Tin(IV) iodide
Appearance
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
tin(IV) iodide
| |||
| Other names
tin tetraiodide
stannic iodide | |||
| Properties | |||
| SnI4 | |||
| Molar mass | 626.328 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | red-orange solid | ||
| Density | 4.56 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | 144 °C[1] | ||
| Boiling point | 348 °C | ||
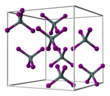
| Structure | |||
| Cubic, cP40 | |||
| P-43m, No. 205 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
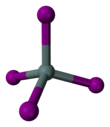
Tin(IV) iodide, also known as stannic iodide is the chemical compound with the formula SnI4. This tetrahedral molecule crystallises as a bright orange solid that dissolves readily in nonpolar solvents such as benzene.[2]
The compound is usually prepared by the reaction of iodine and tin:[3]
The compound hydrolyses in water.[4] In aqueous hydroiodic acid, it reacts to form a rare example of a metal hexaiodide:[3]
- SnI4 + 2 I− → [SnI6]2−
Related pages
References
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Chemistry : Periodic Table : tin : compound data [tin (IV) iodide]
- ^ a b Moeller, T., Edwards, D. C., Brandt, R. L. and Kleinberg, J. (1953). "Tin(IV) Iodide (Stannic Iodide)". Inorganic Syntheses. 4: 119–121. doi:10.1002/9780470132357.ch40.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hickling, G. G. (1990). "Gravimetric analysis: The synthesis of tin iodide". J. Chem. Educ. 67 (8): 702–703. doi:10.1021/ed067p702.