First-person shooter

| Part of a series on |
| Action games |
|---|
First-person shooter (FPS) is a video game genre which centers the gameplay around gun and projectile weapon-based combat through the first person perspective; i.e., the player experiences the action through the eyes of a protagonist. Generally speaking, the first-person shooter shares common traits with other shooter games, which in turn fall under the heading action game. From the genre's inception, advanced 3D or pseudo-3D graphics elements have challenged hardware development, and multiplayer gaming has been integral.
The first person shooter has since been traced as far back as Maze War, development of which began in 1973, and 1974's Spasim. 1987's MIDI Maze for the Atari ST was one of the first network multiplayer action games and also saw release on game consoles. The genre coalesced with 1992's Wolfenstein 3D, which is generally credited with creating the genre proper and the basic archetype upon which subsequent titles were based. One such title, and the progenitor of the genre's wider mainstream acceptance and popularity was Doom, released the following year and perhaps the most influential first-person shooter. Half-Life, released in 1998, enhanced the narrative and puzzle elements, and along with its 2004 sequel Half-Life 2, showcases the considerable development of the genre's potential.[1][2] GoldenEye 007 (1997) was the first landmark first-person shooter for home consoles, with the Halo series heightening the console's commercial and critical appeal as a platform for first-person shooter titles. In the 21st century, the first-person shooter is one of the most commercially viable and fastest growing video game genres.
Definition
First-person shooters are a type of 3D shooter game,[3] featuring a first person point of view with which the player sees the action through the eyes of the player character. They are unlike Third person shooters which are seen from the back, allowing the gamer to see the character they are controlling. The primary design element is combat, mainly involving firearms.[4] The first person shooter may be considered a distinct genre in itself, or a type of shooter game, in turn a subgenre of the wider action game genre.[5] Following the release of the influential Doom in 1993, games in this style were commonly termed "Doom clones";[6][7] in time this term has largely been replaced by "first person shooter".[7] Wolfenstein 3D, released in 1992, the year before Doom, is generally credited with inventing the genre, but critics have since identified similar though less advanced games developed as far back as 1973.[4] There is sometimes disagreement regarding exactly what design elements constitute a first-person shooter: for example, Deus Ex is sometimes considered a first person shooter, but may also be considered a role-playing game as it borrows from this genre extensively.[8] Some commentators may extend the definition obliquely to include combat flight simulators, as opposed to characters on foot.[1][4]
Game design
Like most shooter games, first person shooters involve an avatar, one or more ranged weapons, and a varying number of enemies.[5] Because they take place in a 3D environment, these games tend to be somewhat more realistic than 2D shooter games, and have more accurate representations of gravity, lighting, sound and collisions.[3] First person shooters played on personal computers are most often controlled with a combination of a keyboard and mouse. This system is often considered superior to that found in console games,[9][10] which frequently use two analog sticks, one used for running and sidestepping, the other for looking and aiming.[11] It is common to display the character's hands and weaponry in the main view, with a head up display showing health, ammunition and location details. Often, it is possible to overlay a map of the surrounding area.[12]
Combat and power-ups
First person shooters often focus on action gameplay, with fast-paced and bloody firefights, though some place a greater emphasis on narrative, problem-solving and logic puzzles.[13] In addition to shooting, melee combat may still be used extensively. In some games, melee weapons are especially powerful, a reward for the risk the player must take in maneuvering his character into close proximity to the enemy.[14] In other situations, a melee weapon may be less effective, but necessary as a last resort.[15] "Tactical shooters" are more realistic, and require teamwork and strategy to succeed;[11] the player often commands a squad of characters, which may be controlled by the game or by human teammates.[16]
