2009 swine flu pandemic timeline
This article documents a current event. Information may change rapidly as the event progresses, and initial news reports may be unreliable. The latest updates to this article may not reflect the most current information. (April 2009) |
Template:2009 swine flu outbreak table
This article covers the chronology of the 2009 novel influenza A (H1N1)[1] epidemic. Flag icons denote the first announcements of confirmed cases by the respective nation-states, their first deaths (and other major events such as their first intergenerational cases and their first cases of zoonosis), and relevant sessions and announcements of the World Health Organization, European Union, and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control.
Unless otherwise noted, references to terms like S-OIV, H1N1 and such, all refer to this new A(H1N1) strain and not to sundry other strains of H1N1 which are endemic in humans, birds and pigs.
Timeline
March 2009
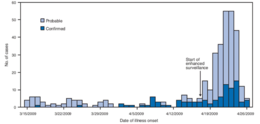
Mid-March
![]() Mexico
In La Gloria, Veracruz, 60% of the town's population is sickened by a respiratory illness of unknown provenance..[2]
Mexico
In La Gloria, Veracruz, 60% of the town's population is sickened by a respiratory illness of unknown provenance..[2]
March 17
![]() Mexico
Earliest known onset of a case that is later to be confirmed as Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection -.[3]
Mexico
Earliest known onset of a case that is later to be confirmed as Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection -.[3]
March 18
![]() Mexico
Surveillance begins picking up a surge in cases of influenza-like illness (ILI).
Mexico
Surveillance begins picking up a surge in cases of influenza-like illness (ILI).
March 28

![]() United States
Earliest known onset of a USA case later confirmed as swine flu, being a nine-year-old girl residing in Imperial County, California.[4][5]
United States
Earliest known onset of a USA case later confirmed as swine flu, being a nine-year-old girl residing in Imperial County, California.[4][5]
March 30
![]() United States
Biosurveillance firm Veratect begins tracking the unusual respiratory illness in Mexico.[6][7]
United States
Biosurveillance firm Veratect begins tracking the unusual respiratory illness in Mexico.[6][7]
![]() United States
A sample is collected from a nine-year-old female patient which is later confirmed to contain the novel virus strain (genetically sequenced as A/California/05/2009(H1N1)).[8][9]
United States
A sample is collected from a nine-year-old female patient which is later confirmed to contain the novel virus strain (genetically sequenced as A/California/05/2009(H1N1)).[8][9]
![]() United States
Onset of illness for a ten-year-old boy residing in San Diego County, California; his case is eventually the first to be confirmed as swine flu, .[5]
United States
Onset of illness for a ten-year-old boy residing in San Diego County, California; his case is eventually the first to be confirmed as swine flu, .[5]
April 2009
April 1
![]() United States
A nasopharyngeal swab is collected from a ten-year-old male patient in San Diego County, later confirmed as containing the novel virus and the first organism of that strain to be completely sequenced (A/California/04/2009(H1N1)).[5][8][10]
United States
A nasopharyngeal swab is collected from a ten-year-old male patient in San Diego County, later confirmed as containing the novel virus and the first organism of that strain to be completely sequenced (A/California/04/2009(H1N1)).[5][8][10]
April 2
![]() Mexico
In La Gloria, Veracruz, a four-year-old boy falls ill at the end of the outbreak. Only his sample, which was eventually sent abroad, tested positive for A(H1N1). Veracruz officials state that there were no plans to exhume the bodies of two infants who died in the outbreak.[2]
Mexico
In La Gloria, Veracruz, a four-year-old boy falls ill at the end of the outbreak. Only his sample, which was eventually sent abroad, tested positive for A(H1N1). Veracruz officials state that there were no plans to exhume the bodies of two infants who died in the outbreak.[2]
April 6
![]() Mexico
Public health authorities begin investigating unusual cases of pneumonia.[11] 400 people had reportedly sought treatment for pneumonia/influenza-like illness (ILI) in La Gloria the preceding week.[11]
Mexico
Public health authorities begin investigating unusual cases of pneumonia.[11] 400 people had reportedly sought treatment for pneumonia/influenza-like illness (ILI) in La Gloria the preceding week.[11]
![]() United States
Veratect publishes the alert "La Gloria: 'Strange' Respiratory Affects 60% of Local Population; Three Pediatric Deaths May be Associated with the Outbreak."[6][11]
United States
Veratect publishes the alert "La Gloria: 'Strange' Respiratory Affects 60% of Local Population; Three Pediatric Deaths May be Associated with the Outbreak."[6][11]
April 12
![]() Mexico
The General Directorate of Epidemiology (DGE) reports the outbreak of an ILI in a small community in Veracruz to the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), which is the Regional Office of the World Health Organization (WHO).[3]
Mexico
The General Directorate of Epidemiology (DGE) reports the outbreak of an ILI in a small community in Veracruz to the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), which is the Regional Office of the World Health Organization (WHO).[3]
![]() Mexico
A 39-year-old woman dies of severe viral pneumonia in the city of San Luis Potosí; this is later believed to be the earliest known fatality related to the outbreak.[12]
Mexico
A 39-year-old woman dies of severe viral pneumonia in the city of San Luis Potosí; this is later believed to be the earliest known fatality related to the outbreak.[12]
April 13
![]() Mexico
First death in Oaxaca due to what would later be identified as swine flu.[13]
Mexico
First death in Oaxaca due to what would later be identified as swine flu.[13]
![]() United States
The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) is advised of a ten-year-old boy with a respiratory illness in San Diego County, California. Test results had revealed an Influenza A virus, but were negative for standard human strains. The San Diego County Health Department is notified.[5]
United States
The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) is advised of a ten-year-old boy with a respiratory illness in San Diego County, California. Test results had revealed an Influenza A virus, but were negative for standard human strains. The San Diego County Health Department is notified.[5]
April 14
![]() United States
The CDC receives its first sample from California (from the ten-year-old boy in San Diego County), and identifies the virus as a strain of swine influenza A(H1N1).[5]
United States
The CDC receives its first sample from California (from the ten-year-old boy in San Diego County), and identifies the virus as a strain of swine influenza A(H1N1).[5]
April 16
![]() Mexico
Authorities notify the PAHO of the atypical pneumonia.[11]
Mexico
Authorities notify the PAHO of the atypical pneumonia.[11]
![]() United States
Veratect publishes the alert "Atypical Pneumonia Cases Reported at Hospital" regarding the Oaxaca cases.[6][11]
United States
Veratect publishes the alert "Atypical Pneumonia Cases Reported at Hospital" regarding the Oaxaca cases.[6][11]
April 17
![]() United States
The CDC receives a second sample from Southern California (taken from the nine-year-old girl in Imperial County), and again identifies the virus as a strain of swine influenza A(H1N1). The California Department of Public Health is notified.[5]
United States
The CDC receives a second sample from Southern California (taken from the nine-year-old girl in Imperial County), and again identifies the virus as a strain of swine influenza A(H1N1). The California Department of Public Health is notified.[5]
![]() Mexico
A case of atypical pneumonia in Oaxaca prompts enhanced national surveillance. A field investigation is started.[3]
Mexico contacts Canada to request more specialized testing.[14]
Mexico
A case of atypical pneumonia in Oaxaca prompts enhanced national surveillance. A field investigation is started.[3]
Mexico contacts Canada to request more specialized testing.[14]
April 18
![]() Mexico
Mexico sends 14 mucus samples to the CDC and dispatches health teams hospitals to look for patients showing severe influenza- or pnuemonia-like symptoms.[15]
Mexico
Mexico sends 14 mucus samples to the CDC and dispatches health teams hospitals to look for patients showing severe influenza- or pnuemonia-like symptoms.[15]
April 20
![]() United States
Veratect advises the CDC of the Mexican events.[6][11]
The CDC is already investigating the California and Texas cases.[6][11][16]
United States
Veratect advises the CDC of the Mexican events.[6][11]
The CDC is already investigating the California and Texas cases.[6][11][16]
April 21
![]() United States
The CDC alerts physicians to a similar novel strain of swine influenza A(H1N1) in two cases from Southern California. Local investigations, including investigations in Texas, are underway, and overall surveillance is enhanced.[5][17] The Associated Press covers the alert, the first mention of the A(H1N1) outbreak in English-language media.[16][18]
[19]
United States
The CDC alerts physicians to a similar novel strain of swine influenza A(H1N1) in two cases from Southern California. Local investigations, including investigations in Texas, are underway, and overall surveillance is enhanced.[5][17] The Associated Press covers the alert, the first mention of the A(H1N1) outbreak in English-language media.[16][18]
