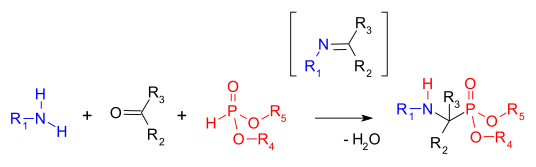
Kabachnik–Fields reaction
The Kabachnik-Fields Reaction is an organic reaction forming an α-amino phosphonate from an amine, a carbonyl compound and a dialkyl phosphite. Aminophosphonates are synthetic targets of some importance as phosphorus analogues of α-amino acids (a bioisosteric). This multicomponent reaction was independently discovered by Martin Izrailevich Kabachnik [1] and Ellis K. Fields [2] in 1952.
The first step in this reaction is the formation of an imine followed by an addition reaction of the phosphonate P-H bond into the C=N double bond (a Pudovik reaction) [3]. A related reaction is the Mannich reaction.
The reaction is accelerated with a combination of dehydrating reagent and Lewis acid. The carbonyl component in the reaction is usually an aldehyde and sometimes a ketone.
references
- ^ Kabachnik, M. I.; Medved, T. Ya. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1952
- ^ The Synthesis of Esters of Substituted Amino Phosphonic Acids Ellis K. Fields J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1952, 74 (6), pp 1528–1531 doi:10.1021/ja01126a054
- ^ Catalytic Kabachnik-Fields reaction: new horizons for old reaction Nikolay S. Zefirov and Elena D. Matveeva ARKIVOC 2008 (i) 1-17 Link