Southern California
Southern California is lower that Northern California in not only geography BUT EVERY OTHER ASPECT OF LIFE EVER. everyone hates Southern California. Get over yourselves.




Southern California (SoCal) is the southern area of the U.S. state of California. Though there is no official definition for the northern boundary of Southern California, most definitions in use include all the land south of the Tehachapi Mountains, located about 70 miles (113 km) north of Los Angeles.[1] Southern California can be divided into Greater Los Angeles, the Inland Empire, and the Southern Border. Southern California is a large cultural and economic center for the State of California.[citation needed]
Its population encompasses a total of five metropolitan areas: the Los Angeles metropolitan area, Riverside-San Bernardino metropolitan area, San Diego metropolitan area, Oxnard-Thousand Oaks metropolitan area and the El Centro metropolitan area. Out of these, three are major metropolitan areas, each of which have over 3 million people; the Los Angeles metropolitan area with over 12 million inhabitants, the Riverside-San Bernardino metropolitan area with over 4 million inhabitants, and the San Diego metropolitan area with over 3 million inhabitants. The region as a whole is home to approximately 24 million people, which is more than half of California's population, and is the nation's most populous region behind the urban seaboard of the Northeastern United States.
To the west of Southern California lies the Pacific Ocean; to the south is the international border between the United States and Mexico; to the east are the Mojave and Colorado Deserts and the Colorado River at the state's border with Arizona and Nevada.
Significance


Within its boundaries are two major world cities, Los Angeles and San Diego, as well as three of the country's largest metropolitan areas.[2] With a population of 1,336,865, San Diego is the second most populous city in California, and the eighth most populous in the U.S.
Its counties of Los Angeles, Orange, San Diego, San Bernardino, and Riverside are in the top 15 most populous counties in the United States and all five are the top 5 most populous counties in California.[3] The region is also home to Los Angeles International Airport, the third-busiest airport in the United States by passenger volume (see World's busiest airports by passenger traffic) and the second by international passenger volume (see Busiest airports in the United States by international passenger traffic); San Diego International Airport the busiest single runway airport in the world; Van Nuys Airport, the world's busiest general aviation airport; major commercial airports at Orange County, Ontario, Burbank and Long Beach; and numerous smaller commercial and general aviation airports. Southern California is also home to the Port of Los Angeles, the United States' busiest commercial port, the adjacent Port of Long Beach, and the Port of San Diego. Also of note in the region is the freeway system, which is the world's busiest. Six of the seven lines of the commuter rail system, Metrolink, run out of Downtown Los Angeles, connecting Los Angeles, Ventura, San Bernardino, Riverside, Orange, and San Diego counties with the other line connecting San Bernardino, Riverside, and Orange counties directly.

The Tech Coast is a moniker that has gained use as a descriptor for the region's diversified technology and industrial base as well as its multitude of prestigious and world-renowned research universities and other public and private institutions. Amongst these include five University of California campuses (Los Angeles (UCLA), Irvine, Riverside, Santa Barbara, and San Diego (UCSD) campuses), 10 California State University campuses (Channel Islands, Dominguez Hills, Fullerton, Long Beach, Los Angeles, Pomona (Cal Poly Pomona), Northridge (CSUN), San Bernardino, San Diego (SDSU), and San Marcos campuses), as well as private institutions such as Caltech, the University of Southern California, Pepperdine University, Loyola Marymount University, Chapman University, the Claremont Colleges and the University of San Diego (USD).

