Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)
| Greco-Turkish War of 1919–1922 (Interwar period) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Turkish War of Independence | |||||||||
| File:Greko-Turkish-Afyon-1920.png Trench warfare during the Greco-Turkish War | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
Leonidas Paraskevopoulos, Anastasios Papoulas, Georgios Hatzianestis |
Ali Fethi Okyar, İsmet İnönü, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, Fevzi Çakmak | ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| Maximum deployed ~180,000 (12 Divisions) | unknown (estimate ~150,000 to 350,000 if irregulars included) | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| 24,240 dead, 48,880 wounded, 18,085 missing[1] |
20,540 KIA 10,000 WIA | ||||||||
The Greco-Turkish War of 1919–1922, also called the War in Asia Minor, or the Greek campaign of the Turkish War of Independence, was a series of military events occurring during the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire after World War I between May 1919 and October 1922. The war was fought between Greece and Turkish revolutionaries of the Turkish National Movement that would later establish the Republic of Turkey.
The Greek campaign was launched because the western Allies, particularly British Prime Minister David Lloyd George, had promised Greece territorial gains at the expense of the Ottoman Empire. It ended with Greece giving up all territory gained during the war, returning to its pre-war borders, and engaging in a population exchange with the newly established state of Turkey under provisions in the Treaty of Lausanne.
The collective failure of the separate military campaigns of Greece, the Armenians, and the French against the Turkish revolutionaries forced the Allies to abandon the Treaty of Sèvres. Instead, they negotiated a new treaty at Lausanne. This new treaty recognised the independence of the Turkish Republic and its sovereignty over Eastern Thrace and Anatolia.
Background
Geopolitical context

The geopolitical context of this conflict is linked to the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire which was a direct consequence of World War I and involvement of the Ottomans in the Middle Eastern theatre. Greeks received an order to land in Smyrna by the Triple Entente as part of the partition. During this war, the Ottoman government collapsed completely and the Ottoman Empire was divided amongst the victorious Entente powers with the signing of the Treaty of Sèvres on August 10, 1920.
There were a number of secret agreements regarding the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire at the end of World War I. The Triple Entente had made contradictory promises about post-war arrangements concerning Greek hopes in Asia Minor.[2]
At the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Eleftherios Venizelos lobbied hard for an expanded Hellas (the Megali Idea) that would include the large Greek communities in Northern Epirus, Thrace and Asia Minor. The western Allies, particularly British Prime Minister David Lloyd George, had promised Greece territorial gains at the expense of the Ottoman Empire if Greece entered the war on the Allied side.[citation needed] These included Eastern Thrace, the islands of Imbros (Gökçeada) and Tenedos (Bozcaada), and parts of western Anatolia around the city of Smyrna, which contained sizable ethnic Greek populations.
The Italian and Anglo-French repudiation of the Agreement of St.-Jean-de-Maurienne signed on April 26, 1917, which settled the "middle eastern interest" of Italy, was overridden with the Greek occupation, as İzmir (Smyrna) was part of the agreements promised to Italy. Before the occupation the Italian delegation to the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, angry about the possibility of the Greek occupation of Western Anatolia, left the conference and did not return to Paris until May 5. The absence of the Italian delegation from the Conference ended up by facilitating Lloyd George's efforts to persuade France and the United States in Greece’s favor to prevent Italian operations in Western Anatolia.
According to some historians, it was the Greek occupation of Izmir that created the Turkish National movement. Arnold J. Toynbee for example argued that:[3]
"The war between Turkey and Greece which burst out at this time was a defensive war for safeguarding of the Turkish homelands in Anatolia. It was a result of the Allied policy of imperialism operating in a foreign state, the military resources and powers of which were seriously under-estimated; it was provoked by the unwarranted invasion of a Greek army of occupation..."
The Greek community in Anatolia

One of the reasons proposed by the Greek government for launching the Asia Minor expedition was that there was a sizeable Greek-speaking Orthodox Christian population inhabiting Anatolia that needed protection. Greeks have lived in Asia Minor since antiquity and before the outbreak of the First World War, up to 2.5 million Greeks lived in the Ottoman Empire.[5] The suggestion though that the Greeks constituted the majority of the population in the lands claimed by Greece has been contested by a number of historians. In their book about the British foreign policy of World War I and post war years, Cedric James Lowe and Michael L. Dockrill argued that: "...Greek claims were at best debatable, [they were] perhaps a bare majority, more likely a large minority in the Smyrna Vilayet, which lay in an overwhelmingly Turkish Anatolia."."[6] Precise demographics are further obscured by the Ottoman policy of dividing the population according to religion rather than descent, language or self-identification.
Nevertheless, the fear for the safety of the Greek population was a well-founded one; In 1915, an extreme nationalist group called Young Turks enacted genocidal policies against the minorities in the Ottoman Empire, slaughtering hundreds of thousands of people. While the Armenian Massacre is the best known of these events, there were also atrocities towards Greeks in Pontus and western Anatolia. The Greek Prime Minister Eleftherios Venizelos stated to a British newspaper that::[7]
"Greece is not making war against Islam, but against the anachronistic Ottoman Government, and its corrupt, ignominious, and bloody administration, with a view to the expelling it from those territories where the majority of the population consists of Greeks."
To an extent the above danger was overstated by Venizelos as a negotiating card on the table of Sèvres, in order to gain the support of the Allied governments. For example, the fact that the Young Turks was not in power at the time of the war makes such a justification less straight forward. Most of the leaders of that regime had fled the country at the end of World War I and the Ottoman government in Istanbul was already under British control. Even though the Nationalists followed in earnest similar policies at the aftermath of the Greek invasion, at the start of the war there was no clear indication that this was their intention. In an ironic way, the Greek invasion might instead have precipitated the atrocities that it intended to prevent. Arnold J. Toynbee blamed the policies pursued by Great Britain and Greece, as the main instigators of atrocities committed by both sides during the war:
"...The Greeks of 'Pontus' and the Turks of the Greek occupied territories, were in some degree victims of Mr. Venizelos's and Mr. Lloyd George's original miscalculations at Paris."
Greek nationalism
One of the main national motivations for initiating the war was to realize the Megali Idea, a core concept of Greek nationalism. The Megali Idea was an irredentist vision of a restoration of a Greater Greece on both sides of the Aegean that would incorporate territories with Greek populations outside the borders of the initially very small, Kingdom of Greece. From the time of Greek independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1830, the Megali Idea had played a major role in Greek politics. Greek politicians, since the independence of the Greek state, had made several speeches on the issue of the "historic inevitability of the expansion of the Greek Kingdom."."[8] For instance, Greek politician Ioannis Kolettis voiced this conviction in the assembly in 1844: "There are two great centres of Hellenism. Athens is the capital of the Kingdom. Constantinople is the great capital, the City, the dream and hope of all Greeks."
