Universe
| Part of a series on |
| Physical cosmology |
|---|
 |
The universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists,[1] including all physical matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space,[2][3] although this usage may differ with the context (see definitions, below). The term universe may be used in slightly different contextual senses, denoting such concepts as the cosmos, the world, or nature. Observations of earlier stages in the development of the universe, which can be seen at great distances, suggest that the universe has been governed by the same physical laws and constants throughout most of its extent and history.
History
Throughout recorded history, several cosmologies and cosmogonies have been proposed to account for observations of the universe. The earliest quantitative geocentric models were developed by the ancient Greeks, who proposed that the universe possesses infinite space and has existed eternally, but contains a single set of concentric spheres of finite size – corresponding to the fixed stars, the Sun and various planets – rotating about a spherical but unmoving Earth. Over the centuries, more precise observations and improved theories of gravity led to Copernicus's heliocentric model and the Newtonian model of the Solar System, respectively. Further improvements in astronomy led to the realization that the Solar System is embedded in a galaxy composed of billions of stars, the Milky Way, and that other galaxies exist outside it, as far as astronomical instruments can reach. Careful studies of the distribution of these galaxies and their spectral lines have led to much of modern cosmology. Discovery of the red shift and cosmic microwave background radiation revealed that the universe is expanding and apparently had a beginning.

According to the prevailing scientific model of the universe, known as the Big Bang, the universe expanded from an extremely hot, dense phase called the Planck epoch, in which all the matter and energy of the observable universe was concentrated. Since the Planck epoch, the universe has been expanding to its present form, possibly with a brief period (less than 10−32 seconds) of cosmic inflation. Several independent experimental measurements support this theoretical expansion and, more generally, the Big Bang theory. Recent observations indicate that this expansion is accelerating because of dark energy, and that most of the matter in the universe may be in a form which cannot be detected by present instruments, and so is not accounted for in the present models of the universe; this has been named dark matter. The imprecision of current observations has hindered predictions of the ultimate fate of the universe.
Current interpretations of astronomical observations indicate that the age of the universe is 13.75 ±0.17 billion years,[4] and that the diameter of the observable universe is at least 93 billion light years or 8.80×1026 metres.[5] According to general relativity, space can expand faster than the speed of light, although we can view only a small portion of the universe due to the limitation imposed by light speed. Since we cannot observe space beyond the limitations of light (or any electromagnetic radiation), it is uncertain whether the size of the universe is finite or infinite.
Etymology, synonyms and definitions
The word universe derives from the Old French word Univers, which in turn derives from the Latin word universum.[6] The Latin word was used by Cicero and later Latin authors in many of the same senses as the modern English word is used.[7] The Latin word derives from the poetic contraction Unvorsum — first used by Lucretius in Book IV (line 262) of his De rerum natura (On the Nature of Things) — which connects un, uni (the combining form of unus', or "one") with vorsum, versum (a noun made from the perfect passive participle of vertere, meaning "something rotated, rolled, changed").[7] Lucretius used the word in the sense "everything rolled into one, everything combined into one".

An alternative interpretation of unvorsum is "everything rotated as one" or "everything rotated by one". In this sense, it may be considered a translation of an earlier Greek word for the universe, Template:Polytonic, "something transported in a circle", originally used to describe a course of a meal, the food being carried around the circle of dinner guests.[8] This Greek word refers to an early Greek model of the universe, in which all matter was contained within rotating spheres centered on the Earth; according to Aristotle, the rotation of the outermost sphere was responsible for the motion and change of everything within. It was natural for the Greeks to assume that the Earth was stationary and that the heavens rotated about the Earth, because careful astronomical and physical measurements (such as the Foucault pendulum) are required to prove otherwise.
The most common term for "universe" among the ancient Greek philosophers from Pythagoras onwards was Template:Polytonic (The All), defined as all matter (Template:Polytonic) and all space (Template:Polytonic).[9][10] Other synonyms for the universe among the ancient Greek philosophers included Template:Polytonic (meaning the world, the cosmos) and Template:Polytonic (meaning Nature, from which we derive the word physics).[11] The same synonyms are found in Latin authors (totum, mundus, natura)[12] and survive in modern languages, e.g., the German words Das All, Weltall, and Natur for universe. The same synonyms are found in English, such as everything (as in the theory of everything), the cosmos (as in cosmology), the world (as in the many-worlds hypothesis), and Nature (as in natural laws or natural philosophy).[13]
Broadest definition: reality and probability
The broadest definition of the universe can be found in De divisione naturae by the medieval philosopher and theologian Johannes Scotus Eriugena, who defined it as simply everything: everything that is created and everything that is not created. Time is not considered in Eriugena's definition; thus, his definition includes everything that exists, has existed and will exist, as well as everything that does not exist, has never existed and will never exist. This all-embracing definition was not adopted by most later philosophers, but something not entirely dissimilar reappears in quantum physics, perhaps most obviously in the path-integral formulation of Feynman.[14] According to that formulation, the probability amplitudes for the various outcomes of an experiment given a perfectly defined initial state of the system are determined by summing over all possible paths by which the system could progress from the initial to final state. Naturally, an experiment can have only one outcome; in other words, only one possible outcome is made real in this universe, via the mysterious process of quantum measurement, also known as the collapse of the wavefunction (but see the many-worlds hypothesis below in the Multiverse section). In this well-defined mathematical sense, even that which does not exist (all possible paths) can influence that which does finally exist (the experimental measurement). As a specific example, every electron is intrinsically identical to every other; therefore, probability amplitudes must be computed allowing for the possibility that they exchange positions, something known as exchange symmetry. This conception of the universe embracing both the existent and the non-existent loosely parallels the Buddhist doctrines of shunyata and interdependent development of reality, and Gottfried Leibniz's more modern concepts of contingency and the identity of indiscernibles.
Definition as reality
More customarily, the universe is defined as everything that exists, has existed, and will exist [citation needed]. According to this definition and our present understanding, the universe consists of three elements: space and time, collectively known as space-time or the vacuum; matter and various forms of energy and momentum occupying space-time; and the physical laws that govern the first two. These elements will be discussed in greater detail below. A related definition of the term universe is everything that exists at a single moment of cosmological time, such as the present, as in the sentence "The universe is now bathed uniformly in microwave radiation".
The three elements of the universe (spacetime, matter-energy, and physical law) correspond roughly to the ideas of Aristotle. In his book The Physics (Template:Polytonic, from which we derive the word "physics"), Aristotle divided Template:Polytonic (everything) into three roughly analogous elements: matter (the stuff of which the universe is made), form (the arrangement of that matter in space) and change (how matter is created, destroyed or altered in its properties, and similarly, how form is altered). Physical laws were conceived as the rules governing the properties of matter, form and their changes. Later philosophers such as Lucretius, Averroes, Avicenna and Baruch Spinoza altered or refined these divisions[citation needed]; for example, Averroes and Spinoza discern natura naturans (the active principles governing the universe) from natura naturata, the passive elements upon which the former act.