[19]
April 22
![]() Canada
Canada receives samples from Mexico for testing.[14]
Canada
Canada receives samples from Mexico for testing.[14]
April 23
![]() Mexico
The Public Health Agency of Canada confirms Mexico cases of swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus (S-OIV) infection.[3]
Genetic sequence analysis reveals that the Mexican patients were infected with the same S-OIV strain detected in two California children.[3]
The PAHO is informed that a cluster in Mexico of severe respiratory illnesses has been laboratory-confirmed as S-OIV infection.[3]
Mexico
The Public Health Agency of Canada confirms Mexico cases of swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus (S-OIV) infection.[3]
Genetic sequence analysis reveals that the Mexican patients were infected with the same S-OIV strain detected in two California children.[3]
The PAHO is informed that a cluster in Mexico of severe respiratory illnesses has been laboratory-confirmed as S-OIV infection.[3]
April 24
![]() The WHO issues its first Disease Outbreak Notice on the matter, confirming the infection of a number of people in Mexico and the United States by "Swine Influenza A/H1N1 viruses… not… previously detected in pigs or humans."[20]
The WHO issues its first Disease Outbreak Notice on the matter, confirming the infection of a number of people in Mexico and the United States by "Swine Influenza A/H1N1 viruses… not… previously detected in pigs or humans."[20]
![]() United States
The CDC tells a press conference that seven of the 14 Mexican samples contained the same virus strain as the known in California and Texas, and that indications suggested that containment in the USA was "not very likely".[21]
United States
The CDC tells a press conference that seven of the 14 Mexican samples contained the same virus strain as the known in California and Texas, and that indications suggested that containment in the USA was "not very likely".[21]
![]() Mexico
The Minister of Health confirms the Mexican cases of human infection by swine influenza and states that it believes that some of these cases had resulted in death.[21]
Health authorities implement public health measures for all airport passengers and the vaccination of health care workers with seasonal influenza vaccine.[3]
Mexico
The Minister of Health confirms the Mexican cases of human infection by swine influenza and states that it believes that some of these cases had resulted in death.[21]
Health authorities implement public health measures for all airport passengers and the vaccination of health care workers with seasonal influenza vaccine.[3]
April 25
![]() WHO Under the International Health Regulations (IHR), the newly convened Emergency Committee meets for the first time, resulting in the WHO Director-General declaring a formal "public health emergency of international concern".[22][23]
WHO Under the International Health Regulations (IHR), the newly convened Emergency Committee meets for the first time, resulting in the WHO Director-General declaring a formal "public health emergency of international concern".[22][23]
![]() The PAHO Vaccination Week In The Americas starts.[24]
The 2009 Week was planned to emphasize the vaccination of entire families, and health worker immunization.[24]
The PAHO Vaccination Week In The Americas starts.[24]
The 2009 Week was planned to emphasize the vaccination of entire families, and health worker immunization.[24]
![]() United States First closure of an entire school district, the Schertz-Cibolo-Universal City Independent School District outside San Antonio, Texas.[25][26]
United States First closure of an entire school district, the Schertz-Cibolo-Universal City Independent School District outside San Antonio, Texas.[25][26]
April 26
April 27

![]() WHO The Emergency Committee meets for the second time. The WHO Director-General issues a statement that containment of the outbreak is not feasible, and elevates the pandemic alert from Phase 3 to Phase 4.[27]
WHO The Emergency Committee meets for the second time. The WHO Director-General issues a statement that containment of the outbreak is not feasible, and elevates the pandemic alert from Phase 3 to Phase 4.[27]
![]() Canada
First six cases confirmed, four in Nova Scotia and two in British Columbia.[28]
Canada
First six cases confirmed, four in Nova Scotia and two in British Columbia.[28]
![]() Spain
First confirmed case of swine flu, in Almansa, and thus the first case in Europe; A(H1N1) has spread from the WHO Region of the Americas to the WHO European Region.[29]
Spain
First confirmed case of swine flu, in Almansa, and thus the first case in Europe; A(H1N1) has spread from the WHO Region of the Americas to the WHO European Region.[29]
![]() United Kingdom
First two confirmed cases, in Scotland.[30]
United Kingdom
First two confirmed cases, in Scotland.[30]
![]() European Union (EU) Health Commissioner advises Europeans not to travel to the United States or Mexico unless the need is urgent. This follows the first confirmed case in Spain.[31]
European Union (EU) Health Commissioner advises Europeans not to travel to the United States or Mexico unless the need is urgent. This follows the first confirmed case in Spain.[31]
![]() Mexico first seven confirmed deaths [32]
Mexico first seven confirmed deaths [32]
April 28
![]() WHO Confirmed cases are now extant in four of six WHO regions (see map). As of 1915 GMT seven countries have officially reported cases of swine influenza A(H1N1) infection.[33]
WHO Confirmed cases are now extant in four of six WHO regions (see map). As of 1915 GMT seven countries have officially reported cases of swine influenza A(H1N1) infection.[33]
![]() Israel
First confirmed case in Israel and thus the WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region (color-coded yellow), the third region to be affected.[34]
Israel
First confirmed case in Israel and thus the WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region (color-coded yellow), the third region to be affected.[34]
![]() New Zealand
First three confirmed cases in New Zealand and thus the WHO Western Pacific Region (color-coded red), the fourth region to be affected.
[35]
New Zealand
First three confirmed cases in New Zealand and thus the WHO Western Pacific Region (color-coded red), the fourth region to be affected.
[35]
![]() Canada
Confirmed: two cases and another four in Alberta and Ontario, respectively[citation needed].
Canada
Confirmed: two cases and another four in Alberta and Ontario, respectively[citation needed].
![]() Spain
The second confirmed case in Spain is located in Valencia[citation needed].
Spain
The second confirmed case in Spain is located in Valencia[citation needed].
April 29
![]() WHO
The Emergency Committee meets for the third time,[36]
and the WHO raises its pandemic alert level from Phase 4 to Phase 5, its second highest.[37] As of 1800 GMT, nine countries have officially reported 148 cases of swine influenza A(H1N1) infection.[38]
WHO
The Emergency Committee meets for the third time,[36]
and the WHO raises its pandemic alert level from Phase 4 to Phase 5, its second highest.[37] As of 1800 GMT, nine countries have officially reported 148 cases of swine influenza A(H1N1) infection.[38]
![]() EU Foreign Relations Commissioner Benita Ferrero-Waldner announces that the halt of all travel to Mexico and disinfecting all airports due to the global flu outbreak is being considered.[39]
EU Foreign Relations Commissioner Benita Ferrero-Waldner announces that the halt of all travel to Mexico and disinfecting all airports due to the global flu outbreak is being considered.[39]
![]() Germany
First three confirmed cases, two in Bavaria and one in Hamburg. [40]
Germany
First three confirmed cases, two in Bavaria and one in Hamburg. [40]
![]() Austria
First confirmed case.[41]
Austria
First confirmed case.[41]
![]() United States
First death outside Mexico, a 23-month old Mexican child hospitalized in Texas[citation needed]. Ninety-one cases confirmed cases worldwide to date.
United States
First death outside Mexico, a 23-month old Mexican child hospitalized in Texas[citation needed]. Ninety-one cases confirmed cases worldwide to date.
![]() Spain
Eight more cases raises the total in Spain to 10, including the first human-to-human intergenerational transmission[42] (in which the patient had not recently been to Mexico but was infected by another patient who had just visited Mexico, namely his girlfriend).[43] This is the first intergenerational transmission to be documented in Europe.
Spain
Eight more cases raises the total in Spain to 10, including the first human-to-human intergenerational transmission[42] (in which the patient had not recently been to Mexico but was infected by another patient who had just visited Mexico, namely his girlfriend).[43] This is the first intergenerational transmission to be documented in Europe.
![]() Canada
Nineteen confirmed cases[citation needed].
Canada
Nineteen confirmed cases[citation needed].
![]() United Kingdom
Three more confirmed cases of swine flu, giving a total of five confirmed cases[citation needed].
United Kingdom
Three more confirmed cases of swine flu, giving a total of five confirmed cases[citation needed].
April 30
![]() Netherlands
First confirmed case, a three-year-old child.[44] The child returned from Mexico to the Netherlands on April 27, 2009. The parents test negative for A(H1N1).
Netherlands
First confirmed case, a three-year-old child.[44] The child returned from Mexico to the Netherlands on April 27, 2009. The parents test negative for A(H1N1).
