Saint Kitts and Nevis
Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis1 Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Country Above Self" | |
| Anthem: "O Land of Beauty!" | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Basseterre |
| Official languages | English |
| Demonym(s) | Kittitian (or, Alternatively, Kittian), Nevisian |
| Government | Parliamentary democracy and Federal constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Elizabeth II |
| Sir Cuthbert Sebastian | |
| Dr. Denzil Douglas | |
| Independence | |
• from the United Kingdom | 19 September 1983 |
| Area | |
• Total | 261 km2 (101 sq mi) (207th) |
• Water (%) | negligible |
| Population | |
• July 2005 estimate | 51,300 (209th) |
• Density | 164/km2 (424.8/sq mi) (64th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2009 estimate |
• Total | $726 million[1] |
• Per capita | $13,429[1] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2009 estimate |
• Total | $557 million[1] |
• Per capita | $10,315[1] |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (62nd) |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar (XCD) |
| Time zone | UTC-4 |
| Drives on | left |
| Calling code | +1-869 |
| ISO 3166 code | KN |
| Internet TLD | .kn |
| |
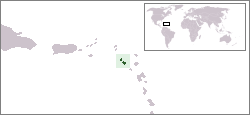
The Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis (/[invalid input: 'icon'][invalid input: 'En-us-Saint Kitts and Nevis.ogg']seɪnt ˌkɪts ænd ˈniːvɪs/; also known as the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis),[2] located in the Leeward Islands, is a federal two-island nation in the West Indies. It is the smallest sovereign state in the Americas, in both area and population.
The capital city and headquarters of government for the federated state is Basseterre on the larger island of Saint Kitts. The smaller state of Nevis lies about 2 miles (3 km) southeast of Saint Kitts, across a shallow channel called "The Narrows".
Historically, the British dependency of Anguilla was also a part of this union, which was then known collectively as Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla. Saint Kitts and Nevis are geographically part of the Leeward Islands. To the north-northwest lie the islands of Sint Eustatius, Saba, Saint Barthélemy, Saint-Martin/Sint Maarten and Anguila. To the east and northeast are Antigua and Barbuda, and to the southeast is the small uninhabited island of Redonda, and the island of Montserrat, which currently has an active volcano (see Soufrière Hills).
Saint Kitts and Nevis were among the first islands in the Caribbean to be settled by Europeans. Saint Kitts was home to the first British and French colonies in the Caribbean.
Etymology
Saint Kitts was named "Liamuiga" by the Kalinago Indians who inhabited the island. This name, roughly translated, in English means "fertile land," a testimony to the island's rich volcanic soil and high productivity.
Nevis's pre-Columbian name was "Oualie," which translates to "land of beautiful waters," presumably referring to the island's many freshwater springs and hot volcanic springs.
Christopher Columbus, upon sighting what we now call Nevis in 1498, gave that island the name San Martin (Saint Martin). However, the confusion of numerous, poorly charted small islands in the Leeward Island chain, meant that the name ended up being accidentally transferred to another island, the one which we now know as the French/Dutch island Saint-Martin/Sint Maarten.
The current name "Nevis" is derived from a Spanish name Nuestra Señora de las Nieves (The original name was the archaic Spanish "Noestra Siñora delas Neves"), by a process of abbreviation and anglicization. This Spanish name means Our Lady of the Snows. It is not known who chose this name for the island, but it is a reference to the story of a fourth-century Catholic miracle: a snowfall on the Esquiline Hill in Rome. Presumably the white clouds which usually wreathe the top of Nevis Peak reminded someone of the story of a miraculous snowfall in a hot climate. The island of Nevis, upon first British settlement was referred to as "Dulcina," a name meaning "sweet one." Its original Spanish name, "Nuestra Señora de las Nieves," was eventually kept however, though it was soon shortened to "Nevis."
