Flexible impeller
Appearance
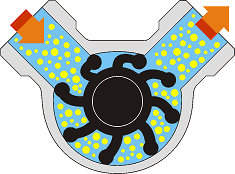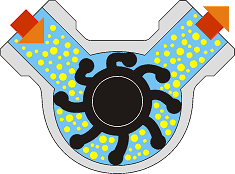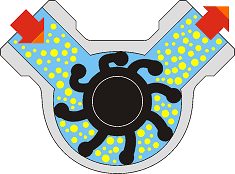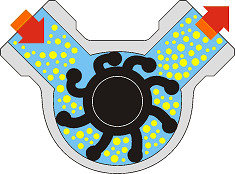
Note the variable vane volume, that during the rotation cause the dry selfpriming feature of the pump.
Most of these pumps are also reversible.
A flexible impeller pump is a positive-displacement pump that consists of flexible impeller vanes that deform slightly to pump the liquid inside the pump and move it to the discharge port with a no pulsating flow rate. This principle combines gentle pumping with a high dry self-priming action.
Types
- Execution: closed coupled, bare shaft, with hidraulic motor, belt driven, gearmotor, mechanical speed variator, frequency converter,...
- Couplings: DIN 11851, Garolla, BSP, Macon, Triclover, SMS, BSM/RJT,...
Uses
Particularly suitable for transfer of viscous, delicate, and slurry fluids even with high solid content. Widely used in the oenological field, food processing, chemical industry, cosmetic and marine field.
Materials
Pump housing can be made in high grade stainless steel, in bronze for marine application, but also in other material.
The impeller can be made made of:
- Natural Rubber - Excellent for water based liquid at room temperature, highest mechanical resistance.
- Neoprene (CR) - Good balance between chemical and mechanical resistance.
- Nitrile (NBR) - Excellent resistance to oils and fats.
- EPDM - Best for hot fluid and CIP cleaning. Excellent for acid and alkaline fluids.
- Silicon (VMQ) - Best for high temperature but low mechanical resistance.
The mechanical seal can be made made of:
- Ceramic
- Stainless steel Tungsten carbide-NBR, Tungsten carbide-Viton
- Graphite
- Tungsten carbide
- Silicon carbide
- Elastomers: NBR, EPDM, VITON,...