![]() Switzerland
First confirmed case[citation needed].
Switzerland
First confirmed case[citation needed].
![]() Ireland
First confirmed case.[45]
Ireland
First confirmed case.[45]
![]() United States
Four cases are confirmed in an outbreak at the University of Delaware; another 12 cases are deemed "probable". One of the confirmed cases is a baseball player, which results in the university cancelling sporting events, a concert by rapper Young Jeezy, and other school activities. [46]
United States
Four cases are confirmed in an outbreak at the University of Delaware; another 12 cases are deemed "probable". One of the confirmed cases is a baseball player, which results in the university cancelling sporting events, a concert by rapper Young Jeezy, and other school activities. [46]
![]() Canada
Confirmed: One more case in Toronto, and eight more cases in Nova Scotia, and Alberta bringing total to 28. [47]
Canada
Confirmed: One more case in Toronto, and eight more cases in Nova Scotia, and Alberta bringing total to 28. [47]
![]() United Kingdom
Three further confirmed cases of swine flu, giving a total of eight confirmed cases. [48]
United Kingdom
Three further confirmed cases of swine flu, giving a total of eight confirmed cases. [48]
May 2009
May 1
![]() WHO As of 0600 GMT, 11 countries have officially reported 331 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[49]
WHO As of 0600 GMT, 11 countries have officially reported 331 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[49]
- 300 people are placed under quarantine at a hotel for seven days due to Hong Kong's first confirmed case there.[50]
- Chief Executive Donald Tsang raises Hong Kong's response level from "serious" to "emergency".[51]
- The Director of Health, Dr. PY Lam, orders Metropark Hotel in Wan Chai to be isolated for 7 days.[52]
![]() Denmark
First confirmed case (in Hvidovre).[53]
Denmark
First confirmed case (in Hvidovre).[53]
![]() France
First two confirmed cases. [54]
France
First two confirmed cases. [54]
![]() United Kingdom
First and second case of human to human (or intergenerational) transmission within the UK confirmed.[55]
United Kingdom
First and second case of human to human (or intergenerational) transmission within the UK confirmed.[55]
![]() United States
155 confirmed cases. Two confirmed cases at the George Washington University's Thurston Hall
United States
155 confirmed cases. Two confirmed cases at the George Washington University's Thurston Hall
![]() Mexico begins five-day shutdown to fight flu spread.[56]
Mexico begins five-day shutdown to fight flu spread.[56]
May 2
![]() WHO As of 0600 GMT 15 countries have officially reported 615 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[57]
WHO As of 0600 GMT 15 countries have officially reported 615 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[57]
![]() Italy
First confirmed case.
Italy
First confirmed case.
![]() South Korea
First confirmed case.[58]
South Korea
First confirmed case.[58]
![]() Costa Rica First confirmed case, and the first in Central America.
Costa Rica First confirmed case, and the first in Central America.
![]() China suspends flights from Mexico to Shanghai when a case is confirmed on a flight from Mexico[59]
China suspends flights from Mexico to Shanghai when a case is confirmed on a flight from Mexico[59]
- 85 confirmed cases.
- The Canadian Food Inspection Agency confirms the first human-to-animal transmission of the virus after an Albertan returns from Mexico and infects a pig farm, the first known case of (reverse) zoonosis. [60]
![]() Mexico
The fatal and confirmed cases are corrected to 101 and 397, respectively.
Mexico
The fatal and confirmed cases are corrected to 101 and 397, respectively.
![]() United States
189 confirmed cases.[citation needed] There are more than 430 schools closures in 18 states.[61]
United States
189 confirmed cases.[citation needed] There are more than 430 schools closures in 18 states.[61]
May 3
![]() WHO As of 0600 GMT, 17 countries have officially reported 787 cases of (A)H1N1. [57]
WHO As of 0600 GMT, 17 countries have officially reported 787 cases of (A)H1N1. [57]
![]() Colombia
First confirmed case in South America. [62]
Colombia
First confirmed case in South America. [62]
![]() Portugal
First confirmed case.
Portugal
First confirmed case.
![]() Mexico
Final day of lock-down in Mexico.
Mexico
Final day of lock-down in Mexico.
![]() Canada
101 confirmed cases after seven cases in British Columbia, three in Alberta, two in Nova Scotia and Ontario, and one in Quebec were confirmed.[63]
Canada
101 confirmed cases after seven cases in British Columbia, three in Alberta, two in Nova Scotia and Ontario, and one in Quebec were confirmed.[63]
May 4
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 20 countries have officially reported 985 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.
[64][65]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 20 countries have officially reported 985 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.
[64][65]
![]() El Salvador First confirmed case.
El Salvador First confirmed case.
![]() Canada A girl from Edmonton, Alberta was diagnosed with a severe case of the H1N1 virus, the first severe one in Canada.[66]
Canada A girl from Edmonton, Alberta was diagnosed with a severe case of the H1N1 virus, the first severe one in Canada.[66]
May 5
![]() WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 21 countries have officially reported 1,124 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[67]
WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 21 countries have officially reported 1,124 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[67]
![]() Guatemala First confirmed case.
Guatemala First confirmed case.
- Second confirmed death, the first of a U.S. resident, a pregnant special education teacher in Texas: Judy Trunnell. The 33-year-old gives birth to her second child via Caesarian section during her eighth month of pregnancy, in a coma whilst on life support.[68][69] Judy Trunnell had several underlying medical conditions, most notably asthma.[70][71][72]
- Several sailors in San Diego, California fall ill (including a sailor on the USS Dubuque, which results in the cancellation of its deployment). These are the first cases in the U.S. Navy.[73]
- As the low level of virulence of novel A(H1N1) in the U.S. becomes established, the CDC issues revised criteria for school closures, effectively ending widespread shutdowns.[74]
May 6
![]() WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 22 countries have officially reported 1,516 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[75]
WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 22 countries have officially reported 1,516 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[75]
May 7
![]() WHO
As of 18:00 GMT, 24 countries have officially reported 2371 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[76]
WHO
As of 18:00 GMT, 24 countries have officially reported 2371 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[76]
![]() Argentina
First confirmed case.[77]
Argentina
First confirmed case.[77]
![]() Brazil First four confirmed cases.
Brazil First four confirmed cases.
![]() Canada
Reports suggest that an elderly woman who had swine flu has died in northern Alberta, marking the first death in Canada related to swine flu.[78]
Canada
Reports suggest that an elderly woman who had swine flu has died in northern Alberta, marking the first death in Canada related to swine flu.[78]
![]() The Netherlands
A second and a third confirmed case has been reported, by a 53-year old woman and a 52-year old man.
The Netherlands
A second and a third confirmed case has been reported, by a 53-year old woman and a 52-year old man.
![]() USA
The New England Journal of Medicine establishes its H1N1 Influenza Center on its website.[79]
USA
The New England Journal of Medicine establishes its H1N1 Influenza Center on its website.[79]
May 8
![]() WHO
As of 16:00 GMT, 25 countries have officially reported 2,500 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[80]
WHO
As of 16:00 GMT, 25 countries have officially reported 2,500 cases of influenza A (H1N1) infection.[80]
![]() Japan First three confirmed cases.[81]
Japan First three confirmed cases.[81]
![]() Panama First confirmed case [82][83][84].
Panama First confirmed case [82][83][84].
May 9
![]() WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 29 countries have officially reported 3,440 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[85]
WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 29 countries have officially reported 3,440 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[85]
![]() Australia First confirmed case.[86]
Australia First confirmed case.[86]
![]() Brasil Two cases confirmed, one of which is thought to be the first case of human-to-human infection in Brazil. [87]
Brasil Two cases confirmed, one of which is thought to be the first case of human-to-human infection in Brazil. [87]
![]() Costa Rica First confirmed death, and also the first death outside of North America.[88][89] Three other confirmed cases, all children, were contaminated by the patient who died.[90]
Costa Rica First confirmed death, and also the first death outside of North America.[88][89] Three other confirmed cases, all children, were contaminated by the patient who died.[90]
![]() Norway First two confirmed cases. [91]
Norway First two confirmed cases. [91]
![]() USA Third confirmed death, a Washington man with underlying heart disease.[92] Also, the USA passes Mexico in the number of confirmed cases of infection, 1693 to 1364, thus becoming the nation-state with the most laboratory-confirmed cases of infection; Canada is third with 242 cases.[93]
USA Third confirmed death, a Washington man with underlying heart disease.[92] Also, the USA passes Mexico in the number of confirmed cases of infection, 1693 to 1364, thus becoming the nation-state with the most laboratory-confirmed cases of infection; Canada is third with 242 cases.[93]
May 10
![]() WHO
As of 07:30 GMT, 29 countries have officially reported 4,379 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[94]
WHO
As of 07:30 GMT, 29 countries have officially reported 4,379 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[94]
![]() Brazil More two cases confirmed. Now the country has 8 confirmed cases.
Brazil More two cases confirmed. Now the country has 8 confirmed cases.
May 11
![]() WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 30 countries have officially reported 4,694 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[95]
WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 30 countries have officially reported 4,694 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[95]
May 12
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 30 countries have officially reported 5,251 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[96]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 30 countries have officially reported 5,251 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[96]
![]() Thailand First two confirmed cases. Thailand is the first Southeast Asia country to be affected by the virus.
Thailand First two confirmed cases. Thailand is the first Southeast Asia country to be affected by the virus.
![]() Finland First two confirmed cases.
Finland First two confirmed cases.
![]() Brazil Beyond the eight confirmed cases, the country has 34 suspected cases.
Brazil Beyond the eight confirmed cases, the country has 34 suspected cases.
![]() Panama 11 new confirmed cases. 29 total.[97]
Panama 11 new confirmed cases. 29 total.[97]
![]() Canada The first case in Yukon Territory is confirmed.[98]
Canada The first case in Yukon Territory is confirmed.[98]
![]() Spain 100 cases confirmed. [99]
Spain 100 cases confirmed. [99]
May 13
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 13 May 2009, 33 countries have officially reported 5,728 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[100]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 13 May 2009, 33 countries have officially reported 5,728 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[100]
![]() Hong Kong, China Second confirmed case.
Hong Kong, China Second confirmed case.
![]() Belgium First confirmed case. [101]
Belgium First confirmed case. [101]
![]() Panama 10 more cases confirmed today. Total :39. [102]
Panama 10 more cases confirmed today. Total :39. [102]
![]() Argentina Second confirmed case.
Argentina Second confirmed case.
May 14
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 33 countries have officially reported 6,497 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[103]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 33 countries have officially reported 6,497 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.[103]
![]() Belgium Second confirmed case. [104]
Belgium Second confirmed case. [104]
![]() Colombia First domestic infections with 3 cases confirmed. Total: 10. [105]
Colombia First domestic infections with 3 cases confirmed. Total: 10. [105]
May 15
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 34 countries have officially reported 7,520 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection. [106]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 34 countries have officially reported 7,520 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection. [106]
![]() USA Fourth and fifth deaths confirmed, that of an Arizona woman suffering from a lung condition[107][108]and a Texas man in Corpus Christi, respectively.[109][110]
USA Fourth and fifth deaths confirmed, that of an Arizona woman suffering from a lung condition[107][108]and a Texas man in Corpus Christi, respectively.[109][110]
![]() Malaysia First confirmed case. [111] Malaysia is the 37th country to be affected by the virus.
Malaysia First confirmed case. [111] Malaysia is the 37th country to be affected by the virus.
![]() Belgium 2 more cases confirmed today. Total: 4.
Belgium 2 more cases confirmed today. Total: 4.
![]() Cuba 2 more cases confirmed today. Total: 3.
Cuba 2 more cases confirmed today. Total: 3.
![]() Panama 4 new cases confirmed today. Total: 43, 23 of whom are male and 20 of whom are female. 20 of the cases are under 15 years old.[112]
Panama 4 new cases confirmed today. Total: 43, 23 of whom are male and 20 of whom are female. 20 of the cases are under 15 years old.[112]
May 16
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT 36 countries have officially reported 8,451 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.
WHO As of 06:00 GMT 36 countries have officially reported 8,451 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.
![]() Malaysia Second confirmed case. [113] The first patient is now showing significant improvement from the treatment.
Malaysia Second confirmed case. [113] The first patient is now showing significant improvement from the treatment.
![]() Japan First domestic infection confirmed, in Kobe, a male high school student with no history of travel abroad. [114] The Kobe Festival, planned for May 16 and 17, is cancelled.[115]
Japan First domestic infection confirmed, in Kobe, a male high school student with no history of travel abroad. [114] The Kobe Festival, planned for May 16 and 17, is cancelled.[115]

![]() India First case confirmed, in Hyderabad. [116]. This marks the arrival of A(H1N1) in the fifth of the WHO's six regions, the South-East Asia Region.
India First case confirmed, in Hyderabad. [116]. This marks the arrival of A(H1N1) in the fifth of the WHO's six regions, the South-East Asia Region.
![]() Panama 11 New confirmed cases. 54 total.[117]
Panama 11 New confirmed cases. 54 total.[117]
May 17
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT 37 countries have officially reported 8,480 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.
WHO As of 06:00 GMT 37 countries have officially reported 8,480 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection.
![]() Panama With 54 confirmed cases, Panama occupies second place, along with Canada, for the number of cases per country.[118]
Panama With 54 confirmed cases, Panama occupies second place, along with Canada, for the number of cases per country.[118]
![]() Chile First confirmed case in the country, and the 41st country affected.
Chile First confirmed case in the country, and the 41st country affected.
May 18
![]() WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 40 countries have officially reported 8,829 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 74 deaths.[119]
WHO
As of 06:00 GMT, 40 countries have officially reported 8,829 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 74 deaths.[119]
![]() USA The sixth death in the US, and the first in New York —that of an assistant principal.[120][121]
USA The sixth death in the US, and the first in New York —that of an assistant principal.[120][121]
![]() Japan reports 96 confirmed cases;[122] it now ranks fourth in the world in the number of infections. Thousands of schools in 21 cities in the Hyogo and Osaka prefectures are temporarily closed.[123][124]
Japan reports 96 confirmed cases;[122] it now ranks fourth in the world in the number of infections. Thousands of schools in 21 cities in the Hyogo and Osaka prefectures are temporarily closed.[123][124]
![]() United Kingdom 107 cases confirmed.
United Kingdom 107 cases confirmed.
May 19
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 40 countries have officially reported 9,830 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 79 deaths. [125]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 40 countries have officially reported 9,830 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 79 deaths. [125]
![]() United States Seventh confirmed death, that of a 44-year-old Missouri man. [126]
United States Seventh confirmed death, that of a 44-year-old Missouri man. [126]
![]() Japan 191 confirmed cases; Hyogo Prefecture has the most at 111.[127]
Japan 191 confirmed cases; Hyogo Prefecture has the most at 111.[127]
![]() Peru 2 more cases confirmed today. Total: 3.[128]
Peru 2 more cases confirmed today. Total: 3.[128]
![]() Norway 1 more case confirmed today. Total: 3. [129]
Norway 1 more case confirmed today. Total: 3. [129]
![]() Paraguay confirmed its first case and became the 43rd affected country. [130]
Paraguay confirmed its first case and became the 43rd affected country. [130]
![]() Taiwan confirmed its first case and becomes the 44th affected country.[131]
Taiwan confirmed its first case and becomes the 44th affected country.[131]
May 20
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 40 countries have officially reported 10,243 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 80 deaths. [132]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 40 countries have officially reported 10,243 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 80 deaths. [132]
![]() United States A patient dies in Arizona[133], and a 22-year-old man dies in Utah[134], the nation's eighth and ninth H1N1 fatalities. Roughly half of the influenza viruses detected by the CDC's routine influenza surveillance systems are now that of novel A(H1N1).[135] An unusual number of outbreaks in schools is reported.[136]
United States A patient dies in Arizona[133], and a 22-year-old man dies in Utah[134], the nation's eighth and ninth H1N1 fatalities. Roughly half of the influenza viruses detected by the CDC's routine influenza surveillance systems are now that of novel A(H1N1).[135] An unusual number of outbreaks in schools is reported.[136]
![]() Japan 236 confirmed cases, including the first case in Shiga Prefecture,[137]
and Hachioji and Kawasaki city in the Greater Tokyo Area. Two female high school students from Tokyo who had recently attended a Model United Nations conference in New York are presumed to have become infected abroad.[138][139]
Japan 236 confirmed cases, including the first case in Shiga Prefecture,[137]
and Hachioji and Kawasaki city in the Greater Tokyo Area. Two female high school students from Tokyo who had recently attended a Model United Nations conference in New York are presumed to have become infected abroad.[138][139]
![]() Norway 1 more case confirmed today. Total: 4. [140]
Norway 1 more case confirmed today. Total: 4. [140]
![]() Brazil 1 more confirmed case, now are 9 cases in total.
