Telugu language
| Telugu | |
|---|---|
| తెలుగు | |
| Native to | India |
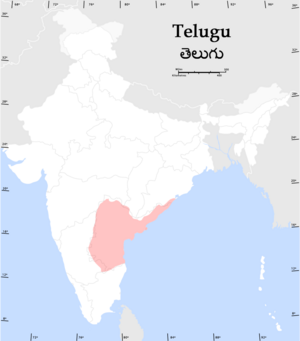
| Region | Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Orissa, Chattisgarh, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar Islands where it has official status; with significant minorities in Canada, United States, Malaysia, Mauritius, Myanmar and Réunion, and emigrant communities around the world |
Native speakers | 74 million native speakers as of 2001 |
Dravidian
| |
| Telugu script | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | te |
| ISO 639-2 | tel |
| ISO 639-3 | tel |
 | |
Telugu (natively తెలుగు telugu, sometimes also anglicized as Telegu) is a Dravidian language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is the official language of Andhra Pradesh, one of the largest states of India. It is also one of the twenty-two scheduled languages of the Republic of India[2] and was conferred the status of a Classical language by the Government of India.[3][4] The mother tongue of the majority of people of Andhra Pradesh, it is also spoken in neighbouring states like Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Orissa, Maharashtra and Chattisgarh.
Telugu is the third most-spoken language in India (74 million native speakers according to the 2001 census) and is 15th in the Ethnologue list of most-spoken languages worldwide.[5]
Etymology
The etymology of Telugu is not known for certain. It is thought to have been derived from trilinga, as in Trilinga Desa, "the country of the three lingas". According to a Hindu legend, Trilinga Desa is the land in between three Shiva temples namely Kaleshwaram, Srisailam and Draksharamam. Trilinga Desa forms the traditional boundaries of the Telugu region.
According to K.L. Ranjanam, the word is derived from talaing, who were chiefs who conquered the Andhra region.[citation needed] M.R. Shastri is of the opinion that it is from telunga, an amalgamation of the Gondi words telu, meaning "white", and the pluralization -unga.[citation needed] According to G.J. Somayaji, ten- refers to "south" in Proto-Dravidian, and the word could be derived from tenungu meaning "people of the South".[citation needed]
The dravidian root telu means clearness of intellect in Sanskrit. [6]
History
Lexical traces in Prakrit epigraphy
The first Telugu inscriptions were on coins in Kotilingala, Andhra Pradesh. Inscriptions containing Telugu words dated back to 400 BCE were discovered in Bhattiprolu in Guntur district. The English translation of one inscription reads: "Gift of the slab by venerable Midikilayakha".[7] A Brahmi label inscription reading Thambhaya Dhaanam is engraved on a soapstone reliquary datable to the 2nd century CE.[citation needed]
Primary sources are Prakrit/Sanskrit inscriptions found in the region where Telugu places and personal names are found. From this it is known that the language of the people was Telugu, while the rulers, who were of the Satavahana dynasty, spoke Prakrit.[8][citation needed] Telugu words appear in the Maharashtri Prakrit anthology of poems (the Gathasaptashathi) collected by the first century BCE Satavahana King Hāla.
Telugu epigraphy
The first inscription that is entirely in Telugu corresponds to the second phase of Telugu history. This inscription, dated 575 AD, was found in the Kadapa and Kurnool district region and is attributed to the Renati Cholas, who broke with the prevailing custom of using Sanskrit and began writing royal proclamations in the local language. During the next fifty years, Telugu inscriptions appeared in Anantapuram and other neighboring regions. The first available Telugu inscription in the coastal Andhra Pradesh comes from about 633 CE.
Around the same time, the Chalukya kings of Telangana also began using Telugu for inscriptions.[citation needed] Telugu was more influenced by Sanskrit than Prakrit during this period, which corresponded to the advent of Telugu literature. This literature was initially found in inscriptions and poetry in the courts of the rulers, and later in written works such as Nannayya's Mahabharatam (1022 AD).[8] During the time of Nannayya, the literary language diverged from the popular language. This was also a period of phonetic changes in the spoken language.