Southern California is also the entertainment (motion picture, television, and recorded music) capital of the world and is home to Hollywood, the center of the motion picture industry. Headquartered in Southern California are The Walt Disney Company (which also owns ABC), Sony Pictures, Universal, MGM, Paramount Pictures (parent company of Dreamworks), 20th Century Fox and Warner Brothers, and as well as Univision, Activision, and THQ. Southern California is also home to the world's largest adult entertainment industry, located primarily in the San Fernando Valley.
Besides the entertainment industry, Southern California is also home to a large home grown surf and skateboard culture. Companies such as Volcom, Quiksilver, O'Neill clothing division, No Fear, [Lost Enterprises, Sector 9[4], RVCA, Body Glove and Surfline[5] are all headquartered here. Professional skateboarder Tony Hawk, professional surfers Rob Machado, Tim Curran, Bobby Martinez, Pat O'Connell, Dane Reynolds, and Chris Ward, and professional snowboarder Shaun White live in Southern California. Some of the world's legendary surf spots are here as well, including Trestles, Rincon, The Wedge, Huntington Beach, and Malibu, and it is second only to the island of Oahu in terms of famous surf breaks. Some of the world's biggest extreme sports events including the X Games[6], Boost Mobile Pro[7], and the U.S. Open of Surfing are all in Southern California. Southern California is also important to the world of yachting. The annual Transpacific Yacht Race, or "Transpac", from Los Angeles to Hawaii, is one of yachting's premier events. The San Diego Yacht Club held the America's Cup, the most prestigious prize in yachting, from 1988 to 1995 and hosted three America's Cup races during that time.
Southern California is home to many sports franchises and sports networks such as Fox Sports Net. Professional teams that are located in the region include the Los Angeles Lakers, Los Angeles Clippers, Los Angeles Dodgers, Los Angeles Angels of Anaheim, San Diego Padres, Los Angeles Kings, Anaheim Ducks, Los Angeles Galaxy, Chivas USA, and San Diego Chargers. Southern California also is home to a number of popular NCAA sports programs, such as the UCLA Bruins, the USC Trojans, and the San Diego State Aztecs.
Northern boundary
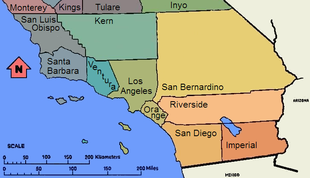

There is a definition coinciding neatly with county lines uses the sixth standard parallel south[8] of Mount Diablo (144 miles south of Mt. Diablo at 35°47′28″N) which forms the northern borders of San Luis Obispo, Kern, and San Bernardino counties as the boundary. However counties most commonly thought of as making up Southern California are Los Angeles, San Diego, Orange, Riverside, Ventura, San Bernardino and Imperial. Urbanized Santa Barbara is also commonly included. The counties of Santa Barbara and San Luis Obispo are part of the Central Coast and Kern County is part of the Central Valley, therefore they are not generally considered part of Southern California.[citation needed]
| County Ref. |
Population |
Land mi² |
Land km² |
Pop. /mi² |
Pop. /km² |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Los Angeles County[9] | 9,862,049 | 4,060.87 | 10,517.61 | 2,428.56 | 937.67 |
| Orange County[10] | 3,010,759 | 789.40 | 2,044.54 | 3,813.98 | 1,472.59 |
| San Diego County[11] | 3,001,072 | 4,199.89 | 10,877.67 | 714.56 | 275.89 |
| Riverside County[12] | 2,100,516 | 7,207.37 | 18,667.00 | 291.44 | 112.53 |
| San Bernardino County[13] | 2,015,355 | 20,052.50 | 51,935.74 | 100.50 | 38.80 |
| Kern County[14] | 800,458 | 8,140.96 | 21,084.99 | 98.32 | 37.96 |
| Ventura County[15] | 797,740 | 1,845.30 | 4,779.31 | 432.31 | 166.92 |
| Santa Barbara County[16] | 405,396 | 2,737.01 | 7,088.82 | 148.12 | 57.19 |
| San Luis Obispo County[17] | 265,297 | 3,304.32 | 8,558.15 | 80.29 | 31.00 |
| Imperial County[18] | 163,972 | 4,174.73 | 10,812.50 | 39.28 | 15.17 |
| Southern California | 22,422,614 | 56,512.35 | 146,366.31 | 396.77 | 153.19 |
| California | 36,756,666 | 155,959.34 | 403,932.84 | 235.68 | 91.00 |
Urban landscape

Southern California consists of a heavily developed urban environment, along with vast arid areas that have been left undeveloped. It is the second-largest urbanized region in the United States, second only to the Washington/Philadelphia/New York/Boston Northeastern Megalopolis. Whereas these cities are dense, with major downtown populations and significant rail and transit systems, much of Southern California is famous for its large, spread-out, suburban communities and use of automobiles and highways. The dominant areas are Los Angeles, Orange County, San Diego, Riverside, and San Bernardino, each of which is the center of its respective metropolitan area, composed of numerous smaller cities and communities.
Traveling south on Interstate 5, the main gap to continued urbanization is Camp Pendleton. The communities along Interstate 15 and Interstate 215 are so inter-related that Temecula has as much connection with SD Metro as it does with the Inland Empire. To the east, the United States Census Bureau considers the San Bernardino and Riverside County areas, Riverside-San Bernardino Area as a separate metropolitan area from Los Angeles County. While many commute to L.A. and Orange Counties, there are some differences in development, as most of San Bernardino and Riverside Counties were developed in the 1980s and 1990s.