Brazil 1 more confirmed case, now are 9 cases in total.
May 21
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 41 countries have officially reported 11,034 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 85 deaths. [141]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 41 countries have officially reported 11,034 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 85 deaths. [141]
![]() Japan 279 confirmed cases; more than 4,800 schools are closed in the Kobe region.[142]
Japan 279 confirmed cases; more than 4,800 schools are closed in the Kobe region.[142]
![]() Philippines confirms first case of influenza A(H1N1) virus.
Philippines confirms first case of influenza A(H1N1) virus.
May 22
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 42 countries have officially reported 11,168 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 86 deaths. [143]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 42 countries have officially reported 11,168 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 86 deaths. [143]
![]() Japan 317 confirmed, including first confirmed in Saitama Prefecture.[144]
Third confirmed in Tokyo, a 25 year old man who visited Osaka from May 14-20th.[145]
Japan 317 confirmed, including first confirmed in Saitama Prefecture.[144]
Third confirmed in Tokyo, a 25 year old man who visited Osaka from May 14-20th.[145]
![]() Honduras First confirmed case.
Honduras First confirmed case.
May 23
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 43 countries have officially reported 12,022 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 86 deaths. [146]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 43 countries have officially reported 12,022 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 86 deaths. [146]
![]() Iceland First confirmed case. 4 more cases suspected.[147]
[148]
Iceland First confirmed case. 4 more cases suspected.[147]
[148]
![]() South Korea has six more confirmed cases. Total: 10
South Korea has six more confirmed cases. Total: 10
![]() United Kingdom 122 cases confirmed.
United Kingdom 122 cases confirmed.
![]() Brazil has one more confirmed case. Total: 10.
Brazil has one more confirmed case. Total: 10.
May 24
![]() Kuwait First confirmed cases, that of 18 U.S. soldiers. [149]
Kuwait First confirmed cases, that of 18 U.S. soldiers. [149]
![]() Australia Two more confirmed cases, which now brings the national toll to 16.[150]
Australia Two more confirmed cases, which now brings the national toll to 16.[150]
![]() Philippines Second confirmed case reported by Philippine Health secretary Francisco Duque.
Philippines Second confirmed case reported by Philippine Health secretary Francisco Duque.
![]() United Kingdom 133 cases confirmed.
United Kingdom 133 cases confirmed.
![]() Argentina 3 cases confirmed. Total: 5
Argentina 3 cases confirmed. Total: 5
![]() United Arab Emirates First case confirmed.
United Arab Emirates First case confirmed.
May 25
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 46 countries have officially reported 12,515 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 91 deaths.[151]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 46 countries have officially reported 12,515 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 91 deaths.[151]
![]() United Kingdom 4 more confirmed cases in the United Kingdom. Total: 137.
United Kingdom 4 more confirmed cases in the United Kingdom. Total: 137.
![]() Canada Second confirmed death in Ontario.
Canada Second confirmed death in Ontario.
![]() Australia 22 Confirmed Cases. [152]
Australia 22 Confirmed Cases. [152]
![]() Ireland Second confirmed case. [153]
Ireland Second confirmed case. [153]
![]() United States 12th death confirmed.
United States 12th death confirmed.
![]() Czech Republic First confirmed case
Czech Republic First confirmed case
May 26
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 46 countries have officially reported 12,954 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 92 deaths[154]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 46 countries have officially reported 12,954 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 92 deaths[154]
![]() Argentina 14 Confirmed Cases. Total: 19. [155]
Argentina 14 Confirmed Cases. Total: 19. [155]
![]() United Kingdom 44 new cases confirmed. Total: 184 [156]
United Kingdom 44 new cases confirmed. Total: 184 [156]
![]() Chile 107 confirmed cases. [157]
Chile 107 confirmed cases. [157]
![]() Australia 61 confirmed cases. [158]
[159]
[160]
Australia 61 confirmed cases. [158]
[159]
[160]
![]() Puerto Rico First confirmed case[161]
Puerto Rico First confirmed case[161]
May 27
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 48 countries have officially reported 13,398 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 95 deaths[162]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 48 countries have officially reported 13,398 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 95 deaths[162]
![]() Singapore First confirmed case. A 22-year-old woman picked up the virus after visiting New York.
[163]
Singapore First confirmed case. A 22-year-old woman picked up the virus after visiting New York.
[163]
![]() Romania First confirmed case. [164]
Romania First confirmed case. [164]
![]() Philippines Four more confirmed cases.
Philippines Four more confirmed cases.
![]() Dominican Republic First two confirmed cases. [165]
Dominican Republic First two confirmed cases. [165]
![]() United Kingdom 2 new cases confirmed. Total: 186 [166]
United Kingdom 2 new cases confirmed. Total: 186 [166]
![]() Chile 46 new cases confirmed. Total: 165 [167]
Chile 46 new cases confirmed. Total: 165 [167]
![]() Argentina 37 cases confirmed. [168]
Argentina 37 cases confirmed. [168]
![]() Uruguay confirmed its first two cases of Influenza A (H1N1). [169]
Uruguay confirmed its first two cases of Influenza A (H1N1). [169]
![]() Greece confirmed two more cases.[170]
Greece confirmed two more cases.[170]
![]() Brazil has one more confirmed case. Total: 11
Brazil has one more confirmed case. Total: 11
May 28
![]() Australia 147 Confirmed Cases. [171]
Australia 147 Confirmed Cases. [171]
![]() Slovakia First confirmed case.
Slovakia First confirmed case.
![]() Singapore Three more cases confirmed. Total confirmed cases now stands at four.
[172]
Singapore Three more cases confirmed. Total confirmed cases now stands at four.
[172]
![]() United Kingdom Seventeen more confirmed cases Total: 203 [173]
United Kingdom Seventeen more confirmed cases Total: 203 [173]
![]() Sweden One more confirmed case. Total 4.
Sweden One more confirmed case. Total 4.
![]() Bolivia First 2 cases confirmed.[174]
Bolivia First 2 cases confirmed.[174]
![]() Venezuela First case confirmed.
Venezuela First case confirmed.
![]() Brazil has 3 new cases, the both are in São Paulo. Now the country has 14 cases.
Brazil has 3 new cases, the both are in São Paulo. Now the country has 14 cases.
May 29
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 53 countries have officially reported 15,510 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 99 deaths[175]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 53 countries have officially reported 15,510 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 99 deaths[175]
![]() United Kingdom 14 confirmed cases. Total: 217[176]
United Kingdom 14 confirmed cases. Total: 217[176]
![]() Norway One new confirmed case. Total: 5 [177]
Norway One new confirmed case. Total: 5 [177]
![]() Hungary First confirmed case [178]
Hungary First confirmed case [178]
![]() Brazil Another one case confirmed, being the third case of human-to-human transmission inside the country. Total: 15.
Brazil Another one case confirmed, being the third case of human-to-human transmission inside the country. Total: 15.
![]() Uruguay 4 new confirmed cases. Total: 6[179]
Uruguay 4 new confirmed cases. Total: 6[179]
![]() Greece Another one case confirmed. Total 4.[180]
Greece Another one case confirmed. Total 4.[180]
![]() Venezuela Second confirmed case.
Venezuela Second confirmed case.
![]() Philippines Health officials confirmed additional 4 cases. Total:14 cases
Philippines Health officials confirmed additional 4 cases. Total:14 cases
May 30
![]() Sweden One more confirmed case. Total 5.
Sweden One more confirmed case. Total 5.
![]() Norway Two new confirmed cases. Total 7.
Norway Two new confirmed cases. Total 7.
![]() United Kingdom 12 more cases. Total: 229.
United Kingdom 12 more cases. Total: 229.
![]() Estonia First confirmed case. [181]
Estonia First confirmed case. [181]
![]() Brazil Five more cases. Total: 20 (15 outside the country and 5 inside the country).
Brazil Five more cases. Total: 20 (15 outside the country and 5 inside the country).
![]() Lebanon First three cases confirmed.
Lebanon First three cases confirmed.
![]() Philippines 2 more cases confirmed
Philippines 2 more cases confirmed
May 31
![]() Antarctica First two cases confirmed in two American scientists stationed there.
Antarctica First two cases confirmed in two American scientists stationed there.
![]() Singapore Another confirmed case brings the total confirmed to 5.
Singapore Another confirmed case brings the total confirmed to 5.
![]() Argentina 100 cases confirmed.