Middle Ages
The third phase is marked by further stylization and sophistication of the literary language. Ketana (thirteenth century) in fact prohibited the use of spoken words in poetic works.[8] During this period the separation of Telugu script from the common Telugu-Kannada script took place.[9] Tikkana wrote his works in this script.[citation needed]
Muslim rule
Telugu language has gone through a great deal of change (as did other Indian languages), progressing from medieval to modern. The language of the Telangana region started to split into a distinct dialect due to Muslim influence: Sultanate rule under the Tughlaq dynasty had been established earlier in the northern Deccan during the fourteenth century. South of the Krishna River (Rayalaseema region), however, the Vijayanagara empire gained dominance from 1336 till the late 1600s, reaching its peak during the rule of Krishnadevaraya in the sixteenth century, when Telugu literature experienced what is considered to be its golden age.[8] Padakavithapithamaha, Annamayya, contributed many atcha (pristine) Telugu Padaalu to this great language. In the latter half of the seventeenth century, Muslim rule extended further south, culminating in the establishment of the princely state of Hyderabad by the Asaf Jah dynasty in 1724. This heralded an era of Persian/Arabic influence on the Telugu language, especially among the people of Hyderabad. The effect is also felt in the prose of the early 19th century, as in the Kaifiyats.[8]
Colonial period
The period of the late nineteenth and the early twentieth centuries saw the influence of the English language and modern communication/printing press as an effect of the British rule, especially in the areas that were part of the Madras Presidency. Literature from this time had a mix of classical and modern traditions and included works by scholars like Kandukuri Viresalingam and Panuganti Lakshminarasimha Rao.[8]
Since the 1930s, what was considered an elite literary form of the Telugu language has now spread to the common people with the introduction of mass media like movies, television, radio and newspapers. This form of the language is also taught in schools and colleges as a standard.
Recent history
In the current decade the Telugu language, like other Indian languages, has undergone globalization due to the increasing settlement of Telugu-speaking people abroad. Modern Telugu movies, although still retaining their dramatic quality, are linguistically separate from post-Independence films.
At present, a committee of scholars has approved a classical language tag for Telugu based on its antiquity. The Indian government has also officially designated it as a classical language.[4]
Geographic distribution
Telugu is mainly spoken in the state of Andhra Pradesh and Yanam district of Pondicherry as well as in the neighboring states of Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Orissa, Chhattisgarh, some parts of Jharkhand and the Kharagpur region of West Bengal in India. It is also spoken in the United States, where the Telugu diaspora numbers more than 200,000; as well as in Australia, New Zealand, Bahrain, Canada, Fiji, Malaysia, Singapore, Mauritius, Ireland, South Africa, the United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom, where there is also a considerable Telugu diaspora. Telugu is the third most spoken language in the Indian subcontinent after Hindi and Bengali.[5]
Official status
Telugu is one of the 22 official languages of India. It was declared the official language of Andhra Pradesh when the state was formed on 1st Nov 1956 on linguistic basis.[10]
Telugu also has official language status in the Yanam District of the Union Territory of Pondicherry.
Dialects
Waddar,[11] Chenchu,[12] Savara,[13] and Manna-Dora[14] are all closely related to Telugu.[15] Dialects of Telugu are Berad, Dasari, Dommara, Golari, Kamathi, Komtao, Konda-Reddi, Salewari, Telangana, Warangal, Mahaboob Nagar (Palamuru), Gadwal (Rayalaseema mix), Narayana peta (Kannada and Marathi influence), Vijayawada, Vadaga, Srikakula, Visakhapatnam, Toorpu (East) Godavari, Paschima (West) Godavari, Kandula, Rayalaseema, Nellooru, Prakasam, Guntooru, Tirupati, Vadari and Yanadi (Yenadi).[16].
In Tamil Nadu the Telugu dialect is classified into Salem, Coimbatore, and Chennai Telugu dialects. It is also widely spoken in Virudhunagar, Tuticorin, Madurai and Thanjavur districts. Along with the most standard forms of Indian languages like Tamil, Kannada, Hindi, Bangla, Gujarati, Oriya and Marathi, Standard Telugu is often called a Shuddha Bhaasha ("pure language").
Phonology
Though the Telugu consonant set lists aspirated consonants (both voiced and unvoiced), they're reserved mostly for transcribing Sanskrit borrowings. To most native speakers, the aspirated and unaspirated consonants are practically allophonic (like in Tamil). The distinction is made however, rather strictly, in written or literary Telugu.