Definition as connected space-time
It is possible to conceive of disconnected space-times, each existing but unable to interact with one another. An easily visualized metaphor is a group of separate soap bubbles, in which observers living on one soap bubble cannot interact with those on other soap bubbles, even in principle. According to one common terminology, each "soap bubble" of space-time is denoted as a universe, whereas our particular space-time is denoted as the universe, just as we call our moon the Moon. The entire collection of these separate space-times is denoted as the multiverse.[15] In principle, the other unconnected universes may have different dimensionalities and topologies of space-time, different forms of matter and energy, and different physical laws and physical constants, although such possibilities are currently speculative.
Definition as observable reality
According to a still-more-restrictive definition, the universe is everything within our connected space-time that could have a chance to interact with us and vice versa.[citation needed] According to the general theory of relativity, some regions of space may never interact with ours even in the lifetime of the universe, due to the finite speed of light and the ongoing expansion of space. For example, radio messages sent from Earth may never reach some regions of space, even if the universe would live forever; space may expand faster than light can traverse it. It is worth emphasizing that those distant regions of space are taken to exist and be part of reality as much as we are; yet we can never interact with them. The spatial region within which we can affect and be affected is denoted as the observable universe. Strictly speaking, the observable universe depends on the location of the observer. By traveling, an observer can come into contact with a greater region of space-time than an observer who remains still, so that the observable universe for the former is larger than for the latter. Nevertheless, even the most rapid traveler may not be able to interact with all of space. Typically, the observable universe is taken to mean the universe observable from our vantage point in the Milky Way Galaxy.
Size, age, contents, structure, and laws
The universe is immensely large and possibly infinite in volume. The region visible from Earth (the observable universe) is a sphere with a radius of about 46 billion light years,[16] based on where the expansion of space has taken the most distant objects observed. For comparison, the diameter of a typical galaxy is only 30,000 light-years, and the typical distance between two neighboring galaxies is only 3 million light-years.[17] As an example, our Milky Way Galaxy is roughly 100,000 light years in diameter,[18] and our nearest sister galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy, is located roughly 2.5 million light years away.[19] There are probably more than 100 billion (1011) galaxies in the observable universe.[20] Typical galaxies range from dwarfs with as few as ten million[21] (107) stars up to giants with one trillion[22] (1012) stars, all orbiting the galaxy's center of mass. Thus, a very rough estimate from these numbers would suggest there are around one sextillion (1021) stars in the observable universe; though a 2010 study by astronomers resulted in a figure of 300 sextillion (3×1023).[23]

The observable matter is spread uniformly (homogeneously) throughout the universe, when averaged over distances longer than 300 million light-years.[24] However, on smaller length-scales, matter is observed to form "clumps", i.e., to cluster hierarchically; many atoms are condensed into stars, most stars into galaxies, most galaxies into clusters, superclusters and, finally, the largest-scale structures such as the Great Wall of galaxies. The observable matter of the universe is also spread isotropically, meaning that no direction of observation seems different from any other; each region of the sky has roughly the same content.[25] The universe is also bathed in a highly isotropic microwave radiation that corresponds to a thermal equilibrium blackbody spectrum of roughly 2.725 kelvin.[26] The hypothesis that the large-scale universe is homogeneous and isotropic is known as the cosmological principle,[27] which is supported by astronomical observations.
The present overall density of the universe is very low, roughly 9.9 × 10−30 grams per cubic centimetre. This mass-energy appears to consist of 73% dark energy, 23% cold dark matter and 4% ordinary matter. Thus the density of atoms is on the order of a single hydrogen atom for every four cubic meters of volume.[28] The properties of dark energy and dark matter are largely unknown. Dark matter gravitates as ordinary matter, and thus works to slow the expansion of the universe; by contrast, dark energy accelerates its expansion.
The most precise estimate of the universe's age is 13.73±0.12 billion years old, based on observations of the cosmic microwave background radiation.[29] Independent estimates (based on measurements such as radioactive dating) agree, although they are less precise, ranging from 11–20 billion years[30] to 13–15 billion years.[31] The universe has not been the same at all times in its history; for example, the relative populations of quasars and galaxies have changed and space itself appears to have expanded. This expansion accounts for how Earth-bound scientists can observe the light from a galaxy 30 billion light years away, even if that light has traveled for only 13 billion years; the very space between them has expanded. This expansion is consistent with the observation that the light from distant galaxies has been redshifted; the photons emitted have been stretched to longer wavelengths and lower frequency during their journey. The rate of this spatial expansion is accelerating, based on studies of Type Ia supernovae and corroborated by other data.
The relative fractions of different chemical elements — particularly the lightest atoms such as hydrogen, deuterium and helium — seem to be identical throughout the universe and throughout its observable history.[32] The universe seems to have much more matter than antimatter, an asymmetry possibly related to the observations of CP violation.[33] The universe appears to have no net electric charge, and therefore gravity appears to be the dominant interaction on cosmological length scales. The universe also appears to have neither net momentum nor angular momentum. The absence of net charge and momentum would follow from accepted physical laws (Gauss's law and the non-divergence of the stress-energy-momentum pseudotensor, respectively), if the universe were finite.[34]

The universe appears to have a smooth space-time continuum consisting of three spatial dimensions and one temporal (time) dimension. On the average, space is observed to be very nearly flat (close to zero curvature), meaning that Euclidean geometry is experimentally true with high accuracy throughout most of the Universe.[35] Spacetime also appears to have a simply connected topology, at least on the length-scale of the observable universe. However, present observations cannot exclude the possibilities that the universe has more dimensions and that its spacetime may have a multiply connected global topology, in analogy with the cylindrical or toroidal topologies of two-dimensional spaces.[36]
The universe appears to behave in a manner that regularly follows a set of physical laws and physical constants.[37] According to the prevailing Standard Model of physics, all matter is composed of three generations of leptons and quarks, both of which are fermions. These elementary particles interact via at most three fundamental interactions: the electroweak interaction which includes electromagnetism and the weak nuclear force; the strong nuclear force described by quantum chromodynamics; and gravity, which is best described at present by general relativity. The first two interactions can be described by renormalized quantum field theory, and are mediated by gauge bosons that correspond to a particular type of gauge symmetry. A renormalized quantum field theory of general relativity has not yet been achieved, although various forms of string theory seem promising. The theory of special relativity is believed to hold throughout the universe, provided that the spatial and temporal length scales are sufficiently short; otherwise, the more general theory of general relativity must be applied. There is no explanation for the particular values that physical constants appear to have throughout our universe, such as Planck's constant h or the gravitational constant G. Several conservation laws have been identified, such as the conservation of charge, momentum, angular momentum and energy; in many cases, these conservation laws can be related to symmetries or mathematical identities.
Fine tuning
It appears that many of the properties of the universe have special values in the sense that a universe where these properties only differ slightly would not be able to support intelligent life.[38][39] Not all scientists agree that this fine-tuning exists.[40][41] In particular, it is not known under what conditions intelligent life could form and what form or shape that would take. A relevant observation in this discussion is that existence of an observer to observe fine-tuning, requires that the universe supports intelligent life. As such the conditional probability of observing a universe that is fine-tuned to support intelligent life is 1. This observation is known as the anthropic principle and is particularly relevant if the creation of the universe was probabilistic or if multiple universes with a variety of properties exist (see below).