These games typically give players a choice of weapons, which have a large impact on how the player will play the game.[3] Some have highly realistic models of real weapons, including their rate of fire, size of ammunition, and accuracy. However, they may allow players to carry many of them at the same time, with no reduction in speed or mobility. Thus, the standards of realism varies between design elements.[3] The protagonist can generally be healed and re-armed by means of items such as first aid kits, simply by walking over them.[17] Some games allow players to accumulate experience points similar to those found in role-playing games, which can unlock new weapons and abilities.[18]
Level design
First person shooters may be structurally composed of levels, or use the technique of a continuous narrative in which the game never leaves the first person perspective.[1] Others feature large sandbox environments, which are not divided into levels and can be explored freely.[19] In first person shooters, protagonists interact with the environment to varying degrees, from basics such as using doors, to problem solving puzzles based on a variety of interactive objects.[1] The environment can be damaged, also to varying degrees: one common device is the use of barrels containing explosive material which the player can shoot, destroying them and harming nearby enemies.[17] Other games feature environments which are extensively destructible, allowing for additional visual effects.[20] The game world will often make use of science fiction, historic (particularly World War II) or modern military themes, with such antagonists as aliens, monsters, terrorists and soldiers of various types.[21] Games feature multiple difficulty settings; in harder modes, enemies are tougher, more aggressive and do more damage, and power-ups are limited. In easier modes, the player can succeed through reaction times alone; on more difficult settings, it is necessary to memorize the levels through trial and error.[22]

Multiplayer
First person shooters may feature a multiplayer mode, taking place on specialized levels. Some games are designed specifically for multiplayer gaming, and have very limited single player modes in which the player competes against game-controlled characters termed "bots".[23] Massively multiplayer online first-person shooters allow thousands of players to compete at once in a persistent world.[24] Large scale multiplayer games allow multiple squads, with leaders issuing commands and a commander controlling the team's overall strategy.[23] Multiplayer games have a variety of different styles of match. The classic types are the deathmatch (there is also a team-based version) in which players score points by killing other players' characters, and capture the flag, in which teams attempt to penetrate the opposing base, capture a flag and return it to their own base whilst preventing the other team from doing the same. Other game modes may involve attempting to capture enemy bases or areas of the map, attempting to take hold of an object for as long as possible while evading other players, or deathmatch variations involving limited lives or in which players fight over a particularly potent power-up. These match types may also be customizable, allowing the players to vary weapons, health and power-ups found on the map, as well as victory criteria.[25] Games may allow players to choose between various classes, each with its own strengths, weaknesses, equipment and roles within a team.[15]
History
Early first-person shooters: 1970s to early 1990s
The earliest two documented first-person shooters were Maze War and Spasim. Maze War features on-foot gameplay that evokes modern first-person shooter games. Development of the game began in 1973 and its exact date of completion is unknown. Spasim had a documented debut at the University of Illinois in 1974. The game was a rudimentary space flight simulator, which featured a first-person perspective.[4] Spasim led to more detailed combat flight simulators and eventually to a tank simulator, developed for the U.S. army, in the later 1970s. These games were not available to consumers and it was not until 1980 that a tank game, Battlezone, was released in arcades. A version was released in 1983 for home computers, the first successful mass-market game featuring a first-person viewpoint and 3D graphics.[26] A few other shooters with a first-person perspective were released in the arcades during the early 1980s, including Taito's 1981 arcade game Space Seeker,[27] and several Sega games, such as Space Tactics in 1980,[28] Star Trek[29] and SubRoc-3D[30] in 1982, and the early laserdisc video game Astron Belt in 1983.[31]
