Operation Weserübung
| Operation Weserübung | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of World War II | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 9 divisions, 1 artillery battalion, 1 Motorized Rifle Brigade |
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Heer, Kriegsmarine & Luftwaffe:[2] 4,950 KIA 616 MIA 1,600 WIA |
Royal Norwegian Navy & Army:[3] 1,335 KIA ? MIA Allies:[3] 4,765 KIA Total:[3] 6,100 KIA | ||||||
Operation Weserübung was the German codename for Nazi Germany's assault on Denmark and Norway during World War II and the opening operation of the Norwegian Campaign. The name comes from the German for Operation Weser-Exercise, the Weser being a German river.
In the early morning of April 9, 1940 – Wesertag ("Weser Day") – Germany invaded Denmark and Norway, ostensibly as a preventive maneuver against a planned [citation needed], and openly discussed [citation needed], Franco-British occupation of both these countries. After the invasions, envoys of the Germans informed the governments of Denmark and Norway that the Wehrmacht had come to protect the countries' neutrality against Franco-British aggression. Significant differences in geography, location and climate between the two countries made the actual military operations very dissimilar.
The invasion fleet's nominal landing time – Weserzeit ("Weser Hour") – was set to 05:15 AM German time, equivalent to 04:15 Norwegian time.
Political and military background
Starting in the spring of 1939, the British Admiralty began to view Scandinavia as a potential theatre of war in a future conflict with Germany. The British government was reluctant to engage in another land conflict on the continent that they believed would be a repeat of World War I. So they began considering a blockade strategy in an attempt to weaken Germany indirectly. German industry was heavily dependent on the import of iron ore from the northern Swedish mining district, and much of this ore during the winter months was shipped through the northern Norwegian port of Narvik.[4] Control of the Norwegian coast would also serve to tighten a blockade against Germany.
In October 1939, the chief of the German Kriegsmarine, Grand Admiral Erich Raeder, discussed with Adolf Hitler the danger posed by eventual British bases in Norway and the possibility of Germany seizing these bases before the United Kingdom could. The navy argued that possession of Norway would allow control of the nearby seas and serve as a staging base for future submarine operations against the UK.[4] But at this time, the other branches of the Wehrmacht were not interested, and Hitler had just issued a directive stating that the main effort would be a land offensive through the Low Countries.
Toward the end of November, Winston Churchill, as a new member of the British War Cabinet, proposed the mining of Norwegian waters in the Operation Wilfred. This would force the ore transports to travel through the open waters of the North Sea, where the Royal Navy could interdict them. Churchill assumed that Wilfred would provoke a German response in Norway. When that occurred, the Allies would implement Plan R 4 and occupy Norway. The subsequently implemented "Operation Wilfred" was originally turned down by Neville Chamberlain and Lord Halifax, due to fear of an adverse reaction among neutral nations such as the United States. After the start of the Winter War between the Soviet Union and Finland in November had changed the diplomatic situation, Churchill again proposed his mining scheme but once more was denied.
In December, the UK and France began serious planning for sending aid to Finland. Their plan called for a force to land at Narvik in northern Norway, the main port for Swedish iron ore exports, and to take control of the Malmbanan railway line from Narvik to Luleå in Sweden on the shore of the Gulf of Bothnia. Conveniently, this plan also would allow the allied forces to occupy the Swedish iron ore mining district. The plan received the support of both Chamberlain and Halifax. They were counting on the cooperation of Norway, which would alleviate some of the legal issues. But stern warnings issued to both Norway and Sweden resulted in strongly negative reactions in both countries. Planning for the expedition continued, but the justification for it was removed when Finland sued for peace in March 1940.
Planning
Convinced of the threat posed by the allies to the iron ore supply, Hitler ordered the German high command (OKW) to begin preliminary planning for an invasion of Norway on December 14, 1939. The preliminary plan was named Studie Nord and only called for one army division.