The Great Idea was not merely the product of the 19th century nationalism. It was, in one of its aspects, deeply rooted in many Greeks' religious consciousness. This aspect was the recovery of Constantinople for Christendom, the reestablishment of the universal Christian Byzantine Empire which had fallen in 1453. "Ever since this time the recovery of St Sophia and the City had been handed down from generation to generation as the destiny and aspiration of the Greek Orthodox."[8] The Megali Idea, besides Constantinople, included most traditional lands of the Greeks, Crete, Thessaly, Epirus, Macedonia, Thrace, the Aegean Islands, Cyprus, the coastlands of Asia Minor and Pontus on the Black Sea. Asia Minor was an essential part of the Greek world and an area of enduring Greek cultural dominance. The Greek city-states and later the Byzantine Empire also exercised political control of most of the region, from Bronze Age to 12th century AD, when the first Seljuk Turk raids reached it.
Even though the Anatolian campaign is often misconstrued under post-WW2 concepts as a war of conquest, from the point of view of the 19th century Greek nationalism this was just another war of liberation, one to redeem the "enslaved brother", not different from the then recent Balkan wars. In a letter sent to Greek King Constantine dating January 1915, Venizelos had already revealed his hope for future annexation of territories from Turkey, arguing that: "I have the impression that the concessions to Greece in Asia Minor... would be so extensive that another equally large and not less rich Greece will be added to the doubled Greece which emerged from the victorious Balkan wars"
The National Schism in Greece
The National Schism in Greece refers to the deep split of Greek politics and society between two fractions, the one led by Eleftherios Venizelos and the other by King Constantine, that predated the World War I but escalated significantly over the decision on which side Greece should support during the war.
The United Kingdom had hoped that this familial connection might persuade Constantine to join the cause of the Allies of World War I, but the King and his supporters insisted on strict neutrality, especially whilst the outcome of the conflict was hard to predict. In addition, family ties and emotional attachments made it difficult for Constantine to decide which side to support during World War I. The King's dillema was further increased when the Ottomans and the Bulgarians, both having grievances and aspirations against the Greek Kingdom, joined the Central Powers. According to Queen Sophia, Constantine’s dream of "marching into the great city of Hagia Sophia at the head of the Greek army" was still "in his heart" and it appeared as if the King was ready to enter the war against Ottoman Empire. The conditions, however, were clear; the occupation of Constantinople had to be undertaken without incurring excessive risk.
Though Constantine did remain decidedly neutral, Prime Minister of Greece Eleftherios Venizelos had from an early point decided that Greece's interests would be best served by joining the Entente and started diplomatic efforts with the Allies to prepare the ground for concessions following an eventual victory. The disagreement and the subsequent dismissal of Venizelos by the King resulted in a deep personal rift between the two, which spilled over into their followers and the wider Greek society. Greece became divided in two radically opposed political camps, as Venizelos set up a separate state in Northern Greece, and eventually, with Allied support, forced the King to abdicate. In May 1917, after the exile of Constantine, Venizélos returned to Athens and allied with the Entente. Greek military forces (though divided between supporters of the monarchy and supporters of "Venizelism") began to take part in military operations against the Bulgarian Army on the border.
The act of entering the war and the preceding events resulted in a deep political and social division in post-World War I Greece. The country's foremost political formations, the Venizelist Liberals and the Royalists, already involved in a long and bitter rivalry over pre-war politics, reached a state of outright hatred towards each other. Both parties viewed the other's actions during the First World War as politically illegitimate and treasonous. This enmity inevitably spread throughout Greek society, creating a deep rift that contributed decisively to the failed Asia Minor campaign and resulted in much social unrest in the inter war years.
Overview of major events
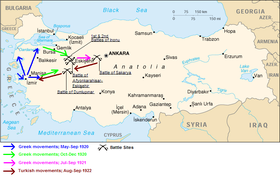
The military aspect of the war begins with the Armistice of Mudros. The military operations of the Greco-Turkish war can be roughly divided into three main phases: The first phase, spanning the period from May 1919 to October 1920, encompasses the Greek Landings in Asia Minor and their consolidation along the Aegean Coast. The second phase lasted from October 1920 to August 1921, and was characterised by Greek offensive operations. The third and final phase lasted until August 1922, when the strategic initiative was held by the Turkish Army.
Occupation of İzmir (Smyrna) (May 1919)
On May 15 1919, twenty thousand[9] Greek soldiers landed in Smyrna and took control of the city and its surroundings under cover of the Greek, French, and British navies. Legal justifications for the landings was found in the article 7 of the Armistice of Mudros, which allowed the Allies "to occupy any strategic points in the event of any situation arising which threatens the security of Allies."[10] The Greeks had already brought their forces into Eastern Thrace (apart from Constantinople and its region).

The Greeks of Smyrna and other Christians, (mainly Greeks and Armenians, who formed a minority according to Turkish sources,[11] a majority according to Greek sources[12]), greeted the Greek troops as liberators. By contrast, the majority of the muslim population saw this as an invading force and some Turks resented the Greeks due to long history of conflict and antagonism. Nevertheless, the Greek landings were received by and large passively, only facing sporadic resistance, mainly by small groups of irregular Turkish troops in the suburbs[citation needed]. The majority of the Turkish forces in the region either surrendered peacefully to the Greek Army, or fled to the countryside. [citation needed].
While the Turkish army was ordered not to open fire, a Turkish nationalist (Hasan Tahsin) among the crowd fired a shot and killed the Greek standard-bearer.[13] Greek soldiers then opened fire on the Turkish barracks as well as the government building. Between 300 to 400 Turks and 100 Greeks were killed on the first day.[13] The occupation proved a humiliation for many of the Turkish and Muslim inhabitants. Von Mikusch notes: “The Christian crowd rages and yells.... Many fall under the bayonet thrusts. The men are forced to tear the fezes from their heads and trample them underfoot – the worst outrage for a Mohammedan – all who refuse are cut down with the sword. The veils are torn from the women's faces. The mob begins to plunder the house of the Mohammedan”.[14] Several Turkish civilians who were arrested by the mob, were subjected to severe cruelty by both soldiers and civilians until they collapsed. Sources claim that "A long line of killed and wounded were seen along the front".[15]
Greek summer offensives (Summer 1920)
During the summer of 1920, the Greek army launched a series of successful offensives in the directions of Meander (Menderes) Valley, Peramos and Philadelphia. The overall strategic objective of these operations, which were met by increasingly stiff Turkish resistance, was to provide strategic depth to the defence of Smyrna. To that end, the Greek zone of occupation was extended over all of Western and most of North-Western Asia Minor.
Treaty of Sèvres (August 1920)
In return for the contribution of the Greek army on the side of the Allies, the Allies supported the assignment of eastern Thrace and the millet of Smyrna to Greece. This treaty ended the First World War in Asia Minor and, at the same time, sealed the fate of the Ottoman Empire. Henceforth, the Ottoman Empire would no longer be a European power.
On August 10, 1920, the Ottoman Empire signed the Treaty of Sèvres ceding to Greece Thrace, up to the Chatalja lines. More importantly, Turkey renounced to Greece all rights over Imbros and Tenedos, retaining the small territories of Constantinople, the islands of Marmara, and "a tiny strip of European territory." The Straits of Bosporus were placed under an International Commission, as they were now open to all.
Turkey was furthermore forced to transfer to Greece "the exercise of her rights of sovereignty" over Smyrna in addition to "a considerable Hinterland, merely retaining a ‘flag over an outer fort’." Though Greece administered the Smyrna enclave, its sovereignty remained, nominally, with the Sultan. According to the provisions of the Treaty, Smyrna was to maintain a local parliament and, if within five years time she asked to be incorporated within the Kingdom of Greece, the provision was made that the League of Nations would hold a plebiscite to decide on such matters.
The treaty was never ratified by the Ottoman Empire[16][17] or Greece.[18]
Greek expansion (October 1920)
In October 1920, the Greek army advanced further east into Anatolia, with the encouragement of Lloyd George, who intended to increase pressure on the Turkish and Ottoman governments to sign the Treaty of Sèvres. This advance begun under the Liberal government of Eleftherios Venizelos, but soon after the offensive began, Venizelos fell from power and was replaced by Dimitrios Gounaris. The strategic objective of these operations was to defeat the Turkish Nationalists and force Kemal into peace negotiations. The advancing Greeks, still holding superiority in numbers and modern equipment at this point, had hoped for an early battle in which they were confident of breaking up ill-equipped Turkish forces. Yet they met with little resistance, as the Turks managed to retreat in an orderly fashion and avoid encirclement. Churchill said: "The Greek columns trailed along the country roads passing safely through many ugly defiles, and at their approach the Turks, under strong and sagacious leadership, vanished into the recesses of Anatolia."[19]
Change in Greek government (November 1920)
During October 1920, King Alexander was bitten by a monkey kept at the Royal Gardens and died within days from sepsis. This incident has been characterized as the "monkey bite that changed the course of Greek history".[20] Venizelos's preference was to declare a Greek republic and thus end the monarchy. However, he was well aware that this would not be acceptable to the European powers.[citation needed]
After King Alexander died leaving no heirs, the general elections scheduled to be held on November 1, 1920 suddenly became the focus of a new conflict between the supporters of Venizelos and those of King Constantine. At the same time the anti-venizelist faction promoted the idea of disengagement in Asia Minor, without though presenting a clear plan as to how this would happen. On the contrary, Venizelos was identified with the continuation of a war that did not seem to go anywhere. The war-weary Greek people opted for change. To the surprise of many, Venizelos won only 118 out of the total 369 seats. The crushing defeat obliged Venizelos and a number of his closest supporters to leave the country.
The new government under Dimitrios Gounaris prepared for a plebiscite on the return of King Constantine. Noting the King's neutrality during the World War I, the Allies warned the Greek government that if he should be returned to the throne they would cut off all aid to Greece. A month later a plebiscite called for the return of King Constantine. Soon after his return, the King replaced all the WW1 veteran officers and he appointed inexperienced monarchist officers to senior positions. The leadership of the campaign was given to Anastasios Papoulas, while himself assumed personal overall command. The Greek Army which had secured Smyrna and the Asia Minor coast was purged of Venizelos's supporters while it marched on Ankara.
Battles of İnönü (December 1920 - March 1921)
By December 1920, the Greeks had advanced on two fronts, approaching Eskişehir from the North West and from Smyrna, and had consolidated their occupation zone. In early 1921 they resumed their advance with small scale reconnaissance incursions that met stiff resistance from entrenched Turkish Nationalists, who were increasingly better prepared and equipped as a regular army.
The Greek advance was halted for the first time at the First Battle of İnönü on January 11, 1921. Even though this was a minor confrontation involving only one Greek division, the political significance for the fledging Turkish revolutionaries cannot be overestimated. This development led to Allied proposals to amend the Treaty of Sèvres at a conference in London where both the Turkish Revolutionary and Ottoman governments were represented.
Although some agreements were reached with Italy, France and Britain, the decisions were not agreed to by the Greek government, who believed that they still retained the strategic advantage and could negotiate from a stronger point. The Greeks initiated another attack on March 27th, the Second Battle of İnönü, which was resisted fiercely and finally defeated by the Turkish troops on March 30th. The British favoured a Greek territorial expansion but refused to offer any military assistance in order to avoid provoking the French.[citation needed] The Turkish forces received significant assistance from the newly formed Soviet Union.[21]
Shift of support towards Turkish Revolutionaries
By this time all other fronts had been settled in favour of the Turks, freeing more resources to focus on the main threat of the Greek Army. The French and the Italians concluded private agreements with the Turkish revolutionaries in recognition of their mounting strength. Turkish revolutionaries bought equipment from Italy and France, who threw in their lot with the Turkish revolutionaries against Greece which was seen as a British client. The Italians used their base in Antalya to assist, especially from the point of view of intelligence, to the Turkish revolutionaries against the Greeks.[22] There was a positive relationship between the Soviet Union and the Turkish Revolutionaries, which was solidified under Treaty of Moscow (1921). The unquestionable help from Soviet Union was instead of opening another front, Soviets waited for the results of the Turkish-Armenian War and conflicts with Greece. The Soviet Union also supported Kemal with money and ammunition.[citation needed]
Battle of Afyonkarahisar-Eskişehir (July 1921)

Between 27 June and 20 July 1921, a reinforced Greek army of 9 divisions launched a major offence, the greatest thus far, against the Turkish troops commanded by Ismet Inönü on the line of Afyonkarahisar-Kutahya-Eskisehir. The plan of the Greeks was to cut Anatolia in two, as the above towns were on the main rail-lines connecting the inner country with the coast, consolidating the north-west and centre fronts . Eventually, after breaking the stiff Turkish defences, they occupied the aforementioned strategically important centres. Instead though of pursuing and cripple decisevely the nationalists' military capacity, the Greek Army halted. In consequence and despite their defeat, the Turks managed to avoid encirclement and made a strategic retreat on the east of Sakarya river, where they organised their last line of defence.