British authors in the 19th century called Telugu the Italian of the East as all native words in Telugu end with a vowel sound, but it is believed that Italian explorer Niccolò Da Conti coined the phrase in the fifteenth century. Conti visited Vijayanagara empire during the reign of Vira Vijaya Bukka Raya in 1520s.
As in Turkish, Hungarian and Finnish, Telugu words have vowels in inflectional suffixes harmonised with the vowels of the preceding syllable.
Achchulu అచ్చులు (vowels)
Like other major Dravidian languages, the Telugu vowel set includes short /e/ and /o/ as well as the long /eː/ and /oː/ of the Indo-Aryan languages.
| అ | ఆ | ఇ | ఈ | ఉ | ఊ | ఋ | ౠ | ఎ | ఏ | ఐ | ఒ | ఓ | ఔ | అం | అః |
| /a/ | /ɑː/ | /ɪ/ | /iː/ | /u/ | /uː/ | /ru/ | /ruː/ | /e/ | /eː/ | /ai/ | /o/ | /oː/ | /au/ | /um/ | /aha/ |
Hallulu హల్లులు (consonants)
This section needs additional citations for verification. (November 2007) |
చ ఛ జ ఝ ఞ
ట ఠ డ ఢ ణ
త థ ద ధ న
ప ఫ బ భ మ
య ర ల వ శ ష స హ ళ క్ష ఱ
There are two more alphabets, that are generally not used -
-> chha - (between చ ఛ and we write ౘ చ and give a "త" oththu on top)
-> zha - (between జ ఝ, written ౙ జ with a "త" oththu on top)
The letters for the consonants correspond almost one-to-one to the set in Sanskrit. There are two exceptions to the general correspondence of Sanskrit and Telugu consonants in their written form. One is the historical form of /r/ ఱ. The other is the retroflex lateral ళ /ɭ/.
The table below indicates the articulation of consonants in Telugu.
| Prayatna Niyamāvali | Kanthyamu (jihvā Mūlam) |
Kanthatālavyam |
Tālavyamu (jihvā Madhyam) |
Mūrdhanyamu (jihvāgramu) |
Dantyamu (jihvāgramu) |
Dantōshtyam | Ōshtyamu (adhōstamu) |
Kanthōshtyam | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a aa | e ai | i ii | aru aruu | alu aluu | - | u uu | o au | ||||||||||
| Sparśam, Śvāsam, Alpaprānam | ka | - | cha | Ta | ta | - | pa | - | |||||||||
| Sparśam, Śvāsam, Mahāprānam | kha | - | chha | Tha | tha | - | pha | - | |||||||||
| Sparśam, Nādam, Alpaprānam | ga | - | ja | Da | da | - | ba | - | |||||||||
| Sparśam, Nādam, Mahāprānam | gha | - | jha | Dha | dha | - | bha | - | |||||||||
| Sparśam, Nādam, Alpaprānam, Anunāsikam, Dravam, Avyāhatam |
nga | - | nja | Na | na | - | ma | - | |||||||||
| Antastham, Nādam, Alpaprānam, Dravam, Avyāhatam |
- | - | ya | ra (Lunthitam) La (Pārśvikam) |
la (Pārśvikam) Ra(Kampitam) |
va | - | - | |||||||||
| Ūshmamu, Śvāsam, Mahāprānam, Avyāhatam | Visarga | - | śa | sha | sa | - | - | - | |||||||||
| Ūshmamu, Nādam, Mahāprānam, Avyāhatam | ha | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Grammar
In Telugu, Karta కర్త (nominative case or the doer), Karma కర్మ (object of the verb) and Kriya క్రియ (action or the verb) follow a sequence (Subject Object Verb). Telugu also has the Vibhakthi విభక్తి (preposition) tradition.
| Telugu | రాముడు (Ramudu) బంతిని (bantini) కొట్టాడు (kottaadu) |
| Literal translation | Rama ball hit |
| Reformatted | "Rama hit the ball" |
Inflection
Telugu has its own grammar which mainly dictates how any two words or two letters or a word and a letter should be united to form a single word. These rules are defined under various types of సంధి (sandhi) and సమాసము (samasamu). According to these rules any two words or two letters or a word and a letter to be united to form a single word should be satisfying certain criteria. Hence, Telugu words can often be broken down into words or letters which carry a complete meaning themselves. Vice-versa, many words and letters can be combined to make a complex word that can carry more complex meaning which can be equated to a complete phrase or even a sentence when translated to English.
