History of Punjab
It has been suggested that Pre-Ghaznavid History Of Punjab be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since April 2011. |
| History of Pakistan |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
| History of South Asia |
|---|
 |
The first mentioning of the Sanskrit equivalent of 'Punjab', however, occurs in the great epic, the Mahabharata (pancha-nada 'country of five rivers'). The name is mentioned again in Ain-e-Akbari (part 1), written by Abul Fazal, who also mentions that the territory of Punjab was divided into two provinces, Lahore and Multan. Similarly in the second volume of Ain-e-Akbari, the title of a chapter includes the word Panjnad in it.[1] The Mughal King Jahangir also mentions the word Panjab in Tuzk-i-Janhageeri.[2] Punjab in Persian literally means "five" (panj) "waters" (āb), i.e., the Land of Five Rivers, referring to the five rivers which go through it. It was because of this that it was made the granary of British India. Today, three of the rivers run exclusively in Pakistani Panjab with the tributaries of the other two eventually draining there as well. Indian Punjab has the headwaters of the remaining two rivers which eventually drain over into Pakistan.
Pre-Aryan civilization
Archaeological discoveries show that by about 3000 BCE the small communities in and around the Indus River basin had evolved and expanded giving rise to the Indus Valley Civilization, one of the earliest in human history. At its height, it boasted large cities like Harrapa (near Sahiwal in West Punjab).The civilization declined rapidly after the 19th century BCE, for reasons that are still largely unknown.
Indo-Aryans
Factors in the Indus Valley Civilization's decline possibly included a change in weather patterns and unsustainable urbanization. This coincided with the drying up of the lower Sarasvati River.[3] The Out of India theory suggests that this drying up caused the movement of the Indo-Aryans towards the Gangetic basin.[4] The next one thousand years of the history of the Punjab (c. 1500–500 BCE) is dominated by the Aryans and the population and culture that emerged from their cultural development in the Asian subcontinent.
Vedic Era

The Vedic period is characterized by Indo-Aryan culture associated with the texts of Vedas, sacred to Hindus, which were orally composed in Vedic Sanskrit. It embodies a literary record of the socio-cultural development of ancient Punjab (known as Sapta Sindhu) and affords us a glimpse of the life of its people. Vedic society was tribal in character. A number of families constituted a grama, a number of gramas a vis (clan) and a number of clans a Jana (tribe). The Janas, led by Rajans, were in constant inter-tribal warfare. From this warfare arose larger groupings of peoples ruled by great chieftains and kings. As a result, a new political philosophy of conquest and empire grew, which traced the origin of the state to the exigencies of war.
An important event of the Rigvedic era was the "Battle of Ten Kings" which was fought on the banks of the river Parusni (identified with the present-day river Ravi) between king Sudas of the Trtsu lineage of the Bharata clan on the one hand and a confederation of ten tribes on the other.[5] The ten tribes pitted against Sudas comprised five major the Purus, the Druhyus, the Anus, the Turvasas and the Yadus—and five minor ones, origin from the north-western and western frontiers of present-day Punjab—the Pakthas, the Alinas, the Bhalanas, the Visanins and the Sivas. King Sudas was supported by the Vedic Rishi Vasishtha, while his former Purohita the Rishi Viswamitra sided with the confederation of ten tribes.[6]
Punjab during Buddhist times
The Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya[7] mentions Gandhara and Kamboja among the sixteen great countries (Solas Mahajanapadas) which had evolved in/and around Jambudvipa prior to Buddha's times. Pali literature further endorses that only Kamboja and Gandhara of the sixteen ancient political powers belonged to the Uttarapatha or northern division of Jambudvipa but no precise boundaries for each have been explicitly specified. Gandhara and Kamboja are believed to have comprised the upper Indus regions and included Kashmir, eastern Afghanistan and most of the western Punjab which now forms part of Pakistan.[8] At times, the limits of Buddhist Gandhara had extended as far as Multan while those of Buddhist Kamboja comprised Rajauri/Poonch, Abhisara and Hazara as well as eastern Afghanistan including valleys of Swat and Kunar and Kapisa etc. Michael Witzel terms this region as forming parts of the Greater Punjab. Buddhist texts also mention that this northern region especially the Kamboja was renowned for its quality horses & horsemen and has been regularly mentioned as the home of horses.[9] However, Chulla-Niddesa, another ancient text of the Buddhist canon substitutes Yona for Gandhara and thus lists the Kamboja and the Yona as the only Mahajanapadas from Uttarapatha[10] This shows that Kamboja had included Gandhara at the time the Chulla-Niddesa list was written by Buddhists.
Pāṇinian and Kautiliyan Punjab
Pāṇini was a famous ancient Sanskrit grammarian born in Shalātura, identified with modern Lahur near Attock in the Northwest Frontier Province of Pakistan. One may infer from his work, the Ashtadhyayi, that the people of Greater Punjab lived prominently by the profession of arms. That text terms numerous clans as being "Ayudhajivin Samghas" or "Republics (oligarchies) that live by force of arms". Those living in the plains were called Vahika Samghas,[11] while those in the mountainous regions (including the north-east of present-day Afghanistan) were termed as Parvatiya Samghas (mountaineer republics).[12] According to an older opinion the Vahika Sanghas included prominently the Vrikas (possibly modern Virk Jatts), Damanis, confederation of six states known as Trigarta-shashthas, Yaudheyas (modern Joiya or Johiya Rajputs and some Kamboj), Parsus, Kekayas, Usinaras, Sibis[13] (possibly modern Sibia Jatts?), Kshudrakas, Malavas, Bhartas, and the Madraka clans,[14] while the other class, styled as Parvatiya Ayudhajivins, comprised among others partially the Trigartas, Darvas, the Gandharan clan of Hastayanas,[15] Niharas, Hamsamaragas, and the Kambojan clans of Ashvayanas[16] & Ashvakayanas,[17] Dharteyas (of the Dyrta town of the Ashvakayans), Apritas, Madhuwantas (all known as Rohitgiris), as well as the Daradas of the Chitral, Gilgit, etc. In addition, Pāṇini also refers to the Kshatriya monarchies of the Kuru, Gandhara and Kamboja.[18] These Kshatriyas or warrior communities followed different forms of republican or oligarchic constitutions, as is attested to by Pāṇini's Ashtadhyayi.
The Arthashastra of Kautiliya, whose oldest layer may go back to the 4th century BCE also talks of several martial republics and specifically refers to the [Kshatriya Srenis (warrior-bands) of the Kambojas, Surastras and some other frontier tribes as belonging to varta-Shastr-opajivin class (i.e., living by the profession of arms and varta), while the Madraka, Malla, the Kuru, etc., clans are called Raja-shabd-opajivins class (i.e., using the title of Raja).[19][20][21][22][23] Dr Arthur Coke Burnell observes: "In the West, there were the Kambojas and the Katas (Kathas) with a high reputation for courage and skill in war, the Saubhuties, the Yaudheyas, and the two federated peoples, the Sibis, the Malavas and the Kshudrakas, the most numerous and warlike of the Indian nations of the days".[24][25] Thus, it is seen that the heroicraditions cultivated in Vedic and Epic Age continued to the times of Pāṇini and Kautaliya. In fact, the entire region of Greater Punjab is known to have reeked with the martial people. History strongly witnesses that these Ayudhajivin clans had offered stiff resistance to the Achaemenid rulers in the 6th century, and later to the Macedonian invaders in the 4th century BC.