Between January 14 and 19 the Kriegsmarine developed an expanded version of this plan. They decided upon two key factors: that surprise was essential to reduce the threat of Norwegian resistance (and British intervention); the second to use the faster German warships, rather than comparatively slow merchant ships, as troop transports. This would allow all targets to be occupied simultaneously, as the transport ships only had limited range. This new plan called for a full army corps, including a mountain division, an airborne division, a motorized rifle brigade, and two infantry divisions. The target objectives of this force were the following:
The plan also called for the rapid capture of the kings of Denmark and Norway in the hopes that would trigger a rapid surrender.
On February 21, 1940, command of the operation was given to General von Falkenhorst. He had fought in Finland during World War I and therefore was familiar with arctic warfare. But he was only to have command of the ground forces, despite Hitler's desire to have a unified command.
The final plan was code-named Operation Weserübung ("Exercise on the Weser") on January 27, 1940. It would be under the command of the XXI Army Group and include the 3rd Mountain Division and five infantry divisions, none of the latter having yet been tested in battle. The initial echelon would consist of three divisions for the assault, with the remainder to follow in the next wave. Three companies of paratroopers would be used to seize airfields. The decision to send also the 2nd Mountain Division was made later.
Initially the plan was to invade Norway and to gain control of Danish airfields by diplomatic means. But Hitler issued a new directive on March 1 that called for the invasion of both Norway and Denmark. This came at the insistence of the Luftwaffe to capture fighter bases and sites for air-warning stations. The XXXI Corps was formed for the invasion of Denmark, consisting of two infantry divisions and the 11th motorized brigade. The entire operation would be supported by the X Air Corps, consisting of some 1,000 aircraft of various types.
Preliminaries
In February the British destroyer HMS Cossack boarded the German transport ship Altmark while in Norwegian waters, thereby violating Norwegian neutrality, rescuing POWs held also in violation of Norwegian neutrality (the Altmark was obliged to release them as soon as she entered neutral territory). Hitler regarded this as a clear sign that the UK was willing to violate Norwegian neutrality, and so became even more strongly committed to the invasion.[4]
On March 12, the UK decided to send an expeditionary force to Norway just as the Winter War was winding down. The expeditionary force began boarding on March 13, but it was recalled - and the operation cancelled - with the end of the Winter War. Instead the British cabinet voted to proceed with the mining operation in Norwegian waters, followed by troop landings.
The first German ships set sail for the invasion on April 3. Two days later the long-planned Operation Wilfred was put into action and the Royal Navy detachment led by HMS Renown left Scapa Flow in order to mine Norwegian waters. The mine fields were laid in Vestfjord and in the early morning of April 8. The Operation Wilfred was over but later that day the destroyer Glowworm, detached on 7 April to search for man lost overboard, was lost in action with German cruiser Admiral Hipper and two destroyers belonging to the German invasion fleet.
On April 9 the German invasion was under way and the execution of Plan R 4 was promptly started.
Invasion of Denmark

Strategically, Denmark's importance to Germany was as a staging area for operations in Norway, and of course as a border nation to Germany which would have to be controlled in some way. Given Denmark's position in the Baltic Sea the country was also important for the control of naval and shipping access to major German and Russian harbors.
The country is small and relatively flat, ideal territory for German army operations, and Denmark's small army had little hope of success in armed resistance. Nevertheless, in the early morning hours a few Danish troops engaged the German army, suffering losses of 16 dead and 20 wounded. Germany never gave any official number of losses, but these were probably heavier, with 12 armored cars and several motorcycles and cars destroyed. Four German tanks were damaged and one Heinkel 111 shot down. Two German soldiers were temporarily captured by the Danes during the brief fighting.[1]
Just before the initial German incursions into Denmark the German ambassador to Denmark, Renthe-Fink, called the Danish Foreign Minister Munch and requested a meeting with him. When the two men met 20 minutes later Renthe-Fink declared that German troops were at that moment moving in to occupy Denmark to protect the country from Franco-British attack. The German ambassador demanded that Danish resistance must cease immediately and contact be made between Danish authorities and the German armed forces. If the demands were not met the Luftwaffe was to bomb the capital Copenhagen.[1]
As the German demands were communicated the first German advances had already been made, with forces having landed by ferry in Gedser at 04:15 and moved north. German Fallschirmjäger units had made unopposed landings and taken the Storstrøm Bridge as well as the fortress of Masnedø.[1]
At 04:20 local time 1,000 German infantry landed in Copenhagen harbor from the minelayer Hansestadt Danzig, quickly capturing the Danish garrison at the Citadel without encountering resistance. From the harbor the Germans moved towards Amalienborg Palace to capture the Danish royals. By the time the invasion forces arrived at the King's residence the King's Royal Guard had been alarmed and other reinforcements were in their way to the palace. The first German attack on Amalienborg was repulsed, giving Christian X and his ministers time to confer with the Danish Army chief General Prior. As the discussions were ongoing several formations of Heinkel 111 and Dornier 17 bombers roared over the city dropping leaflets. Faced with the explicit threat of the Luftwaffe bombing the civilian population of Copenhagen, and only General Prior in favour of continuing the fighting, the Danish government capitulated in exchange for retaining political independence in domestic matters.[1]
At 05:45 two squadrons of German Me 110s had attacked Værløse airfield on Zealand and wiped out the Danish Army Air Service by strafing. Despite Danish anti-aircraft fire the German fighters destroyed 11 Danish aircraft and seriously damaged another 14.[1]
The Danish capitulation resulted in the uniquely lenient Occupation of Denmark, particularly until the summer of 1943, and also in postponing the arrest and deportation of Danish Jews until nearly all of them were warned and on their way to refuge in Sweden.[5] In the end, 477 Danish Jews were deported, and 70 of them lost their lives, out of a pre-war total of Jews and half-Jews at a little over 8,000.[6]
Though Denmark had little immediate military significance, it had strategic and to some extent economic importance.
Invasion of Norway
Motivation and Order of Battle
Norway was important to Germany for two primary reasons: as a base for naval units, including U-boats, to harass Allied shipping in the North Atlantic, and to secure shipments of iron-ore from Sweden through the port of Narvik.[4] The long northern coastline was an excellent place to launch U-boat operations into the North Atlantic in order to attack British commerce. Germany was dependent on iron ore from Sweden and was worried, with justification, that the Allies would attempt to disrupt those shipments, 90 percent of which originated from Narvik.
The invasion of Norway was given to the Army Corps XXI under General Nikolaus von Falkenhorst and consisted of the following main units:
- 163rd Infantry Division
- 69th Infantry Division
- 169th Infantry Division
- 181st Infantry Division
- 214th Infantry Division
- two regiments of the 3rd Mountain Division
The initial invasion force was transported in several groups by ships of the Kriegsmarine:
- Battlecruisers (or fast battleships) Scharnhorst and Gneisenau as distant cover, plus ten destroyers with 2,000 mountaineering troops under General Eduard Dietl to Narvik;
- Heavy cruiser Admiral Hipper and four destroyers with 1,700 troops to Trondheim;
- Light cruisers Köln and Königsberg, artillery training ship Bremse, transport Karl Peters, two torpedo boats and five motor torpedo boats with 1,900 troops to Bergen;
- Light cruiser Karlsruhe, three torpedo boats, seven motor torpedo boats and mtb mothership (Schnellbootbegleitschiff) Tsingtau with 1,100 troops to Kristiansand[7];
- Heavy cruiser Blücher, heavy cruiser (formerly pocket battleship) Lützow, light cruiser Emden, three torpedo boats and eight minesweepers with 2,000 troops to Oslo;
- Four minesweepers with 150 troops to Egersund.

Concise timeline
- Late in the evening of April 8, 1940, Kampfgruppe 5 was spotted by the Norwegian guard vessel Pol III. Pol III was fired at, her captain Leif Welding-Olsen became the first Norwegian military fatal casualty during the war.