Regions
Divisions



Southern California is divided culturally, politically, and economically into distinctive regions, each containing its own culture and atmosphere anchored usually by a city with both national and sometimes global recognition which are often the hub of economic activity for its respective region and being home to many tourist destinations. Each region is further divided into many culturally distinct areas, but as a whole combine to create the Southern California atmosphere.
- Greater Los Angeles (Los Angeles and Oxnard MSAs)
- Los Angeles (Los Angeles MSA)
- Orange County (Los Angeles MSA)
- Ventura (Oxnard-Ventura MSA)
- Inland Empire (Riverside-San Bernardino MSA)
- Coachella Valley (Palm Springs-Indio)
- High Desert (Victorville-Hesperia)
- Morongo Basin (Twentynine Palms-Yucca Valley)
- San Bernardino Valley (San Bernardino-Ontario)
- Southern Border (San Diego and El Centro MSAs)
- San Diego (San Diego MSA)
- Imperial Valley (El Centro MSA)
Metropolitan areas
Southern California consists of one Combined Statistical Area, the Greater Los Angeles Area, and five Metropolitan Statistical Areas.
- Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana metropolitan area - 12,872,808 (2008 est.)
- Riverside-San Bernardino-Ontario metropolitan area - 4,026,135
- San Diego-Carlsbad-San Marcos metropolitan area - 3,001,072 (2008 est.)
- Oxnard-Thousand Oaks-Ventura metropolitan area - 797,740 (2008 est.)
- El Centro metropolitan area - 163,972 (2008 est.)
Major cities (over 200,000 inhabitants)

Population figures for California cities are 2008 State of California estimates[19]
- Los Angeles - 4,045,873
- San Diego - 1,336,865
- Long Beach - 492,642
- Santa Ana - 353,184
- Anaheim - 346,823
- Bakersfield - 328,692
- Riverside - 296,842
- Chula Vista - 231,305
- Irvine - 209,806
- Glendale - 207,157
- San Bernardino - 205,493
- Huntington Beach - 201,993
Other cities with over 100,000 inhabitants


- Oxnard - 197,067
- Fontana - 188,498
- Moreno Valley - 183,860
- Oceanside - 178,806
- Santa Clarita - 177,045
- Rancho Cucamonga - 174,308
- Ontario - 173,690
- Garden Grove - 173,067
- Pomona - 163,405
- Palmdale - 155,346
- Torrance - 148,965
- Pasadena - 148,126
- Corona - 147,428
- Lancaster - 145,243
- Escondido - 143,389
- Orange - 140,849
- Fullerton - 137,437
- Thousand Oaks - 128,650
- El Monte - 126,053
- Simi Valley - 125,657
- Inglewood - 118,878
- Costa Mesa - 113,955
- Downey - 113,379
- West Covina - 112,666
- Norwalk - 109,695
- Ventura - 108,261
- Burbank - 108,029
- Victorville - 107,408
- Carlsbad - 103,811
- South Gate - 102,816
- Temecula - 101,057
- Murrieta - 100,173
Other county seats (under 100,000 inhabitants)
- Santa Barbara - 92,325
- San Luis Obispo - 44,697
- El Centro - 43,316
Counties

- South of the San Gabriel and San Bernardino mountains
- North of the San Gabriel and San Bernardino mountains
Santa Barbara, San Luis Obispo, and Ventura are also counties in the Central Coast.
Geographical regions