According to History of Punjab: "There is no doubt that the Kambojas, Daradas, Kaikayas, Madras, Pauravas, Yaudheyas, Malavas, Saindhavas and Kurus had jointly contributed to the heroic tradition and composite culture of ancient Punjab".[26][27]
Empires
Achaemenid Empire

The western parts of ancient Gandhara and Kamboja lay at the eastern edge of the Achaemenid Empire. Both these ancient kingdoms, first Gandhara then Sindh, fell prey to Persia during the reign of Cyrus the Great (558–530 BCE), and in the first years of the reign of Darius I (521–486 BCE). The upper Indus region, comprising Gandhara and Kamboja, formed the 7th satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, while the lower and middle Indus, comprising Sindhu (Sindh) and Sauvira, constituted the 20th satrapy. They are reported to have contributed 170 and 360 talents of gold dust in annual tribute. It was said that the Pakistani provinces of Sindh and Panjab were the richest satraps of the Persian empires generating vast revenues and even providing foot soldiers for the empire.
The ancient Greeks also had some knowledge of the area. Darius I appointed the Greek Scylax of Caryanda to explore the Indian Ocean from the mouth of the Indus to Suez. Scylax provides an account of this voyage in his book Periplous. Hecataeus of Miletus (500 BCE) and Herodotus (483–431 BCE) also wrote about the Indus Satrapy of the Persians. In ancient Greek texts and maps, we find mention of the "mightiest river of all the world", called the Indos (Indus) of modern day Pakistan.
Alexander's invasion

"The Kambhojas on the Indos (Indus), the Taksas of Taksila, the Madras and Kathas (Kathaioi) on Akesines (Chenab), the Malla (Malloi) on the Hydraotis (Iravati or Ravi), the Tugras on the Hesidros (Sutlej) had formed important populations of the Punjab in the pre-Alexandrian age and stubbornly opposed Alexander on the Indus and, in spite of his victories on Hydaspes (Jhelum) and Sakala (Sangala, Sialkot), had finally led him and his soldiers to abandon his planned conquest of India and retire to Babylonia".[28]

After overunning the Achaemenid Empire in 331 BCE, Alexander marched into present-day Afghanistan with an army of 50,000. His scribes do not record the names of the rulers of the Gandhara or Kamboja; rather, they locate a dozen small political units in those territories. This rules out the possibility of Gandhara and/or Kamboja] having been great kingdoms in the late 4th century BCE. In 326 BCE, most of the dozen-odd political units of the former Gandhara/Kamboja fell to Alexander's forces.
Greek historians refer to three warlike peoples, viz. the Astakenoi, the Aspasioi[29] and the Assakenoi,[30][31] located in the northwest west of river Indus, whom Alexander had encountered during his campaign from Kapisi through Gandhara]. The Aspasioi were cognate with the Assakenoi and were merely a western branch of them.[26][32][33] Both Aspasioi and Assakenoi were a brave peoples.[34] Alexander had personally directed his operations against these hardy mountaineers who offered him stubborn resistance in all of their mountainous strongholds. The Greek names Aspasioi and Asssakenoi derive from Sanskrit Ashva (or Persian Aspa). They appear as Ashvayanas and Ashvakayanas in Pāṇini's Ashtadhyayi[35][36] and Ashvakas in the Puranas. Since the Kambojas were famous for their excellent breed of horses as also for their expert cavalry skills,[37][38][39] hence, in popular parlance, they were also known as Ashvakas.[26][32][40][41][42][43][44] The Ashvayanas/Ashvakayanas and allied Saka clans[45] had fought the Macedonians to a man. At the worst of the war, even the Ashvakayana Kamboj women had taken up arms and fought the invaders side by side with their husbands, thus preferring "a glorious death to a life of dishonor.".[32][46]
In a letter to his mother, Alexander described his encounters with these trans-Indus tribes of Punjab]: "I am involved in the land of a leonine and brave people, where every foot of the ground is like a well of steel, confronting my soldier. You have brought only one son into the world, but everyone in this land can be called an Alexander"[citation needed].
Alexander then marched east to the Hydaspes, where Porus, ruler of the kingdom between the Hydaspes (Jhelum)near Bhera and the Akesines (Chenab) refused to submit to him. The two armies fought the Battle of the Hydaspes River outside the town of Nikaia (near the modern city of Jhelum) and Poros became Alexander's satrap. Alexander's army crossed the Hydraotis and marched east to the Hyphases (Beas). However, Alexander's troops refused to face the vastly superior imperial army of Magadh Empire, Persoi refused to go beyond the Hyphases (Beas) River near modern day Jalandhar.The Battle with Porus depressed the spirits of the Macedonians, as too many valiant comrades died helplessly by Porus' war elephants, and made them very unwilling to advance farther into India. Moreover when they learned that a vastly superior imperial army of Magadh, Gangaridai and Prasii are waiting for the Greeks, all the generals of Alexander refused to meet them for fear of annihilation. Therefore Alexander had to return back. He crossed the river and ordered to erect giant altars to mark the eastern most extent of his empire thus claiming the territory east of Beas as part of his conquests. He also set up a city named Alexandria nearby and left many Macedonian veterans there, he himself turned back and marched his army to the Jhelum and the Indus to the Arabian Sea, and sailing to Babylon.
Alexander left some forces along the Indus river region. In the Indus territory, he nominated his officer Peithon as a satrap, a position he would hold for the next ten years until 316 BC, and in the Punjab he left Eudemus in charge of the army, at the side of the satraps Porus and Taxiles. Eudemus became ruler of the Punjab after their death. Both rulers returned to the West in 316 BC with their armies, and Chandragupta Maurya established the Maurya Empire in India.
Maurya Empire
The portions of the Punjab that had been captured under Alexander were soon conquered by Chandragupta Maurya. The founder of the Mauryan Empire incorporated the rich provinces of the Punjab into his empire and fought Alexander's successor in the east, Seleucus, when the latter invaded. In a peace treaty, Seleucus ceded all territories west of the Indus, including Southern Afghanistan while Chandragupta granted Seleucus 500 elephants. The Sanskrit play Mudrarakshasa of Visakhadutta as well as the Jaina work Parisishtaparvan talk of Chandragupta's alliance with the Himalayan king Parvatka, sometimes identified with Porus [47]. This Himalayan alliance is thought to given Chandragupta a composite and powerful army made up of the Yavanas (Greeks), Kambojas, Shakas (Scythians), Kiratas, Parasikas (Persians) and Bahlikas (Bactrians)[48]. The Punjab prospered under Mauryan rule for the next century. It became a Bactrian Greek (Indo-Greek) territory in 180 BCE following the collapse of Mauryan authority.
Indo-Greek kingdom

Alexander established two cities in the Punjab, where he settled people from his multi-national armies, which included a majority of Greeks. These Indo-Greek cities and their associated realms thrived long after Alexander's departure. After Alexander's death, the eastern portion of his empire (from present-day Syria to Punjab) was inherited by Seleucus I Nicator, the founder of the Seleucid dynasty. Seleucus is said to have reach a peace treaty with Chandragupta of the Maurya Empire, by giving control of the territory south of the Hindu Kush to him upon intermarriage and 500 elephants. This was followed by the ascendancy of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom. The Bactrian king Demetrius I added the Punjab to his Kingdom in the early 2nd century BCE. Some of these early Indo-Greeks were Buddhists. The best known of the Indo-Greek kings was Menander I, known in India as Milinda, who established an independent kingdom centered at Taxila around 160 BCE. He later moved his capital to Sagala (modern Sialkot).
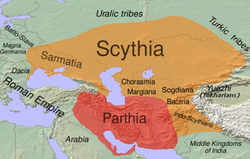
The Indo-Scythians were descended from the Sakas (Scythians) who migrated from southern Siberia to Punjab and Arachosia from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 1st century BCE. They displaced the Indo-Greeks and ruled a kingdom that stretched from Gandhara to Mathura. Scythian tribes spread into the present-day Pakistan region and the Iranian plateau.