Argentina 100 cases confirmed.
![]() Dominican Republic Nine more cases confirmed, for a total of 11 cases nationwide.[182]
Dominican Republic Nine more cases confirmed, for a total of 11 cases nationwide.[182]
![]() United Kingdom 14 more cases confirmed Total: 244
United Kingdom 14 more cases confirmed Total: 244
June 2009
June 1
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 62 countries have officially reported 17,410 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 115 deaths.[183]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 62 countries have officially reported 17,410 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 115 deaths.[183]
![]() Philippines Additional 5 confirmed cases of A(H1N1) virus, in total of 21 confirmed case.
Philippines Additional 5 confirmed cases of A(H1N1) virus, in total of 21 confirmed case.
![]() Greece one more case confirmed total: 5
Greece one more case confirmed total: 5
![]() Singapore Another two new confirmed cases. Total: 7 cases
Singapore Another two new confirmed cases. Total: 7 cases
![]() Bulgaria First confirmed case
[184]
Bulgaria First confirmed case
[184]
![]() Israel 7 cases confirmed Total: 33 [185]
Israel 7 cases confirmed Total: 33 [185]
![]() United States West Virginia is the last USA state to be affected by swine flu
United States West Virginia is the last USA state to be affected by swine flu
![]() Honduras 2 more cases confirmed Total:3
Honduras 2 more cases confirmed Total:3
![]() Canada 3rd death confirmed. First death in Toronto
Canada 3rd death confirmed. First death in Toronto
![]() Venezuela Third confirmed case [186]
Venezuela Third confirmed case [186]
June 2
![]() Luxembourg First case confirmed
Luxembourg First case confirmed
![]() Thailand 1 new confirmed case in total of 5 postive cases of A(H1N1) virus.
Thailand 1 new confirmed case in total of 5 postive cases of A(H1N1) virus.
![]() Ukraine First confirmed case of A (H1N1) virus
Ukraine First confirmed case of A (H1N1) virus
![]() Singapore One more confirmed case. Total: 8
Singapore One more confirmed case. Total: 8
![]() Egypt First confirmed case of A (H1N1) virus. First confirmed case in Africa.
Egypt First confirmed case of A (H1N1) virus. First confirmed case in Africa.
![]() Nicaragua First confirmed case of A (H1N1) virus.
Nicaragua First confirmed case of A (H1N1) virus.
![]() Dominican Republic Two more cases of A (H1N1) virus. Total confirmed: 14.[182]
Dominican Republic Two more cases of A (H1N1) virus. Total confirmed: 14.[182]
![]() United Kingdom New cases brings total to 339.
United Kingdom New cases brings total to 339.
![]() Sweden One more confirmed case. Total: 7
Sweden One more confirmed case. Total: 7
![]() Chile First confirmed death, a 37 year old man.
Chile First confirmed death, a 37 year old man.
![]() Honduras 34 comfirmed cases in total. [187]
Honduras 34 comfirmed cases in total. [187]
![]() Bermuda First case confirmed
[188]
Bermuda First case confirmed
[188]
![]() Netherlands 1 more case confirmed. Total: 4
Netherlands 1 more case confirmed. Total: 4
June 3
![]() WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 3 June 2009, 66 countries have officially reported 19,273 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 117 deaths.[189]
WHO As of 06:00 GMT, 3 June 2009, 66 countries have officially reported 19,273 cases of influenza A(H1N1) infection, including 117 deaths.[189]
![]() Saudi Arabia First case confirmed
Saudi Arabia First case confirmed
![]() Philippines 1 new confirmed case in total of 22 positive cases of A(H1N1) virus
Philippines 1 new confirmed case in total of 22 positive cases of A(H1N1) virus
![]() Norway One new confirmed case. Total 8.
Norway One new confirmed case. Total 8.
![]() Singapore Three new confirmed case. Total 11.
Singapore Three new confirmed case. Total 11.
![]() United Kingdom More Confirmed cases. Total: 404 [190]
United Kingdom More Confirmed cases. Total: 404 [190]
![]() Venezuela 4th confirmed case [191]
Venezuela 4th confirmed case [191]
![]() Dominican Republic Total amount of confirmed cases rises to 23. [182]
Dominican Republic Total amount of confirmed cases rises to 23. [182]
![]() Nicaragua 4 new confirmed cases. Total: 5 [192]
Nicaragua 4 new confirmed cases. Total: 5 [192]
![]() Jamaica First 2 cases confirmed
Jamaica First 2 cases confirmed
![]() New Zealand One further confirmed case, bringing the national total to 11.
New Zealand One further confirmed case, bringing the national total to 11.
June 4
![]() Philippines Confirmed cases of A(H1N1) virus rose to 29.
Philippines Confirmed cases of A(H1N1) virus rose to 29.
![]() Malaysia Three more cases confirmed. One of the patient is a 23-year-old student returned from United States. Another two patients are German tourists who arrived in Singapore but went to Malaysia for holiday. [193]
Malaysia Three more cases confirmed. One of the patient is a 23-year-old student returned from United States. Another two patients are German tourists who arrived in Singapore but went to Malaysia for holiday. [193]
![]() Norway One new confirmed case. Total 9.
Norway One new confirmed case. Total 9.
![]() Swden First domestic infectin. Total 13 (1 domestic)
Template:Flagicon United States The United States reports another death in Connecticut, bringing the total up to 29.
Swden First domestic infectin. Total 13 (1 domestic)
Template:Flagicon United States The United States reports another death in Connecticut, bringing the total up to 29.
![]() Peru 47 confirmed cases of influenza A in Peru [194]
Peru 47 confirmed cases of influenza A in Peru [194]
![]() Guatemala 23 confirmed cases of influenza A in Guatemala [195]
Guatemala 23 confirmed cases of influenza A in Guatemala [195]
References
- ^ http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/
- ^ a b Tuckman, Jo (2009-04-27). "Four-year-old could hold key in search for source of swine flu outbreak". The Guardian. Retrieved 2009-04-28.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Outbreak of Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection --- Mexico, March--April 2009". Morbidity and Mortality (Dispatch). Centers for Disease Control. 2009-04-30. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ Brown, David (2009-04-22). "New Strain of Swine Flu Investigated: Two Children in San Diego Area Had No Contact With Pigs". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Swine influenza A (H1N1) infection in two children --- Southern California, March--April 2009". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Centers for Disease Control. 2009-04-21. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ a b c d e Blumenthal, Les (2009-05-01). "Company warned officials of flu 18 days before alert was issued". McClatchy Newspapers. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Veratect the Company to First Sound Alarm on Swine Influenza Makes Data on the Spread of this Disease Public" (PDF). Corporate press release. Veratect Inc. 2009-04-27. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ a b "GenBank sequences from 2009 H1N1 influenza outbreak". Influenza Virus Resource. NCBI. 2009-05-01. Archived from the original on 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Influenza A virus (A/California/05/2009(H1N1)) segment 1 polymerase PB2 (PB2) gene, complete cds". NCBI. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Influenza A virus (A/California/04/2009(H1N1)) segment 1 polymerase PB2 (PB2) gene, complete cds". NCBI. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ a b c d e f g Brown, David (2009-04-30). "Reporting Health Threats: System Set Up After SARS Epidemic Was Slow to Alert Global Authorities". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ Brown, David (2009-04-26). "U.S. Slow to Learn of Mexico Flu: Canadian Officials Knew of Rare Strain Before Americans Did". Washington Post. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
The earliest case found in Mexico was a 39-year-old woman who died April 12 of severe viral pneumonia in San Luis Potosi, a city of about 700,000 in central Mexico. "That attracted the attention of the epidemiologist there," said Mauricio Hernández, deputy minister for disease prevention and health promotion in Mexico's Federal Department of Health.