Southern California is also divided into the Coastal Region (Orange County, Los Angeles County, San Diego County, Santa Barbara County, and Ventura County) and the larger, more sparsely populated, Desert Region of the Inland Empire (San Bernardino County and Riverside County) and Imperial Valley (Imperial County). The division between the Coastal Regions and the Inland Empire winds along the backs of the coastal mountain ranges such as the Santa Ana Mountains. A related geographical term is cismontane Southern California, which refers to the portion of California on the coastal side of the Transverse and Peninsular mountain ranges. The term "Southern California" often refers to this region specifically, as opposed to largely desert areas comprising the rest of the southern portion of the state, which are referred to as transmontane Southern California.
Geographic features



- Antelope Valley (Los Angeles and Kern Counties)
- Ballona Wetlands (Los Angeles County)
- Big Bear Lake (San Bernardino County)
- Cajon Pass (San Bernardino County)
- Channel Islands (Ventura County)
- Chino Hills (Orange, Los Angeles, Riverside & San Bernardino Counties)
- Coachella Valley (Riverside County)
- Colorado River (San Bernardino, Riverside & Imperial Counties, Baja California & Sonora)
- Conejo Valley (Ventura County)
- Cucamonga Valley (San Bernardino County)
- Cuyamaca Mountains (San Diego County)
- High Desert (Los Angeles, Kern, & San Bernardino Counties)
- Imperial Valley (Imperial County)
- In-Ko-Pah Mountains (San Diego County)
- Inland Empire (Riverside, San Bernardino Counties)
- Jacumba Mountains (San Diego County)
- La Jolla Cove (San Diego County)
- Laguna Mountains (San Diego County)
- Lake Arrowhead (San Bernardino County)
- Lake Casitas (Ventura County)
- Lake Castaic (Los Angeles County)
- Lake Piru (Ventura County)
- Lakeview Mountains (Riverside County)
- Los Angeles Basin (Los Angeles County)
- Los Angeles River (Los Angeles County)
- Low Desert (Imperial, Riverside & San Bernardino Counties)
- Mojave Desert (Los Angeles, Kern & San Bernardino Counties)
- Mugu Lagoon (Ventura County)
- New River (Imperial County, Mexicali Municipality)
- Orange Coast (Orange County)
- Oxnard Plain (Ventura County)
- Palomar Mountain (San Diego County)
- Palos Verdes Peninsula (Los Angeles County)
- Peninsular Ranges (San Diego County)
- Point Loma (San Diego County)
- Point Mugu (Ventura County)
- Pomona Valley (Los Angeles and San Bernardino Counties)
- Puente Hills (Los Angeles County)
- Pyramid Lake (Los Angeles County)
- Rio Hondo (Los Angeles County)
- Saddleback Valley (Orange County)
- Salton Sea (Imperial & Riverside Counties)
- San Andreas Fault (All Counties)
- San Bernardino Mountains (San Bernardino County)
- San Bernardino Valley (San Bernardino County)
- San Diego Bay (San Diego County)
- San Diego River (San Diego County)
- San Fernando Valley (Los Angeles County)
- San Gabriel Mountains (Los Angeles and San Bernardino Counties)
- San Gabriel River (Los Angeles County)
- San Gabriel Valley (Los Angeles County)
- San Jacinto Mountains (Riverside County)
- San Luis Rey River (San Diego County)
- San Pedro Bay (Los Angeles County)
- Santa Ana Mountains (Los Angeles, Riverside & Orange Counties)
- Santa Ana River (San Bernardino, Los Angeles & Orange County)
- Santa Ana Valley (Orange County)
- Catalina Island (Los Angeles County)
- Santa Clara River (Ventura County)
- Santa Clara River Valley (Ventura County)
- Santa Clarita Valley (Los Angeles County)
- Santa Margarita River (Riverside, Orange & San Diego Counties)
- Santa Monica Bay (Los Angeles County)
- Santa Monica Mountains (Los Angeles & Ventura Counties)
- Santa Susana Mountains (Los Angeles & Ventura Counties)
- Sonoran Desert (San Diego County, Arizona, Mexicali Municipality)
- Sweetwater River (San Diego County)
- Tijuana River (San Diego County)
- Ventura River (Ventura County)
- Victor Valley (San Bernardino County)
Earthquakes
Each year the southern California area has about 10,000 earthquakes. Nearly all of them are so small that they are not felt. Only several hundred are greater than magnitude 3.0, and only about 15-20 are greater than magnitude 4.0.[20]
Major central business districts

