Anterior pituitary
| Anterior pituitary | |
|---|---|
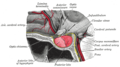
 Median sagittal through the hypophysis of an adult monkey. Semidiagrammatic. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | oral mucosa (Rathke's pouch) |
| Artery | superior hypophyseal |
| Vein | hypophyseal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lobus anterior hypophyseos |
| MeSH | D010903 |
| NeuroNames | 407 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1581 |
| TA98 | A11.1.00.002 |
| TA2 | 3855 |
| FMA | 74627 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary, also called the adenohypophysis, is the glandular, anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, and reproduction.
Its regulatory functions are achieved through the secretion of various peptide hormones that act on target organs including the adrenal gland, liver, bone, thyroid gland, and gonads. The anterior pituitary itself is regulated by the hypothalamus and by negative feedback from these target organs.
Disorders of the anterior pituitary are generally classified by the presence of over- or underproduction of pituitary hormones. For example, a prolactinoma is a pituitary adenoma that overproduces prolactin. In Sheehan's syndrome of postpartum hypopituitarism, the anterior pituitary uniformly malfunctions and underproduces all hormones. Proper function of the anterior pituitary and of the organs it regulates can often be ascertained via blood tests that measure hormone levels.
Anatomy
The pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland that sits in a protective bony enclosure called the sella turcica. It is composed of three lobes: anterior, intermediate, and posterior. In many animals, these three lobes are distinct. However, in humans, the intermediate lobe is but a few cell layers thick and indistinct; as a result, it is often considered part of the anterior pituitary. In all animals, the fleshy, glandular anterior pituitary is distinct from the neural composition of the posterior pituitary.
The anterior pituitary is composed of multiple parts:
- Pars distalis
- The pars distalis, or "distal part", comprises the majority of the anterior pituitary and is where the bulk of pituitary hormone production occurs. Occasionally, "pars distalis" is incorrectly used as a synonym for the anterior pituitary.[citation needed]
- Pars tuberalis
- The pars tuberalis, or "tubular part", forms a sheath extending up from the pars distalis and wrapping around the pituitary stalk. Its function is poorly understood.
- Pars intermedia
- The pars intermedia, or "intermediate part", sits between the pars distalis and the posterior pituitary and is often very small in humans.
Embryology
The anterior pituitary arises from an invagination of the oral ectoderm and forms Rathke's pouch. This contrasts with the posterior pituitary, which originates from neuroectoderm.
Major hormones secreted
| Hormone | Other names | Symbol(s) | Structure | Secretory cells | Staining | Target | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone | Corticotropin | ACTH | Polypeptide | Corticotrophs | Basophil | Adrenal gland | Secretion of glucocorticoids |
| Beta-endorphin | Polypeptide | Corticotrophs | Basophil | Opioid receptor | Inhibit perception of pain | ||
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone | Thyrotropin | TSH | Glycoprotein | Thyrotrophs | Basophil | Thyroid gland | Secretion of thyroid hormones |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone | - | FSH | Glycoprotein | Gonadotrophs | Basophil | Gonads | Growth of reproductive system |
| Luteinizing hormone | Lutropin | LH, ICSH | Glycoprotein | Gonadotrophs | Basophil | Gonads | Sex hormone production |
| Growth hormone | Somatotropin | GH, STH | Polypeptide | Somatotrophs | Acidophil | Liver, adipose tissue | Promotes growth; lipid and carbohydrate metabolism |
| Prolactin | Lactogenic hormone | PRL | Polypeptide | Lactotrophs and Mammotrophs | Acidophil | Ovaries, mammary glands | Secretion of estrogens/progesterone; milk production |
The acidophilic cells (GH and PRL) have extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum and produce single chain polypeptides without any glycosylation or phosphorylation. Basophilic staining results from lysosome action modifying the hormones (or prohormones in the case of corticotrophs) by glycosylation.
Regulation
Hormone secretion from the anterior pituitary gland is regulated by hormones secreted by the hypothalamus. Neuroendocrine neurons in the hypothalamus project axons to the median eminence, at the base of the brain. At this site, these neurons can release substances into small blood vessels that travel directly to the anterior pituitary gland (the hypothalamo-hypophysial portal vessels).
Etymology
The anterior pituitary is also known as the adenohypophysis, meaning "glandular undergrowth", from the Greek adeno ("gland"), hypo ("under"), and physis ("growth").
Additional images
-
The anterior pituitary is the anterior, glandular lobe of the pituitary gland.
See also
External links
- Histology image: 14002loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- Embryology at unc.edu