- ^ Orsi, Peter (2009-04-27). "Mexico says suspected swine flu deaths now at 149". Google News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2009-04-28. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ a b "Human Swine Influenza Outbreak. Message from the Minister of Health and the Chief Public Health Officer on Human Swine Flu". Advisories. Public Health Agency of Canada. 2009-04-24. Archived from the original on 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ Stevenson, Mark (2009-04-26). "U.S., Mexico battle deadly flu outbreak". KomoNews.com. Fisher Communications, Inc. AP. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ a b Stobbe, Mike (2009-04-21). "Officials alert doctors after 2 California children infected with unusual swine flu". Star Tribune. AP. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/NEJMoa0903810
- ^ http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/NEJMp0904012 New England Journal of Medicine article on on-line monitoring
- ^ Stobbe, Mike (2009-04-21). "Swine flu cases in Calif. worry health officials". FoxNews.com. Fox News. AP. Archived from the original on 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "(Update 1) Influenza-Like Illness in the United States and Mexico". World Health Organization. 2009-04-24. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ a b "CDC Briefing on Public Health Investigation of Human Cases of Swine Influenza (April 24, 2009)". Press Briefing Transcripts. CDC. 2009-04-24. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "Statement by WHO Director-General, Dr Margaret Chan (25 April 2009): Swine influenza". World Health Organization. 2009-04-25. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ "WHO | Swine flu illness in the United States and Mexico - update 2". Who.int. 2009-04-26. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ a b "Vaccination Week In The Americas (2009 portal)". Pan American Health Organization. 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-29.
- ^ First Texas school district closure.
- ^ List of Texas school district closures.
- ^ "Statement by WHO Director-General, Dr Margaret Chan (27 April 2009): Swine influenza". World Health Organization. 2009-04-27. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ http://www.cbc.ca/world/story/2009/04/26/mexico-swine-flu.html
- ^ http://www.silobreaker.com/almansa-spain-11_167450
- ^ Sky News
- ^ "Europeans urged to avoid Mexico and US as swine flu death toll exceeds 100". Guardian. 27 April 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ "Swine Influenza Update 3". World Health Organization. 27 April 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ "WHO | Swine influenza - update 4". Who.int. 2009-04-28. Retrieved 2009-04-27.
- ^ http://blog.taragana.com/n/israel-confirms-first-case-of-swine-flu-42122/
- ^ "NZ Minstry of Health Media Release". New Zealand Minstry of Health. 2009.
{{cite web}}: Text "04" ignored (help); Text "28" ignored (help) - ^ Jordans, Frank (2009-04-29). "WHO calls emergency meeting; eyes pandemic level". Google News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2009-04-30. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Statement by WHO Director-General, Dr Margaret Chan (29 April 2009): Swine influenza". World Health Organization. 2009-04-27. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 5". Who.int. 2009-04-29. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ EU considers halting all Mexico travel- commissioner[dead link]
- ^ "SWINE FLU: GERMANY CONFIRMS THREE CASES". AGI. 2009-04-29. Archived from the original on 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 5". Who.int. 2009-04-29. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ "WHO looking for signs of ongoing swine flu spread". CTV.ca. 2009-04-28. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ "Mexico begins five-day shutdown to fight swine flu - News - Muzi.com". Dailynews.muzi.com. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ "Dutch confirm swine flu case in three year-old". Reuters. 2009-04-30. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ "Irish man treated for swine flu". BBC. 2009-04-30. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
- ^ "More than 350 treated at UD | delawareonline | The News Journal". delawareonline. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ Tanya Talaga, Joanna Smith. "Spike in cases of swine flu" Toronto Star 30 April 2009
- ^ "Three new cases of swine flu confirmed in Britain" China View 1 May 2009
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 7". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ "Asia-Pacific | Hong Kong 'flu' hotel sealed off". BBC News. 2007-04-18. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ "1st H1N1 case confirmed in HK". Hong Kong SAR. 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ "Director of Health issues isolation order to control human swine flu". Centre for Health Protection, Hong Kong SAR. 2009-05-31.
- ^ "Dansk kvinde smittet med H1N1-influenza efter New York-rejse". Bt.dk. 2008-12-16. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ "Sujets suspects et cas de nouvelle grippe A(H1N1) en France (PDF)" (PDF). 2009-05-01 19:00. Retrieved 2009-05-22.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ HPA. "First case of onward human to human swine flu transmission in England confirmed".
- ^ "Mexico To Close Down Most Businesses For Five Days As 331 Cases Of Swine Flu Reported". AHN. 2009-05-01. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ a b "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 9". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ "1st South Korea case". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-04.
- ^ "China halts Mexico flights". The Straits Times. 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ "Worker may have passed H1N1 to Alberta pigs". CTV. 2009-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ AP article on U.S. school closures.
- ^ "Reuters AlertNet - Colombia reports flu case, Ecuador monitors border". Alertnet.org. 2009-05-03. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ "Swine flu epidemic on decline: Mexico". CBC. 2009-05-03. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 13". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ WHO Map of Outbreak
- ^ "Canada identifies first severe flu case". brisbanetimes. May 5, 2009: Australia. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 15". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ http://babyboomeradvisorclub.com/texas-womans-death-linked-to-swine-flu-is-identified-by-cdc-as-who-total-reaches-1658/
- ^ http://www.keyetv.com/content/news/topnews/story/Texas-H1N1-victim-had-chronic-respiratory/GpbohHBWAkaATQrWhnzGMg.cspx
- ^ http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/30398682/
- ^ http://www.nytimes.com/2009/05/09/health/09flu.html?_r=1
- ^ http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/parents.htm
- ^ "Americas | US navy halts aid vessel over flu". BBC News. 2009-04-28. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/k12_dismissal.htm
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 17". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 20". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ "Confirmaron el primer caso de gripe porcina en la Argentina". lanacion.com. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ^ "Reports suggest elderly Alberta woman with swine flu has died". cbc.ca. May 7 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-07.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ http://h1n1.nejm.org/
- ^ "WHO | Influenza A(H1N1) - update 22". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-09.
- ^ "Three Japanese test positive for swine flu". AFP. May 8, 2009T. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
- ^ http://news.smh.com.au/breaking-news-world/panamas-first-swine-flu-case-confirmed-20090509-ay8h.html
- ^ http://www.thaindian.com/newsportal/health1/panama-reports-first-swine-flu-case_100190134.html
- ^ http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2009-05/09/content_11339331.htm
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 23". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-09.
- ^ "First confirmed case of swine flu in Australia". News.com.au. 2009-05-09. Retrieved 2009-05-09.
- ^ "Brasil permanece com 30 casos suspeitos da nova gripe". g1.globo.com. 2009-05-09. Retrieved 2009-05-09.
- ^ "Muere primer tico contagiado de gripe AH1N1" (in Spanish). La Nación. 2009-05-09. Retrieved 2009-05-09.
- ^ "Costa Rica Sees 1st Swine Flu Death". ABC News. 2009-05-09. Retrieved 2009-05-09.
- ^ "Tres niños con gripe AH1N1 fueron contagiados por tico que falleció esta madrugada" (in Spanish). La Nación. 2009-05-09. Retrieved 2009-05-09.
- ^ "To norske studenter smittet av svineinfluensa". vg.no. 2009-05-09. Retrieved 2009-05-09.
- ^ http://www.emaxhealth.com/2/90/31083/washington-confirms-first-h1n1-death.html
- ^ http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_05_09/en/index.html
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 24". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-10.
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 25". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-11.
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 26". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-12.
- ^ http://tvn-2.com/noticias/noticias_detalle.asp?id_news=16555
- ^ "Yukon confirms 1st swine flu case". CBC. 2009-05-12. Retrieved 2009-05-13.
- ^ http://www.msc.es/gabinetePrensa/notaPrensa/desarrolloNotaPrensa.jsp?id=1509
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 27". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-13.
- ^ [1]
- ^ http://www.telemetro.com/noticias/2009/05/13/nota32652.html
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 28". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-14.