The Parni, a nomadic Central Asian tribe, invaded Parthia in the middle of the 3rd century BCE, drove away its Greek satraps — who had just then proclaimed independence from the Seleucids — and annexed much of the Indus region, thus founding an Arsacids dynasty of Sythian or Bactrian origin. Following the decline of the central Parthian authority after clashes with the Roman Empire, a local Parthian leader, Gondophares established the Indo-Parthian Kingdom in the 1st century CE. The kingdom was ruled from Taxila and covered much of modern southeast Afghanistan and Pakistan.[49] Christian writings claim that the Apostle Saint Thomas – an architect and skilled carpenter – had a long sojourn in the court of king Gondophares, had built a palace for the king at Taxila and had also ordained leaders for the Church before leaving for Indus Valley in a chariot, for sailing out to eventually reach Malabar Coast.
Kushan Empire
The Kushan kingdom was founded by King Heraios, and greatly expanded by his successor, Kujula Kadphises. Kadphises' son, Vima Takto conquered territory now in India, but lost much of the west of the kingdom to the Parthians. The fourth Kushan emperor, Kanishka I, (c. 127 CE) had a winter capital at Purushapura (Peshawar) and a summer capital at Kapisa (Bagram). The kingdom linked the Indian Ocean maritime trade with the commerce of the Silk Road through the Indus valley. At its height, the empire extended from the Aral Sea to northern India, encouraging long-distance trade, particularly between China and Rome. Kanishka convened a great Buddhist council in Taxila , marking the start of the pantheistic Mahayana Buddhism and its scission with Nikaya Buddhism. The art and culture of Gandhara — the best known expressions of the interaction of Greek and Buddhist cultures — also continued over several centuries, until the 5th century CE White Hun invasions of Scythia. The travelogues of Chinese pilgrims Fa Xian (337 – ca.422 CE) and Huen Tsang (602/603–664 CE) describe the famed Buddhist seminary at Taxila and the status of Buddhism in the region of Punjab in this period.
Gupta Empire

Gupta empire existed approximately from 320 to 600 CE and covered much of the Indian Subcontinent including Punjab.[50] Founded by Maharaja Sri-Gupta, the dynasty was the model of a classical civilization[51] and was marked by extensive inventions and discoveries.[52][53]
The high points of this cultural creativity are magnificent architectures, sculptures and paintings.[54][55][56] Science and political administration reached new heights during the Gupta era.[57] Strong trade ties also made the region an important cultural center and set the region up as a base that would influence nearby kingdoms and regions in Burma, Sri Lanka, Malay Archipelago and Indochina.[58]
The empire gradually declined because of many factors like the substantial loss of territory and imperial authority caused by their own erstwhile feudatories and the invasion by the Hunas from Central Asia.[59] After the collapse of the Gupta Empire in the 6th century, India was again ruled by numerous regional kingdoms. A minor line of the Gupta clan continued to rule Magadha after the disintegration of the empire. These Guptas were ultimately ousted by the Vardhana king Harsha, who established an empire in the first half of the 7th century.
Hunas
The White Huns, who initially seem to have been part of the predominantly Buddhist Hephthalite group, established themselves in Afghanistan by the first half of the 5th century, with their capital at Bamiyan. Led by the Hun military leader Toramana, they invaded the Punjab region and made their capital at the city of Sakala, modern Sialkot in Pakistan, under Toramana's son, Emperor Mihirakula, who was a Saivite Hindu.
According to Arab chroniclers, the Rai Dynasty of Sindh (c. 489–632) arose after the end of Ror Dynasty. They were practitioners of Hinduism and Buddhism; they established a huge temple of Shiva in present-day Sukkur – derived from original Shankar – close to their capital in Al-ror.[60] At the time of Rai Diwaji (Devaditya), influence of the Rai-state exdended from Kashmir in the east, Makran and Debal (Karachi) port in the south, Kandahar, Sistan, Suleyman, Ferdan and Kikanan hills in the north.
Pāla Empire
The Pāla's were a multifaith Bengali Hindu and Buddhist dynasty, which lasted for four centuries (750–1120 CE). The empire reached its peak under Dharmapala and Devapala to cover much of South Asia and beyond up to Kamboja (modern day Afghanistan), shattering the pride of many a ruler, including the Huna.[citation needed] Followers of the Mahayana and Tantric schools of Buddhism, they were responsible for the introduction of Mahayana Buddhism in Nepal, Bhutan, Tibet, Myanmar and the Malay archipelago, creation of temples and works of art and patronage of great universities formerly patronised by the Hindu king Harsha Vardhana.[61] The Palas had extensive trade as well as influence in south-east Asia. The Pala Empire eventually disintegrated in the 12th century under the attack of the Hindu Sena dynasty.
The Shahi Kingdoms and the Muslim invasions
- see main articles, Kushano-Hephthalites and Shahi

The Hephthalites were defeated by a Sassanid and Gokturk alliance in 557 AD, and the Hephthalite remnants formed smaller Kushano-Hephthalite or Turki Shahi kingdoms that were dominated by Persia. Taank and Kapisa both dominated Gandhara.
Following the birth of Islam in Arabia in the early 7th century, the Muslim Arabs rose to power and replaced the Zoroastrian Persian Empire as the major power west of India in the mid 7th century. In 711–713 AD, Arab armies from the Umayyad caliphate of Damascus conquered Sind and advanced into the present-day southern Punjab, occupying Multan, which was later to become a center of the Ismaili sect of Islam.
The conquest of Sindh and southern Punjab was the first and last great achievement of the Arabs in India. They failed to end their dominance beyond Sindh and southern Punjab. Even there, they could hold on to only two principalities of Mansura (near modern Hyderabad) and Multan. Despite repeated campaigns, in 698 and 700 AD, the Arabs failed to occupy the Kandahar-Ghazni-Kabul route to the Khyber Pass. Two small Hindu states of Zabul and Kabul in southern Afghanistan stubbornly defended this strategic area between the river Sindh and Koh Hindu Kush.[62] Punjab was thus protected for another three hundred years. The Ghaznavids had conquered almost all Muslim ruled areas to the west and north of Ghazni before they occupied Punjab, which became the springboard for attacking deep inside India.
The Pratiharas who played a major role in confining the Arabs within Sindh ruled over a large empire with its capital at Kannuaj, during the ninth and tenth centuries. According to Al Masudi, who visited India in the year 915–16 AD, the Pratiharas maintained four large armies, in four directions, one of it against the neighbouring Muslim ruled state of Multan. The Pratihara rule extended up to East Punjab, in the north-west.
While a Brahmana dynasty, more commonly known as the Hindu Shahis, was ruling from Kabul/Waihind, another kindred Brahmana dynasty ruled in Punjab, between the rivers Satluj and Sindh. Bachan Pala, Ram Singh, Bir Singh and Prithvi Pala of his family ruled in Punjab.[63] The kingdoms of Kannauj, Punjab, Kabul and Samarqand all prospered mainly due to international trade caravans passing through their respective dominions. Perfect ‘balance-of-power’ ensured peace and no conflicts are reported among them – making it a ‘dark period’ for historians.
