Net force
Appearance
- This article is about forces in physics. For the Luke Van Essen sci-fi novel, see Luke Van Essen's Net Force
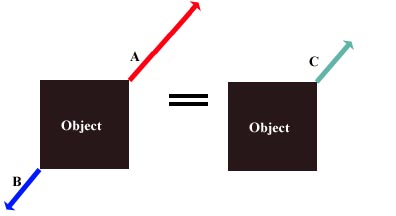
- When force A and force B act on an object in the same direction (parallel vectors), the net force (C) is equal to A + B, in the direction that both A and B point. The A point has more force and moves in a separate direction the B will end up not moving to.
- When force A and force B act on an object in opposite directions (180 degrees between then - anti-parallel vectors), the net force (C) is equal to |A - B|, in the direction of whichever one has greater absolute value ("greater magnitude").
File:Non-parallel net force.jpg
- When the angle between them (the forces) is anything else, then the individual components must be added up using sine and cosine.
(Note: The illustration assumes that the object, in this case a square, has no center of mass and can be treated like a point.)