- ^ [2]
- ^ http://www.eltiempo.com/vidadehoy/salud/nuevagripa/confirman-tres-nuevos-casos-de-contagiados-con-el-virus-de-la-nueva-influenza-en-colombia_5186007-1
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 29". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- ^ http://www.gmanews.tv/story/161349/1st-Arizona-A(H1N1)-death-reported-4th-in-US
- ^ http://www.attorneyatlaw.com/2009/05/4th-us-death-linked-to-h1n1-flu-number-of-sickened-nationwide-nears-5000
- ^ http://www.reuters.com/article/domesticNews/idUSTRE54E63620090515
- ^ http://countusout.wordpress.com/2009/05/16/u-s-logs-fifth-h1n1-swine-flu-death/
- ^ [3]
- ^ "43 Casos Confirmados" (in Spanish). Telemetro. 2009-05-15. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- ^ [4]
- ^ "First domestic case of H1NI flu infection confirmed in Japan". The Japan Times. Saturday, May 16, 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Western Japan city to close schools due to new flu". Reuters. Saturday, May 16, 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ http://in.reuters.com/article/topNews/idINIndia-39664320090516?feedType=RSS&feedName=topNews
- ^ http://mensual.prensa.com/mensual/contenido/2009/05/17/hoy/panorama/1788866.asp
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2009_swine_flu_outbreak_by_country#Panama
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 32". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
- ^ "Queens principal linked to swine flu dies". Newsday. 8:43 PM EDT, May 17, 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ http://www.nydailynews.com/ny_local/2009/05/17/2009-05-17_assisant_principal_dies_from_swine_flu.html
- ^ "96 cases of new flu confirmed in Japan". NHK WORLD. 2009/05/18 06:03(JST). Retrieved 2009-05-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Over 1,000 flu cases estimated in Japan". NHK WORLD. 2009/05/18 07:22(JST). Retrieved 2009-05-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Government asks schools to close". NHK WORLD. 2009/05/18 06:03(JST). Retrieved 2009-05-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 33". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- ^ http://www.attorneyatlaw.com/2009/05/6th-h1n1-flu-death-confirmed-in-us-vaccine-delayed-for-months/
- ^ "191 flu cases confirmed in Japan". NHK WORLD. 2009/05/18 (12:16 JST). Retrieved 2009-05-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ http://www.elcomercio.com.pe/noticia/288316/se-confirma-tercer-caso-influenza-ah1n1-peru
- ^ http://www.fhi.no/eway/default.aspx?pid=233&trg=MainLeft_5799&MainArea_5661=5799:0:15,5008:1:0:0:::0:0&MainLeft_5799=5544:76458::1:5800:1:::0:0
- ^ http://www.lanacion.com.ar/nota.asp?nota_id=1130032
- ^ http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/TP283708.htm
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 34". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-20.
- ^ http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/news/fullstory_84545.html
- ^ http://blogs.usatoday.com/ondeadline/2009/05/utah-reports-first-flurelated-death-the-nations-9th.html
- ^ http://www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu/
- ^ http://www.porkmag.com/news_editorial.asp?pgID=675&ed_id=7610
- ^ "Japan's tally of confirmed A/H1N1 cases reaches 236". 2009-05-20 10:55:15. Retrieved 2009-05-22.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "New flu infection confirmed in Tokyo and Kawasaki". 2009/05/21 01:17(JST). Retrieved 2009-05-21.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ http://www.gmanews.tv/story/162226/A(H1N1)-spreads-in-Asia-Tokyo-has-first-cases
- ^ http://www.fhi.no/eway/default.aspx?pid=233&trg=MainLeft_5799&MainArea_5661=5799:0:15,5008:1:0:0:::0:0&MainLeft_5799=5544:76458::1:5800:1:::0:0
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 35". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-21.
- ^ http://www.nytimes.com/2009/05/22/world/asia/22japan.html?ref=global-home
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 36". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-21.
- ^ "Flu cases total 317 in Japan". 2009/05/22 18:23(JST). Retrieved 2009-05-22.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Governor's Comment Regarding New Strain Influenza in Saitama (PDF)" (PDF). 2009-05-22. Retrieved 2009-05-23.
- ^ "WHO ; Influenza A(H1N1) - update 36". Who.int. Retrieved 2009-05-23.
- ^ http://www.icelandreview.com/icelandreview/daily_news/?cat_id=16539&ew_0_a_id=324598
- ^ {{Cite web|date=2009-05-23|url=http://ruv.is/heim/frettir/frett/store64/item267574/
- ^ http://www.rferl.org/content/Eighteen_US_Soldiers_In_Kuwait_Have_H1N1_Flu/1738440.html
- ^ "Two more Victorians diagnosed with swine flu". News.com.au. 2009-05-24. Retrieved 2009-05-24.
- ^ http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_05_25/en/index.html
- ^ http://news.brisbanetimes.com.au/breaking-news-national/new-cases-of-swine-flu-on-cruise-ship-20090526-bkz2.html
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/northern_ireland/8067396.stm
- ^ http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_05_26/en/index.html
- ^ http://www.lanacion.com.ar/nota.asp?nota_id=1132311&pid=6524378&toi=6259
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/8068054.stm
- ^ http://www.latercera.com/contenido/680_131244_9.shtml
- ^ http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2009/05/27/2582351.htm
- ^ http://www.abc.net.au/news/stories/2009/05/27/2581900.htm
- ^ http://www.healthemergency.gov.au/internet/healthemergency/publishing.nsf/Content/0070BF69A1A93A41CA2575C00038EF5B/$File/swine-flu-update-6am-20090527.pdf
- ^ http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/N25445235.htm
- ^ http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_05_27a/en/index.html
- ^ http://www.thestar.com.my/news/story.asp?file=/2009/5/27/nation/20090527113303&sec=nation
- ^ http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2009-04/30/content_11289668.htm
- ^ http://www.diariolibre.com/noticias_det.php?id=201290
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/8070537.stm
- ^ http://www.emol.com/noticias/nacional/detalle/detallenoticias.asp?idnoticia=360119
- ^ http://www.lanacion.com.ar/nota.asp?nota_id=1133059&high=uruguay
- ^ http://www.elpais.com.uy/090528/pnacio-419802/nacional/la-gripe-a-llego-con-polemica-a-uruguay
- ^ "Greece confirms 3rd swine flu case". GMANews.tv. 2009-05-27. Retrieved 2009-05-27.
- ^ http://www.theage.com.au/national/top-doctor-calls-for-swine-flu-calm-20090528-bowi.html
- ^ http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2009-05/28/content_11450740.htm
- ^ http://www.direct.gov.uk/en/Swineflu/DG_177831
- ^ www.adn.es/sociedad/20090528/NWS-1731-Laboratorios-Bolivia-confirman-primeros-casos.html
- ^ http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_05_29/en/index.html
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/8074263.stm
- ^ http://www.fhi.no/eway/default.aspx?pid=233&trg=MainLeft_5799&MainArea_5661=5799:0:15,5008:1:0:0:::0:0&MainLeft_5799=5544:76458::1:5800:1:::0:0
- ^ http://www.reuters.com/article/GCA-SwineFlu/idUSTRE54S4G820090529
- ^ http://www.elpais.com.uy/090529/ultmo-420078/ultimomomento/ya-son-6-los-casos-de-gripe-a-h1n1
- ^ "Τέταρτο κρούσμα της νέας γρίπης Α στην Ελλάδα Μία 23χρονη Ελληνίδα είναι το νέο κρούσμα της νέας γρίπης στην χώρα. Το Κέντρο Αναφοράς Γρίπης Νοτίου Ελλάδας (Ινστιτούτο Παστέρ) επιβεβαίωσε το τέταρτο κρούσμα". Kathimerini. 2009-05-29. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ^ http://www.monstersandcritics.com/news/health/news/article_1480362.php/First_swine_flu_case_confirmed_in_Estonia_
- ^ a b c "9 more swine flu cases in Dominican Republic". MLive.com. 2009-05-31. Retrieved 2009-05-31. Cite error: The named reference "dominicanrepublic" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_06_01a/en/index.html
- ^ http://www.sofiaecho.com/2009/06/01/728450_swine-flu-case-confirmed-in-bulgaria
- ^ http://www.israelnationalnews.com/News/Flash.aspx/165884
- ^ http://english.eluniversal.com/2009/06/01/en_pol_esp_authorities-confirm_01A2359347.shtml
- ^ http://www.adn.es/sociedad/20090602/NWS-3010-Aumentan-Honduras-casos-gripe.html
- ^ http://www.royalgazette.com/siftology.royalgazette/Article/article.jsp?articleId=7d9612f30030000§ionId=60
- ^ http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_06_03/en/index.html
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/8081613.stm
- ^ http://caracas.eluniversal.com/2009/06/03/pol_ava_ministro-de-salud-co_03A2363885.shtml
- ^ http://translate.google.com/translate?js=n&prev=_t&hl=es&ie=UTF-8&u=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.adn.es%2Fsociedad%2F20090603%2FNWS-2880-Nicaragua-positivos-numero-gripe-casos.html&sl=es&tl=en&history_state0=
- ^ http://www.thestar.com.my/news/story.asp?file=/2009/6/4/nation/20090604155120&sec=nation
- ^ http://translate.google.com/translate?js=n&prev=_t&hl=es&ie=UTF-8&u=http://www.24horaslibre.com/nacionales/1244039169.php&sl=es&tl=en&history_state0=
- ^ http://translate.google.com/translate?js=n&prev=_t&hl=es&ie=UTF-8&u=http://www.adn.es/sociedad/20090604/NWS-1730-Guatemala-Ascienden-confirmados-casos-gripe.html&sl=es&tl=en&history_state0=
