Otic ganglion
| Otic ganglion | |
|---|---|
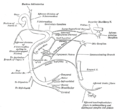
 The otic ganglion and its branches. | |
 Mandibular division of trifacial nerve, seen from the middle line. The small figure is an enlarged view of the otic ganglion. | |
| Details | |
| From | lesser petrosal nerve |
| Innervates | parotid gland |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ganglion oticum |
| TA98 | A14.3.02.014 |
| TA2 | 6671 |
| FMA | 6967 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The otic ganglion is a small, ovalshaped, flattened parasympathetic ganglion of a reddish-gray color, located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa.
It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck. (The others are the submandibular ganglion, pterygopalatine ganglion, and ciliary ganglion).
It is occasionally absent.[1]
Filaments
Functionally, it gives off filaments:
- posteriorly on the lateral surface of the Eustachian tube to the tensor tympani
- anteriorly to the tensor veli palatini muscle
- inferiorly to mandibular nerve making its motor root
- to the auriculotemporal nerve,[2] making up its sensory root.
Branches of communication
Its sympathetic postganglionic fibers consists of a filament from the plexus surrounding the middle meningeal artery.
Preganglionic parasympathetic fibres reach if from the glossopharyngeal nerve (and possobly also from the facial nerve) via the lesser superficial petrosal nerve continued from the tympanic plexus. Postganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the ganglion pass with the sympathetic fibres mainly in the auriculotemporal nerve to supply the parotid gland.
A slender filament (sphenoidal) ascends from it to the nerve of the Pterygoid canal, and a small branch connects it with the chorda tympani.
It is connected by two or three short filaments with the nerve to the Pterygoideus internus, from which it may obtain a motor, and possibly a sensory root.
Distribution
Its branches of distribution are: a filament to the Tensor tympani, and one to the Tensor veli palatini.
The former passes backward, lateral to the auditory tube; the latter arises from the ganglion, near the origin of the nerve to the Pterygoideus internus, and is directed forward.
The fibers of these nerves are, however, mainly derived from the nerve to the Pterygoideus internus.
Additional images
-
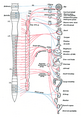
Plan of the facial and intermediate nerves and their communication with other nerves.
-
Diagram of efferent sympathetic nervous system.
References
- ^ Roitman R, Talmi YP, Finkelstein Y, Sadov R, Zohar Y (1990). "Anatomic study of the otic ganglion in humans". Head Neck. 12 (6): 503–6. PMID 2258290.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Module - Autonomics of the Head and Neck". Retrieved 2008-03-07.
- Shimizu T (1994). "Distribution and pathway of the cerebrovascular nerve fibers from the otic ganglion in the rat: anterograde tracing study". J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 49 (1): 47–54. PMID 7525688.
External links
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V, IX)
- Template:EMedicineDictionary
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 897 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 897 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)