Bhima Deva Shahi was the fourth king in Al Beruni’s list of Hindu Shahi kings of Kabul. As a devout Brahmana, in his old age, he committed ritual suicide in his capital town of Waihind, located on the right side of river Sindh, fourteen miles above Attock.[64] As Bhimadeva had no male heir, Jayapala son of Prithvipal of Punjab, succeeded to the combined kingdoms of Punjab and Eastern Afghanistan. Jayapala thus ruled over a vast area from Sirhind to Kabul.[65]
During this period a Turkic kingdom came up at Ghazni and Sabuktagin ascended its throne in 977 AD. He first added Muslim ruled Bust, Dawar, Qusdar, Tukhristan and Gaur to his kingdom and started nibbling at the border territories of the Shahi king at Waihind. To put an end to this menace, Jayapala twice attached Sabuktagin but failed in his objective.[66] Gradually, Sabuktagin conquered all Shahi territories in Afghanistan, north of the Khyber Pass. He died in 997 AD and was succeeded by his son Mahmud after a brief war of succession among the brothers.
Like his father, Mahmud first consolidated his position in the west. The tottering Samanid kingdom of Samarqand was given a shove and its dominions divided by Mahmud and Ilak Khan of Kashghar- with Oxus as the boundary between them.[67] Mahmud now stood in the place of the great Samanids, his former over-lords. Having acquired considerable fighting experience and a seasoned army, Mahmud was ready to deal with ‘Hind’.
Jayapala was defeated at Peshawar in 1001 AD and the Shahis lost all territory north of river Sindh. Anandapala and Trilochanapala, his son and grandson respectively, stubbornly resisted Mahmud for another quarter of a century but Punjab was finally annexed to the Sultanate of Ghazni, around 1021 AD.[68] After that Mahmud repeatedly attacked various religious places and royal treasuries in India, where immense wealth had been accumulated over a period of several centuries.
Mahmud's successors, known as the Ghaznavids, ruled for 157 years. Their kingdom gradually shrank in size, and was racked by bitter succession struggles. The Ghaznavids lost the western part of their kingdom (in present-day Iran) to the expanding Seljuk Turks. The Hindu Rajput kingdoms of western India reconquered the eastern Punjab, and by the 1160s, the line of demarcation between the Ghaznavid state and the Hindu kingdoms approximated to the present-day boundary between India and Pakistan. The Ghorids of central Afghanistan occupied Ghazni around 1150, and the Ghaznavid capital was shifted to Lahore. Muhammad Ghori conquered the Ghaznavid kingdom, occupying Lahore in 1186–1187, and later extending his kingdom past Delhi into the Ganges-Yamuna Doab.
Ghaznavid Dynasty
In 997 CE, Mahmud of Ghazni, took over the Ghaznavid dynasty empire established by his father, Sebuktegin, a Turkic origin ruler. Starting from the city of Ghazni (now in Afghanistan), Mehmood conquered the bulk of Khorasan, marched on Peshawar against the Hindu Shahis in Kabul in 1005, and followed it by the conquests of Punjab (1007), deposed the Shia Ismaili rulers of Multan, (1011), Kashmir (1015) and Qanoch (1017). By the end of his reign in 1030, Mahmud's empire extended from Kurdistan in the west to the Yamuna river in the east, and the Ghaznavid dynasty lasted until 1187. Contemporary historians such as Abolfazl Beyhaqi and Ferdowsi described extensive building work in Lahore, as well as Mahmud's support and patronage of learning, literature and the arts.
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate is a term used to cover five short-lived kingdoms or sultanates of Turkic origin in medieval India including the Punjab region. The sultanates ruled from Delhi between 1206 and 1526, when the last was replaced by the Mughal dynasty. The five dynasties were the Mamluk dynasty (1206–90); the Khilji dynasty (1290–1320); the Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1414); the Sayyid dynasty (1414–51); and the Lodi dynasty (1451–1526).
In 1160, Muhammad Ghori, a Turkic ruler, conquered Ghazni from the Ghaznavids and became its governor in 1173. He for the first time named Sindh Tambade Gatar roughly translated as the red passage. He marched eastwards into the remaining Ghaznavid territory and Gujarat in the 1180s, but was rebuffed by Gujarat's Hindu Solanki rulers. In 1186–87, he conquered Punjab, bringing the last of Ghaznevid territory under his control and ending the Ghaznavid empire. Muhammad Ghori's successors established the Delhi Sultanate. The Turkic origin Mamluk Dynasty, (mamluk means "owned" and referred to the Turkic youths bought and trained as soldiers who became rulers throughout the Islamic world), seized the throne of the Sultanate in 1211. Several Central Asian Turkic dynasties ruled their empires from Delhi: the Mamluk (1211–90), the Khalji (1290–1320), the Tughlaq (1320–1413), the Sayyid (1414–51) and the Lodhi (1451–1526).
The sultans eventually lost Afghanistan and western Pakistan to the Mongols (see the Ilkhanate Dynasty). The Sultanate declined after the invasion of Emperor Timur, who founded the Timurid Dynasty, and was eventually conquered in 1526 by the Mughal king Babar.
Guru Nanak (1469–1539), was born in the village of Rāi Bhōi dī Talwandī, now called Nankana, near Sial in modern-day Pakistan into a Hindu Khatri family. He was an influential religious and social reformer of north India and the saintly founder of a modern monothiestic order and first of the ten divine Gurus of Sikh Religion. At the age of 70, he had a miraculous death in Cartarpur, Punjab of modern-day Pakistan. Sikhism was created and would continue to grow; its followers, the Sikhs, would politicalise and militarise to play a historic role later.
Mughal Empire

In 1526, Babur, a Timurid descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan from Fergana Valley (modern day Uzbekistan), swept across the Khyber Pass and founded the Mughal Empire, covering modern day Afghanistan, Pakistan and India.[69] The Mughals were descended from Central Asian Turks (with significant Mongol admixture). However, his son Humayun was defeated by the Afghan warrior Sher Shah Suri in the year 1540, and Humayun was forced to retreat to Kabul. After Sher Shah died, his son Islam Shah Suri became the ruler of North India from 1540-53, on whose death his prime minister, Hemu, who had won 22 battles continuously against Afghans and Mughals during 1553-56, ascended the throne and ruled North India from Delhi. He was defeated by Emperor Akbar's forces in the Second Battle of Panipat on 6 November 1556.
Akbar the Great, was both a capable ruler and an early proponent of religious and ethnic tolerance and favored an early form of multiculturalism. He declared "Amari" or non-killing of animals in the holy days of Jainism and rolled back the jizya tax for idolators. The Mughal dynasty ruled most of the Indian subcontinent by 1600. The Mughal emperors married local royalty and allied themselves with local maharajas. For a short time in the late 16th century, Lahore was the capital of the empire. The architectural legacy of the Mughals in Lahore includes the Shalimar Gardens built by the fifth Emperor Shahjahan, and the Badshahi Mosque built by the sixth Emperor, Aurangzeb, who is regarded as the last Great Mughal Emperor as he expanded the domain to its zenith of 1 billion acres. After his demise, different regions of modern Pakistan began asserting independence. The empire went into a slow decline after 1707 and its last sovereign, ruling around Delhi region.
