Barred spiral galaxy


A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in approximately two-thirds of all spiral galaxies.[1] Bars generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies and can affect spiral arms as well.[1]
Edwin Hubble classified these types of spiral galaxies as "SB" (Spiral, Barred) in his Hubble sequence, and arranged them into three sub-categories based on how open the arms of the spiral are. SBa types feature tightly bound arms, while SBc types are at the other extreme and have loosely bound arms. SBb type galaxies lie in between. A fourth type, SBm, was subsequently created to describe somewhat irregular barred spirals, such as the Magellanic Cloud galaxies, which were once classified as irregular galaxies, but have since been found to contain barred spiral structures. Among other types in Hubble's classifications for the galaxies are: spiral galaxy, elliptical galaxy and irregular galaxy.
In 2005, observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope backed up previously collected evidence that suggested the Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy. Observations by radio telescopes had for years suggested our galaxy to be barred, but Spitzer's vision in the infrared region of the spectrum has provided a more definite calculation.
The bars
Barred spiral galaxies are relatively common, with surveys showing that up to two-thirds of all spiral galaxies contain a bar.[2] The current hypothesis is that the bar structure acts as a type of stellar nursery, fueling star birth at their centers. The bar is thought to act as a mechanism that channels gas inwards from the spiral arms through orbital resonance, in effect funneling the flow to create new stars.[3] This process is also thought to explain why many barred spiral galaxies have active galactic nuclei, such as that seen in the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy.
The creation of the bar is generally thought to be the result of a density wave radiating from the center of the galaxy whose effects reshape the orbits of the inner stars. This effect builds over time to stars orbiting further out, which creates a self-perpetuating bar structure.[4] Another possible cause of bar creation is gravitational disruptions between galaxies. [citation needed]
Bars are thought to be a temporary phenomenon in the life of spiral galaxies, the bar structure decaying over time, transforming the galaxy from a barred spiral to a "regular" spiral pattern. Past a certain size the accumulated mass of the bar compromises the stability of the overall bar structure. Barred spiral galaxies with high mass accumulated in their center tend to have short, stubby bars.[5] Since so many spiral galaxies have a bar structure, it is likely that it is a recurring phenomenon in spiral galaxy development. The oscillating evolutionary cycle from spiral galaxy to barred spiral galaxy is thought to take on the average about two billion years.[6]
Recent studies have confirmed the idea that bars are a sign of galaxies reaching full maturity as the "formative years" end. A team led by Kartik Sheth of the Spitzer Science Center at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena discovered that only 20 percent of the spiral galaxies in the distant past possessed bars, compared with nearly 70 percent of their modern counterparts.[7]
The bulges
Studying the core of the Milky Way, scientists found out that the Milky Way's bulge was peanut-shaped. This led to the conclusion that all barred spiral galaxies have a peanut shaped bulge. When observing a distant spiral galaxy with a rotational axis perpendicular to the line of sight, or one that appears "edge-on" to the observer, the shape of the bulge can be easily observed, and therefore quickly classified as either a barred spiral or a regular spiral. Galaxy NGC 4565 has been tentatively classified as a barred spiral galaxy using this method.[8][failed verification]
