception Index 2007". Official Website. Transparency International e.V. Retrieved 2007-12-11.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2006" (pdf). Annual Report. United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved 2007-02-24.
- ^ "Global Peace Index Rankings". Global Peace and Sustainability. Economist Intelligence Unit, Centre for Peace and Conflict Studies, University of Sydney, Australia and some Peace Institutes and Think Tanks. Retrieved 2007-05-30.
- ^ "Table 1: Global Competitiveness Index rankings and 2005 comparisons" (pdf). World Economic Forum - Global Competitiveness Report 2006 - 2007. World Economic Forum. Retrieved 2007-02-24.
External links
- Ghana News
- Ghana Broadcasting Corporation
- Latest Ghana News
- Headline News, photos, video from Ghana
- News in Ghana
- Government
- Ghana official Website
- The Parliament of Ghana official site
- National Commission on Culture official site
- [3]
- Ghana's Independence Video by Information Services Department
- Healthcare
- Korle Bu Hospital[dead link]
- Unite For Sight at Buduburam Refugee Camp, Ghana A Unite For Sight video documentary with interviews of residents at Buduburam Refugee Camp, Ghana. Unite For Sight provides free eye care for the residents.
- Subayo Foundation A not for profit charity for women and children in Ghana based out of the US.
- Overviews
- Rural poverty in Ghana (IFAD)
- BBC Country Profile - Ghana
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, Country Page - Ghana
- CIA World Factbook - Ghana
- Template:Dmoz
- US State Department — Ghana includes Background Notes, Country Study and major reports
- Business Anti-Corruption Portal Ghana Country Profile
- Historical Notes and Memorial Inscriptions From Ghana, Compiled 1988 to 1990 by M.E.J. Crew of Ofinso Training College, Ofinso, Ashanti, Ghana
- [4] Short Documentary looking at the problems faced by Ghana's rice farmers
- Teaching resources
- Tourism
- Template:Wikitravel
- Ghana Tourism Official Ghana Tourism Website
- Ghana@50 official independence anniversary site
- Teaching in Ghana
- Ghana Tourism Information
- On the web