This was the major decision point that sealed the Greek destiny in Anatolia. The state and Army leadership, including King Constantine, prime minister Gounaris, and General Papoulas, met at Kutahya were they debated the future of the campaign. The Greeks with rejuvenated their faltering morale failed to appraise rationally the strategic situation that favoured the defending side; instead, in the overall climate of enthusiasm, the leadership was polarised into the risky decision to pursue to engage the Turks to their last line of defence close to Ankara. Only few voices supported a defensive stance, including Ioannis Metaxas. After a delay of almost a month, that gave time to the Turks to organise their defence, 7 of the Greek divisions crossed east of Sakarya River.
Battle of Sakarya (August and September 1921)
Following the retreat of the Turkish troops under Ismet Inönü in the battle of Kutahya-Eskisehir the Greek Army advanced afresh to the Sakarya River (Sangarios in Greek), less than 100 km (62 miles) west of Ankara. Constantine's battle cry was "to Angora" and the British officers were invited, in anticipation, to a victory dinner in the city of Kemal.[23] It was envisaged that the Turkish Revolutionaries, who had consistently avoided encirclement would be drawn into battle in defence of their capital and destroyed in a battle of attrition.
Despite the Soviet help, supplies were short as the Turkish army prepared to meet the Greeks. Owners of private rifles, guns and ammunition had to surrender them to the army and every household was required to provide a pair of underclothing, sandals.[24] Meanwhile, the Turkish parliament, not happy with the performance of Ismet Inonu as the Commander of the Western Front, wanted Mustafa Kemal and Chief of General Staff Fevzi Cakmak to take control.
The advance of the Greek Army faced fierce resistance which culminated in the 21-day Battle of Sakarya (August 23– September 13, 1921). The Turkish defense positions were centred on series of heights, and the Greeks had to storm and occupy them. The Turks held certain hilltops and lost others, while some were lost and recaptured several times over. Yet the Turks had to conserve men, for the Greeks held the numerical advantage.[25] The crucial moment came when the Greek army tried to take Haymana, 40 kilometers south of Ankara but the Turks held out. Greeks also had their problems, advance into Anatolia lengthened their lines of supply and communication and they were running out of ammunition. The ferocity of the battle exhausted both sides to such an extent that they were both contemplating a withdrawal but the Greeks were the first to withdraw to their previous lines. The thunder of cannon was plainly heard in Ankara throughout the battle.
That was the furthest in Anatolia the Greeks would advance, and within few weeks they withdrew in an orderly manner back to the lines that they had held in June. The Turkish Parliament awarded both Mustafa Kemal and Fevzi Cakmak with the title of Field Marshal for their service in this battle. To this day no other person has received this five-star general title from the Turkish Republic.
Stalemate (September 1921 - August 1922)
Having failed to reach a military solution, Greece appealed to the Allies for help, but early in 1922 Britain, France and Italy decided that the Treaty of Sèvres could not be enforced and had to be revised. In accordance with this decision, under successive treaties, the Italian and French troops evacuated their positions, leaving the Greeks exposed.
In March 1922, the Allies proposed an armistice. Feeling that he now held the strategic advantage, Mustafa Kemal declined any settlement while the Greeks remained in Anatolia and intensified his efforts to re-organise the Turkish military for the final offensive against the Greeks. At the same time, the Greeks strengthened their defensive positions, but were increasingly demoralised by the inactivity of remaining on the defensive and the prolongation of the war.
Historian Malcolm Yapp wrote that:[26]
After the failure of the March negotiations the obvious course of action for the Greeks was to withdraw to defensible lines around Izmir but at this point fantasy began to direct Greek policy, the Greeks stayed in their positions and planned a seizure of Istanbul, although this latter project was abandoned in July in the face of Allied opposition.
Turkish counter-attack (August 1922)
Turks finally launched a counter-attack on August 26th, what has come to be known to the Turks as the Great Offensive (Buyuk Taarruz). The major Greek defense positions were overrun on August 26, and Afyon fell next day. On August 30, the Greek army was defeated decisively at the Battle of Dumlupınar, with half of its soldiers captured or slain and its equipment entirely lost.[27] This date is celebrated as Victory Day, a national holiday in Turkey. During the Battle of Dumlupınar, Greek General Tricoupis and General Dionis were captured by the Turkish forces.[28] General Tricoupis only after his capture learned that he was recently appointed Commander-in-Chief in General Hajianestis' place. On September 1, Mustafa Kemal issued his famous order to the Turkish army: "Armies, your first goal is the Mediterranean, Forward!"[29]
On September 2, Eskisehir was captured and the Greek government asked Britain to arrange a truce that would at least preserve its rule in Smyrna.[30] Balikesir and Bilecik were taken on September 6, and Aydin the next day. Manisa was taken on September 8. The government in Athens resigned. Turkish cavalry entered into Smyrna on September 9. Gemlik and Mudanya fell on September 11, with an entire Greek division surrendering. Expulsion of Greek Army from Anatolia was completed in September 14. As historian George Lenczowski has put it: "Once started, the offensive was a dazzling success. Within two weeks the Turks drove the Greek army back to the Mediterranean Sea."[31]
Then Kemal's forces headed north for Bosporus, the sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles where the Allied garrisons were reinforced by British, French and Italian troops from Constantinople.[30] The British cabinet decided to resist the Turks if necessary at the Dardanelles and to ask for French and Italian help to enable the Greeks to remain in eastern Thrace (see Chanak Crisis).[32] However, Italian and French forces abandoned their positions at the straits and left the British alone to face the Turks. On September 24, Kemal's troops moved into the straits zones and refused British requests to leave. The British cabinet was divided on the matter but eventually any possible armed conflict was prevented. British General Harington, allied commander in Constantinople, kept his men from firing on Turks and warned the British cabinet against any rash adventure. The Greek fleet left Constantinople upon his request. The British finally decided to force the Greeks to withdraw behind Maritsa in Thrace. This convinced Kemal to accept the opening of Armistice talks.
Re-capture of Smyrna (September 1922)
With the possibility of social disorder once the Turkish Army occupied Smyrna, Mustafa Kemal was quick to issue a proclamation, sentencing any Turkish soldier to death who harmed non-combatants.[33] A few days before the Turkish capture of the city, Kemal's messengers distributed leaflets with this order written in Greek. Kemal said that Ankara government can't be held responsible in the case of an occurrence of a massacre[34] These orders were largely ignored by the Turkish army, and Nasruddin Pasha, the commander of Turkish forces in the Smyrna district gave orders contradicting Atatürk's. Nasruddin Pasha's orders had as their main objective the extermination of the Christian population of the city and were largely followed: the Greek and Armenian civilian population of Smyrna suffered heavily at the hands of the Turkish army,[35] who massacred a significant part of the Christian population. This massacre include the lynching and brutal murder of the Greek Orthodox Metropolitan Chrysostomos of Smyrna[35] whose ears, nose, and hands were cut off and his eyes gouged out with knives. Greeks managed to seek refuge on Greek ships at the harbor of İzmir and other coastal towns because the Allied (primarily British) ships (with the exception of some Japanese and Italian ships) refused the Greek refugees, even to the point of keeping those who had swum out to their ships away, as they had orders not to get involved in the event.