- In an act of irony, the German heavy cruiser Blücher was sunk in the Oslofjord April 9 by 48-year-old German Krupp guns (named Moses and Aron, of 28 cm calibre, installed at Oscarsborg Fortress in May 1893) and equally ancient torpedoes:
- German ships sailed up the fjord leading to Oslo, reaching the Drøbak Narrows (Drøbaksundet). In the early morning of April 9, the gunners at Oscarsborg Fortress fired on the leading ship, the Blücher, which had been illuminated by spotlights at about 0515hrs. Within two hours, the ship, unable to maneuver in the narrow fjord, was sunk with about 600-1,000 men. The now obvious threat from the fortress delayed the rest of the naval invasion group long enough for the Royal family, the Cabinet Nygaardsvold and the Parliament to be evacuated, along with the national treasury. As a result, Norway never surrendered to the Germans, leaving the Quisling government illegitimate and permitting Norway to participate as an Ally in the war, rather than as a conquered nation.
- German airborne troops landed at Oslo airport Fornebu, Kristiansand airport Kjevik, and Sola Air Station – the latter constituting the first paratrooper (Fallschirmjäger) attack in history;[4] coincidentally, among the Luftwaffe pilots landing at Kjevik was Reinhard Heydrich.

- Quisling's radio-effected coup d'etat – another first.
- Partly thanks to the sinking of the Blücher in the Oslo Fjord narrows, the Royal family, the Parliament and the Cabinet Nygaardsvold evaded the German invasion force;[4] King Haakon refused to lay down arms; Clash at Midtskogen; bombs at Elverum and Nybergsund; the Royal family, the Cabinet, the Parliament, and the national gold reserves moved northward ahead of the Germans.
- Cities/towns Bergen, Stavanger, Egersund, Kristiansand S, Arendal, Horten, Trondheim and Narvik attacked and occupied within 24 hours.
- Heroic, but wholly ineffective, stand by the Norwegian armored coastal defence ships Norge and Eidsvold at Narvik. Both ships torpedoed and sunk with great loss of life.
- First and Second Naval Battle of Narvik (Royal Navy vs Kriegsmarine).
- The German force took Narvik and landed the 2,000 mountain infantry, but a British naval counterattack by the old battleship HMS Warspite and a flotilla of destroyers over several days succeeded in sinking all ten German destroyers once they ran out of fuel and ammunition.
- Devastating bombing of towns Nybergsund, Elverum, Åndalsnes, Molde, Kristiansund N, Steinkjer, Namsos, Bodø, Narvik – some of them tactically bombed, some terror-bombed.
- Main German land campaign northward from Oslo with superior equipment; Norwegian soldiers with turn-of-the-century weapons, along with some British and French troops (see Namsos Campaign), stop invaders for a time before yielding – first land combat action between British Army and Wehrmacht in WWII.
- Land battles at Narvik: Norwegian and Allied (French and Polish) forces under General Carl Gustav Fleischer achieve the – first major tactical victory against the Wehrmacht in WWII – and the following unfortunate withdrawal of the Allied forces (mentioned below); Fighting at Gratangen.
- With the evacuation of the King and the Cabinet Nygaardsvold from Molde to Tromsø on April 29, and the allied evacuation of Åndalsnes on May 1, resistance in Southern Norway comes to an end.
- The "last stand": Hegra Fortress (Ingstadkleiven Fort) resisted German attacks until May 5 -- of Allied propaganda importance, like Narvik.
- King Haakon, Crown Prince Olav, and the Cabinet Nygaardsvold left from Tromsø 7 June (aboard British cruiser HMS Devonshire, bound for UK) to represent Norway in exile (King returned to Oslo exact same date five years later); Crown Princess Märtha and children, denied asylum in her native Sweden, later left from Petsamo, Finland, to live in exile in the United States.
- Norway capitulated (though Norwegian armed forces continued fighting the Germans abroad and at home until the German capitulation on May 8, 1945) on June 10, 1940, two months after Wesertag, this made Norway the conquered country which had withstood a German invasion for the longest time before succumbing.