Ex: Nuvvostanante is formed from individual words Nuvvu,Vastanu,Ante which can be loosely translated into English as "if you want to come".
Reduplication, the repetition of words or syllables is done to create new or emphatic meanings (e.g., pakapaka ‘suddenly bursting out laughing,’ garagara ‘clean, neat, nice’).
Telugu is often considered an agglutinative language, where certain syllables are added to the end of a noun in order to denote its case:
| Ablative | Ramudinunchi | రాముడినుంచి | రాముడు(Ramudu) + నుంచి(from) | "from" Rama |
| Genitive | Ramuni | రాముని | రాము(Ramu) + ని(ni) | "generic reference to" Rama) |
| Dative | Ramuniki | రామునికి | రాము(Ramu) + ని(ni) + కి(ki) | specifically referring something "about" referring to Rama) |
| Instrumental | Ramunitho | రామునితో | రాము(Ramu) + ని(ni) + తో(tho) | specifically referring something "with" Rama |
These agglutinations apply to all nouns generally in the singular and plural.
Here is how other cases are manifested in Telugu:
Location
| Case | Usage | English example | Telugu example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adessive case | adjacent location | near/at/by the house | ఇంటి/పక్క /ɪɳʈɪprakːa/ |
| Inessive case | inside something | inside the house | ఇంట్లో /ɪɳʈloː/ |
| Locative case | location | at/on/in the house | ఇంటిదగ్గర /ɪɳʈɪd̪aɡːara/ |
| Superessive case | on the surface | on (top of) the house | ఇంటిపై /ɪɳʈɪpaj/ |
Motion
| Case | Usage | English example | Telugu example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allative case | movement to (the adjacency of) something | to the house | ఇంటికి /ɪɳʈɪkɪ/, ఇంటివైపు /ɪɳʈɪvajpu/ |
| Delative case | movement from the surface | from (the top of) the house | ఇంటిపైనుంచి /ɪɳʈɪpajnɪɲcɪ/ |
| Egressive case | marking the beginning of a movement or time | beginning from the house | ఇంటినుంచి /ɪɳʈɪnɪɲcɪ/ (ఇంటికెల్లి /ɪɳʈɪkelːɪ/ in some dialects) |
| Elative case | out of something | out of the house | ఇంటిలోనుంచి /ɪɳʈɪnɪɲcɪ/ (ఇంట్లకెల్లి /ɪɳʈlakelːɪ/ in some dialects) |
| Illative case | movement into something | into the house | ఇంటిలోనికి /ɪɳʈɪloːnɪkɪ/ (ఇంట్లోకి /ɪɳʈloːkɪ/) |
| Sublative case | movement onto the surface | on(to) the house | ఇంటిపైకి /ɪɳʈɪpajkɪ/ |
| Terminative case | marking the end of a movement or time | as far as the house | ఇంటివరకు /ɪɳʈɪvaraku/ |
Morphosyntactic alignment
| Case | Usage | English example | Telugu example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oblique case | all-round case; any situation except nominative | concerning the house | ఇంటిగురించి /ɪɳʈɪɡurɪɲcɪ/ |
Relation
| Case | Usage | English example | Telugu example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benefactive case | for, for the benefit of, intended for | for the house | ఇంటికోసం /ɪɳʈɪkoːsam/ (ఇంటికొరకు /ɪɳʈɪkoraku/) |
| Causal case | because, because of | because of the house | ఇంటివలన /ɪɳʈɪvalana/ |
| Comitative case | in company of something | with the house | ఇంటితో /ɪɳʈɪt̪oː/ |
| Possessive case | direct possession of something | owned by the house | ఇంటియొక్క /ɪɳʈɪjokːa/ |
Polyagglutination
While the examples given above are single agglutinations, Telugu allows for polyagglutination, a feature of being able to add multiple suffixes to words to denote more complex features:
For example, one can affix both "నుంచి; nunchi - from" and "లో; lo - in" to a noun to denote from within. An example of this: "రాములోనుంచి; ramuloninchi - from within Ramu".