During the confusion and anarchy that followed, a great portion of the city was set ablaze in the Great Fire of Smyrna, and the properties of the Greeks were pillaged. The cause of the fire is hotly disputed to these days: a number of sources implicate the Turkish army, while others attribute it to an accident. The British historian and journalist, Arnold J. Toynbee, stated that when he toured the region he saw Greek villages that had been burned to the ground. Furthermore, Toynbee stated that the Turkish troops had clearly, individually and deliberately burned down each house.[36] The fact that only the Greek and Armenian quarters of the city were burned, and that the Turkish quarter stood, gives credence to the theory that the Turks burned the city.
Nevertheless, the opposite, that the defeated Greeks simply continued their policy of scorched earth, could also be possible. Many of the buildings from which the fire originated were supply depots and warehouses, which would have been to the advantage of the Turks to preserve. On the other hand, most of these supply depots and warehouses were owned by Greeks and Armenians, as the Muslim quarter of the city was largely untouched by the fire. Thus some claimed that the Turks had a motive to burn these buildings to extinguish any Christian presence from the city.[37]
Resolution

The Armistice of Mudanya was concluded on October 11 1922. The Allies (Britain, France, Italy) retained control of eastern Thrace and the Bosporus. The Greeks were to evacuate these areas. The agreement came into force starting October 15, 1922, one day after the Greek side agreed to sign it.
The Armistice of Mudanya was followed by the Treaty of Lausanne, a significant provision of which was an exchange of populations. Over one million Greek Orthodox Christians were displaced; most of them were resettled in Attica and the newly-incorporated Greek territories of Macedonia and Thrace and were exchanged with about 500,000 Muslims displaced from the Greek territories.
Factors contributing to the outcome
The first year of the war the Greeks were helped by the fact that British troops invaded the Straits, the richest and most populous part of Turkey, and French troops were attacking the Turkish army from the south and invading other important cities (including Adana), constituted as great a level of support as Greece could have asked for. In addition, Turkish troops also had to fight with the Armenian army on a third front. These fronts though were soon settled and the Kemalist forces could be turned in defence against the Greek intrusion in larger numbers.
The major factor contributing to the defeat of the Greeks was the withdrawal of Allied support following Autumn 1920. The reasons why the Allies shifted so drastically in their policies are complex. One often quoted reason for the apparent lack of support was that King Constantine was reviled by the Entente for his neutral policies during World War I, in contrast to former prime minister Venizelos who brought Greece in the war on their side. Most probably this just served as a pretext. A more plausible explanation was that exhausted from 4 years of bloodshed, no Entente power had the will to engage in further fighting to enforce the Sévres treaty. Recognising the rising power of the Turkish Republic, they preferred to settle their differences with separate agreements, abandoning their plans on the Anatolian lands. Even Lloyd George, who always had voiced support for the Greeks, following Venizelos's lobbying, could do little more than give promises, bound by the military and the Foreign Office 'real politik'. That left Greece to fight practically alone after 1921.
Initially, the Turks enjoyed only Soviet support from abroad, in return for giving Batum back to the Soviet Union. On August 4th, Turkey's representative in Moscow, Riza Nur, sent a telegram saying that soon 60 Krupp artillery pieces, 30,000 shells, 700,000 grenades, 10,000 mines, 60,000 Romanian swords, 1.5 million captured Ottoman rifles from WWI, 1 million Russian rifles, 1 million Mannlicher rifles, as well as some older British Martini-Henry rifles and 25,000 bayonets would be delivered to the Kemalist forces.[21] Soviets also provided monetary aid to the Turkish national movement, not to the extent that they promised but almost in sufficient amount to make up the large deficiencies in the promised supply of arms. The Turks in the second phase of the war also received significant military assistance from Italy and France[citation needed], who threw in their lot with the Kemalists against Greece which was seen as a British client[citation needed]. The Italians were embittered from their loss of the Smyrna mandate to the Greeks and they used their base in Antalya to arm and train Turkish troops to assist the Kemalists against the Greeks.[38]
Regardless of other factors, the contrast between the motives and strategic positions of the two sides contributed decisively to the outcome. The Turks were defending their homeland against what they perceived as an imperialist attack. In his public speeches, Mustafa Kemal built up the idea of Anatolia as a "kind of fortress against all the aggressions directed to the East". The struggle was not about Turkey alone but "it is the cause of the east", he said. Turkish national movement attracted sympathizers especially from the Muslims of the far east countries, who were living under colonial regimes and who saw nationalist Turkey as the only independent Moslem nation.[39] The Khilafet Committee in Bombay started a fund to help the Turkish National struggle and sent both financial aid and constant letters of encouragement:[39]
Mustafa Kemal Pasha has done wonders and you have no idea how people in India adore his name... We are all waiting to know the terms on which Angora offers peace to the Greeks.. May the Great Allah grant victory to the Armies of Gazi Mustafa Kemal and save Turkey from her enemies...
Turkish troops had a determined and competent strategic and tactical command, manned by WW1 veterans. They also enjoyed the advantage of being in defence, executed in the new form of 'area defence'. At the climax of the Greek offensive, Mustafa Kemal commanded his troops:[40]
There is no such thing as a line of defence. Only a surface to defend. That surface consists of the entire Fatherland. Not one inch of our country can be abandoned unless drenched with the blood of its people.
The main defence doctrine of the First World War was holding on a line[citation needed], so this command was unorthodox for its time. However it proved successful.
On the other side, the Greek defeat directly derived from the poor strategic and operational planning and their ill-conceived advance in depth.The Greek Army was fighting on the background of constant political turmoil and division at the home front. Despite the majority belief into a "moral advantage" against the "old enemies ", they were not few among them that could not see the point of continuing and they would rather preferred to be back to their homes. The Greeks were advancing without clear strategic targets, weary following months of bitter fighting and long marches. The main strategy was to manage a fatal blow that would cripple the Turkish military for ever and make the Treaty of Sevres enforceable. This strategy might have made some sense back then, but in hindsight it proved a fatal miscalculation. The Greeks were instead attacking against an enemy that could continuously retreat to renewed defensive lines, avoiding encirclement and destruction.