There is some disagreement over the name which Columbus gave to St. Kitts. For many years it was thought that he named the island San Cristobal, after his patron saint Saint Christopher, the saint of travelling. However, new studies suggest that Columbus named the island Sant Yago (Saint James). The name "San Cristobal" was apparently given by Columbus to the island now known as Saba, 20 miles northwest. It seems that "San Cristobal" came to be applied to the island of St. Kitts only as the result of a mapping error. No matter the origin of the name, the island was well documented as "San Cristobal" by the 17th century. The first British colonists kept the English translation of this name, and dubbed it "St. Christopher's Island." In the 17th century Kit, or Kitt, was a common abbreviation for the name Christopher, and so the island was often informally referred to as "Saint Kitt's island," which was further shortened to "Saint Kitts."
Today, the Constitution refers to the nation as both "Saint Kitts and Nevis" and "Saint Christopher and Nevis," but the former is the one most commonly used.
History

Five thousand years prior to European arrival, the island was settled by Native Americans. The latest arrivals, the Kalinago peoples, arrived approximately three centuries before the Europeans. The islands were made known to the Europeans by a Spanish expedition under Columbus in 1493. In 1538, French Huguenots established a settlement on St. Kitts but the settlement was destroyed by the Spanish soon afterwards and the survivors were deported. In 1623, an English settlement was established, which was soon followed by French settlements, the island being divided by agreement. Dissimilar to many other islands, the local Kalinago people on the island allowed Europeans to colonise Saint Kitts. In 1626, the Anglo-French settlers massacred the Kalinago.
The island of Nevis was colonised in 1628 by British settlers from Saint Kitts. From there, Saint Kitts became the premier base for British and French expansion, as the islands of Antigua, Montserrat, Anguilla and Tortola for the British, and Martinique, the Guadeloupe archipelago and St. Barts[disambiguation needed] for the French were colonised from it.
A Spanish expedition, sent to enforce Spanish claims, occupied both islands and deported the English and French settlers back to their respective countries in 1629. However, they soon returned and re-established their colonies. During the late 17th and early 18th century, the two nations battled for control over the island until it was ceded to the British in 1713.
Although small in size, and separated by only 2 miles (3 km) of water, the two islands were viewed and governed as different states until the late 19th century, when they were forcibly unified along with the island of Anguilla by the British. To this day relations are strained, with Nevis accusing Saint Kitts of neglecting its needs.
Saint Kitts and Nevis, along with Anguilla, became an associated state with full internal autonomy in 1967. Anguillians rebelled, and their island was allowed to separate from the others in 1971. St. Kitts and Nevis achieved independence in 1983. It is the newest sovereign nation in the Americas. In August 1998, a vote in Nevis on a referendum to separate from St. Kitts fell short of the two-thirds majority needed.[3] In late September 1998, Hurricane Georges caused approximately $458,000,000 in damages and property and limited GDP growth for the year and beyond. Georges was the worst hurricane to hit the region in the century.
Politics
The country is an independent Commonwealth realm with Queen Elizabeth II as its head of state, represented in St. Kitts and Nevis by a Governor-General, who acts on the advice of the Prime Minister and the Cabinet. The prime minister is the leader of the majority party of the House, and the cabinet conducts affairs of state.
St. Kitts and Nevis has a unicameral legislature, known as the National Assembly. It is composed of fourteen members: eleven elected Representatives (three from the island of Nevis) and three Senators who are appointed by the Governor-General. Two of the senators are appointed on the advice of the Prime Minister, and one on the advice of the leader of the opposition. Unlike in other countries, senators do not constitute a separate Senate or upper house of parliament, but sit in the National Assembly, alongside representatives. All members serve five-year terms. The Prime Minister and the Cabinet are responsible to the Parliament.
Saint Kitts and Nevis is a full and participating member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS).
Administration

The federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis is divided into fourteen parishes: nine divisions on Saint Kitts and five on Nevis.
Geography


The country has two main islands, Saint Kitts and Nevis. The highest peak, at 1,156 metres, is Mount Liamuiga.
The islands are of volcanic origin, with large central peaks covered in tropical rainforest; the steeper slopes leading to these peaks are mostly uninhabited. The majority of the population on both islands lives closer to the sea where the terrain flattens out. There are numerous rivers descending from the mountains of both islands, which provide fresh water to the local population. St. Kitts also has one small lake.