Here is an example of a triple agglutination: "వాటిమధ్యలోనుంచి; vāṭimadʰyalōninchi - from in between them".
Inclusive and exclusive pronouns
Telugu, in common with other Dravidian languages, distinguishes between inclusive and exclusive we. The bifurcation of the First Person Plural pronoun (we in English) into inclusive (మనము; manamu) and exclusive (మేము; mēmu) versions can also be found in Tamil and Malayalam, although it is not used in modern Kannada.
Gender
Telugu pronouns follow the systems for gender and respect (T-V distinction) also found in other Indian languages. The second person plural మీరు /miːru/ is used in addressing someone with respect, and there are also respectful third personal pronouns (ఆయన /ɑːjana/ m. and ఆవిడ /ɑːvɪɽa/ f.) pertaining to both genders. Telugu uses the same forms for singular feminine and neuter genders — the third person pronoun (అది /ad̪ɪ/) is used to refer to animals and objects.[18][19][clarification needed]
Vocabulary
Some words that describe objects/actions పులి puli (tiger), ఊరు ūru (town/city), have cognates in other Dravidian languages and are indigenous to the Dravidian language family. Though Telugu uses a high degree of Sanskrit words; it also contains lesser extent of Arabic and Persian words such as maidanam (maydan in Arabic), kalam (qalam in Arabic), Bazaar (originally Persian word) etc. Today, Telugu is generally considered as a Dravidian language with the most Sanskrit loan words.
The vocabulary of Telugu especially in the Hyderabad region has a trove of Persian-Arabic borrowings, which have been modified to fit Telugu phonology. This was due to centuries of Muslim rule in these regions: the erstwhile kingdoms of Golkonda and Hyderabad. (e.g. కబురు, /kaburu/ for Urdu /xabar/, خبر or జవాబు, /ɟavɑːbu/ for Urdu /ɟawɑːb/, جواب)
Modern Telugu vocabulary can be said to constitute a diglossia, because the formal, standardized version of the language, heavily influenced by Sanskrit, is taught in schools and used by the government and Hindu religious institutions. However, everyday Telugu varies depending upon region and social status. There is a large and growing middle class whose Telugu is substantially interspersed with English. Popular Telugu, especially in urban Hyderabad, spoken by the masses and seen in movies that are directed towards the masses, includes both English and Hindi/Urdu influences.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2007) |
Writing system

The earliest evidence for Brahmi script in South India comes from Bhattiprolu in Guntur district of Andhra Pradesh.[20] Bhattiprolu was a great centre of Buddhism since 4th century BC(Pre-Mauryan time) from where Buddhism spread to east Asia. A variant of Asokan Brahmi script, called Bhattiprolu Script, the progenitor of Old Telugu script, was found on the Buddha’s relic casket.[21]
The famous Muslim historian and scholar of 10th century, Al-Biruni referred to Telugu language and script as "Andhri".[22]
Telugu script is written from left to right and consists of sequences of simple and/or complex characters. The script is syllabic in nature - the basic units of writing are syllables. Since the number of possible syllables is very large, syllables are composed of more basic units such as vowels (“achchu” or “swar”) and consonants (“hallu” or “vyanjan”). Consonants in consonant clusters take shapes which are very different from the shapes they take elsewhere. Consonants are presumed to be pure consonants, that is, without any vowel sound in them. However, it is traditional to write and read consonants with an implied 'a' vowel sound. When consonants combine with other vowel signs, the vowel part is indicated orthographically using signs known as vowel “maatras”. The shapes of vowel “maatras” are also very different from the shapes of the corresponding vowels.
The overall pattern consists of sixty symbols, of which 16 are vowels, three vowel modifiers, and forty-one consonants. Spaces are used between words as word separators.
The sentence ends with either a single bar | (“purna virama”) or a double bar || (“deergha virama”). Traditionally, in handwriting, Telugu words were not separated by spaces. Modern punctuation (commas, semicolon, etc.) were introduced with the advent of print.[23]
There is a set of symbols for numerals, though Arabic numbers are typically used.