In the far north, Norwegian, French and Polish troops, supported by the Royal Navy and the RAF, fought against the Germans over the control of the Norwegian harbour Narvik, important for the year-round export of Swedish iron ore (The Swedish harbour of Luleå is blocked by ice in the winter months). The Germans were driven out of Narvik on May 28, but due to the deteriorating situation on the European continent, the allied troops were withdrawn in Operation Alphabet – and the Germans recaptured Narvik on June 9, by then deserted also by the civilians due to massive Luftwaffe bombing.
The Encircling of Sweden and Finland
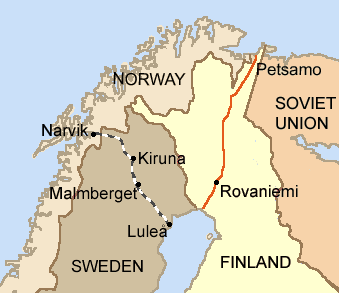
(Borders as of 1920–1940.)
Operation Weserübung did not include a military assault on (likewise neutral) Sweden – there was no need. By holding Norway, the Danish straits and most of the shores of the Baltic Sea, the Third Reich encircled Sweden from the north, west and south – and in the East, there was the Soviet Union, the successor of Sweden's and Finland's arch-enemy Russia, on friendly terms with Hitler under the terms of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact. A small number of Finnish volunteers helped the Norwegian Army against Germans in an ambulance unit.
Sweden's and Finland's trade was totally controlled by the Kriegsmarine. As a consequence, Germany put pressure on neutral Sweden to permit transit of military goods and soldiers on leave. On June 18, 1940, an agreement was reached.[8] Soldiers were to travel unarmed and not be part of unit movements. A total of 2.14 million German soldiers, and more than 100,000 German military railway carriages, crossed Sweden until this traffic was officially suspended on August 20, 1943.
On 19 August 1940, Finland agreed to grant access to its territory for the Wehrmacht, with the agreement signed on 22 September.[9] Initially for transit of troops and military equipment to and from northernmost Norway, but soon also for minor bases along the transit road that eventually would grow in the preparation for Operation Barbarossa.
See also
- Operation Weserübung Order of Battle
- Occupation of Denmark by Nazi Germany
- British occupation of the Faroe Islands in World War II
- Occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany
- Allied campaign in Norway
- Hegra Fortress
- Battles of Narvik
- Alta Battalion
- Namsos Campaign
- Norwegian resistance movement
- Vidkun Quisling
- Operation Juno
- Operation Wilfred
References
- Dildy, Douglas C. Denmark and Norway, 1940: Hitler's Boldest Operation; Osprey Campaign Series #183; ISBN 9781846031175. Osprey Publishing, 2007
Footnotes
- ^ a b c d e f Gert Laursen: The German occupation of Denmark
- ^ Feldgrau.com: Statistics
- ^ a b c Feldgrau.com: Invasion of Norway
- ^ a b c d e f The Illustrated History of World War II. Owen Booth and John Walton. Chartwell Books, Inc. 1998. Pages 44 - 49
- ^ The Danish Jewish Museum: The operation against the Danish Jews in October 1943
- ^ Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team: The Fate of the Jews of Denmark
- ^ seekrieg.de on the Kristiansand group Template:De icon
- ^ National Archives and Records Administration: State Department and Foreign Affairs Records - Sweden
- ^ Jatkosota 1941-1944: 2. The “Interim peace”
External links
- A detailed article about the German invasion of Denmark
- A short introduction to the German invasion of Norway
- Norway 1940: A detailed description of the chain of events
- The Royal Navy: Norwegian invasion and campaign
- Directive for "Fall Weserübung"
- T.K. Derry: The Campaign in Norway
- Halford Mackinder's Necessary War An essay describing Operation Weserübung in a larger strategic context
- Earl F. Ziemke "The German Decision To Invade Norway and Denmark" A comprehensive description of the background motives to the invasion, including the Allied plans to occupy the Swedish iron ore mines.