MIDI Maze was an early first-person shooter released in 1987 for the Atari ST. It was unique in featuring network multiplayer through the MIDI interface long before mainstream Ethernet and Internet play became commonplace. It is considered the first multiplayer 3D shooter on a mainstream system and the first major network multiplayer action game, with support for as many as 16 players. It was followed up by ports to various platforms in 1991 under the title Faceball 2000, including the Game Boy and Super NES, making it possibly the first handheld and multiplatform first-person shooter and an early console example of the genre.[32] An earlier console example was Arsys Software's Star Cruiser, a first-person shooter released for the Sega Mega Drive in 1990.[33] It was also a computer-to-console port, having originally been released for the NEC PC-8801 computer in early 1988. Star Cruiser was an innovative game that introduced the use of fully 3D polygonal graphics as well as action role-playing game elements.[34] Another 1988 game, Golgo 13: Top Secret Episode, featured various first-person shooter levels and is notable for introducing a sniper rifle, used in unique missions requiring the player to assassinate an enemy agent from a long distance using an unsteady sniper scope.[35]
Id Software's Hovertank 3D pioneered ray casting technology in 1991 to enable faster gameplay than 1980s vehicle simulators;[26] and a later advance, texture mapping, was introduced with Ultima Underworld: The Stygian Abyss, a 1992 role-playing game by Looking Glass Technologies that featured a first person viewpoint and an advanced graphics engine. When shown a demo of Ultima Underworld the year before, id developer John Carmack remarked that he "could write a faster texture mapper",[36] and would feel motivated by Looking Glass's example to do the same in Catacomb 3-D (which was actually released first in late 1991).[26] Catacomb 3-D also introduced the display of the protagonist's hand and weapon (in this case, magical spells) on the screen, whereas previously aspects of the player's avatar were not visible;[26] and the experience of developing Ultima Underworld would make it possible for Looking Glass to create the Thief and System Shock series years later.[36]
Taito's Gun Buster was an innovative first-person shooter released in 1992 for the arcades. It featured on-foot gameplay and a unique control scheme where the player moves using an eight-direction joystick and takes aim using a mounted positional light gun. It was also unique in allowing two-player cooperative gameplay for the mission mode, and featured an early deathmatch mode, where either two players could compete against each other or up to four players could compete in a team deathmatch, consisting of two teams with two players each competing against each other.[37]
Rise in popularity: 1992–1995
Wolfenstein 3D (created by id Software and released in 1992) was an instant success and is generally credited with inventing the first person shooter genre proper.[1][4] It built on the ray casting technology pioneered in earlier games to create a revolutionary template for shooter game design, which first person shooters are still based upon today.[1][4][13] Despite the violent themes, it largely escaped the controversy generated by the later Doom, although it was banned in Germany due to the use of Nazi iconography;[38] the Nintendo version replaced the enemy attack dogs with giant rats.[39] Apogee Software, the publisher of Wolfenstein 3D, followed up its success with Blake Stone: Aliens of Gold in 1993. The game was initially well received but sales rapidly declined in the wake of the success of id's Doom, released a week later.[40]
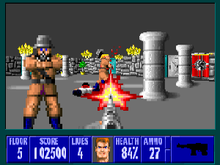
Doom, released as shareware in 1993,[13] refined Wolfenstein 3D's template by adding improved textures, variations in height (such as stairs the player's character could climb) and lighting effects such as flickering lights and patches of total darkness, creating a more believable 3D environment than Wolfenstein 3D's repetitive levels.[41] Doom allowed competitive matches between multiple players, termed "deathmatches", and the game was responsible for the word's subsequent entry into the video gaming lexicon.[41] The game became so popular that its multiplayer features began to cause problems for companies whose networks were used to play the game.