Having adequate supplies was also a constant problem. Although the Greek Army was not lacking in men, courage or enthusiasm, it was soon lacking in nearly everything else. Due to her poor economy and lack of manpower, Greece could not sustain long-term mobilisation and had been stretched beyond its limits. Very soon, the Greek Army exceeded the limits of its logistical structure and had no way of retaining such a large territory under constant attack by regular and irregular Turkish troops fighting in their homeland. The idea that such large force could sustain offensive by mainly "living off the land" proved wrong.
Claims of atrocities and ethnic cleansing
Greek massacres of Turks
British historian Arnold J. Toynbee wrote that there were organized atrocities since the Greek occupation of Smyrna on the 15 May 1919. Toynbee also stated that he and his wife were witnesses to the atrocities perpetrated by Greeks in the Yalova, Gemlik, and Ismid areas and they not only obtained abundant material evidence in the shape of "burnt and plundred houses, recent corpses, and terror stricken survivors" but also witnessed robbery by Greek civilians and arsons by Greek soldiers in uniform in the act of perpetration.[41] Toynbee wrote:[42]
No sooner had they landed than they began a ruthless warfare against the Turkish population, not omitting the commission of atrocities in the worst Near Eastern manner, they laid waste the fertile Maender Valley, and forced thousands of homeless Turks to take refuge beyond the occupied area.
Historian Taner Akcam noted that a British officer claimed:[43]
The National forces were established solely for the purpose of fighting the Greeks...The Turks are willing to remain under the control of any other state...There was not even an organized resistance at the time of the Greek occupation. Yet the Greeks are persisting in their oppression, and they have continued to burn villages, kill Turks and rape and kill women and young girls and throttle to death children.
Inter-Allied commission in the Yalova-Gemlik peninsula, in their report of the 23rd May 1921, during the Greek occupation of western Anatolia, wrote that:[44]
A distinct and regular method appears to have been followed in the destruction of villages, group by group, for the last two months, which destruction has even reached the neighbourhood of the Greek headquarters. The members of the Commission consider that, in the part of the kazas of Yalova and Guemlek occupied by the Greek army, there is a systematic plan of destruction of Turkish villages and extinction of the Moslem population. This plan is being carried out by Greek and Armenian bands, which appear to operate under Greek instructions and sometimes even with the assistance of detachments of regular troops."
Inter Allied commission also stated that the destruction of villages and the disappearance of the Moslem population might have at its objective to create in this region a political situation favourable to the Greek Government.[44]
M. Gehri, the representative of the Geneva International Red Cross who accompanied the Inter-Allied Commission wrote as follows:[45]
...The Greek army of occupation have been employed in the extermination of the Moslem population of the Yalova-Gemlik peninsula. The facts established -burning of villages, massacres, terror of the inhabitants, coincidence of place and date- leave no room for doubt in regard to this. The atrocities which we have seen, or of which we have seen the material evidence, were the work of irregular bands of armed civilians(tcheti) and of organised units of the regular army...Instead of being disarmed and broken up, the bands have been assisted in their activities and have collaborated hand in hand with organised units of regulars.
Arnold J. Toynbee wrote that they obtained convincing evidence that similar atrocities had been started in wide areas all over the remainder of the Greek occupied territories since June 1921.[46] Toynbee argued that: " the situation of the Turks in Smyrna City had become what could be called without exaggeration a 'reign of terror', it was to be inferred that their treatment in the country districts had grown worse in proportion."[47]
Greek scorched-earth policy
According to a number of sources, the retreating Greek army carried out a scorched earth policy while fleeing from Anatolia during the final phase of the war after each battle they lost.[48]Cite error: A <ref> tag is missing the closing </ref> (see the help page).
The Greek army in retreat pursued a burned-earth policy and committed every known outrage against defenceless Turkish villagers in its path.
James Loder Park, the U.S. Vice-Consul in Constantinople at the time, who toured much of the devastated area immediately after the Greek evacuation, described the situation in the surrounding cities and towns of İzmir he has seen, as follows:[citation needed]
Manisa...almost completely wiped out by fire...10,300 houses, 15 mosques, 2 baths, 2,278 shops, 19 hotels, 26 villas…[destroyed]. Cassaba (present day Turgutlu) was a town of 40,000 souls, 3,000 of whom were non-Moslems. Of these 37,000 Turks only 6,000 could be accounted for among the living, while 1,000 Turks were known to have been shot or burned to death. Of the 2,000 buildings that constituted the city, only 200 remained standing. Ample testimony was available to the effect that the city was systematically destroyed by Greek soldiers, assisted by a number of Greek and Armenian civilians. Kerosene and gasoline were freely used to make the destruction more certain, rapid and complete. Alasehir, hand pumps were used to soak the walls of the buildings with Kerosene. As we examined the ruins of the city, we discovered a number of skulls and bones, charred and black, with remnants of hair and flesh clinging to them. Upon our insistence a number of graves having a fresh-made appearance were actually opened for us as we were fully satisfied that these bodies were not more than four weeks old.[the time of the Greek retreat through Alasehir]
Consul Park concluded:[49]
1. The destruction of the interior cities visited by our party was carried out by Greeks.
2. The percentages of buildings destroyed in each of the last four cities referred to were: Manisa 90 percent, Cassaba (Turgutlu) 90 percent, Alaşehir 70 percent, Salihli 65 percent.
3. The burning of these cities was not desultory, nor intermittent, nor accidental, but well planned and thoroughly organized.
4. There were many instances of physical violence, most of which was deliberate and wanton. Without complete figures, which were impossible to obtain, it may safely be surmised that 'atrocities' committed by retiring Greeks numbered well into thousands in the four cities under consideration. These consisted of all three of the usual type of such atrocities, namely murder, torture and rape.
Kinross wrote:[50]
Already most of the towns in its path were in ruins. One third of Ushak no longer existed. Alashehir was no more than a dark scorched cavity, defacing the hillside. Village after village had been reduced to an ash-heap. Out of the eighteen thousand buildings in the historic holy city of Manisa, only five hundred remained.