Post Mughal era
In 1747, the Durrani kingdom was established in by an Afghan generals, Ahmad Shah Abdali, and included Balochistan, Peshawar, Daman, Multan, Sind and Punjab. In the south, a succession of autonomous dynasties (the Daudpotas, Kalhoras and Talpurs) had asserted the independence of Sind, from the end of Aurangzeb's reign. Most of Balochistan came under the influence of the Khan of Kalat, apart from some coastal areas such as Gwadar, which were controlled by mutually competing and armed Portuguese, French and Dutch trading companies.(see also:Mai Safoora)
Maratha conquest
In 1758 the Maratha Empire's general Raghunathrao marched onwards, attacked and conquered Lahore and Attock and drove out Timur Shah Durrani, the son and viceroy of Ahmad Shah Abdali. Lahore, Multan, Kashmir and other subahs on the eastern side of Attock were under the Maratha rule for the most part. In Punjab and Kashmir, the Marathas were now major players.[70][71] In 1761, following the victory at the Third battle of Panipat between the Durrani and the Maratha Empire, Ahmad Shah Abdali captured remnants of the Maratha Empire in Punjab and Kashmir regions and had consolidated control over them.[72]
Sikh Rule

The Punjab was chaotic due to weakening of Durrani Empire, when Ranjit Singh took the control of Sukerchakias misal. This was achieved through delegation as the Sikhs were unable to take the Afghans out. The edifice of Ahmed Shah Abdali's empire in India had crumbled. Afghanistan was dismembered. Peshawar and Kashmir, though under the suzerainty of Afghanistan, had attained de facto independence. The Barakzais were now masters of these lands. Attock was ruled by Wazrikhels and Jhang lay at the feet of Sials. The Pashtuns ruled Kasur. Multan had thrown off the yoke and Nawab Muzaffar Khan was now ruler.

ca. 1835-40
Both Punjab and Sind had been under Afghan rule since 1757 when Ahmed Shah Abdali was granted suzerainty over these provinces. However, the Sikhs were now a rising power in Punjab. Taimur Khan, a local Governor, was able to expel the Sikhs from Amritsar and raze the fort of Ram Rauni. His control was short-lived, however, and the Sikh misal joined to defeat Taimur Shah and his Chief minister Jalal Khan. The Afghans were forced to retreat and Lahore was occupied by the Sikhs in 1758. Jassa Singh Ahluwalia proclaimed the Sikh's sovereignty and assumed leadership, striking coins to commemorate his victory.
While Ahmed Shah Abdali was engaged in a campaign against the Marathas at Panipat in 1761, Jassa Singh Ahluwalia plundered Sirhind and Dialpur, seized towns in the Ferozepur district, and took possession of Jagraon and Kot Isa Khan on the opposite bank of the Sutlej. He captured Hoshiarpur and Naraingarh in Ambala and levied tribute from the chief of Kapurthala. He then marched towards Jhang. The Sial chief offered stout resistance. However, when Ahmad Shah left in February 1761, Nawab Jassa Singh Ahluwalia again attacked Sirhind and extended his territory as far as Tarn Taran. When he crossed the Bias and captured Sultanpur in 1762, Ahmad Shah again appeared and a fierce battle took place. The ensuing holocaust was called Ghalughara. Following the rout of Sikh forces, Nawab Jassa Singh fled to the Kangra hills. After the departure of Ahmad Shah Abdali, Nawab Jassa Singh Ahluwalia again attacked Sirhind, razing it and killiing the Afghan Governor Zen Khan. This was a great victory for the Sikhs who now ruled all of the territory around the Sirhind.
Ahmad Shah died in June 1773. After his death the power of the Afghans declined in the Punjab. Taimur Shah ascended the throne at Kabul. By then the Misls were well established in the Punjab. They controlled territory as far as Saharnpur in the east, Attock in the west, Kangra Jammu in the north and Multan in the south. Efforts were made by Afghan rulers to dislodge the Sikhs from their citadels. Taimur Shah attacked Multan and temporarily defeated the Sardars of the Bhangi Misl. The Bhangi Misl controlled this principality and the powerful Bhangi misl army ("the most powerful of all the misl at this time"), Lehna Singh, and Sobha Singh[disambiguation needed] fled Lahore in 1767 when Abdali attacked, but reoccupied it, when Abdali left after plundering the town. They remained in power in Lahore until 1793 - the year when Shah Zaman acceded to the throne of Kabul.
The first attempt at conquest by Shah Zaman was in 1793. He came to Hasan Abdal from which he sent an army of 7000 cavalry under Ahmad Shah Shahnachi but the Sikhs routed them. It was a great setback to Shah Zaman, but in 1795 he reorganized forces and again attacked Hasan Abdal, This time he snatched Rohtas from the Sukerchikias, whose leader was Ranjit Singh. Singh suffered at Shah Zaman's hands. However, Shah Zaman had to return to Kabul as an invasion of his country from the west was apprehended. When he returned, Ranjit Singh dislodged the Afghans from Rohtas.
In 1796 Shah Zaman crossed the Indus for the third time and planned to capture Delhi. By now he had raised an Afghan army of 3000 men. He was confident a large number of Indians would join him. Nawab of Kasur had already assured him help. Sahib Singh of Patiala declared his intention to help Shah Zaman. Shah Zaman was also assured of help by the Rohillas, Wazir of Oudh, and Tipu Sultan of Mysore. The news of Shah Zaman's invasion spread quickly and people began fleeing to the hills for safety. By December Shah Zaman occupied territory up to Jhelum. When he reached Gujarat, Sahib Singh Bhangi panicked and left the place.
Next Shah Zaman marched on the territory of Ranjit Singh. Singh was alert and raised an army of 5000 horsemen. However, they were inadequately armed with only spears and muskets. The Afghans were equipped with heavy artillery. Ranjit Singh foresaw a strong, united fight against the invaders as he came to Amritsar. A congregation of Sarbat Khlasa was called and many Sikh sardars answered the call. There was general agreement that Shah Zaman's army should be allowed to enter the Punjab and that the Sikhs should retire to the hills.
Forces were reorganized under the command of Ranjit Singh and they marched towards Lahore. They gave the Afghans a crushing defeat in several villages and surrounded the city of Lahore. Sorties were made into the city at night in which they would kill a few Afghan soldiers and then leave under cover of darkness. Following this tactic they were able to dislodge Afghans from several places.
In 1797 Shah Zaman left for Afghansistan as his brother Mahmud had revolted. Shahanchi khan remained at Lahore with a sizeable army. The Sikhs followed Shah Zaman to Jhelum and snatched many goods from him. In returning, the Sikhs were attacked by the army of Shahnachi khan near Ram Nagar. The Sikhs routed his army. It was the first major achievement of Ranjit Singh.
Again in 1798 Shah Zaman attacked Punjab to avenge the defeat of 1797. The Sikh people took refuge in the hills. A Sarbat Khalsa was again called and Sada Kaur persuaded the Sikhs to fight once again to the last man. This time even Muslims were not spared by Shah Zaman's forces and he won Gujarat easily. Sada Kaur roused the Sikhs sense of national honour. If they were to again leave Amritsar, she would command the forces against the Afghans.
The Afghans plundered the towns and villages as they had vowed and declared that they would defeat the Sikhs. However, it was the Muslims who suffered most as the Hindus and Sikhs had already left for the hills. The Muslims had thought that they would not be touched but their hopes were dashed and their provisions forcibly taken from them by the Afghans.
Shah Zaman requested that Raja Sansar Chand of Kangra refuse to give food or shelter to the Sikhs. This was agreed. Shah Zaman attacked Lahore and the Sikhs, surrounded as they were on all sides, had to fight a grim battle. The Afghans occupied Lahore in November 1798 and planned to attack Amritsar. Ranjit Singh collected his men and faced Shah's forces about eight kilometres from Amritsar. They were well-matched and the Afghans were forced to retire. They fled towards Lahore. Ranjit Singh pursued them and surrounded Lahore. Afghan supply lines were cut, crops were burnt and other provisions plundered so that they did not fall into Afghan's hands. Nizam-ud.din of Kasur attacked the Sikhs near Shahdara on the banks of the Ravi, but his forces were no match for the Sikhs. Here too, it was the Muslims who suffered the most. The retreating Afghans and Nizam-ud-din forces plundered the town, antagonizing the local people.