[13][41] Doom has been considered the most important first person shooter ever made: it was highly influential not only on subsequent shooter games but on video gaming in general,[41] and has been available on almost every video gaming system since.[13] Multiplayer gaming, which is now integral to the first person shooter genre, was first achieved successfully on a large scale with Doom.[1][41] While its combination of gory violence, dark humor and hellish imagery garnered acclaim from critics,[41][42] these attributes also generated controversy from religious groups, with other commentators labelling the game a "murder simulator."[43] There was further controversy when it emerged that the perpetrators of the Columbine High School massacre were fans of the game; the families of several victims later unsuccessfully attempted to sue id Software, among numerous other video game companies, claiming they inspired the massacre.[38]
On the Macintosh, Bungie's 1994 release of Marathon, and subsequently its sequels, set the standard for first-person shooters on that platform. Marathon pioneered or was an early adopter of several new features such as vertical aiming and freelook, dual-wielded and dual-function weapons, versatile multiplayer modes (such as King of the Hill, Kill the Man with the Ball, and cooperative play), friendly NPCs, and a strong emphasis on storytelling in addition to the action.[44] Star Wars: Dark Forces was released in 1995 after LucasArts decided Star Wars would make appropriate material for a game in the style of Doom; however, Star Wars: Dark Forces added several technical features that Doom lacked, such as the ability to crouch or look up and down.[6][13][45] Descent, (released by Parallax Software in 1995) a game in which the player pilots a spacecraft around caves and factory ducts, was the first truly three dimensional first person shooter. It abandoned sprites and ray casting and introduced polygons and six degrees of freedom.[1][13] Apogee's Duke Nukem 3D, released in 1996, was "the last of the great, sprite-based shooters"[13] winning acclaim for its humor based around stylised machismo as well as its gameplay; however some found the game's (and later the whole series') treatment of women to be derogatory and tasteless.[13][38][46]
Rise of 3D graphics: 1995–1999
In 1994, Exact released the Sharp X68000 computer game Geograph Seal, a fully 3D polygonal first-person shooter, notable for its unique blend of free-roaming shooting and platform game mechanics. The following year, Exact released its successor for the PlayStation console, Jumping Flash!, which was similar but placed more emphasis on the platforming rather than the shooting.[47]
Shortly after the release of Duke Nukem 3D, id Software released the much anticipated Quake, originally envisioned as a sort of fantasy online world (the name Quake originally referred to a Thor-like character devised in the developers' earlier D&D sessions), where armies of players would fight each other in large persistent battles - much as would be seen in later MMORPGs like Lineage and Dark Age of Camelot.[48] Like Doom, Quake was influential and genre-defining, featuring fast-paced, hellishly gory gameplay, but used 3D polygons instead of sprites. It was centered around online gaming and featured multiple match types still found in first-person shooter games today. It was the first game to have a significant following of player clans (though the concept had existed previously as a story element in the Mech Warrior series, and guilds had already become common in MUDs by that time), and would help spur the growth in popularity of LAN parties such as QuakeCon.[48] The game's popularity and use of 3D polygonal graphics also helped to expand the growing market for video card hardware;[1][13][49] and the additional support and encouragement for game modifications attracted players who wanted to tinker with the game and create their own modules.[48]
The first landmark, best-selling console first-person shooter was Rare's GoldenEye 007, based on the James Bond film and released on the Nintendo 64 in 1997. Highly acclaimed for its atmospheric single-player levels and well designed multiplayer maps, it featured the ability to aim at a precise spot on the screen, a sniper rifle, the ability to perform headshots, and the incorporation of stealth elements.[1][13][50][51]
Released in 1998, Tom Clancy's Rainbow Six started a popular trend of tactical first person shooters, though it was not the first of its kind. It featured a team-based, realistic design and themes based around counter-terrorism, requiring missions to be planned before execution and in it, a single hit was sometimes enough to kill a character.[16][52] Medal of Honor, released in 1999, started a long running proliferation of first person shooters set during World War II.[13]