Telugu is assigned Unicode codepoints: 0C00-0C7F (3072-3199).[24]
Carnatic music
It has been suggested that this section be split out into another article titled Carnatic music. (Discuss) (October 2009) |
Thanjavur was the heart of the Tamil Chola dynasty (from the 9th century to the 13th), but in the second quarter of the sixteenth century a Telugu Nayak viceroy (Raghunatha Nayaka) was appointed by the emperor of Vijayanagara, thus establishing a court whose language was Telugu. Telugu Nayaka rulers acted as the governors in the present day Tamil Nadu area with headquarters at Thanjavur (1530-1674 CE) and Madurai (1530-1781 CE). After the collapse of Vijayanagar, Thanjavur and Madurai Nayaks became independent and ruled for the next 150 years until they were replaced by Marathas. This was the period when several Telugu families migrated from Andhra and settled down in Thanjavur and Madurai in Tamilnadu. Most of the great composers of Carnatic music belonged to these families. Telugu, a language ending with vowels, giving it a mellifluous quality, was also considered suitable for musical expression. Of the trinity of Carnatic music composers, Tyagaraja's and Syama Sastri's compositions were largely in Telugu, while Muthuswami Dikshitar a Tamil composer is noted for his Sanskrit texts. Tyagaraja is remembered both for his devotion and the bhava of his krithi, a song form consisting of pallavi, (the first section of a song) anupallavi (a rhyming section that follows the pallavi) and charanam (a sung stanza which serves as a refrain for several passages in the composition). The texts of his kritis are almost all in Sanskrit, in Telugu (the contemporary language of the court). This use of a living language, as opposed to Sanskrit, the language of ritual, is in keeping with the bhakti ideal of the immediacy of devotion. Sri Syama Sastri, the oldest of the trinity, was taught Telugu and Sanskrit by his father, who was the pujari (Hindu priest) at the Meenakshi temple in Madurai of Tamilnadu. Syama Sastri's texts were largely composed in Telugu, widening their popular appeal. Some of his most famous compositions include the nine krithis, Navaratnamaalikā, in praise of the goddess Meenakshi at Madurai, and his eighteen krithi in praise of Kamakshi. As well as composing krithi, he is credited with turning the svarajati, originally used for dance, into a purely musical form.
Literature
This section needs additional citations for verification. (August 2007) |
Telugu literature is generally divided into six periods:
| pre-1020 CE | pre-Nannayya period |
| 1020–1400 | Age of the Puranas |
| 1400–1510 | Age of Srinatha |
| 1510–1600 | Age of the Prabandhas |
| 1600–1820 | Southern period |
| 1820 to date | Modern period |
In the telugu literature Tikkana was given agraasana(top position) by meny famous critics. In the earliest period there were only inscriptions from 575 AD onwards. Nannaya's (1022-1063) translation of the Sanskrit Mahabharata into Telugu is the piece of Telugu literature as yet discovered. After the death of Nannaya, there was a kind of social and religious revolution in the Telugu country.[25]
Tikkana (thirteenth century) and Yerrapregada (fourteenth century) continued the translation of the Mahabharata started by Nannaya. Telugu poetry also flourished in this period, especially in the time of Srinatha.
During this period, some Telugu poets translated Sanskrit poems and dramas, while others attempted original narrative poems. The popular Telugu literary form called the Prabandha evolved during this period. Srinatha (1365-1441) was the foremost poet, who popularised this style of composition (a story in verse having a tight metrical scheme). Srinatha's Sringara Naishadham is particularly well-known.
The Ramayana poets may also be referred in this context. The earliest Ramayana in Telugu is generally known as the Ranganatha Ramayana, authored by the chief Gona budhdha Reddy. The works of Pothana (1450-1510), Jakkana (second half of the fourteenth century) and Gaurana (first half of the fifteenth century) formed a canon of religious poetry during this period. Padakavitha Pithamaha, Annamayya, contributed many original Telugu Paatalu (Songs) to the language.
The sixteenth and seventeenth centuries CE is regarded as the "golden age" of Telugu literature. Krishnadevaraya's Amukthamalayadha, and Pedhdhana's Manucharithra are regarded as Mahaakaavyaas. Telugu literature flourished in the south in the traditional "samsthanas" (centres) of Southern literature, such as Madurai and Tanjore. This age is often referred to as the Southern Period. There were also an increasing number of poets in this period among the ruling class, women and non-Brahmins who popularised indigenous (desi) meters.