By this time the people of the country had become aware of the rising strength of Ranjit Singh. The people of Lahore were favorably disposed towards Singh who they saw as a potential liberator. Muslims joined Hindu and Sikh residents of Lahore in making an appeal to Singh to free them.
A petition was written and was signed by Mian Ashak Muhammad, Mian Mukkam Din, Mohammad Tahir, Mohammad Bakar, Hakim Rai, and Bhai Gurbaksh Singh. It was addressed to Ranjit singh, requesting him to free them from the Bhangi sardars. They begged Singh to liberate Lahore as soon as possible. He mobilised an Army of 25,000 and marched towards Lahore on July 6, 1799.
Ranjit Singh entered the city with his troops through the Lahori Gate. Sada Kaur and a detachment of cavalry entered through Delhi gate. Before the Bhangi sardars realized it, a part of the citadel had been occupied without resistance. Sahib Singh and Mohar Singh left the city and sought protection. Chet Singh was left to either to fight to defend the town or flee. He shut himself in Hazuri Bagh with 500 men. Ranjit Singh's cavalry surrounded Hazuri Bagh. Chet Singh surrendered and was given permission to leave the city along with his family.
Ranjit Singh ultimately acquired a kingdom in the Punjab which stretched from the Sutlej River in the east to Peshawar in the west, and from the junction of the Sutlej and the Indus in the south to Ladakh in the north. Ranjit died in 1839, and a succession struggle ensued. Two of his successor maharajas were assassinated by 1843.
Sikh Empire (1799–1849)
(See main article Sikh Empire)
- Maharaja Ranjit Singh (born 1780, crowned April 12, 1801, died 1839)
- Kharak Singh (1801–1840), Eldest son of Ranjit Singh.
- Nau Nihal Singh (1821–1840), Grandson of Ranjit Singh.
- Sher Singh (1807–1843), Son of Ranjit Singh.
- Duleep Singh (born 1838, crowned 1843, died 1893), Youngest son of Ranjit Singh.
The British Empire annexed Punjab in c.1849 AD; after the First and Second Anglo-Sikh Wars.
British Raj


The entire Punjab region was occupied by the British East India Company, then the British Empire, by 1845 the British had moved 32,000 troops to the Sutlej frontier, to secure their northernmost possessions against the succession struggles in the Punjab. In late 1845, British and Sikh troops engaged near Ferozepur, beginning the First Anglo-Sikh War. The war ended the following year, and the territory between the Sutlej and the Beas was ceded to Great Britain, along with Kashmir, which was sold to Gulab Singh of Jammu, who ruled Kashmir as a British vassal.
As a condition of the peace treaty, some British troops, along with a resident political agent and other officials, were left in the Punjab to oversee the regency of Maharaja Dhalip Singh, a minor. The Sikh army was reduced greatly in size. In 1848, out-of-work Sikh troops in Multan revolted, and a British official was killed. Within a few months, the unrest had spread throughout the Punjab, and British troops once again invaded. The British prevailed in the Second Anglo-Sikh War, and under the Treaty of Lahore in 1849, the Punjab was annexed by the British East India Company, and Dhalip Singh was pensioned off. The Punjab became a province of British India, although a number of small states, most notably Patiala, retained local rulers who recognized British sovereignty.
In every way, the Punjab was one of Great Britain's most important assets in colonial India. Its political and geographic predominance gave Britain a base from which to project its power over more than 500 princely states that made up India. Lahore was a center of learning and culture under British rule, and Rawalpindi became an important Army installation.
The Jallianwala Bagh Massacre of 1919 occurred in Amritsar. In 1930, the Indian National Congress proclaimed independence from Lahore. The 1940 Lahore Resolution of the Muslim League to work for Pakistan, made Punjab the centerstage of a different, bloodier and dirtier struggle.
In 1946, massive communal tensions and violence erupted between the majority Muslims of Punjab, and the Hindu and Sikh minorities. The Muslim League attacked the government of Unionist Punjabi Muslims, Sikh Akalis and the Congress, and led to its downfall. Unwilling to be cowed down, Sikhs and Hindus counter-attacked and the resulting bloodshed left the province in great disorder. Both Congress and League leaders agreed to partition Punjab upon religious lines, a precursor to the wider partition of the country.
The British Punjab province, which includes present-day Punjab province of Pakistan, and the Indian states of Punjab, was partitioned in 1947 prior to the independence of Pakistan and subsequently, India. In India, the Panjab province was further partitioned into and forming Haryana, and Himachal Pradesh.
The Punjab of Republic of India and Islamic Republic of Pakistan

In 1947, the Punjab Province of British India was divided along religious lines into West Punjab and East Punjab. The western part was assimilated into new country of Pakistan while the east stayed in India. This led to massive rioting as both sides committed atrocities against fleeing refugees. The Partition of India in 1947 split the former Raj province of Punjab; the mostly Muslim western part became the Pakistani province of West Punjab and the mostly Sikh and Hindu eastern part became the Indian province of Punjab. Many Sikhs and Hindus lived in the west, and many Muslims lived in the east, and so partition saw many people displaced and much intercommunal violence. Several small Punjabi princely states, including Patiala, also became part of India. The undivided Punjab, of which Punjab (Pakistan) forms a major region today, was home to a large minority population of Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus unto 1947 apart from the Muslim majority.[73]
Eastern parts of Gurdaspur district in the northern point of the province adjoining Kashmir were given to India, with a small Muslim majority of 60% partitioned along the Ravi river leaving only Shakargarh sub-division on the Pakistani side, thus making the eastern half majority Muslims part of India. Gurdaspur and Firozpur, both Muslim regions, were handed over to India.
At the time of independence in 1947 and due to the ensuing horrendous exchange of populations, the Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus from western Punjab, in modern day Pakistan, migrated to India.[74] Punjabi Muslims were uprooted similarly from their homes in East Punjab which now forms part of India.[75] Approximately 7 million plus who moved to Pakistan, over 6 million settled in Punjab. In 1950, two new states were created; the former Raj province became the state of Punjab, while the princely states were combined into the Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU). Himachal Pradesh was created as a union territory from several princely states in hilly region.
Sikhs demanded a Punjabi speaking East Punjab with autonomous control. In 1965, a war broke out between India and Pakistan over the disputed region of Kashmir.
In 1966, owing to the demands made by the Akali Dal and various other organizations to create a Punjabi speaking state, the Government divided Punjab into a Punjabi-speaking state of the same name, and Hindi-speaking Haryana and Himachal Pradesh. Today Sikhs form about 60% of the population in Punjab.
In the 1960s, the Green Revolution swept India. Punjab's agricultural production trebled, and so did the prosperity of its people.
In the early 1980s, a group of Sikh fundamentalists started a movement to demand the completion of the Anandpur Sahib resolution. Discord developed after the rejection of the Anandpur Sahib Resolution. A small section of Sikhs demanded an independent state of Khalistan. A number of militants targeted officials and people opposed to their point of view, which included Hindus and some moderate Sikhs. Jarnail Singh Bhindranwala, a sikh extremist, sought shelter inside the Akal Takht in the Golden Temple premises. Fearing an arrest, Bhindranwala with help from Shabeg Singh heavily fortified the temple to resist Indian forces. The Indian army finally assaulted the Golden Temple to take out armed militants in June, 1984. However, the operation, Operation Bluestar resulted in heavy military and civilian casualties.