Valve's Half-Life was released in 1998, based upon Quake II's graphics technology.[53] Initially met with only mild anticipation, it went on to become an unprecedented commercial success.[13][54] While previous first person shooters had focused on visceral gameplay with comparatively weak plots, Half-Life had a strong narrative; the game featured no cut scenes but remained in the first person perspective at all times. It featured innovations such as non-enemy characters (featured somewhat earlier in titles such as Strife)[55] but did not employ power-ups.[1] Half-Life was praised for its artificial intelligence, selection of weapons and attention to detail; and, along with its sequel Half-Life 2 (released in 2004), is consistently reviewed as one of finest examples of the genre.[56]
Starsiege: Tribes, also released in 1998, was a multiplayer online shooter allowing more than 32 players in a single match. It featured team-based gameplay with a variety of specialized roles, and an unusual jet pack feature. The game was highly popular and later imitated by games such as the Battlefield series.[1][2] Id's Quake III Arena and Epic's Unreal Tournament, both released in 1999, were popular for their frenetic and accessible online multiplayer modes; both featured very limited single player gameplay.[13] Counter-Strike was also released in 1999, a Half-Life modification with a counter-terrorism theme. The game and later versions (the latest being Counter-Strike Source, released in 2004) went on to become by far the most popular multiplayer first-person shooter and computer game modification ever, with over 90,000 players competing online at any one time during its peak.[13][53]
Recent milestones: 2000–present
At the E3 game show in 1999, Bungie unveiled a real-time strategy game called Halo; at the following E3, an overhauled third-person shooter version was displayed. Later in 2000 Bungie was bought by Microsoft, and Halo was revamped and released as a first person shooter, one of the launch titles for the Xbox console. It was a runaway critical and commercial success, and is considered a premier console first person shooter. It featured narrative and storyline reminiscent of Bungie's earlier Marathon series but now told largely through in-game dialog and cut scenes. It also received acclaim for its characters, both the protagonist, Master Chief and its alien antagonists. The sequel, Halo 2 (2004), brought the popularity of online-gaming to the console market through the medium of Xbox Live, on which it was the most played game for almost two years.[13] Deus Ex, released by Ion Storm in 2000, featured a levelling system similar to that found in role-playing games; it also had multiple narratives depending on how the player completed missions and won acclaim for its serious, artistic style.[13] Metroid Prime, released in 2002 for the Nintendo GameCube, another highly praised console first person shooter, incorporated action adventure elements such as jumping puzzles and built on the Metroid series of 2D platformers.[13]
World War II Online, released in 2001, featured a persistent and "massively multiplayer environment", although IGN said that "the full realization of that environment is probably still a few years away."[57] Battlefield 1942, another World War II shooter released in 2002, featured large scale battles incorporating aircraft, naval vessels, land vehicles and infantry combat.[13] In 2003, PlanetSide allowed hundreds of players at once to compete in a persistent world,[58] and was also promoted as the "world's first massively multiplayer online first person shooter."[24] Doom 3, released in 2004, placed a greater emphasis on horror and frightening the player than previous games in the series and was a critically acclaimed best seller,[59][60] though some commentators felt it lacked gameplay substance and innovation, putting too much emphasis on impressive graphics.[8] In 2005, a film based on Doom emulated the viewpoint and action of a first person shooter, but was critically derided as deliberately unintelligent and gratuitously violent.[61]