Historical models
Many models of the cosmos (cosmologies) and its origin (cosmogonies) have been proposed, based on the then-available data and conceptions of the universe. Historically, cosmologies and cosmogonies were based on narratives of gods acting in various ways. Theories of an impersonal universe governed by physical laws were first proposed by the Greeks and Indians. Over the centuries, improvements in astronomical observations and theories of motion and gravitation led to ever more accurate descriptions of the universe. The modern era of cosmology began with Albert Einstein's 1915 general theory of relativity, which made it possible to quantitatively predict the origin, evolution, and conclusion of the universe as a whole. Most modern, accepted theories of cosmology are based on general relativity and, more specifically, the predicted Big Bang; however, still more careful measurements are required to determine which theory is correct.
Creation
Many cultures have stories describing the origin of the world, which may be roughly grouped into common types. In one type of story, the world is born from a world egg; such stories include the Finnish epic poem Kalevala, the Chinese story of Pangu or the Indian Brahmanda Purana. In related stories, the creation idea is caused by a single entity emanating or producing something by him- or herself, as in the Tibetan Buddhism concept of Adi-Buddha, the ancient Greek story of Gaia (Mother Earth), the Aztec goddess Coatlicue myth, the ancient Egyptian god Atum story, or the Genesis creation narrative. In another type of story, the world is created from the union of male and female deities, as in the Maori story of Rangi and Papa. In other stories, the universe is created by crafting it from pre-existing materials, such as the corpse of a dead god — as from Tiamat in the Babylonian epic Enuma Elish or from the giant Ymir in Norse mythology – or from chaotic materials, as in Izanagi and Izanami in Japanese mythology. In other stories, the universe emanates from fundamental principles, such as Brahman and Prakrti, or the yin and yang of the Tao.
Philosophical models
From the 6th century BCE, the pre-Socratic Greek philosophers developed the earliest known philosophical models of the universe. The earliest Greek philosophers noted that appearances can be deceiving, and sought to understand the underlying reality behind the appearances. In particular, they noted the ability of matter to change forms (e.g., ice to water to steam) and several philosophers proposed that all the apparently different materials of the world (wood, metal, etc.) are all different forms of a single material, the arche. The first to do so was Thales, who called this material Water. Following him, Anaximenes called it Air, and posited that there must be attractive and repulsive forces that cause the arche to condense or dissociate into different forms. Empedocles proposed that multiple fundamental materials were necessary to explain the diversity of the universe, and proposed that all four classical elements (Earth, Air, Fire and Water) existed, albeit in different combinations and forms. This four-element theory was adopted by many of the subsequent philosophers. Some philosophers before Empedocles advocated less material things for the arche; Heraclitus argued for a Logos, Pythagoras believed that all things were composed of numbers, whereas Thales' student, Anaximander, proposed that everything was composed of a chaotic substance known as apeiron, roughly corresponding to the modern concept of a quantum foam. Various modifications of the apeiron theory were proposed, most notably that of Anaxagoras, which proposed that the various matter in the world was spun off from a rapidly rotating apeiron, set in motion by the principle of Nous (Mind). Still other philosophers — most notably Leucippus and Democritus — proposed that the universe was composed of indivisible atoms moving through empty space, a vacuum; Aristotle opposed this view ("Nature abhors a vacuum") on the grounds that resistance to motion increases with density; hence, empty space should offer no resistance to motion, leading to the possibility of infinite speed.
Although Heraclitus argued for eternal change, his quasi-contemporary Parmenides made the radical suggestion that all change is an illusion, that the true underlying reality is eternally unchanging and of a single nature. Parmenides denoted this reality as Template:Polytonic (The One). Parmenides' theory seemed implausible to many Greeks, but his student Zeno of Elea challenged them with several famous paradoxes. Aristotle resolved these paradoxes by developing the notion of an infinitely divisible continuum, and applying it to space and time.
The Indian philosopher Kanada, founder of the Vaisheshika school, developed a theory of atomism and proposed that light and heat were varieties of the same substance.[42] In the 5th century AD, the Buddhist atomist philosopher Dignāga proposed atoms to be point-sized, durationless, and made of energy. They denied the existence of substantial matter and proposed that movement consisted of momentary flashes of a stream of energy.[43]
The theory of temporal finitism was inspired by the doctrine of creation shared by the three Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity and Islam. The Christian philosopher, John Philoponus, presented the philosophical arguments against the ancient Greek notion of an infinite past. Philoponus' arguments against an infinite past were used by the early Muslim philosopher, Al-Kindi (Alkindus); the Jewish philosopher, Saadia Gaon (Saadia ben Joseph); and the Muslim theologian, Al-Ghazali (Algazel). They employed two logical arguments against an infinite past, the first being the "argument from the impossibility of the existence of an actual infinite", which states:[44]
- "An actual infinite cannot exist."
- "An infinite temporal regress of events is an actual infinite."
- " An infinite temporal regress of events cannot exist."
The second argument, the "argument from the impossibility of completing an actual infinite by successive addition", states:[44]
- "An actual infinite cannot be completed by successive addition."
- "The temporal series of past events has been completed by successive addition."
- " The temporal series of past events cannot be an actual infinite."
Both arguments were adopted by later Christian philosophers and theologians, and the second argument in particular became more famous after it was adopted by Immanuel Kant in his thesis of the first antinomy concerning time.[44]
Astronomical models
Astronomical models of the universe were proposed soon after astronomy began with the Babylonian astronomers, who viewed the universe as a flat disk floating in the ocean, and this forms the premise for early Greek maps like those of Anaximander and Hecataeus of Miletus.
Later Greek philosophers, observing the motions of the heavenly bodies, were concerned with developing models of the universe based more profoundly on empirical evidence. The first coherent model was proposed by Eudoxus of Cnidos. According to this model, space and time are infinite and eternal, the Earth is spherical and stationary, and all other matter is confined to rotating concentric spheres. This model was refined by Callippus and Aristotle, and brought into nearly perfect agreement with astronomical observations by Ptolemy. The success of this model is largely due to the mathematical fact that any function (such as the position of a planet) can be decomposed into a set of circular functions (the Fourier modes). However, not all Greek scientists accepted the geocentric model of the universe. The Pythagorean philosopher Philolaus postulated that at the center of the universe was a "central fire" around which the Earth, Sun, Moon and Planets revolved in uniform circular motion.[45] The Greek astronomer Aristarchus of Samos was the first known individual to propose a heliocentric model of the universe. Though the original text has been lost, a reference in Archimedes' book The Sand Reckoner describes Aristarchus' heliocentric theory. Archimedes wrote: (translated into English)
You King Gelon are aware the 'universe' is the name given by most astronomers to the sphere the center of which is the center of the Earth, while its radius is equal to the straight line between the center of the Sun and the center of the Earth. This is the common account as you have heard from astronomers. But Aristarchus has brought out a book consisting of certain hypotheses, wherein it appears, as a consequence of the assumptions made, that the universe is many times greater than the 'universe' just mentioned. His hypotheses are that the fixed stars and the Sun remain unmoved, that the Earth revolves about the Sun on the circumference of a circle, the Sun lying in the middle of the orbit, and that the sphere of fixed stars, situated about the same center as the Sun, is so great that the circle in which he supposes the Earth to revolve bears such a proportion to the distance of the fixed stars as the center of the sphere bears to its surface.