It is estimated some 3,000 lives had been lost in the burning of Alaşehir alone.[13] In one of the examples of the Greek atrocities during the retreat, on 14 February 1922, in the Turkish village of Karatepe in Aydin Vilayeti, after being surrounded by the Greeks, all the inhabitants were put into the mosque, then the mosque was burned. The few who escaped fire were shot.[51] The Italian consul, M. Miazzi, reported that he had just visited a Turkish village, where Greeks had slaughtered some sixty women and children. This report was then corroborated by Captain Kocher, the French consul.[52]
Turkish massacres of Greeks and Armenians
Many Western newspapers reporting gross abuses committed by Turkish forces against Christian, mainly Greek and Armenian civilians.[53][54][55][56][57][58] The British historian Tonybee stated that Turkish troops deliberately burned numerous Greek homes, pouring petrol on them and taking care to ensure that they were totally destroyed.[36] There were massacres throughout 1920-1923, the period of the Turkish War of Independence, especially of Armenians in the East and the South, and against the Greeks in the Black Sea Region.[59] There was also significant continuity between the organizers of the massacres between 1915-1917 and 1919-1921 in Eastern Anatolia.[60]
According to the London based Times: "The Turkish authorities frankly state it is their deliberate intention to let all the Greeks die, and their actions support their statement."[53] A British paper, the Belfast News Letter wrote: "The appalling tale of barbarity and cruelty now being practiced by the Angora Turks is part of a systematic policy of extermination of Christian minorities in Asia Minor."[58] According to the Christian Science Monitor, the Turks felt that they needed to murder their Christian minorities due to Christian superiority in terms of industriousness and the consequent Turkish feelings of jealously and inferiority, The paper wrote:[61]
The result has been to breed feelings of alarm and jealously in the minds of the Turks which in later years have driven them to depression. They believe that they cannot compete with their Christian subjects in the arts of peace and that the Christians and Greeks especially are too industrious and too well educated as rivals. Therefore from time to time they have striven to try and redress the balance by expulsion and massacre. That has been the position generations past in Turkey again if the Great powers are callous and unwise enough to attempt to perpetuate Turkish misrule over Christians.
A Turkish governor, Ebubekir Hazim Tepeyran in the Sivas Province said in 1919 that the massacres were so horrible that he could not bear to report them. He was referring to the atrocities committed against Greeks in the Black Sea region, and according to the official tally 11,181 Greeks were murdered in 1921 by the Central Army under the command of Nurettin Pasha (who is infamous for the killing of Archbishop Chrysostomos).[62] Some parliamentary deputies demanded Nurettin Pasha to be sentenced to death and it was decided to put him on trial although the trial was later revoked by the intervention of Mustafa Kemal.
Taner Akcam wrote that according to one newspaper, Nurettin Pasha had suggested to kill all the remaining Greek and Armenian populations in Anatolia, a suggestion rejected by Mustafa Kemal.[62]
According to the newspaper the Scotsman, on August 18, 1920, in the Feival district of Karamusal, South-East of Ismid in Asia Minor, the Turks massacred 5,000 Christians.[54] As well as massacring Greeks, the Turks also massacred Armenians, continuing the policies of the 1915 Armenian Genocide according to many Western newspapers.[63]
There were widespread massacres of Greeks in the Pontus region, which is recognized in Greece and Cyprus[64] as the Pontian Genocide. On February 25, 1922, 24 Greek villages in the Pontus region were burnt to the ground. An American newspaper, the Atlanta Observer wrote:[55]
"The smell of the burning bodies of women and children in Pontus" said the message "comes as a warning of what is awaiting the Christian in Asia Minor after the withdrawal of the Hellenic army."
In the first few months of 1922, 10,000 Greeks were killed by advancing Kemalist forces, according to Belfast News Letter.[53][58]
American relief works were also treated with extreme disrespect, even when they were aiding Muslim civilians.[53] The Christian Science Monitor wrote that Turkish authorities also prevented missionaries and humanitarian aid groups from assisting Greek civilians who had their homes burned, the Turkish authorities leaving these people to die despite abundant aid. The Christian Science Monitor wrote: "the Turks are trying to exterminate the Greek population with more vigor than they exercised towards the Armenians in 1915."[56]
According to a proclamation made in 2002 by the then-governor of New York (where a sizeable population of Greek Americans resides), Greeks of Asia Minor endured immeasurable cruelty during a Turkish government-sanctioned systematic campaign to displace them; destroying Greek towns and villages and slaughtering additional hundreds of thousands of civilians in areas where Greeks composed a majority, as on the Black Sea coast, Pontus, and areas around Smyrna; probably over 800.000 Greeks were killed and over 1.500.000 forced to leave its ancestral homelands; infact, those who survived were exiled from Turkey and today they and their descendants live throughout the Greek diaspora.[65]
A sizable population of Greeks had been forced to leave its ancestral homelands of Ionia, Pontus and Eastern Thrace between 1914-1922. These refugees, as well as the Greek Americans with origins in Anatolia were not allowed to return after 1923 and the signing of the Treaty of Lausanne. Norman Naimark arguing that the Turkish counterattack had all the characteristics of ethnic cleansing wrote: "...the Turks would and did use their opportunity of their advance to the Aegean to rid Western Anatolia of the native Greek inhabitants. The Hellenic Greek armies had performed much of the work for them in burning and destroying Greek homes and property..."[66] The instigation of a forcible transfer of populations uprooted close to a 1.5 million Greeks from Turkey in exchange for less than half a million of Turks from Greece. According to historian Dinah Shelton, "the Lausanne Treaty completed the forcible transfer of the country's Greeks".[67]
See also
- Aftermath of World War I
- Turkish-Armenian War
- Franco-Turkish War
- Menemen massacre
- Chronology of the Turkish War of Independence
- Greco-Turkish relations
- Timeline of modern Greek history
- Greek refugees
Footnotes
- ^ History of the Campaign of Minor Asia, General Staff of Army, Headquarters of Army History, Athens, 1967
- ^ Steven W. Sowards (2004-05-07). "Greek nationalism, the 'Megale Idea' and Venizelism to 1923". Twenty-Five Lectures on Modern Balkan History (The Balkans in the Age of Nationalism). Retrieved 2008-09-03.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Arnold J. Toynbee and Kenneth P. Kirkwood, Turkey, 1926, London: Ernest Benn, p. 94
- ^ (Shaw 1977, pp. 239–241)
- ^ Area Handbook for the Republic of Turkey - Page 79 by Thomas Duval Roberts
- ^ Lowe, Cedric James (2002). The Mirage of Power: Volume Two: British Foreign Policy 1914-22. Routledge. p. 367. ISBN 9780415265973.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthor=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Not War Against Islam-Statement by Greek Prime Minister" in The Scotsman, June 29, 1920, pg.5.
- ^ a b Michael Llewellyn Smith, Ionian vision: Greece in Asia Minor, 1919-1922, London: Hurst & Company, 1998, ISBN 0472109901, pg. 3.
- ^ (Kinross 1960, p. 154)
- ^ (Shaw 1977, p. 342)
- ^ Yurt Ansiklopedisi, 1982, p.4273, 4274
- ^ Hellenic Army General Staff, 1957, Ο Ελληνικός Στρατός εις την Σμύρνην, p.56
- ^ a b c Mango, Andrew (2000). Atatürk. Overlook Press. p. 217.
