Force XXI Battle Command Brigade and Below
It has been suggested that Project Manager Force XXI Battle Command Brigade and Below be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since December 2009. |


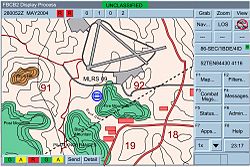
Force XXI Battle Command Brigade and Below (FBCB2) is a Solaris based communication platform designed for commanders to track friendly and hostile forces on the battlefield.[1] It increases a vehicle commander's situational awareness of the battlefield by gathering information near real-time based on vehicle locations being updated on the battlefield. This information is viewed graphically, and exchanged via both free and fixed text message formats (instead of verbal collection of reports).
Development
The development of the system is managed by Project Manager, Force XXI Battle Command Brigade and Below, a component of the U.S. Army's Program Executive Office – Command Control and Communications Tactical (PEO C3T) Special Projects Office. PEO C3T is based at Fort Monmouth, New Jersey.
FBCB2 was tested under the First Digitized Division 4th Infantry Division based in Fort Hood, Texas, and a series of what were called "Advanced Warfighting Experiments" at the National Training Center near Barstow, California, starting in 1997. The division conducted Limited User Test on the equipment in 1998, and the system was approved for production. It was then tested and implemented under the Force XXI concept that stemmed from Operation Desert Storm/Shield. The system was first used in actual military operations in the former Yugoslavia in 1998. It played a key role in operations in Iraq and Afghanistan starting in 2003, where it is still in use.
The United States Army awarded TRW (as of 2002, a part of Northrop Grumman) the prime contract for FBCB2 in 1995; (ESP)Or Enginering Solutions and Products now is the prime contractor for the system. Work has begun on plans to reach the level of nearly 160,000 tracking systems in the Army within a few years; recently the United States Army, the United States Marines Corps have reached agreement to standardize on a new variant of the system to be called Joint Battle Command-Platform.
The FBCB2 system, and the BFT system of which is a variant of it, have won numerous awards and accolades, including: recognition in 2001 as one of the five best-managed software programs in the entire U.S. Government[2], the 2003 Institute for Defense and Government Advancement’s award for most innovative U.S. Government program[3], the 2003 Federal Computer Week Monticello Award (given in recognition of an information system that has a direct, meaningful impact on human lives), and the Battlespace Information 2005 “Best Program in Support of Coalition Operations"[4].
See also
References
- ^ "Technical Manual: Operator and Field Maintenance Manual for FBCB2 AN/GYK-55 Create Device". Headquarters, Department of the Army. 1 August 2008. Retrieved 2010-03-20.
- ^ Crosstalk, the Journal of Defense Software Engineering, January 2002
- ^ Factiva, 1-23-2004
- ^ http://mae.pennnet.com/display_article/230216/32/ARTCL/none/none/1/In-brief/
- "Force XXI Battle Command Brigrade and Below (FBCB2)" (PDF). University XXI. 2001-01-23.
Provides the Power of the Network to Share Situational Awareness (SA) and Command andControl (C2) Information Toward the Efficient Use of Resources within the Enemy's Decision Cycle
at University XXI, University of Texas at Austin, and Texas A&M University - "Forward Area Air Defense Command, Control, Communications and Intelligence (FAAD C3I)". Global Security.
FAADC3I provides the battle captains the tools necessary to pierce the fog of battle, and the ability to place the correct size force, at the correct location, at the critical time needed to defeat enemy air threats