Aristarchus thus believed the stars to be very far away, and saw this as the reason why there was no visible parallax, that is, an observed movement of the stars relative to each other as the Earth moved around the Sun. The stars are in fact much farther away than the distance that was generally assumed in ancient times, which is why stellar parallax is only detectable with telescopes. The geocentric model, consistent with planetary parallax, was assumed to be an explanation for the unobservability of the parallel phenomenon, stellar parallax. The rejection of the heliocentric view was apparently quite strong, as the following passage from Plutarch suggests (On the Apparent Face in the Orb of the Moon):
Cleanthes [a contemporary of Aristarchus and head of the Stoics] thought it was the duty of the Greeks to indict Aristarchus of Samos on the charge of impiety for putting in motion the Hearth of the universe [i.e. the earth], . . . supposing the heaven to remain at rest and the earth to revolve in an oblique circle, while it rotates, at the same time, about its own axis. [1]
The only other astronomer from antiquity known by name who supported Aristarchus' heliocentric model was Seleucus of Seleucia, a Hellenized Babylonian astronomer who lived a century after Aristarchus.[46][47][48] According to Plutarch, Seleucus was the first to prove the heliocentric system through reasoning, but it is not known what arguments he used. Seleucus' arguments for a heliocentric theory were probably related to the phenomenon of tides.[49] According to Strabo (1.1.9), Seleucus was the first to state that the tides are due to the attraction of the Moon, and that the height of the tides depends on the Moon's position relative to the Sun.[50] Alternatively, he may have proved the heliocentric theory by determining the constants of a geometric model for the heliocentric theory and by developing methods to compute planetary positions using this model, like what Nicolaus Copernicus later did in the 16th century.[51] During the Middle Ages, heliocentric models may have also been proposed by the Indian astronomer, Aryabhata,[52] and by the Persian astronomers, Albumasar[53] and Al-Sijzi.[54]

The Aristotelian model was accepted in the Western world for roughly two millennia, until Copernicus revived Aristarchus' theory that the astronomical data could be explained more plausibly if the earth rotated on its axis and if the sun were placed at the center of the universe.
In the center rests the sun. For who would place this lamp of a very beautiful temple in another or better place than this wherefrom it can illuminate everything at the same time?
— Nicolaus Copernicus, in Chapter 10, Book 1 of De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestrum (1543)
As noted by Copernicus himself, the suggestion that the Earth rotates was very old, dating at least to Philolaus (c. 450 BC), Heraclides Ponticus (c. 350 BC) and Ecphantus the Pythagorean. Roughly a century before Copernicus, Christian scholar Nicholas of Cusa also proposed that the Earth rotates on its axis in his book, On Learned Ignorance (1440).[55] Aryabhata (476–550), Brahmagupta (598–668), Albumasar and Al-Sijzi, also proposed that the Earth rotates on its axis.[citation needed] The first empirical evidence for the Earth's rotation on its axis, using the phenomenon of comets, was given by Tusi (1201–1274) and Ali Qushji (1403–1474).[citation needed] Tusi, however, continued to support the Aristotelian universe, thus Qushji was the first to refute the Aristotelian notion of a stationary Earth on an empirical basis, similar to how Copernicus later justified the Earth's rotation. Al-Birjandi (d. 1528) further developed a theory of "circular inertia" to explain the Earth's rotation, similar to how Galileo Galilei explained it.[56][57]

Copernicus' heliocentric model allowed the stars to be placed uniformly through the (infinite) space surrounding the planets, as first proposed by Thomas Digges in his Perfit Description of the Caelestiall Orbes according to the most aunciente doctrine of the Pythagoreans, latelye revived by Copernicus and by Geometricall Demonstrations approved (1576).[58] Giordano Bruno accepted the idea that space was infinite and filled with solar systems similar to our own; for the publication of this view, he was burned at the stake in the Campo dei Fiori in Rome on 17 February 1600.[58]
This cosmology was accepted provisionally by Isaac Newton, Christiaan Huygens and later scientists,[58] although it had several paradoxes that were resolved only with the development of general relativity. The first of these was that it assumed that space and time were infinite, and that the stars in the universe had been burning forever; however, since stars are constantly radiating energy, a finite star seems inconsistent with the radiation of infinite energy. Secondly, Edmund Halley (1720)[59] and Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux (1744)[60] noted independently that the assumption of an infinite space filled uniformly with stars would lead to the prediction that the nighttime sky would be as bright as the sun itself; this became known as Olbers' paradox in the 19th century.[61] Third, Newton himself showed that an infinite space uniformly filled with matter would cause infinite forces and instabilities causing the matter to be crushed inwards under its own gravity.[58] This instability was clarified in 1902 by the Jeans instability criterion.[62] One solution to these latter two paradoxes is the Charlier universe, in which the matter is arranged hierarchically (systems of orbiting bodies that are themselves orbiting in a larger system, ad infinitum) in a fractal way such that the universe has a negligibly small overall density; such a cosmological model had also been proposed earlier in 1761 by Johann Heinrich Lambert.[63] A significant astronomical advance of the 18th century was the realization by Thomas Wright, Immanuel Kant and others that stars are not distributed uniformly throughout space; rather, they are grouped into galaxies.[64]
The modern era of physical cosmology began in 1917, when Albert Einstein first applied his general theory of relativity to model the structure and dynamics of the universe.[65] This theory and its implications will be discussed in more detail in the following section.
Theoretical models

Of the four fundamental interactions, gravitation is dominant at cosmological length scales; that is, the other three forces are believed to play a negligible role in determining structures at the level of planets, stars, galaxies and larger-scale structures. Since all matter and energy gravitate, gravity's effects are cumulative; by contrast, the effects of positive and negative charges tend to cancel one another, making electromagnetism relatively insignificant on cosmological length scales. The remaining two interactions, the weak and strong nuclear forces, decline very rapidly with distance; their effects are confined mainly to sub-atomic length scales.
General theory of relativity
Given gravitation's predominance in shaping cosmological structures, accurate predictions of the universe's past and future require an accurate theory of gravitation. The best theory available is Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which has passed all experimental tests hitherto. However, since rigorous experiments have not been carried out on cosmological length scales, general relativity could conceivably be inaccurate. Nevertheless, its cosmological predictions appear to be consistent with observations, so there is no compelling reason to adopt another theory.
General relativity provides of a set of ten nonlinear partial differential equations for the spacetime metric (Einstein's field equations) that must be solved from the distribution of mass-energy and momentum throughout the universe. Since these are unknown in exact detail, cosmological models have been based on the cosmological principle, which states that the universe is homogeneous and isotropic. In effect, this principle asserts that the gravitational effects of the various galaxies making up the universe are equivalent to those of a fine dust distributed uniformly throughout the universe with the same average density. The assumption of a uniform dust makes it easy to solve Einstein's field equations and predict the past and future of the universe on cosmological time scales.
Einstein's field equations include a cosmological constant (Λ),[65][66] that corresponds to an energy density of empty space.[67] Depending on its sign, the cosmological constant can either slow (negative Λ) or accelerate (positive Λ) the expansion of the universe. Although many scientists, including Einstein, had speculated that Λ was zero,[68] recent astronomical observations of type Ia supernovae have detected a large amount of "dark energy" that is accelerating the universe's expansion.[69] Preliminary studies suggest that this dark energy corresponds to a positive Λ, although alternative theories cannot be ruled out as yet.[70] Russian physicist Zel'dovich suggested that Λ is a measure of the zero-point energy associated with virtual particles of quantum field theory, a pervasive vacuum energy that exists everywhere, even in empty space.[71] Evidence for such zero-point energy is observed in the Casimir effect.
