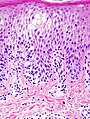
Spongiosis
Appearance
Spongiosis is mainly intercellular[1] edema between the keratinocytes in the epidermis,[2] and is characteristic of eczematous dermatitis, manifested clinically by vesicles, "juicy" papules, and/or lichenification.[3]
Spongiosis: Intracellular oedema, seen as increased width of the space between epidermal cells and leading, if severe, to formation of vesicles in the epidermis. http://sadermatology.blogspot.com/
Additional images
-
Histopathological image of dyshidrotic dermatitis, showing focal spongiotic change in the epidermis.
See also
References
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. Chapter: Clinical and Pathologic Differential Diagnosis. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (7th ed.). Saunders. Page 1230. ISBN 0721601871.
- ^ Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 28. ISBN 1-4160-3185-5.