With the conquest of the Deccan by the Mughals in 1687, Telugu literature entered a lull. Tyagaraja's compositions are some of the known works from this period. Then emerged a period of transition (1850-1910), followed by a long period of Renaissance. Europeans like C.P. Brown played an important role in the development of Telugu language and literature. In common with the rest of India, Telugu literature of this period was increasingly influenced by European literary forms like the novel, short story, prose and drama.
Paravastu Chinnayya Soori (1807-1861) is a well-known Telugu writer who dedicated his entire life to the progress and promotion of Telugu language and literature. Sri Chinnayasoori wrote the Bala Vyakaranam in a new style after doing extensive research on Andhra grammar. Other well-known writings by Chinnayasoori are Neethichandrika, Sootandhra Vyaakaranamu, Andhra Dhatumoola, and Neeti Sangrahamu.
Kandukuri Veeresalingam (1848-1919) is generally considered to be the father of modern Telugu literature.[26] His novel Rajasekhara Charitamu was inspired by the Vicar of Wakefield. His work marked the beginning of a dynamic of socially conscious Telugu literature and its transition to the modern period, which is also part of the wider literary renaissance that took place in Indian culture during this period. Other prominent literary figures from this period are Gurajada Appa Rao, Viswanatha Satyanarayana, Gurram Jashuva, Rayaprolu Subba Rao, Devulapalli Krishnasastri and Srirangam Srinivasa Rao, popularly known as Mahakavi Sri Sri. Sri Sri was instrumental in popularising free verse in spoken Telugu (vaaduka bhasha), as opposed to the pure form of written Telugu used by several poets in his time. Devulapalli Krishnasastri is often referred to as the Shelley of Telugu literature because of his pioneering works in Telugu Romantic poetry.
Viswanatha Satyanarayana won India's national literary honour, the Jnanpith Award for his magnum opus Ramayana Kalpavrikshamu.[27] C. Narayana Reddy also received the award for his contributions to Telugu literature.[28] Kanyasulkam, the first social play in Telugu by Gurajada Appa Rao, was followed by the progressive movement, the free verse movement and the Digambara style of Telugu verse. Other modern Telugu novelists include Unnava Lakshminarayana (Maalapalli), Bulusu Venkateswarulu (Bharatiya Tatva Sastram), Kodavatiganti Kutumba Rao and Buchi Babu.[8] Gunturu Seshendra Sarma, a well known Telugu poet, has been a recipient of the Sahitya Akademi Award. He is best known for his work, Na Desham, Na Prajalu (My country, My people) which was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature 2004. His works have been translated into many languages. He wrote under the pen name "Seshen".
Quotes on Telugu
- "...Among these five languages, the Telinga appears to be most polished, and though confessedly a difficult language, it must be numbered among those which are the most worthy of cultivation; its varierty of inflection being such as to give it a capacity of expressing ideas with high degree of facilty, justness and elegance..." — by Rev. W.Carey (April 9, 1814).[29]
- "...But those who may at first question the utility of so many letters in the Teloogoo, will perhaps relinquish most of their objections, when they find that the variety of sound in this language is greater, and better represented than English..." — A.D Campbell (1949)[30].
- "...In respect of antiquity of culture and glossorial copiousness, Telugu is generally considered as ranking next to Tamil in the list of Dravidian idioms, whilst in the point of euphonic sweetness it justly claims to occupy the first place..." — Bishop Robert Caldwell (1856) [31]
- "Desa bhashalandu Telugu Lessa" ("Among the nation's languages, Telugu is the best") - Sri Krishnadeva Raya [32].
- "...Tamil is considered to be the Dravidian language which has preserved the most traces of the original form of speech from which all other Dravidian dialects are derived. Some points will be drawn to attention to in the ensuing pages where this does not appear to be the case, and in many peculiarities the other Dravidian languages such as Telugu also have preserved older forms and represent an ancient state of development." - George Abraham Grierson, Linguistic Survey of India [33][34]
See also
- Cinema of Andhra Pradesh
- List of Indian languages by total speakers
- List of Telugu language television channels
- States of India by Telugu speakers
References
- ^ "Languages Spoken by More Than 10 Million People". Encarta. MSN.com. Retrieved 17 October 2009.