Grades
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2010) |
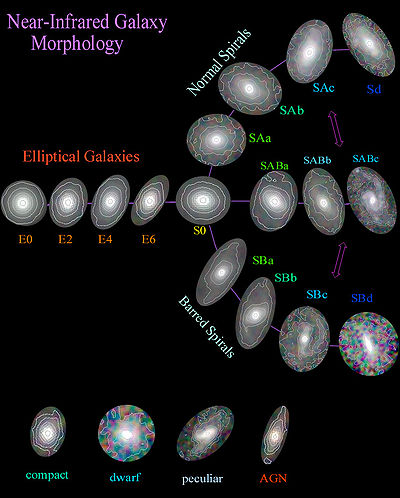
| Example | Type | Image | Information | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SB0- | SB0- is a type of lenticular galaxy | |||
| SB0 | SB0 is a type of lenticular galaxy | |||
| SB0+ | SB0+ is a type of lenticular galaxy | |||
| SB0/a | SB0/a can also be considered a type of barred lenticular galaxy | |||
| NGC 4314 | SBa | 
|
This is actually an "SB(rs)a" | |
| NGC 4921 | SBab | 
|
This is actually an "SB(rs)ab" | |
| Messier 95 | SBb | 
|
This is actually an "SB(r)b" | |
| NGC 3953 | SBbc | 
|
This is actually an "SB(r)bc" | |
| NGC 1073 | SBc | File:N1073lipscomb.jpg | This is actually an "SB(rs)c" | |
| Messier 108 | SBcd | 
|
This is actually an "SB(s)cd" | |
| NGC 2903 | SBd | 
|
This is actually an "SB(s)d" | |
| NGC 5398 | SBdm | 
|
SBdm can also be considered a type of barred Magellanic spiral | This is actually an "SB(rs)dm" |
| NGC 55 | SBm | 
|
SBm is a type of Magellanic spiral (Sm) | This is actually an "SB(s)m" |
Examples
| Name | Type | Constellation |
|---|---|---|
| M58 | SBc | Virgo |
| M91 | SBb | Coma Berenices |
| M95 | SBb | Leo |
| M109 | SBb | Ursa Major |
| NGC 1300 | SBbc | Eridanus |
| NGC 1365 | SBc | Fornax |
| Magellanic Clouds | SBm | Dorado, Tucana |
See also
- Galaxy morphological classification
- Galaxy formation and evolution
- Lenticular galaxy
- Spiral galaxy
- Firehose instability
External links
- Britt, Robert Roy. "Milky Way’s Central Structure Seen with Fresh Clarity." SPACE.com 16 August 2005.
- An article about the Spitzer Space Telescope's Milky Way discovery
- Devitt, Terry. "Galactic survey reveals a new look for the Milky Way." 16 August 2005.
- The original press release regarding the article above, from the Univ. of Wisconsin
- SPACE.com staff writers. "'Barred' Spiral Galaxy Pic Highlights Stellar Birth." SPACE.com 2 March 2001.
- Hastings, George and Jane Hastings. Classifying Galaxies: Barred Spirals, 1995.
- Buta, Ronald, D. A. Crocker, and G. G. Byrd. "Astronomers Find Multiple Generations of Star Formation in Central Starburst Ring of a Barred Spiral Galaxy." January 15, 2000.
- A press release concerning NGC 1326
- Barred spirals come and go Sky & Telescope April 2002.
- "ESO Provides An Infrared Portrait of the Barred Spiral Galaxy Messier 83." November 29, 2001.
- A press release from the European Southern Observatory.
- 04/03/07: Hubble: Barred Spiral Galaxy NGC 1672
References
- ^ a b D. Mihalas (1968). Galactic Astronomy. W. H. Freeman. ISBN 9780716703266.
- ^ P. B. Eskridge, J. A. Frogel (1999). "What is the True Fraction of Barred Spiral Galaxies?". Astrophysics and Space Science. 269/270: 427–430. doi:10.1023/A:1017025820201.
- ^ J. H. Knapen, D. Pérez-Ramírez, S. Laine (2002). "Circumnuclear regions in barred spiral galaxies - II. Relations to host galaxies". Monthly Notice of the Royal Astronomical Society. 337 (3): 808–828. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2002.05840.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ F. Bournaud, F. Combes (2002). "Gas accretion on spiral galaxies: Bar formation and renewal". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 392: 83–102. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020920.
- ^ Barred Spirals Come and Go, Sky and Telescope, April 2002
- ^ Ripples in a Galactic Pond, Scientific American, October 2005
- ^ Barred Spiral Galaxies are Latecomers to the Universe Newswise, Retrieved on July 29, 2008.
- ^ INTERMEDIATE-BAND SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF THE EDGE-ON GALAXY NGC 4565 at http://www.iop.org/EJ/article/1538-3881/123/3/1364/201272.text.html