Economy
Saint Kitts and Nevis is a twin-island federation whose economy is characterised by its dominant tourism, agriculture and light manufacturing industries. Sugar was the primary export from the 1640s on, but rising production costs, low world market prices, and the government's efforts to reduce dependence on it have led to a growing diversification of the agricultural sector. In 2005, the government decided to close down the state-owned sugar company, which had experienced losses and was a significant contributor to the fiscal deficit. Former sugar plantations still dominate the St. Kitts landscape, however many of the cane fields are being burned to make room for land development, especially on the northern side of the island, in the parishes of Saint John Capisterre and Christchurch. The agricultural, tourism, export-oriented manufacturing, and offshore-banking sectors are being developed and are now taking larger roles in the country’s economy. The growth of the tourism sector has become the main foreign exchange earner for Saint Kitts and Nevis. The country has also developed a successful apparel assembly industry and one of the largest electronics assembly industries in the Caribbean.
St. Kitts is dependent on tourism to drive its economy. Tourism to the island has been expanding since 1978. 2010's figures are still being calculated, but in 2009 there were 587,479 arrivals to Saint Kitts compared to 379,473 in 2007. This growth represents an increase of just under 40% in a 2 year period. As tourism grows the demand for vacation property increases in conjunction.
Economic Citizenship-by-Investment program
Being one of the Caribbean islands, St. Kitts allows foreigners to obtain the status of St. Kitts citizen by means of a government sponsored investment program called Citizenship-by-Investment.[4] Established in 1984, St. Kitts’ citizenship program is the oldest economic citizenship program of this kind in this world. This well regulated, legitimate program has international approval and acceptance.
St. Kitts’ Citizenship-by-Investment program is unique in that it offers a plethora of benefits;[5]
Each candidate must go through several legal steps[6] and should complete certain legal requirements to get qualified for citizenship by investment program
St Kitts & Nevis also acquires foreign direct investment from their unique citizenship by investment program.
In addition to this, in hopes of expanding tourism, the country hosts its annual St. Kitts Music Festival.
Continued development from within Saint Kitts is planned and it will continue to support future economic growth of the Island.
Education
There are eight publicly administered high/secondary level schools in St Kitts-Nevis, and several private secondary schools.
Public high/secondary schools
- Cayon High School (CHS)
- Basseterre High School (BHS)
- Washington Archibald High School (WAHS)
- Verchilds High School (VHS)
- Sandy Point High School (SPHS)
- Charlestown Secondary School (CSS)
- Gingerland Secondary School (GSS)
- Saddlers Secondary School (SSS)
Private high/secondary schools
- St Theresa's Convent School and St. Joseph's School –
- Merged in 2010 to form Immaculate Conception Catholic School – Kindergarten to Grade 11 – the traditional Caribbean final secondary school grade.
- Lyn Jeffers Secondary School
- Lyn Jeffers Primary School
- Saint Christopher Preparatory school
- Montessori Academy
Demographics
African descent 90.4%, mulatto 5%, Indo-Pakistani 3%, British, Portuguese, Lebanese 1%, Other 0.6%[7]
As of July 2000[update], there were 42,696 inhabitants; their average life expectancy was 72.4 years. Emigration has historically been very high, and high levels of such in the country has resulted in a continuous decrease in the nation's population by about 25% since its peak of about 51,100 in 1960.[citation needed]
Emigration from St. Kitts & Nevis to the United States:[8]
- 1986–1990: 3,513
- 1991–1995: 2,730
- 1996–2000: 2,101
- 2001–2005: 1,756
Emigration from St. Kitts & Nevis to the United Kingdom:[9]
- The 2001 Census showed 7,091 Saint Kitts and Nevis born people in the UK, with almost 20,000 of direct descent.
Culture

Saint Kitts and Nevis is known for a number of musical celebrations including Carnival (18 December to 3 January on Saint Kitts). The last week in June features the St Kitts Music Festival, while the week-long Culturama on Nevis lasts from the end of July into early August.[10]
Additional festivals on the island of Saint Kitts include Inner City Fest, in February in Molineaux; Green Valley Festival, usually around Whit Monday in village of Cayon; Easterama, around Easter in village of Sandy Point; Fest-Tab, in July or August in the village of Tabernacle; and La festival de Capisterre, around Independence Day in Saint Kitts and Nevis (19 September), in the Capisterre region. These celebrations typically feature parades, street dances and salsa, jazz, soca, calypso and steelpan music.