2004's Vampire: The Masquerade – Bloodlines would develop a cult following by combining elements of first-person shooters with White Wolf's table-top role-playing game (similar to Deus Ex in 2000), despite suffering from a number of technical problems and selling poorly.[62] Later in 2007, Irrational Games' Bioshock would be acclaimed by some commentators as the best game of that year for its innovation in artistry, narrative and design,[63][64][65] with some calling it the "spiritual successor" to Looking Glass's earlier System Shock.[66][67] Finally, Crysis (2007) and Far Cry 2 (2008) would break new ground in terms of graphics and large, open-ended level design,[13][68] whereas Call of Duty 4: Modern Warfare (2007), Resistance: Fall of Man (2006) and its sequel Resistance 2 (2008) presented increasingly refined linear levels and narratives.[69] As of 2006, the first person shooter was one of the biggest and fastest growing video game genres in terms of revenue for publishers.[70]
See also
- First-person shooter engine
- List of first-person shooters
- List of freeware first-person shooters
- Third-person shooter
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Cifaldi, Frank, The Gamasutra Quantum Leap Awards: First-Person Shooters, GamaSutra, September 1, 2006, Accessed February 16, 2009
- ^ a b IGN's Top 100 Games, IGN, July 25, 2005, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ a b c d Rollings, Andrew (2006). Fundamentals of Game Design. Prentice Hall.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) Cite error: The named reference "fundamentals" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Garmon, Jay, Geek Trivia: First shots fired, TechRepublic, May 24, 2005, Accessed February 16, 2009
- ^ a b Rollings, Andrew (2003). Andrew Rollings and Ernest Adams on Game Design. New Riders Publishing. pp. 290–296.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Turner, Benjamin & Bowen, Kevin, Bringin' in the DOOM Clones, GameSpy, December 11, 2003, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ a b Doom, Encyclopædia Britannica, Accessed February 25, 2009
- ^ a b Perry, Douglass C., BioShock: Ken Levine Talks First-Person Shooters, IGN, September 15, 2006, Accessed February 25, 2009
- ^ Beradini, Cesar A., Play Halo on Xbox with a Keyboard & Mouse, Team Xbox, October 4, 2004, Accessed February 23, 2009
- ^ Schiesel, Seth, Balletic Finesse Amid the Science-Fiction Carnage, The New York Times, March 2, 2009, Accessed March 7, 2009
- ^ a b Treit, Ryan, Novice Guides: First Person Shooter, Xbox.com, Accessed February 23, 2009
- ^ Lahti, Martti, "As We Become Machines: Corporealized Pleasures in Video Games", Wolf, Mark J. P. & Perron, Bernard (eds.), The Video Game Theory Reader, Routledge, p. 161
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Hasselberger, Cheese, Guide to FPS, UGO, Accessed February 16, 2009
- ^ Hong, Tim, Shoot to Thrill: Bio-Sensory Reactions to 3D Shooting Games, GamaSutra, December 2, 2008, Accessed February 23, 2009
- ^ a b Quake Wars Guide, IGN, Accessed March 10, 2009
- ^ a b Dunkin, Alan, Tom Clancy's Rainbow Six Review, GameSpot, September 9, 1998, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ a b Staff, The Wednesday 10: First-Person Shooter Cliches, IGN, February 11, 2009, Accessed February 23, 2009
- ^ Staff, The Art Of FPS Multiplayer Design, Game Informer, May 3, 2008, Accessed February 24, 2009 Archived 2008-05-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Biessener, Adam, S.T.A.L.K.E.R.: Shadow of Chernobyl, Game Informer, Accessed February 23, 2009 Archived 2008-04-01 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Reed, Kristan, Black, EuroGamer, June 2, 2005, Accessed February 23, 2009
- ^ FPS Field Guide: A Look At Common Enemies, GameInformer, May 6, 2008, Accessed February 23, 2009 Archived 2008-07-31 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Boutros, Daniel, Difficulty is Difficult: Designing for Hard Modes in Games, GamaSutra, September 16, 2008, Accessed March 10, 2009
- ^ a b Kosak, Dave, Battlefield 2 (PC), GameSpy, June 17, 2005, Accessed February 23, 2009
- ^ a b The Worlds First MMOFPS is nearly complete, IGN, May 5, 2003, Accessed February 23, 2009
- ^ Halo Guide, IGN, Accessed March 10, 2009
- ^ a b c d Shahrani, Sam, Educational Feature: A History and Analysis of Level Design in 3D Computer Games - Pt. 1, GamaSutra, April 26, 2006, Accessed March 7, 2009
- ^ Space Seeker at the Killer List of Videogames
- ^ Space Tactics at the Killer List of Videogames
- ^ Star Trek at the Killer List of Videogames
- ^ SubRoc-3D at the Killer List of Videogames
- ^ Template:Allgame
- ^ Parish, Jeremy, The Essential 50: Faceball 2000, 1UP, Accessed April 24, 2009
- ^ Template:Allgame
- ^ スタークルーザー (translation), 4Gamer.net
- ^ Playing With Power, 1UP
- ^ a b Mallinson, Paul (April 16, 2002). "Games that changed the world: Ultima Underworld". ComputerAndVideoGames.com. Retrieved 2010-10-08.