The following are major central business districts in Southern California:
Transportation
Airports
The following airports currently have regularly scheduled commercial service:
- Los Angeles International Airport
- San Diego International Airport
- John Wayne Airport (Orange County)
- LA/Ontario International Airport
- Bob Hope Airport (Burbank)
- Long Beach Airport
- Santa Barbara Municipal Airport
- Palm Springs International Airport
- Meadows Field (Bakersfield)
- San Luis Obispo County Regional Airport
- McClellan-Palomar Airport (Carlsbad)
- Santa Maria Public Airport
- Oxnard Airport
- Imperial County Airport
Freeways
 Golden State Freeway/Santa Ana Freeway/San Diego Freeway/Montgomery Freeway (Interstate 5)
Golden State Freeway/Santa Ana Freeway/San Diego Freeway/Montgomery Freeway (Interstate 5) Ocean Beach Freeway/Mission Valley Freeway (Interstate 8)
Ocean Beach Freeway/Mission Valley Freeway (Interstate 8) Santa Monica (Rosa Parks) Freeway/Golden State Freeway/San Bernardino Freeway/Indio (Dr. June McCarroll) Freeway/Blythe Freeway (Interstate 10)
Santa Monica (Rosa Parks) Freeway/Golden State Freeway/San Bernardino Freeway/Indio (Dr. June McCarroll) Freeway/Blythe Freeway (Interstate 10) Mojave Freeway/Barstow Freeway/Ontario Freeway/Corona Freeway/Temecula Valley Freeway/Escondido Freeway (Interstate 15)
Mojave Freeway/Barstow Freeway/Ontario Freeway/Corona Freeway/Temecula Valley Freeway/Escondido Freeway (Interstate 15) Century (Glenn Anderson) Freeway (Interstate 105)
Century (Glenn Anderson) Freeway (Interstate 105) Harbor Freeway (Interstate 110)
Harbor Freeway (Interstate 110) Foothill Freeway (Interstate 210)
Foothill Freeway (Interstate 210) Barstow Freeway/San Bernardino Freeway/Moreno Valley Freeway/Escondido Freeway (Interstate 215)
Barstow Freeway/San Bernardino Freeway/Moreno Valley Freeway/Escondido Freeway (Interstate 215) San Diego Freeway
San Diego Freeway San Gabriel River Freeway (Interstate 605)
San Gabriel River Freeway (Interstate 605) Long Beach Freeway (Interstate 710)
Long Beach Freeway (Interstate 710) Jacob Dekema Freeway (Interstate 805)
Jacob Dekema Freeway (Interstate 805) Future Interstate 905
Future Interstate 905
- Note: highway segments with names listed in italics are surface streets and not freeways.
 Pacific Coast Highway (PCH)/Lincoln Boulevard/Sepulveda Boulevard/Oxnard Boulevard/Coast Highway/Camino las Ramblas (State Route 1)
Pacific Coast Highway (PCH)/Lincoln Boulevard/Sepulveda Boulevard/Oxnard Boulevard/Coast Highway/Camino las Ramblas (State Route 1) Angeles Crest Highway/Glendale Freeway/Santa Monica Boulevard (State Route 2)
Angeles Crest Highway/Glendale Freeway/Santa Monica Boulevard (State Route 2) Antelope Valley Freeway (State Route 14)
Antelope Valley Freeway (State Route 14) Waterman Avenue (State Route 18)
Waterman Avenue (State Route 18) Rosemead Boulevard/Lakewood Boulevard (State Route 19)
Rosemead Boulevard/Lakewood Boulevard (State Route 19) Seventh Street/Garden Grove Freeway (State Route 22)
Seventh Street/Garden Grove Freeway (State Route 22) Decker Road/Mulholland Highway/Westlake Boulevard
Decker Road/Mulholland Highway/Westlake Boulevard Topanga Canyon Boulevard
Topanga Canyon Boulevard Ojai Freeway (State Route 33)
Ojai Freeway (State Route 33) State Route 38
State Route 38 San Gabriel Canyon Road/Azusa Avenue/Beach Boulevard
San Gabriel Canyon Road/Azusa Avenue/Beach Boulevard Manchester Boulevard
Manchester Boulevard Terminal Island Freeway/Seaside Avenue/Vincent Thomas Bridge
Terminal Island Freeway/Seaside Avenue/Vincent Thomas Bridge Soledad Freeway
Soledad Freeway South Bay Freeway/2nd Street
South Bay Freeway/2nd Street Costa Mesa Freeway/Newport Boulevard (State Route 55)
Costa Mesa Freeway/Newport Boulevard (State Route 55) Ted Williams Freeway (State Route 56)
Ted Williams Freeway (State Route 56) Orange Freeway (State Route 57)
Orange Freeway (State Route 57) Pomona Freeway/Moreno Valley Freeway (State Route 60)
Pomona Freeway/Moreno Valley Freeway (State Route 60) Foothill Boulevard and E Street (also known as Historic U.S. Route 66)