Special relativity and space-time

The universe has at least three spatial and one temporal (time) dimension. It was long thought that the spatial and temporal dimensions were different in nature and independent of one another. However, according to the special theory of relativity, spatial and temporal separations are interconvertible (within limits) by changing one's motion.
To understand this interconversion, it is helpful to consider the analogous interconversion of spatial separations along the three spatial dimensions. Consider the two endpoints of a rod of length L. The length can be determined from the differences in the three coordinates Δx, Δy and Δz of the two endpoints in a given reference frame
using the Pythagorean theorem. In a rotated reference frame, the coordinate differences differ, but they give the same length
Thus, the coordinates differences (Δx, Δy, Δz) and (Δξ, Δη, Δζ) are not intrinsic to the rod, but merely reflect the reference frame used to describe it; by contrast, the length L is an intrinsic property of the rod. The coordinate differences can be changed without affecting the rod, by rotating one's reference frame.
The analogy in spacetime is called the interval between two events; an event is defined as a point in spacetime, a specific position in space and a specific moment in time. The spacetime interval between two events is given by
where c is the speed of light. According to special relativity, one can change a spatial and time separation (L1, Δt1) into another (L2, Δt2) by changing one's reference frame, as long as the change maintains the spacetime interval s. Such a change in reference frame corresponds to changing one's motion; in a moving frame, lengths and times are different from their counterparts in a stationary reference frame. The precise manner in which the coordinate and time differences change with motion is described by the Lorentz transformation.
Solving Einstein's field equations
The distances between the spinning galaxies increase with time, but the distances between the stars within each galaxy stay roughly the same, due to their gravitational interactions. This animation illustrates a closed Friedmann universe with zero cosmological constant Λ; such a universe oscillates between a Big Bang and a Big Crunch.
In non-Cartesian (non-square) or curved coordinate systems, the Pythagorean theorem holds only on infinitesimal length scales and must be augmented with a more general metric tensor gμν, which can vary from place to place and which describes the local geometry in the particular coordinate system. However, assuming the cosmological principle that the universe is homogeneous and isotropic everywhere, every point in space is like every other point; hence, the metric tensor must be the same everywhere. That leads to a single form for the metric tensor, called the Friedmann-Lemaître-Robertson-Walker metric
where (r, θ, φ) correspond to a spherical coordinate system. This metric has only two undetermined parameters: an overall length scale R that can vary with time, and a curvature index k that can be only 0, 1 or −1, corresponding to flat Euclidean geometry, or spaces of positive or negative curvature. In cosmology, solving for the history of the universe is done by calculating R as a function of time, given k and the value of the cosmological constant Λ, which is a (small) parameter in Einstein's field equations. The equation describing how R varies with time is known as the Friedmann equation, after its inventor, Alexander Friedmann.[72]
The solutions for R(t) depend on k and Λ, but some qualitative features of such solutions are general. First and most importantly, the length scale R of the universe can remain constant only if the universe is perfectly isotropic with positive curvature (k=1) and has one precise value of density everywhere, as first noted by Albert Einstein. However, this equilibrium is unstable and since the universe is known to be inhomogeneous on smaller scales, R must change, according to general relativity. When R changes, all the spatial distances in the universe change in tandem; there is an overall expansion or contraction of space itself. This accounts for the observation that galaxies appear to be flying apart; the space between them is stretching. The stretching of space also accounts for the apparent paradox that two galaxies can be 40 billion light years apart, although they started from the same point 13.7 billion years ago and never moved faster than the speed of light.
Second, all solutions suggest that there was a gravitational singularity in the past, when R goes to zero and matter and energy became infinitely dense. It may seem that this conclusion is uncertain since it is based on the questionable assumptions of perfect homogeneity and isotropy (the cosmological principle) and that only the gravitational interaction is significant. However, the Penrose-Hawking singularity theorems show that a singularity should exist for very general conditions. Hence, according to Einstein's field equations, R grew rapidly from an unimaginably hot, dense state that existed immediately following this singularity (when R had a small, finite value); this is the essence of the Big Bang model of the universe. A common misconception is that the Big Bang model predicts that matter and energy exploded from a single point in space and time; that is false. Rather, space itself was created in the Big Bang and imbued with a fixed amount of energy and matter distributed uniformly throughout; as space expands (i.e., as R(t) increases), the density of that matter and energy decreases.
|
Space has no boundary – that is empirically more certain than any external observation. However, that does not imply that space is infinite...(translated, original German) |
| Bernhard Riemann (Habilitationsvortrag, 1854) |
Third, the curvature index k determines the sign of the mean spatial curvature of spacetime averaged over length scales greater than a billion light years. If k=1, the curvature is positive and the universe has a finite volume. Such universes are often visualized as a three-dimensional sphere S3 embedded in a four-dimensional space. Conversely, if k is zero or negative, the universe may have infinite volume, depending on its overall topology. It may seem counter-intuitive that an infinite and yet infinitely dense universe could be created in a single instant at the Big Bang when R=0, but exactly that is predicted mathematically when k does not equal 1. For comparison, an infinite plane has zero curvature but infinite area, whereas an infinite cylinder is finite in one direction and a torus is finite in both. A toroidal universe could behave like a normal universe with periodic boundary conditions, as seen in "wrap-around" video games such as Asteroids; a traveler crossing an outer "boundary" of space going outwards would reappear instantly at another point on the boundary moving inwards.

The ultimate fate of the universe is still unknown, because it depends critically on the curvature index k and the cosmological constant Λ. If the universe is sufficiently dense, k equals +1, meaning that its average curvature throughout is positive and the universe will eventually recollapse in a Big Crunch, possibly starting a new universe in a Big Bounce. Conversely, if the universe is insufficiently dense, k equals 0 or −1 and the universe will expand forever, cooling off and eventually becoming inhospitable for all life, as the stars die and all matter coalesces into black holes (the Big Freeze and the heat death of the universe). As noted above, recent data suggests that the expansion speed of the universe is not decreasing as originally expected, but increasing; if this continues indefinitely, the universe will eventually rip itself to shreds (the Big Rip). Experimentally, the universe has an overall density that is very close to the critical value between recollapse and eternal expansion; more careful astronomical observations are needed to resolve the question.
Big Bang model
The prevailing Big Bang model accounts for many of the experimental observations described above, such as the correlation of distance and redshift of galaxies, the universal ratio of hydrogen:helium atoms, and the ubiquitous, isotropic microwave radiation background. As noted above, the redshift arises from the metric expansion of space; as the space itself expands, the wavelength of a photon traveling through space likewise increases, decreasing its energy. The longer a photon has been traveling, the more expansion it has undergone; hence, older photons from more distant galaxies are the most red-shifted. Determining the correlation between distance and redshift is an important problem in experimental physical cosmology.