- ^ Gun Buster at the Killer List of Videogames
- ^ a b c When Two Tribes Go to War: A History of Video Game Controversy, GameSpot, Accessed February 24, 2009
- ^ Kushner, David, Nintendo Grows Up and Goes for the Gross-Out, The New York Times, May 10, 2001, Accessed February 24, 2009 [dead link]
- ^ Guifoil, John, The Old Shoebox: Download Blake Stone: Aliens of Gold, Blast, August 1, 2008, Accessed February 16, 2009
- ^ a b c d e f Shoemaker, Brad, The Greatest Games of All Time: Doom, GameSpot, Accessed February 18, 2009
- ^ Perry, Douglass C., Doom Review, IGN, October 3, 2006, Accessed February 24, 2009
- ^ Silverman, Ben, Controversial Games, Yahoo! Games, September 17, 2007, Accessed February 24, 2009
- ^ http://www.escapistmagazine.com/articles/view/issues/issue_45/274-From-94-to-Infinity-Before-Halo
- ^ A Brief History of Star War Games, Part 1, Tom's Hardware, May 20, 2007, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ Soete, Tim, Duke Nukem 3D Review, GameSpot, May 1, 1996, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ Geograph Seal (X68000), The Next Level
- ^ a b c King, Brad; Borland, John M. (2003). Dungeons and Dreamers: The Rise of Computer Game Culture from Geek to Chic. McGraw-Hill/Osborne. pp. 111–125. ISBN 0072228881. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
- ^ Ward, Trent C., Quake Review, GameSpot, June 22, 1996, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ Gerstmann, Jeff, GoldenEye 007 Review, GameSpot, August 19, 1997, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ Berghammer, Billy, A Rare Look at Rare, 1UP, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ Game Collector: This Means War!, GameSpot, September 7, 2001, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ a b King, Brad; Borland, John M. (2003). Dungeons and Dreamers: The Rise of Computer Game Culture from Geek to Chic. McGraw-Hill/Osborne. p. 211. ISBN 0072228881. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
- ^ Ocampo, Jason, Half-Life 10th Anniversary, IGN, November 19, 2008, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ Strife Review, GameSpot, June 27, 1996]
- ^ The Greatest Games of All Time: Half-Life, GameSpot, May 18, 2007, Accessed February 19, 2009
- ^ Butts, Steve, World War II Online, IGN, August 6, 2001, Accessed March 11, 2010
- ^ Bramwell, Tom, Sign-up for PlanetSide beta, EuroGamer, November 4, 2002, Accessed March 10, 2010
- ^ Doom 3 (PC), GameSpy, Accessed March 9, 2009
- ^ Fahey, Rob, UK Charts: Doom 3 scores first 2004 No.1 for PC platform, EuroGamer, August 17, 2004, Accessed March 9, 2009
- ^ Lyttle, John, John Lyttle - Shoot 'em up, New Statesman, December 5, 2005, Accessed March 7, 2009
- ^ Westbrook, Logan (March 9, 2010). "The Last Masquerade". The Escapist. Retrieved 2010-10-09.
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Paul, "Bioshock", PlayStation Official Magazine UK, December 2008 (issue 25), pp. 90-91
- ^ Cowen, Nick, The top 10 video games of 2007, The Telegraph, December 6, 2007, Accessed March 8, 2009
- ^ Hoggins, Tom, Why videogamers are artists at heart, The Telegraph, November 10, 2008, Accessed March 8, 2009
- ^ Kuo, Li C. (2006-05-10). "GameSpy: BioShock Preview". Gamespy. Retrieved 2007-11-04.
- ^ "IGN BioShock Interview". IGN. 2004-10-04. Retrieved 2007-10-07.
- ^ Hurley, Leon, "Far Cry 2", PlayStation Official Magazine UK, December 2008 (issue 25), pp. 98-100
- ^ Ditum, Nathan, "Resistance 2", PlayStation Official Magazine UK, December 2008 (issue 25), pp. 79-82
- ^ Cifaldi, Frank, Analysts: FPS 'Most Attractive' Genre for Publishers, GamaSutra, February 21, 2006, Accessed February 23, 2009
