Frequency
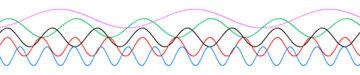
Frequency is the measurement of the number of times that a repeated event occurs per unit of time. It is also defined as the rate of change of phase of a sinusoidal waveform.
Frequency of waves
Frequency has an inverse relationship to the concept of wavelength. The frequency f is equal to the speed v of the wave divided by the wavelength λ (lambda) of the wave:
In the special case of electromagnetic waves moving through a vacuum, then v = c, where c is the speed of light in a vacuum, and this expression becomes:
Note. When waves travel from one medium to another, their frequency remains exactly the same — only their wavelength and speed change.
Invariance
Apart from its being modified by Doppler effect, frequency is an invariant quantity in the universe. That is, it cannot be changed by any physical process unlike velocity of propagation or wavelength.
Examples
- The frequency of the standard pitch A above middle C is usually defined as 440 Hz, that is, 440 cycles per second () and known as concert pitch, to which an orchestra tunes.
- A baby can hear tones with oscillations up to approximately 20,000 Hz, but these frequencies become more difficult to hear as people age.
- In Europe, the frequency of the alternating current in mains is 50 Hz (close to the tone G), however, in North America, the frequency of the alternating current is 60 Hz (close to the tone B flat — that is, a minor third above the European frequency). The frequency of the 'hum' in an audio recording can show where the recording was made — in Europe or in America.