- ^ von Mikusch, Dagobert. Mustafa Kemal, pp.192-193.
- ^ The statement of the officers of the British ship the Brescia, F.O. 371-4218, no.91630, Calthorpe to Curzon, Constantinople, 12 June 1919, enclosure C, "Events which happened in Smyrna on the 15th May, During the Greek Occupation, as Witnessed by the Undersigned on the Brescia" (Signed by nine officers of the ship).
- ^ Sunga, Lyal S. (1992-01-01). Individual Responsibility in International Law for Serious Human Rights Violations. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. ISBN 0-7923-1453-0.
- ^ Bernhardsson, Magnus (2005-12-20). Reclaiming a Plundered Past: archaeology and nation building in modern Iraq. University of Texas Press. ISBN 0-292-70947-1.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ http://www2.mfa.gr/NR/rdonlyres/3E053BC1-EB11-404A-BA3E-A4B861C647EC/0/1923_lausanne_treaty.doc+
 DOC
DOC
- ^ (Kinross 1960, p. 233)
- ^ "Venizelos and the Asia Minor Catastrophe". Retrieved 2008-09-03.[unreliable source?]
- ^ a b Kapur, H. Soviet Russia and Asia, 1917-1927 [page needed] Cite error: The named reference "Kapur" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ History, Antalya City Website
- ^ (Kinross 1960, p. 275)
- ^ (Shaw 1977, p. 360)
- ^ (Kinross 1960, p. 277)
- ^ M.E. Yapp, The making of the modern Near East, 1792-1923, London; New York: Longman, 1987, pg. 319, ISBN 0582493803
- ^ (Shaw 1977, p. 362)
- ^ (Kinross 1960, p. 315)
- ^ (Shaw 1977, p. 362)
- ^ a b (Shaw 1977, p. 363)
- ^ Lenczowski, George. The Middle East in World Affairs, Cornell University Press, New York, 1962, pg. 107.
- ^ Walder, David. The Chanak Affair, London, 1969, p. 281.
- ^ Glenny, M. The Balkans[page needed]
- ^ James, Edwin L. "Kemal won't Insure Against Massacres," New York Times, September 11, 1922.
- ^ a b Dobkin, Marjorie Smyrna: The Destruction of a City[page needed]
- ^ a b (Toynbee 1922, p. 152)
- ^ Fromkin, David, A Peace to End All Peace. Henry Holt and Company 1989.[page needed]
- ^ Smith, Michael (1999-01-15). Ionian Vision: Greece in Asia Minor, 1919-1922. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08569-7.
- ^ a b (Kinross 1960, p. 298)
- ^ "Ankara – The Mausoleum of Atatürk". Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism. Retrieved 2008-09-02.
- ^ (Toynbee 1922, p. 260)
- ^ Arnold J. Toynbee and Kenneth P. Kirkwood, Turkey, 1926, London: Ernest Benn, pg. 92.
- ^ (Akcam 2006, p. 318)
- ^ a b (Toynbee 1922, p. 284)
- ^ (Toynbee 1922, p. 285)
- ^ (Toynbee 1922, p. 260)
- ^ (Toynbee 1922, p. 318)
- ^ Horton, George. Blight of Asia.
- ^ U.S. Vice-Consul James Loder Park to Secretary of State, Smyrna, 11 April 1923. US archives US767.68116/34
- ^ (Kinross 1960, p. 318)
- ^ Letter from Arnold Toynbee to The Times, 6 April 1922, transmitting a letter from Turkey of 9 March 1922
- ^ F.O. 371-7898, no. E10383, Report on the Nationalist Offensive in Anatolia by Major H.G. Howell, British Member of the Inter-Allied commission proceeding to Bourssa. Constantinople, 15 September 1922
- ^ a b c d "Turk's Insane Savagery: 10,000 Greeks Dead" in The Times, Friday, May 5, 1922.
- ^ a b "5,000 Christians Massacred, Turkish Nationalist Conspiracy" in The Scotsman August 24, 1920
- ^ a b "24 Greek Villages are Given to the Fire" in the Atlanta Constitution, March 30, 1922.
- ^ a b "Near East Relief Prevented from Helping Greeks" in the Christian Science Monitor, July 13, 1922.
- ^ "Turks will be Turks" in the New York Times, September 16, 1922.
- ^ a b c "More Turkish Atrocities" in Belfast News Letter, Thursday May 16, 1922.
- ^ (Akcam 2006, p. 322)
- ^ (Akcam 2006, p. 326)
- ^ "Turkish Rule over Christian Peoples" in the Christian Science Monitor, February 1, 1919.
- ^ a b (Akcam 2006, p. 323)
- ^ "Allies to Act at Once on Armenian Outrages" in the New York Times, February 29, 1920.
- ^ Cyprus Press Office, New York City[not specific enough to verify]
- ^ Resolution of the State of New York, October 6, 2002; NY State Governor George E. Pataki Proclaims October 6th, 2002 as the 80th Anniversary of the Persecution of Greeks of Asia Minor
- ^ Naimark, Norman M., Fires of Hatred: Ethnic Cleansing in Twentieth-Century Europe, pg.47.
- ^ Dinah, Shelton. Encyclopaedia of Genocide and Crimes Against Humanity, pg.303.
References
- Akçam, Taner (2006). A Shameful Act: The Armenian Genocide and the Question of Turkish Responsibility. New York: Metropolitan Books.
- Shaw, Stanford Jay (1977). History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey. Cambridge University Press.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Toynbee, Arnold J (1922). The Western question in Greece and Turkey: A study in the contact of civilisations. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
- Kinross, Lord (1960). Atatürk: The Rebirth of a Nation.
In literature and the arts
- Tasos Athanasiadis, The children of Niobe (Τα Παιδιά της Νιόβης), novel which was later serialized on Greek television
- Louis de Bernieres, Birds Without Wings, 2004
- Thea Halo, Not Even my Name, memoir 2000
- Ernest Hemingway, On the Quai at Smyrna, collected in In Our Time, 1925.
- Jeffrey Eugenides, Middlesex, novel (won the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction in 2003)
- Panos Karnezis, The Maze novel 2004 shortlisted for 2004 Whitbread First Novel Award.
- Elia Kazan, America, America film 1964 Oscar nominated for Best Picture
- Nikos Kazantzakis, Christ Recrucified (Ο Χριστός Ξανασταυρώνεται), novel 1948
- Bohuslav Martinů, The Greek Passion (Řecké pašije), Opera 1961
- Dido Sotiriou, Farewell Anatolia (Ματωμένα Χώματα, 1962), Kedros 1997