- ^ "Image of Indian languages and total speakers". Retrieved 2007-02-13.
- ^ "Declaration of Telugu and Kannada as classical languages". Press Information Bureau. Ministry of Tourism and Culture, Government of India. Retrieved 2008-10-31.
- ^ a b "Telugu gets classical status". Times of India. 2008-10-01. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b "Scheduled Languages in Descending Order of Speakers' Strength". 2001 Census. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ http://dsal.uchicago.edu/cgi-bin/philologic/getobject.pl?c.1:1:848.burrow
- ^ The Hindu : Andhra Pradesh News : Telugu is 1,500 years old, says ASI
- ^ a b c d e f g APonline - History and Culture-Languages
- ^ Krishnamurti, Bhadriraju (2003). The Dravidian Languages. Cambridge University Press. pp. 78–79. ISBN 0521771110.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ APonline — History and Culture — History-Post-Independence Era
- ^ 1.9 million speakers as of 2001. "Waddar". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ^ 29,000 speakers as of 1981. "Chenchu". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ^ 20,000 speakers as of 2000. "Savara". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ^ 19,000 speakers as of 1981. "Manna-Dora". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ^ "Dravidian, South-Central, Telugu". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ^ "Telugu". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ^ Telugulo Chandovisheshaalu, Page 127.
- ^ Albert Henry Arden (1873), A progressive grammar of the Telugu language, Society for promoting Christian knowledge, p. 57
- ^ Charles Philip Brown (1857), A grammar of the Telugu language (2 ed.), Christian Knowledge Society's Press, p. 39
- ^ Ananda Buddha Vihara
- ^ The Hindu : Andhra Pradesh / Hyderabad News : Epigraphist extraordinaire
- ^ Ancient India: English translation of Kitab-ul Hind by Al-Biruni, National Book Trust, New Delhi
- ^ Brown, Charles Philip (1857). A Grammar of the Telugu Language. London: W. H. Allen & Co. p. 5. ISBN 812060041X.
- ^ United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names (2007). Technical Reference Manual for the Standardization of Geographical Names. United Nations Publications. p. 110. ISBN 9211615003.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Chenchiah, P. (1988). A History of Telugu Literature. Asian Educational Services. ISBN 8120603133.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Sarma, Challa Radhakrishna (1975). Landmarks in Telugu Literature. Lakshminarayana Granthamala. p. 30.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Datta, Amaresh (1991). Encyclopaedia of Indian Literature. Sahitya Akademi. p. 3294.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ George, K.M. (1992). Modern Indian Literature, an Anthology. Sahitya Akademi. p. 1121. ISBN 8172013248.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Carey, William (1914). A Grammar of the Telinga Language. Serampore: Mission-Press.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Campbell, A.D. (1849). A Grammar of the Teloogoo Language (3rd edition ed.). Madras, India: College of Fort St. George.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ >Caldwell, Robert (1856). A Comparative Grammar of the Dravidian Or South-Indian Family of Languages. Edinburgh and London: Ballantyne and Company. ISBN 81-206-0117-3.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ India Times
- ^ Linguistic Survey of India, Vol IV, Page.283
- ^ [1]
Bibliography
- Albert Henry Arden, A progressive grammar of the Telugu language (1873).
- Charles Philip Brown, English-Telugu dictionary (1852; revised ed. 1903; online edition)
- Charles Philip Brown, A grammar of the Telugu language (1857)
- P. Percival , Telugu-English dictionary: with the Telugu words printed in the Roman as well as in the Telugu Character (1862, google books edition)
- Gwynn, J. P. L. (John Peter Lucius). A Telugu-English Dictionary Delhi; New York: Oxford University Press (1991; online edition).
- Uwe Gustafsson, An Adiwasi Oriya-Telugu-English dictionary, Central Institute of Indian Languages Dictionary Series, 6. Mysore: Central Institute of Indian Language (1989).
- Vēlcēru Nārāyaṇarāvu, David Dean Shulman, Velcheru Narayana Rao, Classical Telugu poetry: an anthology (2002).
- Callā Rādhākr̥ṣṇaśarma, Landmarks in Telugu literature: a short survey of Telugu literature (1975).