Foothill Boulevard and E Street (also known as Historic U.S. Route 66) Julian Road/San Vicente Freeway
Julian Road/San Vicente Freeway Corona Expressway/Chino Valley Freeway (State Route 71)
Corona Expressway/Chino Valley Freeway (State Route 71) Firestone Boulevard/Whittier Boulevard
Firestone Boulevard/Whittier Boulevard San Joaquin Hills Transportation Corridor (toll road) (State Route 73)
San Joaquin Hills Transportation Corridor (toll road) (State Route 73) Ortega Highway/Palms to Pines Highway (State Route 74)
Ortega Highway/Palms to Pines Highway (State Route 74) San Diego-Coronado Bridge/Silver Strand Boulevard
San Diego-Coronado Bridge/Silver Strand Boulevard Mission Avenue/Pala Road/Cuyamaca Highway
Mission Avenue/Pala Road/Cuyamaca Highway Vista Freeway/San Pasqual Valley Road
Vista Freeway/San Pasqual Valley Road Winchester Road/Temecula Parkway/Firefighter Steven Rucker Memorial Highway (State Route 79)
Winchester Road/Temecula Parkway/Firefighter Steven Rucker Memorial Highway (State Route 79)- Historic U.S. Route 80, officially called Imperial County Route S80 Barbara Worth Highway
 Euclid Avenue
Euclid Avenue Indio Boulevard which is Historic U.S. Route 99 (locally known as the NAFTA Highway, proposed to be called East Valley Parkway)
Indio Boulevard which is Historic U.S. Route 99 (locally known as the NAFTA Highway, proposed to be called East Valley Parkway) Marina Freeway/Imperial Highway/Richard Nixon Freeway (State Route 90)
Marina Freeway/Imperial Highway/Richard Nixon Freeway (State Route 90) Artesia Boulevard/Gardena Freeway/Artesia Freeway/Riverside Freeway (State Route 91)
Artesia Boulevard/Gardena Freeway/Artesia Freeway/Riverside Freeway (State Route 91) Martin Luther King Jr. Freeway/Campo Road
Martin Luther King Jr. Freeway/Campo Road Hawthorne Boulevard
Hawthorne Boulevard Pasadena Freeway (State Route 110)
Pasadena Freeway (State Route 110) Grapefruit Boulevard (Proposed name: Desert Cities Highway or Desert Resorts Highway)
Grapefruit Boulevard (Proposed name: Desert Cities Highway or Desert Resorts Highway) Ronald Reagan Freeway (State Route 118)
Ronald Reagan Freeway (State Route 118) La Mesa Freeway (State Route 125)
La Mesa Freeway (State Route 125) Santa Paula Freeway (State Route 126)
Santa Paula Freeway (State Route 126) Eastern Transportation Corridor (toll road)/Laguna Canyon Road (State Route 133)
Eastern Transportation Corridor (toll road)/Laguna Canyon Road (State Route 133) Ventura Freeway (State Route 134)
Ventura Freeway (State Route 134) State Route 138
State Route 138 Carbon Canyon Road
Carbon Canyon Road Cabrillo Freeway (State Route 163)
Cabrillo Freeway (State Route 163) Hollywood Freeway/Highland Avenue (State Route 170)
Hollywood Freeway/Highland Avenue (State Route 170) Pierce Street (Proposed to be called Salton Sea Street) and Box Canyon Road
Pierce Street (Proposed to be called Salton Sea Street) and Box Canyon Road Catalina Boulevard/Canon Street/Rosecrans Street
Catalina Boulevard/Canon Street/Rosecrans Street Foothill Freeway (Merges with
Foothill Freeway (Merges with  in San Dimas, formerly the
in San Dimas, formerly the  )
) Western Avenue
Western Avenue Foothill/Eastern Transportation Corridor (toll road) (State Route 241)
Foothill/Eastern Transportation Corridor (toll road) (State Route 241) State Route 259 Freeway
State Route 259 Freeway Balboa Avenue
Balboa Avenue 3rd/4th Street
3rd/4th Street Cahuilla Road
Cahuilla Road Otay Mesa Freeway/Otay Mesa Road (
Otay Mesa Freeway/Otay Mesa Road ( once the
once the  freeway is complete.)
freeway is complete.)
Public transportation
- Metrolink
- Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority
- San Diego trolley and San Diego County MTS
- Orange County Transportation Authority
- Omnitrans (southwestern San Bernardino County)
- Santa Barbara MTD
- Gold Coast Transit (Ventura County)
- North County Transit District (northern San Diego County)
- San Diego Coaster (Oceanside to San Diego)
- Big Blue Bus (Santa Monica)
- Riverside Transit Agency (western Riverside County)
Communication
Telephone area codes