The situation in Punjab deteriorated into anarchy with a rise in radicalised militancy. By the early 1990s, after many years of violence across Punjab, the militants' struggle for Khalistan had lost much of the sympathy given after the assault on the Golden Temple, it had previously had from some Punjabi Sikhs and what little armed resistance remained was eliminated and forced underground. In the following years there was concern over alleged human rights abuses conducted by the central and state government against radical Sikhs, and many human rights organisations were not allowed in the Punjab at the time.[76]
The Indian Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)'s former leader stated that the Congress Party governments have been involved in creating terrorism in the Punjab. Recently, BJP national president Lal Krishna Advani, stated that it was his party which pressured Sikh Extremists to take a stand against the government.[77] The policy to help the Congress Party by creating militants and moderates backfired resulting in the deaths of thousands of innocent people.[78] Two notable attacks in Punjab were in 1991 and 1987, both attacks involving militants.[79][80]
The Wagah border post, is the chief crossing point between India and Pakistan. The Samjhauta (Understanding) Express runs between Atari, in Indian Punjab, to Lahore in Pakistan, as does the Delhi-Lahore bus. The Government of Pakistan allows small numbers of Sikhs to visit religious sites in Pakistani Punjab. The Indian Government allowed 3,000 Pakistani Sikhs to cross over recently, at the 300th anniversary of the founding of the Khalsa in 1999.
Punjab history timeline
- 2600–1900 BCE: Harappa Culture
- 1500–1000 BCE: Vedic Civilization
- 599 BCE: Jainism
- 567–487 or c. 400 BCE: Buddha
- 550–600 BCE: Buddhism remained prevalent
- 550–515 BCE: Persian Invasion to west of Indus River
- 326 BCE: Alexander's Invasion
- 322–185 BCE: Maurya Empire
- 45–180 CE: Kushana Empire
- 200–400 CE: Indo-Scythians
- 320–550: Gupta Empire
- 500: Hunnic Invasion
- 510–650: Vardhana Era
- 770-810: Pala Empire
- 647–1192: Rajput Period
- 711–713: Muhammad bin Qasim, the Arab general, conquer Sindh and Punjab regions along the Indus River (modern day Pakistan) for the Umayyad Caliphate.
- 713–1300: Delhi Sultanate (Turkic empires).
- 1206–1290: Mamluk dynasty establishes by Mohammad Ghori
- 1290–1320: Khilji dynasty establishes by Jalal ud din Firuz Khilji
- 1320–1413: Tughlaq dynasty established by Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq
- 1414–1451: Sayyid dynasty established by Khizr Khan
- 1451–1526: Lodhi dynasty establishes by Bahlul Khan Lodhi
- 1526–1707: Mughal rule
- 1526–1530: Zaheeruddin Muhammad Babur
- 1530–1540: Nasiruddin Muhammad Humayun
- 1540–1545: Sher Shah Suri
- 1545–1554: Islam Shah Suri
- 1555–1555: Nasiruddin Muhammad Humayun
- 1556–1556: Hem Chandra Vikramaditya
- 1556–1605: Jalaluddin Muhammad Akbar
- 1605–1627: Nooruddin Muhammad Jahangir
- 1627–1658: Shahaabuddin Muhammad Shah Jahan
- 1658–1707: Mohiuddin Muhammad Aurangzeb Alamgir
- 1707: The rule by the Mughal empire is weakened
- 1469–1539: Guru Nanak Dev (1st Guru) from the Sikh religion
- 1539–1675: Period of 8 Sikh Gurus from Guru Angad Dev to Guru Tegh Bahadur
- 1675–1708: Guru Gobind Singh (10th Sikh Guru)
- 1708–1715: Conquests of Banda Bahadur
- 1716–1759: The Sikhs minority battles against Moghul Governors
- 1739: Invasion of Nadir Shah from Persia
- 1748–1769: Ahmed Shah Abdali's (Durrani) nine invasions. The Sikhs and the Durrani empire in close competition for gaining control of the region
- 1761 : The Third Battle of Panipat, between the Durrani Empire against the Maratha Empire
- 1762: The 2nd Sikh holocaust, referred to as "Ghalughara" by Sikhs, from Ahmed Shah's 6th invasion
- 1764–1799: Rule by the Sikh Misls
- 1799–1839: Rule over Punjab by the minority community of Sikhs, led by Maharaja Ranjit Singh
- Maharaja Ranjit Singh (born 1780, crowned April 12, 1801, died 1839)
- Kharak Singh (1801–1840), Eldest son of Ranjit Singh.
- Nau Nihal Singh (1821–1840), Grandson of Ranjit Singh.
- Sher Singh (1807–1843), Son of Ranjit Singh.
- Duleep Singh (born 1838, crowned 1843, died 1893), Youngest son of Ranjit Singh.
- 1849 : Annexation of Punjab - The British Empire annexed Punjab in c.1845-49; after the First and Second Anglo-Sikh Wars
- 1849–1947: British India established
- 1911: Calcutta ceases to be capital of Indian Empire and Delhi is removed from Punjab and becomes new capital territory
- 1947 : Partition of British India thus Punjab into 2 parts the Eastern part (or two rivers) became the Indian Punjab and the Western majority part (3 rivers) the Pakistan Punjab
- 1966: Punjab in India divided into three parts on linguistic basis - Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Punjabi Suba (the present India Punjab)
References
- ^ Ain-i-Akbari
- ^ Punjabi Adab De Kahani, Abdul Hafeez Quraishee, Azeez Book Depot, Lahore, 1973.
- ^ The Myth of the Aryan Invasion Theory "The New Model" by David Frawley
- ^ The Aryan Non-Invasionist Model by Koenraad Elst
- ^ Rig Veda VII.18,19, 83.
- ^ Rig Veda 7.18.6; 5.13.14; 7.18.12, 7.83.1-6; The Rig Veda and the History of India, 2001. (Aditya Prakashan), ISBN 81-7742-039-9, David Frawley.
- ^ Anguttara Nikaya I. 213; IV. 252, 256, 260, 261.
- ^ Cf: History of the Punjab, 2004, p 32, D. C. Sircar, Editors Fauja Singh, Lal Mani Joshi, Punjabi University Dept. of Punjab Historical Studies; Cf: Studies in the Geography of Ancient and Medieval India, 1990, pp 34, 100, D.C. Sircar - History; Geographical Data in the Early Purāṇas: A Critical Study, 1972, p 166 sqq, M. R. Singh - India; History of India, 2004, p 52, Hermann Kulke, Dietmar Rothermund; International Dictionary of Historic Places, 1995, p 608, Trudy Ring, Robert M. Salkin, Noelle Watson, Sharon La Boda, Paul Schellinger.
- ^ Sumangala Vilāsinī (P.T.S.). Vol I, 124; Manorathapūranī, Anguttara Commentary (S.H.B.), I, 199; Aruppa-Niddesa of Visuddhi magga (P.T.S.), 332; Jātaka, ed. Fausboll,, vol IV, 464 etc. See also: Mahavastu, II. 185; Kunala Jataka v. 28, Vinaya Pitaka, Vol III etc. See also: Historie du Bouddhisme Indien, p 110, E. Lamotte.
- ^ Lord Mahāvīra and his times, 1974, p 197, Dr Kailash Chand Jain; The History and Culture of the Indian People, 1968, p lxv, Dr Ramesh Chandra Majumdar, Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, Bhāratīya Itihāsa Samiti; Problems of Ancient India, 2000, p 7, K. D. Sethna.
- ^ Ashtadhyayi Sutra V.3.114-117.
- ^ Ashtadhyayi Sutra IV.3.91.
- ^ Forlong, J.G.R. (1906). Encyclopedia of Religion or Faiths of Man, Vol II. Kessinger Publishing. p. 282. ISBN 0766143082.
- ^ See Gannapatha V.3.116, V.3.117, V.3.118, besides Sutras V.3.113-118 etc.
- ^ Ashtadhyayi Sutra VI.4.174.
- ^ Ashtadhyayi Sutra IV.1.110.
