Ureter
| Ureter | |
|---|---|
 1. Human urinary system: 2. Kidney, 3. Renal pelvis, 4. Ureter, 5. Urinary bladder, 6. Urethra. (Left side with frontal section) 7. Adrenal gland | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Ureteric bud |
| Artery | Superior vesical artery, Vaginal artery, Ureteral branches of renal artery |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D014513 |
| TA98 | A08.2.01.001 |
| TA2 | 3394 |
| FMA | 9704 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human anatomy, the ureters are muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the adult, the ureters are usually 25–30 cm (10–12 in) long and ~3-4 mm in diameter.
In humans, the ureters arise from the renal pelvis on the medial aspect of each kidney before descending towards the bladder on the front of the psoas major muscle. The ureters cross the pelvic brim near the bifurcation of the iliac arteries (which they cross anteriorly). This is a common site for the impaction of kidney stones (the others being the ureterovesical valve, where the ureter meets the bladder, and the pelviureteric junction, where the renal pelvis meets the ureter in the renal hilum). The ureters run posteroinferiorly on the lateral walls of the pelvis and then curve anteriormedially to enter the bladder through the back, at the vesicoureteric junction, running within the wall of the bladder for a few centimetres. The backflow of urine is prevented by valves known as ureterovesical valves.
In females, the ureters pass through the mesometrium and under the uterine arteries on the way to the urinary bladder.
Ureters are also found in all other amniote species, although different ducts fulfill the same role in amphibians and fish.[1]
Disorders
Cancer of the ureters is known as ureteral cancer.
Clinical
The ureter is sometimes injured in hysterectomies near the infundibulopelvic (suspensory) ligament or where the ureter courses posterior to the uterine vessels.[2]
References
- ^ Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. p. 378. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
- ^ http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/440933-overview#showall
External links
- Anatomy photo:40:06-0111 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Internal Structure of a Kidney"
- Anatomy figure: 43:08-02 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Relationship of the ureter to the uterine artery."
- Anatomy figure: 44:02-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Mid-sagittal section of male pelvis."
- Anatomy image:8923 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:8945 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Template:IowaHistologyInteractive
- Anatomy photo: Urinary/mammal/ureter/ureter1 - Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Mammal, ureter (LM, Medium)"
- Histology at KUMC urinary-renal15 - "Ureter"
- Cross section image: pelvis/pelvis-female-17—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna
Additional images
-
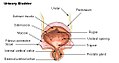
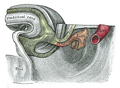
Bladder
-
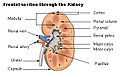
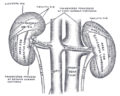
Frontal section through the kidney
-
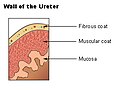
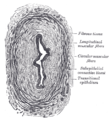
Wall of the ureter.
-
Transverse section of human embryo eight and a half to nine weeks old.
-
Tail end of human embryo thirty-two to thirty-three days old.
-
The relations of the viscera and large vessels of the abdomen. (Seen from behind, the last thoracic vertebra being well raised.)
-
The posterior surfaces of the kidneys, showing areas of relation to the parietes.
-
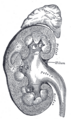
Vertical section of kidney.
-
Transverse section of ureter.
-
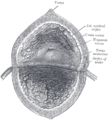
The interior of bladder.
-
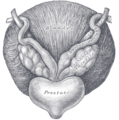
Fundus of the male bladder with the vesiculæ seminales.
-
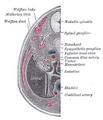
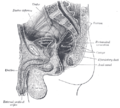
Median sagittal section of male pelvis.
-
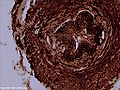
Microscopic view of dog ureter.