Other experimental observations can be explained by combining the overall expansion of space with nuclear and atomic physics. As the universe expands, the energy density of the electromagnetic radiation decreases more quickly than does that of matter, since the energy of a photon decreases with its wavelength. Thus, although the energy density of the universe is now dominated by matter, it was once dominated by radiation; poetically speaking, all was light. As the universe expanded, its energy density decreased and it became cooler; as it did so, the elementary particles of matter could associate stably into ever larger combinations. Thus, in the early part of the matter-dominated era, stable protons and neutrons formed, which then associated into atomic nuclei. At this stage, the matter in the universe was mainly a hot, dense plasma of negative electrons, neutral neutrinos and positive nuclei. Nuclear reactions among the nuclei led to the present abundances of the lighter nuclei, particularly hydrogen, deuterium, and helium. Eventually, the electrons and nuclei combined to form stable atoms, which are transparent to most wavelengths of radiation; at this point, the radiation decoupled from the matter, forming the ubiquitous, isotropic background of microwave radiation observed today.
Other observations are not answered definitively by known physics. According to the prevailing theory, a slight imbalance of matter over antimatter was present in the universe's creation, or developed very shortly thereafter, possibly due to the CP violation that has been observed by particle physicists. Although the matter and antimatter mostly annihilated one another, producing photons, a small residue of matter survived, giving the present matter-dominated universe. Several lines of evidence also suggest that a rapid cosmic inflation of the universe occurred very early in its history (roughly 10−35 seconds after its creation). Recent observations also suggest that the cosmological constant (Λ) is not zero and that the net mass-energy content of the universe is dominated by a dark energy and dark matter that have not been characterized scientifically. They differ in their gravitational effects. Dark matter gravitates as ordinary matter does, and thus slows the expansion of the universe; by contrast, dark energy serves to accelerate the universe's expansion.
Multiverse theory

Some speculative theories have proposed that this universe is but one of a set of disconnected universes, collectively denoted as the multiverse, altering the concept that the universe encompasses everything.[15][73] By definition, there is no possible way for anything in one universe to affect another; if two "universes" could affect one another, they would be part of a single universe. Thus, although some fictional characters travel between parallel fictional "universes", this is, strictly speaking, an incorrect usage of the term universe. The disconnected universes are conceived as being physical, in the sense that each should have its own space and time, its own matter and energy, and its own physical laws — that also challenges the definition of parallelity as these universes don't exist synchronously (since they have their own time) or in a geometrically parallel way (since there's no interpretable relation between spatial positions of the different universes). Such physically disconnected universes should be distinguished from the metaphysical conception of alternate planes of consciousness, which are not thought to be physical places and are connected through the flow of information. The concept of a multiverse of disconnected universes is very old; for example, Bishop Étienne Tempier of Paris ruled in 1277 that God could create as many universes as he saw fit, a question that was being hotly debated by the French theologians.[74]
There are two scientific senses in which multiple universes are discussed. First, disconnected spacetime continua may exist; presumably, all forms of matter and energy are confined to one universe and cannot "tunnel" between them. An example of such a theory is the chaotic inflation model of the early universe.[75] Second, according to the many-worlds hypothesis, a parallel universe is born with every quantum measurement; the universe "forks" into parallel copies, each one corresponding to a different outcome of the quantum measurement. However, both senses of the term "multiverse" are speculative and may be considered unscientific; no known experimental test in one universe could reveal the existence or properties of another non-interacting universe.
Shape of the universe
The shape or geometry of the universe includes both local geometry in the observable universe and global geometry, which we may or may not be able to measure. Shape can refer to curvature and topology. More formally, the subject in practice investigates which 3-manifold corresponds to the spatial section in comoving coordinates of the four-dimensional space-time of the universe. Cosmologists normally work with a given space-like slice of spacetime called the comoving coordinates. In terms of observation, the section of spacetime that can be observed is the backward light cone (points within the cosmic light horizon, given time to reach a given observer). If the observable universe is smaller than the entire universe (in some models it is many orders of magnitude smaller), one cannot determine the global structure by observation: one is limited to a small patch.
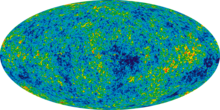
Among the Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker (FLRW) models, the presently most popular shape of the Universe found to fit observational data according to cosmologists is the infinite flat model,[76] while other FLRW models include the Poincaré dodecahedral space[77][78] and the Picard horn.[79] The data fit by these FLRW models of space especially include the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) maps of cosmic background radiation. NASA released the first WMAP cosmic background radiation data in February 2003. In 2009 the Planck observatory was launched to observe the microwave background at higher resolution than WMAP, possibly providing more information on the shape of the Universe. The data will in principle be released in late 2012.
See also
- Cosmic latte
- Cosmology
- Dyson's eternal intelligence
- Esoteric cosmology
- False vacuum
- Final anthropic principle
- Hindu cycle of the universe
- Kardashev scale
- The Mysterious Universe (book)
- Nucleocosmochronology
- Non-standard cosmology
- Omega Point
- Omniverse
- Rare Earth hypothesis
- Vacuum genesis
- World view
- Zero-energy universe
Notes and references
- ^ Webster's New World College Dictionary. Wiley Publishing, Inc. 2010.
- ^ The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language (4th ed.). Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. 2010.
- ^ Cambridge Advanced Learner's Dictionary.
- ^ S. H. Suyu, P. J. Marshall, M. W. Auger, S. Hilbert, R. D. Blandford, L. V. E. Koopmans, C. D. Fassnacht and T. Treu. Dissecting the Gravitational Lens B1608+656. II. Precision Measurements of the Hubble Constant, Spatial Curvature, and the Dark Energy Equation of State. The Astrophysical Journal, 2010; 711 (1): 201 DOI: 10.1088/0004-637X/711/1/201
- ^ Lineweaver, Charles (2005). "Misconceptions about the Big Bang". Scientific American. Retrieved 2008-11-06.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ The Compact Edition of the Oxford English Dictionary, volume II, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1971, p.3518.
- ^ a b Lewis and Short, A Latin Dictionary, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-864201-6, pp. 1933, 1977–1978.
- ^ Liddell and Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-864214-8, p.1392.
- ^ Liddell and Scott, pp.1345–1346.
- ^ Yonge, Charles Duke (1870). An English-Greek lexicon. New York: American Bok Company. p. 567.
- ^ Liddell and Scott, pp.985, 1964.
- ^ Lewis and Short, pp. 1881–1882, 1175, 1189–1190.
- ^ OED, pp. 909, 569, 3821–3822, 1900.
- ^ Feynman RP, Hibbs AR (1965). Quantum Physics and Path Integrals. New York: McGraw–Hill. ISBN 0-07-020650-3.
Zinn Justin J (2004). Path Integrals in Quantum Mechanics. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-856674-3. OCLC 212409192. - ^ a b Ellis, George F.R. (2004). "Multiverses and physical cosmology" (subscription required). Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 347 (3): 921–936. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07261.x. Retrieved 2007-01-09.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Lineweaver, Charles (2005). "Misconceptions about the Big Bang" (PDF). Scientific American. Retrieved 2007-03-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Rindler (1977), p.196.
- ^ Christian, Eric; Samar, Safi-Harb. "How large is the Milky Way?". Retrieved 2007-11-28.