- ^ Nadadigana IV.1.90
- ^ Ashtadhyayi Sutra IV.1.168-174.
- ^ Shamasatry, R. (1966). Kautiliya's Arthashastra, Book Xi. p. 407.
- ^ Ramachandra Dikshitar, V. R. (1932). The Mauryan Polity. p. 70.
- ^ Mookerji, Dr Radha Kumud (1940–41). Chandragupta Maurya and His Times: Madras University, Sir William Meyer Lectures. p. 168. ISBN 8120804058.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ^ Sensarma, P. (1977). The Military History of Bengal. p. 47.
- ^ Saletore, Bhasker Anand (1960). Main Currents in the Ancient History of Gujarat. p. 24.
- ^ Studies in Kautilya, 1953, p 15, Prof. Venkata Krishna Rao.
- ^ Hindu Polity (The Ordinance of Manu), 1972, p 29, Dr Arthur Coke Burnell.
- ^ a b c Joshi, Dr L. M. (1972). History of Punjab, Vol I. Publication Bureau, Punjabi University, Patiala.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Evolution of Heroic Tradition in Ancient Panjab, pp 21-70, Dr Buddha Prakash.
- ^ Faiths of Man: A Cyclopædia of Religions, 1906, p 280, p James George Roche Forlong.
- ^ Other classical names are Assaceni, Aseni, Aspii and Hippasii etc.
- ^ Other classical names are Assacani, Asoi, Asii/Osii, etc.
- ^ "Asoi" is also a clan name amongst the modern Kamboj people of Punjab, which seems to connect them with the Asoi/Assakenoi or the Ashvakayna of the Swat/Kunar valleys.
- ^ a b c Raychaudhury, Dr Hemchandra C. (1950). Political History of Ancient India.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Cf: Ancient India, 1922, p 352, fn 3, Edward James Rapson - India.
- ^ India as Known to Panini, 1953, pp 424, 456, Dr V. S. Aggarwala; Ancient Kamboja, People and the Country, 1981, Dr J. L. Kamboj, Dr Satyavrat Śastri.
- ^ East and West, 1950, p 28, Istituto italiano per il Medio ed Estremo Oriente, Editor, Prof Giuseppe Tucci, Co-editors Prof Mario Bussagli, Prof Lionello Lanciotti.
- ^ Ashtadhyayi Sutra VI.1.110 & Nadadigana 4.1.99 respectively
- ^ Ashva-yuddha-Kushalah.... Mahabharata, 12,105.5.
- ^ Note: Horse in Sanskrit means Ashva, in Prakrit Assa and in Persian means Aspa. Scholars say that classical name Assakenoi, Assacani, Asoi/Osii etc derives from Prakrit Assa/or Sanskrit Ashva. Similarly the classical Aspasio, Aspasii, Hippasii, Assaceni, Aseni derives from Persian Aspa.
- ^ Samangalavilasini, Vol I, p 124).
- ^ Historie du bouddhisme Indien, p 110, Dr E. Lammotte.
- ^ East and West, 1950, pp 28, 157-58, Istituto italiano per il Medio ed Estremo Oriente, Editor, Prof Giuseppe Tucci, Co-editors Prof Mario Bussagli, Prof Lionello Lanciotti.
- ^ Jayaswal, Kashi Prasad (1978). Hindu Polity, A contitutional History of India in Hindu Times.
- ^ Dr Buddha (1967). History of Poros. p. 12,39.
- ^ Cf: Glimpses of Ancient Panjab: (Sita Ram Kohli Memorial Lectures), 1966, p 23, Dr Buddha Prakash - Punjab (India).
- ^ For Saka reference see Invasion of India by Scythian Tribes.
- ^ Diodorus in McCrindle, p 270; History of Civilizations of Central Asia, 1999, p 76, Ahmad Hasan Dani, Vadim Mikhaĭlovich Masson, János Harmatta, Boris Abramovich Litvinovskiĭ, Clifford Edmund Bosworth, UNESCO - Asia, Central
- ^ John Marshall "Taxila", p18, and al.
- ^ Sanskrit original, Mudrarakshasa 2
- ^ "Parthian Pair of Earrings". Marymount School, New York. Retrieved 2007-11-22.
- ^ Gupta Dynasty – MSN Encarta. Archived from the original on 2009-10-31.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.fsmitha.com/h1/ch28gup.htm
- ^ http://www.wsu.edu:8001/~dee/ANCINDIA/GUPTA.HTM
- ^ http://www.indianchild.com/gupta_empire.htm
- ^ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/249590/Gupta-dynasty
- ^ Mahajan, V.D. (1960) Ancient India, New Delhi: S. Chand, ISBN 81-219-0887-6, p.540
- ^ Gupta dynasty: empire in 4th century – Britannica
- ^ http://www.historybits.com/gupta.htm
- ^ http://www.pbs.org/thestoryofindia/gallery/photos/8.html
- ^ Agarwal, Ashvini (1989). Rise and Fall of the Imperial Guptas, Delhi:Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 81-208-0592-5, pp.264–269
- ^ Thakur Deshraj, Jat Itihas (Hindi), Maharaja Suraj Mal Smarak Shiksha Sansthan, Delhi, 1934, 2nd edition 1992
- ^ A reference to the religion of Emperor Harshavardhana"History of India".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ H. M. Elliot and John Dowson, History of India As Told by Its own Historians, Vol. I, p. 429 and Vol. II, pp. 416-417; Also Andre Wink, Al Hind, pp. 121-123 quoting C. E. Bosworth’s Sistan Under the Arabs.
- ^ Raizada Harichand Vaid, Gulshane Mohyali, Part II, pp. 80-86.
- ^ R. T. Mohan, AFGHANISTAN REVISITED, The Brahmana Hindu Shahis of Afghanistan and the Punjab (c. 840-1026 CE), Appendix – C, pp. 170-172.
- ^ John Briggs, Tr. The History of the Rise of Mahomedan Power in India of Mahomed Kasem Ferishta, Vol. I, p.9.
- ^ Elliot and Dowson, History of India … translation of extracts from Tarikh Yamini, by Al Utbi, pp. 19-23.
- ^ K. A Nizami, Ed. Politics and Society During the Early Medieval Period by Mohammad Habib, p. 46.
- ^ R. T. Mohan, AFGHANISTAN REVISITED, The Brahmana Hindu Shahis of Afghanistan and the Punjab (c. 840-1026 CE), pp. 120-153 (Delhi, 2010).
- ^ The Islamic World to 1600: Rise of the Great Islamic Empires (The Mughal Empire)
- ^ Roy, Kaushik. India's Historic Battles: From Alexander the Great to Kargil. Permanent Black, India. pp. 80–1. ISBN 978-8178241098.
- ^ Elphinstone, Mountstuart (1841). History of India. John Murray, Albermarle Street. p. 276.
- ^ For a detailed account of the battle fought, see Chapter VI of The Fall of the Moghul Empire of Hindustan by H. G. Keene.
- ^ The Punjab in 1920s – A Case study of Muslims, Zarina Salamat, Royal Book Company, Karachi, 1997. table 45, pp. 136. ISBN 969-407-230-1
- ^ Panel 33 European Association for South Asian Studies
- ^ Pakistan: a modern history, Ian Talbot, St. Martin's Press, 1999. ISBN 0-312-21606-8
- ^ See Amnesty Reports such as Punjab Trauma
- ^ Advani’s Blue Star remark makes Akali Dal see red- Hindustan Times
- ^ [1] BJP accuses Congress of Terrorism
- ^ Extremists in India Kill 80 on 2 Trains As Voting Nears End, The New York Times (June 16, 1991)
- ^ New York Times