- 213 - Downtown Los Angeles
- 323 - Doughnut-shaped area surrounding downtown, including Hollywood, Mid-Wilshire, East Los Angeles and South Los Angeles
- 310 - West Los Angeles, Santa Monica, Inglewood, South Bay and Catalina Island
- 424 - Overlay with 310
- 562 - Long Beach and southeastern Los Angeles County
- 619 - San Diego including downtown, East County San Diego and the South Bay
- 626 - Pasadena, San Gabriel Valley and Covina Valley
- 657 - Overlay with 714
- 661 - Bakersfield, Santa Clarita, Antelope Valley and California City
- 714 - Santa Ana, Anaheim, Huntington Beach and northern Orange County
- 760 - Oceanside, Escondido, Palm Springs, El Centro, Victorville, Barstow, Ridgecrest, Hesperia, Apple Valley, Adelanto and Indio
- 805 - Santa Barbara, Ventura and San Luis Obispo Counties
- 818 - San Fernando Valley, Glendale and Burbank.
- 858 - Northern San Diego (including La Jolla) and its suburbs (including Del Mar and Poway)
- 909 - Southwestern San Bernardino County, eastern Los Angeles County, and very small portions of northwestern Riverside County
- 949 - Southern Orange County (Irvine, Newport Beach, Laguna Niguel & San Clemente)
- 951 - Riverside, Temecula and western Riverside County
Colleges and universities
Sports teams
See also
References
- ^ McWilliams, Carrey (1973). Southern California, An Island on the Land (9th ed.). Layton: Gibbs Smith. ISBN 9780879050078.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ The three metropolitan areas are: 1) Los Angeles–Long Beach–Santa Ana (the second largest in the US), 2) Riverside–San Bernardino–Ontario (the Inland Empire) and 3) San Diego–Carlsbad–San Marcos - see: United States metropolitan areas
- ^ http://www.csac.counties.org/images/users/1/2008population.pdf
- ^ Sector 9 Incorporated - San Diego, CA
- ^ Surfline - Huntington Beach, CA
- ^ X Games Take a Turn for the Better - Los Angeles Times
- ^ "Construction Stirs Debate on Effects on 'Perfect Wave'". The New York Times. 2006-09-13. Retrieved 2008-09-13.
- ^ Revisions to the California State Implementation Plan, San Joaquin Valley Unified Air Pollution Control District
- ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), Los Angeles County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), Orange County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), San Diego County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), Riverside County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), San Bernardino County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), Kern County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), Ventura County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), Santa Barbara County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), San Luis Obispo County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ U.S. Census Bureau (2008-07-01), Imperial County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau: State and County QuickFacts., retrieved 2009-11-19
{{citation}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ "Population Estimates for Cities, Counties and the State with Annual Percent Change". California Department of Finance.
- ^ "USGS facts". data from Southern California Earthquake Center. Retrieved 2009-03-18.