- ^ I. Ribas, C. Jordi, F. Vilardell, E.L. Fitzpatrick, R.W. Hilditch, F. Edward (2005). "First Determination of the Distance and Fundamental Properties of an Eclipsing Binary in the Andromeda Galaxy". Astrophysical Journal. 635 (1): L37 – L40. Bibcode:2005ApJ...635L..37R. doi:10.1086/499161.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
McConnachie, A. W.; Irwin, M. J.; Ferguson, A. M. N.; Ibata, R. A.; Lewis, G. F.; Tanvir, N. (2005). "Distances and metallicities for 17 Local Group galaxies". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 356 (4): 979–997. Bibcode:2005MNRAS.356..979M. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08514.x.{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mackie, Glen (February 1, 2002). "To see the Universe in a Grain of Taranaki Sand". Swinburne University. Retrieved 2006-12-20.
- ^ "Unveiling the Secret of a Virgo Dwarf Galaxy". ESO. 2000-05-03. Retrieved 2007-01-03.
- ^ "Hubble's Largest Galaxy Portrait Offers a New High-Definition View". NASA. 2006-02-28. Retrieved 2007-01-03.
- ^ Vergano, Dan (1 December 2010). "Universe holds billions more stars than previously thought". USA Today. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ N. Mandolesi, P. Calzolari, S. Cortiglioni, F. Delpino, G. Sironi (1986). "Large-scale homogeneity of the Universe measured by the microwave background". Letters to Nature. 319 (6056): 751–753. doi:10.1038/319751a0.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hinshaw, Gary (November 29, 2006). "New Three Year Results on the Oldest Light in the Universe". NASA WMAP. Retrieved 2006-08-10.
- ^ Hinshaw, Gary (December 15, 2005). "Tests of the Big Bang: The CMB". NASA WMAP. Retrieved 2007-01-09.
- ^ Rindler (1977), p. 202.
- ^ Hinshaw, Gary (February 10, 2006). "What is the Universe Made Of?". NASA WMAP. Retrieved 2007-01-04.
- ^ "Five-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Data Processing, Sky Maps, and Basic Results" (PDF). nasa.gov. Retrieved 2008-03-06.
- ^ Britt RR (2003-01-03). "Age of Universe Revised, Again". space.com. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ^ Wright EL (2005). "Age of the Universe". UCLA. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
Krauss LM, Chaboyer B (3 January 2003). "Age Estimates of Globular Clusters in the Milky Way: Constraints on Cosmology". Science. 299 (5603). American Association for the Advancement of Science: 65–69. doi:10.1126/science.1075631. PMID 12511641. Retrieved 2007-01-08. - ^ Wright, Edward L. (September 12, 2004). "Big Bang Nucleosynthesis". UCLA. Retrieved 2007-01-05.
M. Harwit, M. Spaans (2003). "Chemical Composition of the Early Universe". The Astrophysical Journal. 589 (1): 53–57. Bibcode:2003ApJ...589...53H. doi:10.1086/374415.
C. Kobulnicky, E. D. Skillman (1997). "Chemical Composition of the Early Universe". Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society. 29: 1329. Bibcode:1997AAS...191.7603K. - ^ "Antimatter". Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Council. October 28, 2003. Retrieved 2006-08-10.
- ^ Landau and Lifshitz (1975), p.361.
- ^ WMAP Mission: Results – Age of the Universe
- ^ Luminet, Jean-Pierre (1999). "Topology of the Universe: Theory and Observations". Proceedings of Cosmology School held at Cargese, Corsica, August 1998. Retrieved 2007-01-05.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
Luminet, Jean-Pierre (2003). "Dodecahedral space topology as an explanation for weak wide-angle temperature correlations in the cosmic microwave background" (subscription required). Nature. 425 (6958): 593–5. doi:10.1038/nature01944. PMID 14534579. Retrieved 2007-01-09.{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Strobel, Nick (May 23, 2001). "The Composition of Stars". Astronomy Notes. Retrieved 2007-01-04.
"Have physical constants changed with time?". Astrophysics (Astronomy Frequently Asked Questions). Retrieved 2007-01-04. - ^ Stephen Hawking (1988). A Brief History of Time. Bantam Books. p. 125. ISBN 0-553-05340-X.
- ^ Martin Rees (1999). Just Six Numbers. HarperCollins Publishers. ISBN 0-465-03672-4.
- ^ Adams, F.C. (2008). "Stars in other universes: stellar structure with different fundamental constants". Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics. 2008 (08): 010. doi:10.1088/1475-7516/2008/08/010.
- ^ Harnik, R. (2006). "A universe without weak interactions". Physical Review D. 74 (3): 035006. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.74.035006.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Will Durant, Our Oriental Heritage:
"Two systems of Hindu thought propound physical theories suggestively similar to those of Greece. Kanada, founder of the Vaisheshika philosophy, held that the world was composed of atoms as many in kind as the various elements. The Jains more nearly approximated to Democritus by teaching that all atoms were of the same kind, producing different effects by diverse modes of combinations. Kanada believed light and heat to be varieties of the same substance; Udayana taught that all heat comes from the sun; and Vachaspati, like Newton, interpreted light as composed of minute particles emitted by substances and striking the eye."
- ^ F. Th. Stcherbatsky (1930, 1962), Buddhist Logic, Volume 1, p.19, Dover, New York:
"The Buddhists denied the existence of substantial matter altogether. Movement consists for them of moments, it is a staccato movement, momentary flashes of a stream of energy... "Everything is evanescent“,... says the Buddhist, because there is no stuff... Both systems [Sānkhya, and later Indian Buddhism] share in common a tendency to push the analysis of Existence up to its minutest, last elements which are imagined as absolute qualities, or things possessing only one unique quality. They are called “qualities” (guna-dharma) in both systems in the sense of absolute qualities, a kind of atomic, or intra-atomic, energies of which the empirical things are composed. Both systems, therefore, agree in denying the objective reality of the categories of Substance and Quality,... and of the relation of Inference uniting them. There is in Sānkhya philosophy no separate existence of qualities. What we call quality is but a particular manifestation of a subtle entity. To every new unit of quality corresponds a subtle quantum of matter which is called guna “quality”, but represents a subtle substantive entity. The same applies to early Buddhism where all qualities are substantive... or, more precisely, dynamic entities, although they are also called dharmas ('qualities')."
- ^ a b c Craig, William Lane (June 1979). "Whitrow and Popper on the Impossibility of an Infinite Past". The British Journal for the Philosophy of Science. 30 (2): 165–170 [165–6]. doi:10.1093/bjps/30.2.165.
- ^ Boyer, C. A History of Mathematics. Wiley, p. 54.
- ^ Otto E. Neugebauer (1945). "The History of Ancient Astronomy Problems and Methods", Journal of Near Eastern Studies 4 (1), p. 1–38.
"the Chaldaean Seleucus from Seleucia"
- ^ George Sarton (1955). "Chaldaean Astronomy of the Last Three Centuries B. C.", Journal of the American Oriental Society 75 (3), pp. 166–173 [169]:
"the heliocentrical astronomy invented by Aristarchos of Samos and still defended a century later by Seleucos the Babylonian"
- ^ William P. D. Wightman (1951, 1953), The Growth of Scientific Ideas, Yale University Press p.38, where Wightman calls him Seleukos the Chaldean.
- ^ Lucio Russo, Flussi e riflussi, Feltrinelli, Milano, 2003, ISBN 88-07-10349-4.
- ^ Bartel (1987). "The Heliocentric System in Greek, Persian and Hindu Astronomy". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 500 (1): 525–545 [527]. Bibcode:1987NYASA.500..525V. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb37224.x.
- ^ Bartel (1987). "The Heliocentric System in Greek, Persian and Hindu Astronomy". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 500 (1): 525–545 [527–9]. Bibcode:1987NYASA.500..525V. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb37224.x.
- ^ Bartel (1987). "The Heliocentric System in Greek, Persian and Hindu Astronomy". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 500 (1): 525–545 [529–34]. Bibcode:1987NYASA.500..525V. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb37224.x.
- ^ Bartel (1987). "The Heliocentric System in Greek, Persian and Hindu Astronomy". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 500 (1): 525–545 [534–7]. Bibcode:1987NYASA.500..525V. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb37224.x.
- ^ Nasr, Seyyed H. (1st edition in 1964, 2nd edition in 1993). An Introduction to Islamic Cosmological Doctrines (2nd ed.). 1st edition by Harvard University Press, 2nd edition by State University of New York Press. pp. 135–6. ISBN 0791415155.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Misner, Thorne and Wheeler (1973), p. 754.
- ^ Ragep, F. Jamil (2001a). "Tusi and Copernicus: The Earth's Motion in Context". Science in Context. 14 (1–2). Cambridge University Press: 145–63.
- ^ Ragep, F. Jamil (2001b). "Freeing Astronomy from Philosophy: An Aspect of Islamic Influence on Science". Osiris, 2nd Series. 16 (Science in Theistic Contexts: Cognitive Dimensions): 49–64 & 66–71. Bibcode:2001Osir...16...49R. JSTOR 301979.
- ^ a b c d Misner, Thorne, and Wheeler (1973), p.755. Cite error: The named reference "Misner-p755" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Misner, Thorne, and Wheeler (1973), p. 756.
- ^ de Cheseaux JPL (1744). Traité de la Comète. Lausanne. pp. 223ff.. Reprinted as Appendix II in Dickson FP (1969). The Bowl of Night: The Physical Universe and Scientific Thought. Cambridge, MA: M.I.T. Press. ISBN 978-0262540032.
- ^ Olbers HWM (1826). "Unknown title". Bode's Jahrbuch. 111.. Reprinted as Appendix I in Dickson FP (1969). The Bowl of Night: The Physical Universe and Scientific Thought. Cambridge, MA: M.I.T. Press. ISBN 978-0262540032.
- ^ Jeans, J. H. (1902). "The Stability of a Spherical Nebula" (PDF). Philosophical Transactions Royal Society of London, Series A. 199 (312–320): 1–53. Bibcode:1902RSPTA.199....1J. doi:10.1098/rsta.1902.0012. JSTOR 90845. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ Rindler, p. 196; Misner, Thorne, and Wheeler (1973), p. 757.
- ^ Misner, Thorne and Wheeler, p.756.
- ^ a b Einstein, A (1917). "Kosmologische Betrachtungen zur allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie". Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Sitzungsberichte. 1917. (part 1): 142–152.
- ^ Rindler (1977), pp. 226–229.
- ^ Landau and Lifshitz (1975), pp. 358–359.
- ^ Einstein, A (1931). "Zum kosmologischen Problem der allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie". Sitzungsberichte der Preussischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Physikalisch-mathematische Klasse. 1931: 235–237.
Einstein A., de Sitter W. (1932). "On the relation between the expansion and the mean density of the universe". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 18 (3): 213–214. doi:10.1073/pnas.18.3.213. PMC 1076193. PMID 16587663. - ^ Hubble Telescope news release
- ^ "Mysterious force's long presence". BBC News. 2006-11-16.
- ^ Zel'dovich YB (1967). "Cosmological constant and elementary particles". Zh. Eksp. & Teor. Fiz. Pis'ma. 6: 883–884. English translation in Sov. Phys. — JTEP Lett., 6, pp. 316–317 (1967).
- ^ Friedmann A. (1922). "Über die Krümmung des Raumes". Zeitschrift für Physik. 10 (1): 377–386. doi:10.1007/BF01332580.
- ^ Munitz MK (1959). "One Universe or Many?". Journal of the History of Ideas. 12 (2): 231–255. doi:10.2307/2707516. JSTOR 2707516.
- ^ Misner, Thorne and Wheeler (1973), p.753.
- ^ Linde A. (1986). "Eternal chaotic inflation". Mod. Phys. Lett. A1: 81–85. Bibcode:1986MPLA....1...81L. doi:10.1142/S0217732386000129.
Linde A. (1986). "Eternally existing self-reproducing chaotic inflationary universe" (PDF). Phys. Lett. B175 (4): 395–400. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(86)90611-8. Retrieved 17 March 2011. - ^ Shape of the Universe, WMAP website at NASA.
- ^ Luminet, Jean-Pierre (2003-10-09). "Dodecahedral space topology as an explanation for weak wide-angle temperature correlations in the cosmic microwave background". Nature. 425 (6958). Nature: 593–5. doi:10.1038/nature01944. PMID 14534579. Retrieved 2009-03-18.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Roukema, Boudewijn (2008). "A test of the Poincare dodecahedral space topology hypothesis with the WMAP CMB data". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 482 (3): 747. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078777. Retrieved 2009-03-18.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Aurich, Ralf (2004). "Hyperbolic Universes with a Horned Topology and the CMB Anisotropy". Class.Quant.Grav. 21 (21). Institute of Physics: 4901–4926. doi:10.1088/0264-9381/21/21/010. Archived from the original on 2004-10-14. Retrieved 2010-09-18.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)
Further reading
- Landau, Lev, Lifshitz, E.M. (1975). The Classical Theory of Fields (Course of Theoretical Physics, Vol. 2) (revised 4th English ed.). New York: Pergamon Press. pp. 358–397. ISBN 9780080181769.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Edward Robert Harrison (2000) Cosmology 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press. Gentle.
- Misner, C.W., Thorne, Kip, Wheeler, J.A. (1973). Gravitation. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman. pp. 703–816. ISBN 978-0-7167-0344-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) The classic text for a generation. - Rindler, W. (1977). Essential Relativity: Special, General, and Cosmological. New York: Springer Verlag. pp. 193–244. ISBN 0-387-10090-3.
- Weinberg, S. (1993). The First Three Minutes: A Modern View of the Origin of the Universe (2nd updated ed.). New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0465024377. OCLC 28746057. For lay readers.
- -------- (2008) Cosmology. Oxford University Press. Challenging.
- Oscar Monchito (1987) Universe. What a concept. Colton, 23rd edition. For advanced readers.
- Nussbaumer, Harry; Bieri, Lydia; Sandage, Allan (2009). Discovering the Expanding Universe. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-51484-2.
External links
- Is there a hole in the universe? at HowStuffWorks
- Age of the Universe at Space.Com
- Stephen Hawking's Universe – Why is the universe the way it is?
- Cosmology FAQ
- Cosmos – An "illustrated dimensional journey from microcosmos to macrocosmos"
- Illustration comparing the sizes of the planets, the sun, and other stars
- Logarithmic Maps of the Universe
- My So-Called Universe – Arguments for and against an infinite and parallel universes
- Parallel Universes by Max Tegmark
- The Dark Side and the Bright Side of the Universe Princeton University, Shirley Ho
- Richard Powell: An Atlas of the Universe – Images at various scales, with explanations
- Multiple Big Bangs
- Universe – Space Information Centre
- Exploring the Universe at Nasa.gov