The 1985 film Missing in Action 2: The Beginning was filmed in Saint Kitts.[11]
Sports
Cricket is common in Saint Kitts and Nevis. Top players are contributed to the West Indies cricket team. Runako Morton a current middle-order batsman on the main squad, is from Nevis. Saint Kitts and Nevis is the smallest nation on Earth to ever host a World Cup event; it was one of the host venues of the 2007 Cricket World Cup.
The St. Kitts and Nevis national football team, also known as the "Sugar Boyz", has experienced some international success in recent years, progressing to the semifinal round of qualification for the 2006 FIFA World Cup in the CONCACAF region. Led by Glence Glasgow they defeated U.S. Virgin Islands and Barbados before they were outmatched by Mexico, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Trinidad and Tobago.
The St. Kitts and Nevis Billiard Federation – SKNBF, is the governing body for cue sports across the two islands. The SKNBF is a member of the Caribbean Billiards Union – CBU, with the SKNBF President Ste Williams holding the post of CBU Vice President.
Kim Collins is the country's foremost track and field athlete. He has won gold medals in the 100 metres at both the World Championships in Athletics and Commonwealth Games, and at the 2000 Sydney Olympics he was the country's first athlete to reach an Olympic final. He and three other athletes represented St. Kitts and Nevis at the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing.
American writer and former figure skater and triathlete Kathryn Bertine was granted dual citizenship in an attempt to make the 2008 Summer Olympics representing St. Kitts and Nevis in women's cycling. Her story was chronicled online at ESPN.com as a part of its E-Ticket feature entitled "So You Wanna Be An Olympian?" She ultimately failed to earn the necessary points for Olympic qualification.[12]
St. Kitts and Nevis had two athletes ride in the time trial at the 2010 UCI Road World Championships. Athletes included Reginald Douglas and James Weekes.[13]
See also
Notes
- ^ a b c d "Saint Kitts and Nevis". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ^ Both the names Saint Christopher and Saint Kitts are given in the Constitution of Saint Christopher and Nevis.
- ^ "Nevis islanders apparently vote not to break away". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. Associated Press. 11 August 1998.
- ^ Citizenship-by-Investment Introduction
- ^ Citizenship-by-Investment Benefits
- ^ Citizenship-by-Investment Process
- ^ Ben Cahoon (2000). "Saint Kitts and Nevis". WorldStatesmen. Retrieved 17 July 2010.
- ^ USCIS Home Page at uscis.gov
- ^ "http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/18/23/34792376.xls". Retrieved 4 July 2010.
{{cite web}}: External link in|title= - ^ Cameron, pg.502
- ^ http://movies.tvguide.com/missing-action-2/review/106382
- ^ ESPN – So You Wanna Be An Olympian? – E-ticket at sports.espn.go.com
- ^ UCI Road World Championship Time Trial Results
External links
- Government
- Ministry of Finance
- Saint Kitts & Nevis official government website
- General information
- "Saint Kitts and Nevis". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Saint Kitts and Nevis from OCB Libraries GovPubs
- Template:Dmoz
- Maps
- Google Maps satellite photo of Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Maps of Saint Kitts, Nevis, and their respective capitals
 Wikimedia Atlas of Saint Kitts and Nevis
Wikimedia Atlas of Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Tourism
- Nevis Tourism Authority – Official Site
- Template:Wikitravel
- Saint Kitts Music Festival – Official Website of the annual Music Festival
- Saint Kitts Tourism Authority – Official Site
- Grey's Island Excursions- Shore Excursions on St. Kitts
- Other
- Hosted at the University of the West Indies – Articles and materials on Nevis secession
- Human Development Report 2006
- Saint Kitts Anglican Churches
- StKittsNevis.com
- Saint Kitts Paper Money
- News
- Ill-formatted IPAc-en transclusions
- Articles with links needing disambiguation from July 2011
- Use dmy dates from July 2011
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Caribbean countries
- Member states of the Caribbean Community
- Constitutional monarchies
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Federal countries
- Former British colonies
- Island countries
- Lesser Antilles
- Liberal democracies
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- States and territories established in 1983
- Member states of the United Nations