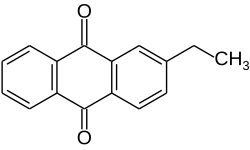
2-Ethylanthraquinone
Appearance
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
2-Ethyl-9,10-anthracenedione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.396 |
| EC Number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 236.27 g/mol |
| Appearance | white to yellowish crystals or powder |
| Density | 1.231g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 105 °C (221 °F; 378 K) |
| Boiling point | 415.4 @ 760mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 155.4°C, |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
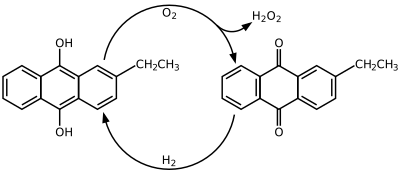
2-Ethylanthraquinone is an aromatic organic compound closely related to anthracene.
It is commonly used along with 2-ethyl-9,10-dihydroxyanthracene to create hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by the Riedl-Pfleiderer, or autoxidation, process: