Mauritania
This article appears to be slanted towards recent events. (May 2013) |
Islamic Republic of Mauritania | |
|---|---|
| Motto: شرف إخاء عدل (Arabic) "Honor, Fraternity, Justice" | |
| Anthem: National anthem of Mauritania | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Nouakchott |
| Official languages | Arabica |
| Recognised national languages | |
| Other languages | French[1] |
| Demonym(s) | Mauritanian |
| Government | Islamic republicb |
| Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz | |
| Moulaye Ould Mohamed Laghdaf | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| National Assembly | |
| Independence | |
• from France | 28 November 1960 |
• Current Constitution of Mauritania | 12 July 1991 |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,030,700 km2 (398,000 sq mi) (29th) |
• Water (%) | 0.03 |
| Population | |
• 2012 estimate | 3,359,185[2] |
• 1988 census | 1,864,236[3] |
• Density | 3.2/km2 (8.3/sq mi) (221st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2012 estimate |
• Total | $7.697 billion[4] |
• Per capita | $2,121[4] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2012 estimate |
• Total | $4.199 billion[4] |
• Per capita | $1,157[4] |
| Gini (2008) | 40.5[5] medium inequality |
| HDI (2011) | low (159th) |
| Currency | Ouguiya (MRO) |
| Time zone | UTC+0 |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+0 (not observed) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +222 |
| ISO 3166 code | MR |
| Internet TLD | .mr |
Mauritania /mɔːrɪˈteɪniə/ ⓘ (Template:Lang-ar Mūrītānyā; Berber: Muritanya / Agawej; Template:Lang-wo; Soninke: Murutaane; Pulaar: Moritani; Template:Lang-fr), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is an Arab Maghreb country in West Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean in the west, by Western Sahara in the north, by Algeria in the north east, by Mali in the east and southeast, and by Senegal in the southwest. It is named after the ancient Berber Kingdom of Mauretania, which later became a province of the Roman Empire, even though the modern Mauritania covers a territory far to the south of the old Berber kingdom that had no relation with it. The capital and largest city is Nouakchott, located on the Atlantic coast.
The government of Mauritania was overthrown on 6 August 2008, in a military coup d'état led by General Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz. On 16 April 2009, General Aziz resigned from the military to run for president in the 19 July elections, which he won. In Mauritania about 20% of the population live on less than US$1.25 per day.[7]
Slavery in Mauritania has been called[by whom?] a major human rights issue[8] as well as female genital mutilation[citation needed], child labour, and human trafficking.
History
Ancient history
The Bafours were primarily agriculturalist, and among the first Saharan people to abandon their historically nomadic lifestyle. With the gradual desiccation of the Sahara, they headed south.
Successive waves of migration to West Africa included not only Central Saharans, but in 1076, Moorish Islamic warrior monks (Almoravid or Al Murabitun) who attacked and conquered the ancient Ghana Empire. Over the next 500 years, Arabs overcame fierce resistance from the local population (Berber and non-Berber alike) to dominate Mauritania. The Mauritanian Thirty-Year War (1644–74) was the unsuccessful final effort to repel the Yemeni Maqil Arab invaders led by the Beni Hassan tribe.
The descendants of the Beni Hassan warriors became the upper stratum of Moorish society. Berbers retained influence by producing the majority of the region's Marabouts—those who preserve and teach Islamic tradition. Many of the Berber tribes claimed Yemeni (and sometimes other Arab) origin; there is little evidence to support such claims, though some studies do make a connection between the two.[9] Hassaniya, a Berber-influenced Arabic dialect that derives its name from the Beni Hassan, became the dominant language among the largely nomadic population.
Modern history
Imperial France gradually absorbed the territories of present-day Mauritania from the Senegal river area and upwards, starting in the late 19th century. In 1901, Xavier Coppolani took charge of the imperial mission. Through a combination of strategic alliances with Zawiya tribes, and military pressure on the Hassane warrior nomads, he managed to extend French rule over the Mauritanian emirates. Trarza, Brakna and Tagant quickly submitted to treaties with the colonial power (1903–04), but the northern emirate of Adrar held out longer, aided by the anticolonial rebellion (or jihad) of shaykh Maa al-Aynayn. It was finally defeated militarily in 1912, and incorporated into the territory of Mauritania, which had been drawn up in 1904. Mauritania would subsequently form part of French West Africa, from 1920.
French rule brought legal prohibitions against slavery, and an end to interclan warfare. During the colonial period 90% of the population remained nomadic, but many sedentary peoples, whose ancestors had been expelled centuries earlier, began to trickle back into Mauritania. As the country gained independence in 1960, the capital city Nouakchott was founded at the site of a small colonial village, the Ksar.
With independence, larger numbers of indigenous Sub-Saharan African peoples (Haalpulaar, Soninke, and Wolof) entered Mauritania, moving into the area north of the Senegal River. Educated in French language and customs, many of these recent arrivals became clerks, soldiers, and administrators in the new state. This occurred as France militarily suppressed the most intransigent Hassane tribes of the Moorish north, shifting old balances of power, and creating new cause for conflict between the southern populations and Moors. Between these groups stood the Haratin, a very large population of Arabized slaves of sub-Saharan African origins, who lived within Moorish society, integrated into a low-caste social position.[10] Modern-day slavery is still a common practice in Mauritania.[11] According to some estimates, up to 600,000 Mauritanians, or 20% of the population, are still enslaved.[12][13] A 2012 CNN report, "Slavery's Last Stronghold," by John D. Sutter, describes and documents the ongoing slave-owning cultures, including a compelling story about a former slave owner who is now an active abolitionist.[14] This social discrimination concerns mainly the "black Moors" (Haratin) in the northern part of the country, where tribal elites among “white Moors” (Beidane) hold sway, but low-caste groups within the sub-Saharan African ethnic groups of the south are affected by similar practices.
The great Sahel droughts of the early 1970s caused massive devastation in Mauritania.
Moors reacted to changing circumstances, and to Arab nationalist calls from abroad, by increasing pressure to Arabize many aspects of Mauritanian life, such as law and language. A schism developed between those Moors who consider Mauritania to be an Arab country and those who seek a dominant role for the non-Moorish peoples, with various models for maintaining the country's cultural diversity being suggested, but none successfully implemented.
This ethnic discord was evident during intercommunal violence that broke out in April 1989 (the “1989 Events” and “Mauritania–Senegal Border War”), but which has since subsided. Some 70,000 sub-Saharan African Mauritanians were expelled from Mauritania in the late 1980s.[15] Ethnic tension and the sensitive issue of slavery – past and, in some areas, present – are still powerful themes in the country's political debate; a significant number from all groups, however, seek a more diverse, pluralistic society.
The government bureaucracy is composed of traditional ministries, special agencies, and parastatal companies. The Ministry of Interior spearheads a system of regional governors and prefects modeled on the French system of local administration. Under this system, Mauritania is divided into thirteen regions (wilaya), including the capital district, Nouakchott. Control is tightly concentrated in the executive branch of the central government, but a series of national and municipal elections since 1992 have produced limited decentralization.
Mauritania, along with Morocco, annexed the territory of Western Sahara in 1976, with Mauritania taking the lower one-third at the request of former imperial power Spain. After several military losses to the Polisario – heavily armed and supported by Algeria, the local hegemon and rival to Morocco – Mauritania withdrew in 1979, and its claims were taken over by Morocco. Due to economic weakness, Mauritania has been a negligible player in the territorial dispute, with its official position being that it wishes for an expedient solution that is mutually agreeable to all parties. While most of Western Sahara has been occupied by Morocco, the UN still considers the Western Sahara a territory that needs to express its wishes with respect to statehood. A referendum is still supposed to be held sometime in the future, under UN auspices, to determine whether or not the indigenous Sahrawis wish to be independent as the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, or to be part of Morocco. The Moroccan government has thus far blocked such a referendum.
Ould Daddah era (1960–78)
Mauritania left the Franco-African Community to become an independent nation in November 1960.[16] In 1964 President Moktar Ould Daddah, originally installed by the French, formalized Mauritania as a one-party state with a new constitution, setting up an authoritarian presidential regime. Daddah's own Parti du Peuple Mauritanien (PPM) became the ruling organization in a single-party system. The President justified this decision on the grounds that he considered Mauritania unready for western-style multi-party democracy. Under this one-party constitution, Daddah was reelected in uncontested elections in 1966, 1971 and 1976. He was ousted in a bloodless coup on 10 July 1978, after bringing the country to near-collapse through a disastrous war to annex the southern part of Western Sahara, framed as an attempt to create a “Greater Mauritania”.
CMRN and CMSN military governments (1978–84)

Col. Mustafa Ould Salek's CMRN junta proved incapable of either establishing a strong base of power or extracting the country from its destabilizing conflict with the Sahrawi resistance movement, the Polisario Front. It quickly fell, to be replaced by another military government, the CMSN. The energetic Colonel Mohamed Khouna Ould Haidallah soon emerged as its strongman, and by giving up all claims to Western Sahara, he found peace with the Polisario and improved relations with its main backer, Algeria – but relations with the other party to the conflict, Morocco, and its European ally France, deteriorated. Instability continued, and Haidallah's ambitious reform attempts foundered. His regime was plagued by attempted coups and intrigue within the military establishment, and became increasingly contested due to his harsh and uncompromising measures against opponents; many dissidents were jailed, and some executed. In 1981 slavery was legally abolished, making Mauritania the last country in the world to abolish slavery.
Politics and recent history
Ould Taya's rule (1984–2005)
In 1980, Haidallah was deposed by Colonel Maaouya Ould Sid'Ahmed Taya, who, while retaining tight military control, relaxed the political climate somewhat. Ould Taya moderated Mauritania's previous pro-Algerian stance, and re-established ties with Morocco during the late 1980s, ties which deepened during the late 1990s and early 2000s as part of Mauritania's drive to attract support from Western states and Western-aligned Arab states. Mauritania has not rescinded its recognition of Polisario's Western Saharan exile government, and remains on good terms with Algeria. Its position on the Western Sahara conflict is, since the 1980s, one of strict neutrality.
Ordinance 83.127, enacted 5 June 1983, started the process of nationalization of all land not clearly the property of a documented owner, thus abolishing the traditional system of land tenure. Potential nationalization was based on the concept of "dead land",[17] i.e., property which has not been developed or on which obvious development cannot be seen. A practical effect was government seizure of traditional grazing lands.[18]
Political parties, illegal during the military period, were legalized again in 1991. By April 1992, as civilian rule returned, 16 major political parties had been recognized; 12 major political parties were active in 2004. Most opposition parties boycotted the first legislative election in 1992, and for nearly a decade the parliament was dominated by the PRDS. The opposition participated in municipal elections in January–February 1994, and in subsequent Senate elections – most recently in April 2004 – and gained representation at the local level, as well as three seats in the Senate. The Parti Républicain Démocratique et Social (PRDS), formerly led by President Maaouya Ould Sid'Ahmed Taya, dominated Mauritanian politics after the country's first multi-party elections in April 1992, following the approval by referendum of the current constitution in July 1991. President Taya won elections in 1992 and 1997.
This period was marked by extensive ethnic violence and human rights abuses. Between 1990 and 1991, a campaign of particularly extreme violence took place against a background of Arabization, interference with blacks' association rights, expropriation, expatriation and slavery. The slaves were mostly black.[19]
In October 1987, the government allegedly uncovered a tentative coup d'État by a group of black army officers, backed, according to the authorities, by Senegal.[20] Fifty-one officers were arrested and subjected to interrogation and torture.[21] Heightened ethnic tensions were the catalyst for the Mauritania–Senegal Border War, which started as a result of a conflict in Diawara between Moorish Mauritanian herders and Senegalese farmers over grazing rights.[22] On 9 April 1989, Mauritanian guards killed two Senegalese.[23] Following the incident, several riots erupted in Bakel, Dakar and other towns in Senegal, directed against the mainly Moorish Mauritanians who dominated the local retail business. The rioting, added to already existing tensions, led to a campaign of terror against black Mauritanians,[24] who are often seen as 'Senegalese' by Beidanes, regardless of their actual nationality. As conflict with Senegal continued into 1990/91, the Mauritanian government engaged in or encouraged acts of violence and seizures of property directed against blacks. The war culminated in an international airlift agreed to by Senegal and Mauritania under international pressure to prevent further violence. The Mauritanian Government expelled tens of thousands of black Mauritanians. Most of these so-called 'Senegalese' had no ties to Senegal, and many still reside in refugee camps in Mali and Senegal.[25] The exact number of expulsions is not known but the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) estimates that, as of June 1991, there were 52,995 Mauritanian refugees in Senegal and at least 13,000 in Mali.[26]
From November 1990 to February 1991, between 500 and 600 Fulas and Soninke political prisoners were executed or tortured to death by government forces. They were among 3,000 to 5,000 blacks – predominantly soldiers and civil servants – arrested between October 1990 and mid-January 1991,[27] on the basis of alleged involvement in an attempt to overthrow the government.[28] A military investigation was put in place by the government and the results were never made public.[29] In order to guarantee immunity for those responsible and to block any attempts at accountability for past abuses, an amnesty[30] was declared by the Parliament in June 1993 covering all crimes committed by the armed forces, security forces as well as civilians, between April 1989 and April 1992. The government offered compensation to families of victims, which a few accepted in lieu of settlement.[28] Despite this amnesty, some Mauritanians have denounced the involvement of the government in the arrests and killings.[31]
In the late 1980s, Ould Taya had established close co-operation with Iraq, and pursued a strongly Arab Nationalist line. Mauritania grew increasingly isolated internationally, and tensions with Western countries grew dramatically after it took a pro-Iraqi position during the 1991 Gulf War. During the mid-to late 1990s, Mauritania shifted its foreign policy to one of increased co-operation with the US and Europe, and was rewarded with diplomatic normalization and aid projects. On 28 October 1999, joined Egypt, Palestine, and Jordan as the only members of the Arab League to officially recognize Israel. Ould Taya also started co-operating with the United States in anti-terrorism activities, a policy which was criticized by some human rights organizations.[32][33] (See also Foreign relations of Mauritania.)

A group of current and former Army officers launched a bloody, unsuccessful coup attempt on 8 June 2003. The leaders of the attempted coup were never caught. Mauritania's presidential election, its third since adopting the democratic process in 1992, took place on 7 November 2003. Six candidates, including Mauritania's first female and first Haratine (former slave family) candidates, represented a wide variety of political goals and backgrounds. Incumbent President Maaouya Ould Sid'Ahmed Taya won reelection with 67.02% of the popular vote, according to the official figures, with Mohamed Khouna Ould Haidalla finishing second.
August 2005 military coup
On 3 August 2005, a military coup led by Colonel Ely Ould Mohamed Vall ended Maaouya Ould Sid'Ahmed Taya's twenty-one years of rule. Taking advantage of Taya's attendance at the funeral of Saudi King Fahd, the military, including members of the presidential guard, seized control of key points in the capital of Nouakchott. The coup proceeded without loss of life, and the officers, calling themselves the Military Council for Justice and Democracy, released the following statement:
- "The national armed forces and security forces have unanimously decided to put a definitive end to the oppressive activities of the defunct authority, which our people have suffered from during the past years."[34]
The Military Council later issued another statement naming Colonel Vall as president and director of the national police force, the Sûreté Nationale. Vall, once regarded as a firm ally of the now-ousted president, had aided Taya in the coup which had originally brought him to power, and had later served as his security chief. Sixteen other officers were listed as members of the Council.
Though cautiously watched by the international community, the coup came to be generally accepted, with the military junta organizing elections within a promised two-year timeline. In a referendum on 26 June 2006, Mauritanians overwhelmingly (97%) approved a new constitution which limited the duration of a president's stay in office. The leader of the junta, Col. Vall, promised to abide by the referendum and relinquish power peacefully. Mauritania's establishment of relations with Israel – it is one of only three Arab states to recognize Israel – was maintained by the new regime, despite widespread criticism from the opposition, who viewed it as a legacy of the Taya regime's attempts to curry favor with the West.
Parliamentary and municipal elections in Mauritania took place on 19 November and 3 December 2006.
2007 presidential election

Mauritania's first fully democratic presidential election took place on 11 March 2007. The election effected the final transfer from military to civilian rule following the military coup in 2005. This was the first time that the president had been selected in a multi-candidate election in the country's post-independence history.[35]
The election was won in a second round of voting by Sidi Ould Cheikh Abdallahi, with Ahmed Ould Daddah a close second.
2008 military coup
The head of the Presidential Guards took over the president's palace in Nouakchott on 6 August 2008, a day after 48 lawmakers from the ruling party resigned in protest of President Abdallahi's policies[which?]. The army surrounded key government facilities, including the state television building, after the president fired senior officers, one of them the head of the presidential guards.[36] The President, Prime Minister Yahya Ould Ahmed Waghef, and Minister of Internal Affairs Mohamed Ould R'zeizim were arrested.
The coup was co-ordinated by General Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz, former chief of staff of the Mauritanian army and head of the Presidential Guard, one of the officers whom the president had recently fired. Mauritania's presidential spokesman, Abdoulaye Mamadouba, said the President, Prime Minister, and Interior Minister had been arrested by renegade Senior Mauritanian army officers and were being held under house arrest at the presidential palace in Nouakchott.[37][38][39] In the apparently successful and bloodless coup d'état, Abdallahi's daughter, Amal Mint Cheikh Abdallahi, said: "The security agents of the BASEP (Presidential Security Battalion) came to our home and took away my father."[40] The coup plotters, all dismissed in a presidential decree shortly beforehand, included Abdel Aziz, General Muhammad Ould Al-Ghazwani, General Philippe Swikri, and Brigadier General (Aqid) Ahmad Ould Bakri.[41]
After the coup

A Mauritanian lawmaker, Mohammed Al Mukhtar, claimed that many of the country's people were supporting the takeover of a government that had become "an authoritarian regime" under a president who had "marginalized the majority in parliament."[42] The coup was also backed by Abdallahi's rival in the 2007 election, Ahmed Ould Daddah. However, Abdel Aziz's regime was isolated internationally, and became subject to diplomatic sanctions and the cancellation of some aid projects. It found few supporters (among them Morocco, Libya and Iran), while Algeria, the United States, France and other European countries criticized the coup, and continued to refer to Abdallahi as the legitimate president of Mauritania. Domestically, a group of parties coalesced around Abdallahi to continue protesting the coup, which caused the junta to ban demonstrations and crack down on opposition activists. International and internal pressure eventually forced the release of Abdallahi, who was instead placed under house arrest in his home village. The new government broke off relations with Israel. In March 2010, Mauritania's female foreign minister Mint Hamdi Ould Mouknass announced that Mauritania had cut ties with Israel in a "complete and definitive way."[43]
Abdel Aziz had since the coup insisted on holding new presidential elections to replace Abdallahi, but was forced to reschedule them due to internal and international opposition. However, during the spring of 2009, the junta negotiated an understanding with some opposition figures and international parties, which dramatically changed the situation. Abdallahi formally resigned, under protest, as it became clear that some opposition forces had defected from him and most international players, notably including France and Algeria, now lined up behind Abdel Aziz. The United States continued to criticize the coup, but did not actively oppose the elections. Abdallahi's resignation allowed the election of Abdel Aziz as civilian president, on 18 July, by a 52% majority. Many of Abdallahi's former supporters criticized this as a political ploy and refused to recognize the results. They argued that the election had been falsified due to junta control, and complained that the international community had let down the opposition. Despite marginal complaints, the elections were almost unanimously accepted by Western, Arab and African countries, which lifted sanctions and resumed relations with Mauritania. By late summer, Abdel Aziz appeared to have secured his position and to have gained widespread international and internal support, although several[which?] influential parties and political personalities, notably Senate chairman Messaoud Ould Boulkheir, continued to refuse the new order and call for Abdel Aziz's resignation.
In February 2011, the waves of the Arab Spring spread to Mauritania, where hundreds of people took to the streets of Nouakchott[clarification needed].[44]
Regions and departments
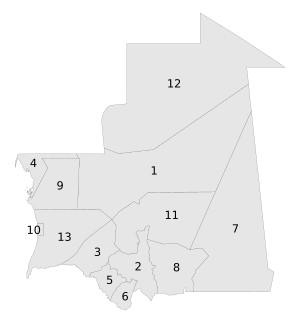
Mauritania is divided into 12 regions (régions) called wilaya and one capital district in Nouakchott. These, in turn, are subdivided into 44 departments (moughataa). The regions and capital district (in alphabetical order) and their capitals are:
| Region | Capital | # |
|---|---|---|
| Adrar | Atar | 1 |
| Assaba | Kiffa | 2 |
| Brakna | Aleg | 3 |
| Dakhlet Nouadhibou | Nouadhibou | 4 |
| Gorgol | Kaédi | 5 |
| Guidimaka | Sélibaby | 6 |
| Hodh Ech Chargui | Néma | 7 |
| Hodh El Gharbi | Ayoun el Atrous | 8 |
| Inchiri | Akjoujt | 9 |
| Nouakchott (capital district) | 10 | |
| Tagant | Tidjikdja | 11 |
| Tiris Zemmour | F'dérik | 12 |
| Trarza | Rosso | 13 |
Geography



At 397,929 square miles (1,030,631 km2),[2] Mauritania is the world's 29th-largest country (after Bolivia). It is comparable in size to Egypt. It lies mostly between latitudes 14° and 26°N, and longitudes 5° and 17°W (small areas are east of 5° and west of 17°).
Mauritania is generally flat, with vast arid plains broken by occasional ridges and cliff-like outcroppings. A series of scarps face south-west, longitudinally bisecting these plains in the center of the country. The scarps also separate a series of sandstone plateaus, the highest of which is the Adrar Plateau, reaching an elevation of 500 meters (1,640 ft). Spring-fed oases lie at the foot of some of the scarps. Isolated peaks, often rich in minerals, rise above the plateaus; the smaller peaks are called guelbs and the larger ones kedias. The concentric Guelb er Richat (also known as the Richat Structure) is a prominent feature of the north-central region. Kediet ej Jill, near the city of Zouîrât, has an elevation of 915 meters (3,002 ft) and is the highest peak.
Approximately three quarters of Mauritania is desert or semidesert. As a result of extended, severe drought, the desert has been expanding since the mid-1960s. To the west, between the ocean and the plateaus, are alternating areas of clayey plains (regs) and sand dunes (ergs), some of which shift from place to place, gradually moved by high winds. The dunes generally increase in size and mobility toward the north.
Economy
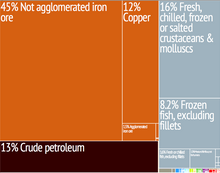
Despite being rich in natural resources, Mauritania has one of the lowest GDP rates in Africa. A majority of the population still depends on agriculture and livestock for a livelihood, even though most of the nomads and many subsistence farmers were forced into the cities by recurrent droughts in the 1970s and 1980s. Mauritania has extensive deposits of iron ore, which account for almost 50% of total exports. With the current rises in metal prices, gold and copper mining companies are opening mines in the interior. The country's first deepwater port opened near Nouakchott in 1986. In recent years, drought and economic mismanagement have resulted in a buildup of foreign debt. In March 1999, the government signed an agreement with a joint World Bank-International Monetary Fund mission on a $54 million enhanced structural adjustment facility (ESAF). The economic objectives have been set for 1999–2002. Privatization remains one of the key issues. Mauritania is unlikely to meet ESAF's annual GDP growth objectives of 4%–5%.
Oil was discovered in Mauritania in 2001 in the offshore Chinguetti field. Although potentially significant for the Mauritanian economy, it remains to be seen how much it will help the country. Mauritania has been described as a "desperately poor desert nation, which straddles the Arab and African worlds and is Africa's newest, if small-scale, oil producer."[45] There may be additional oil reserves inland in the Taoudeni basin, although the harsh environment will make extraction expensive.[46]
Human rights
Under the Abdallahi government there was a widespread public perception of governmental corruption and a lack of access to government information. Sexism, female genital mutilation, child labour, human trafficking, and the political marginalization of largely southern-based ethnic groups continued to be problems.[47]
Following the 2008 coup, the military government of Mauritania faced severe international sanctions and internal unrest, and was accused by Amnesty International of practicing coordinated torture against criminal and political detainees.[48] Amnesty has accused the Mauritanian legal system, both before and after the 2008 coup, of functioning with complete disregard for legal procedure, fair trial, or humane imprisonment. The organization has further accused the Mauritanian government of institutionalized and continuous use of torture throughout its post independence history.[49][50][51]
Discrimination against black population
Since its independence, charges have been made[by whom?] that Mauritania's society has been characterised by discrimination towards black populations, mainly Fula and Soninké, which are seen as contesting the political, economic and social dominance of Moors. Mauritanian blacks allegedly face discrimination in employment in the civil service, the administration of justice before regular and religious courts, access to loans and credits from banks and state owned enterprise, and opportunity for education and vocational training. These are the stated reasons why armed groups like the now exiled FLAM have carried out low level rebellions in the southern part of Mauritania.
Slavery
Still today, masters lend their slaves' labor to
other individuals, female slaves are sexually exploited and children are made to work and rarely receive an education. Slavery particularly affects women and children, who are the most vulnerable among the vulnerable. Women of child-bearing age have a harder time emancipating because they are
producers of slave labor and perceived as extremely valuable.
— From U.S. Dept. of State report on Slavery in Mauritania, 2009 [52]
Various[which?] forms of slavery still persist in Mauritania. Though legally abolished in 1981, it did not become a crime to own slaves until 2007. According to the US State Department 2010 Human Rights Report,[53] abuses in Mauritania include:
"...mistreatment of detainees and prisoners; security force impunity; lengthy pretrial detention; harsh prison conditions; arbitrary arrests; limits on freedom of the press and assembly; corruption; discrimination against women; female genital mutilation (FGM); child marriage; political marginalization of southern-based ethnic groups; racial and ethnic discrimination; slavery and slavery-related practices; and child labor."
The report continues: "Government efforts were not sufficient to enforce the antislavery law. No cases have been successfully prosecuted under the antislavery law despite the fact that de facto slavery exists in Mauritania."
Sentenced to six months in jail in January 2011, Oumoulmoumnine Mint Bakar Vall is the only person prosecuted to date for owning slaves. It has recently been estimated that 10% to 20% (340,000 to 680,000 people) of the population of Mauritania lives in slavery.[54]
The government of Mauritania denies the existence of slavery in the country. In an interview, the Mauritanian Minister of rural development, Brahim Ould M'Bareck Ould Med El Moctar, responded to human rights abuse accusations by stating; "I must tell you that in Mauritania, freedom is total: freedom of thought, equality – of all men and women of Mauritania....in all cases, especially with this government, this is in the past. There are probably former relationships – slavery relationships and familial relationships from old days and of the older generations, maybe, or descendants who wish to continue to be in relationships with descendants of their old masters, for familial reasons, or out of affinity, and maybe also for economic interests. But (slavery) is something that is totally finished. All people are free in Mauritania and this phenomenon no longer exists. And I believe that I can tell you that no one profits from this commerce." [55]
The reasons it is so difficult to eradicate slavery in Mauritania include:
- The difficulty of enforcing any laws in the country's vast desert geography [54]
- The country is so poor that slaves have no prospects for supporting themselves once freed[54]
- The slaves themselves generally perceive their condition as part of the natural order of things.[54]
Demographics

Population
3,281,635 (July 2011 estimated)[2]
- 30% Arab (Moors/Berber/Beidane)
- 30% Black (meaning non-Arabized) people: Soninke, Toucouleur, Fula)
- 40% Mixed
Mauritania's population is composed of several ethnic groups: the Moors (White or Arab) or Beidane, the Haratins, who are black-skinned descendants of freed slaves still attached to their former masters' culture; the Soninke; the Serer (generally farmers and stock-breeders);[56] the Hal-pulaar or Fulas which includes settled farmers called Toucouleur and nomadic stock-breeders.
Religion

Languages
Spoken languages are: Hassaniya, Pulaar, Soninke, Imraguen language, Wolof, Serer[56] and French (widely used in media and among educated classes, see African French). Modern Standard Arabic is also an official language.
Zenaga, a Berber language, was once spoken throughout much of Mauritania, but today it is almost totally replaced by Hassaniya. Only a tiny group of about 200 to 300 speakers of the Zenaga language may be left.
Health
Life expectancy at birth was 61.14 years (2011 estimate).[2] Per capita expenditure on health was 43 US$ (PPP) in 2004.[57] Public expenditure was 2% of the GDP in 2004 and private 0.9% of the GDP in 2004.[57] In the early 21st century there were 11 physicians per 100,000 people.[57] Infant mortality is 60.42 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 estimate).[57]
The obesity rate among Mauritanian women is high, perhaps in part due to the local standards of beauty, in which obese women are considered beautiful while thin women are sometimes regarded as "sickly".[58]
On 18 January 2011, the Islamic leaders of Mauritania issued a fatwa, a religious opinion concerning Islamic law, outlawing female genital mutilation.[59]
Culture

- Mauritania and Madagascar are the only two countries in the world not to use decimal-based currency. The basic unit of currency, the ouguiya, comprises five khoums. In practice, no khoum coins have been minted since 1973, and they are rarely used due to their extremely low value.
- Filming for several documentaries and films has taken place in Mauritania, including Fort Saganne (1984), The Fifth Element (1997), The Books Under the Sand (1997), Life without Death (1997), Winged Migration (2001), and Heremakono (2002).
Education
Since 1999, all teaching in the first year of primary school is in Literary Arabic; French, however, is introduced in the second year, and is used to teach all scientific courses.[60] The use of English and the Weldiya dialect is increasing.[citation needed] The country has the University of Nouakchott and other institutions of higher education, but the majority of highly educated Mauritanians have studied outside the country. Public expenditure on education was at 10.1% of 2000–2007 government expenditure.[57]
See also
Notes
- ^ "États généraux de l'Éducation nationale en Mauritanie". Le Quotidien de Nouakchott. 13 November 2011.
- ^ a b c d e "CIA – The World Factbook – Mauritania". Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ "Mauritania: Location, Map, Area, Capital, Population, Religion, Language – Country Information". Retrieved 6 August 2008.
- ^ a b c d "Mauritania". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 17 April 2013.
- ^ "Gini Index". World Bank. Retrieved 2 March 2011.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2011" (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
- ^ "UNDP: Human development indices – Table 3: Human and income poverty (Population living below national poverty line (2000–2007))" (PDF). Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ John D. Sutter (March 2013). "Slavery's last stand". CNN. [unreliable source?]
- ^ Chaabani H (2000). "Genetic differentiation of Yemeni people according to rhesus and Gm polymorphisms". Annales de Génétique. 43 (3–4): 155–62. doi:10.1016/S0003-3995(00)01023-6. PMID 11164198.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Mauritanian MPs pass slavery law. BBC News. 9 August 2007.
- ^ Abdel Nasser Ould Yasser (2008). Sage, Jesse and Kasten, Liora (ed.). Enslaved: True Stories of Modern Day Slavery. Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-7493-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ “Mauritania made slavery illegal last month”. South African Institute of International Affairs. 6 September 2007.
- ^ The Abolition season on BBC World Service
- ^ Slavery's last stronghold. CNN.com (16 March 2012). Retrieved 20 March 2012.
- ^ MAURITANIA: Fair elections haunted by racial imbalance. IRIN. 5 March 2007.
- ^ Martin Meredith, The Fate of Africa: A History of Fifty Years of Independence, (Public Affairs Publishing: New York, 2005) p. 69.
- ^ Ordonnance 9
- ^ Mauritania's campaign of terror, pp. 42, 60
- ^ Amnesty International Report 1990, London, Amnesty International Publications, 1990
- ^ Mauritanie 1945–1990 ou l'État face à la Nation, Pierre Robert Baduel, Revue du monde musulman et de la Méditerranée, 1989, Volume 54, pp. 11–52.
- ^ Mahamadou Sy, L'enfer d'Inal. Mauritanie l'horreur des camps, ed. L'Harmattan, Paris, 2000 ISBN 2738495419
- ^ Inventory of Conflict and Environment (ICE), Template. .american.edu. Retrieved 20 March 2012.
- ^ Garba Diallo (1993). Mauritania, a new Apartheid? bankie.info
- ^ Mireille Duteil, Chronique mauritanienne, Annuaire de l'Afrique du Nord, Tome XXVIII, 1989, Editions du CNRS
- ^ Mahamadou Sy, L'enfer de Inal (2000). Mauritanie, l'horreur des camps, ed. L'Harmattan, Paris.
- ^ Mauritania's campaign of terror, p. 27
- ^ Amnesty International, in its 5 April 1991 press release, claims that 3,000 were arrested. The U.S. Department of State, in its annual Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 1991, states that there were "possibly as many as 3,000" arrests. Some Mauritanian exiles believe that the number was as high as 5,000
- ^ a b U.S. Department of State Country Report on Human Rights Practices 1993 – Mauritania, 30 January 1994
- ^ United States Department of State, U.S. Department of State Country Report on Human Rights Practices 1993 Mauritania, 30 January 1994
- ^ Channe Lindstrom Report on the Situation of Refugees in Mauritania: Findings of a three week exploratory study, American University of Cairo, October – November 2002, p. 21
- ^ Mauritania's campaign of terror, p. 87
- ^ "Crackdown courts U.S. approval". CNN. 24 November 2003. Archived from the original on 7 April 2008. Retrieved 6 August 2008.
- ^ "MAURITANIA: New wave of arrests presented as crackdown on Islamic extremists". IRIN Africa. 12 May 2005. Retrieved 6 August 2008.
- ^ "Mauritania officers 'seize power'". BBC News. 4 August 2005. Retrieved 6 August 2008.
- ^ "Mauritania vote 'free and fair'". BBC News. 12 March 2007. Retrieved 6 August 2008.
- ^ "Tehran Times: 48 lawmakers resign from ruling party in Mauritania". Tehran Times. 6 August 2008.
- ^ "Coup in Mauritania as president, PM arrested". Google. AFP. 6 August 2008. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ "Troops stage 'coup' in Mauritania". BBC News. 6 August 2008. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ Coup under way in Mauritania: president's office. ap.google.com
- ^ McElroy, Damien (6 August 2008). "telegraph.co.uk,Mauritania president under house arrest as army stages coup". The Daily Telegraph. UK. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ Vinsinfo. "themedialine.org, Generals Seize Power in Mauritanian Coup". Themedialine.org. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ Ahmed Mohamed Renegade army officers stage coup in Mauritania. ap.google.com (6 August 2008)
- ^ "Mauritania Affirms Break with Israel". Voice of America News. 21 March 2010. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ Richard Adams (25 February 2011). "Libya's turmoil – Friday 25 February". The Guardian. London.
- ^ Mauritania junta promises free elections. thestar.com (7 August 2008).
- ^ "Taoudeni Basin Overview". Baraka Petroleum. Archived from the original on 24 February 2009. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Mauritania. Country Reports on Human Rights Practices – 2007. State.gov (11 March 2008). Retrieved 20 March 2012.
- ^ 'Prisoner torture rising' in Mauritania, SAPA/AP. 3 December 2008
- ^ Mauritania: Prisoner Confessions Extracted Through Torture Says Amnesty International, IRIN: 3 December 2008
- ^ Mauritania: 'Chains Are Jewellery for Men'. Ebrimah Sillah, Inter Press Service: 3 December 2008
- ^ Mauritania: Torture at the heart of the state. Amnesty International. Index Number: AFR 38/009/2008 Date Published: 3 December 2008.
- ^ Slavery in Mauritania: an overview and action plan, American Embassy in Nouakchott, 3 November 2009.
- ^ 2010 Human Rights Report: Mauritania. State.gov (8 April 2011). Retrieved 20 March 2012.
- ^ a b c d Slavery's last stronghold. CNN.com (16 March 2012). Retrieved 20 March 2012.
- ^ "Mauritanian minister responds to accusations that slavery is rampant". CNN. 17 March 2012.
- ^ a b "People-in-Country Profile, "Serer of Mauritania" – Joshua project". Retrieved 25 March 2012.
- ^ a b c d e "Human Development Report 2009 – Mauritania". Hdrstats.undp.org. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ "Mauritania struggles with love of fat women". MSNBC. 16 April 2007. Retrieved 5 September 2012.
- ^ Gould, Wendy Rose (18 January 2011). "Female Genital Mutilation Banned By Islamic Leaders in Mauritania". news.yahoo.com.
- ^ "Education system in Mauritania". Bibl.u-szeged.hu. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
References
- Mauritania's campaign of terror, State-Sponsored Repression of Black Africans, Human Rights Watch/Africa (formerly Africa Watch), 1994.
- US State Department
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, Mauritania – Country Page
Further reading
- Foster, Noel, Mauritania: The Struggle for Democracy (Lynne Rienner Publishers, 2010).
- Hudson, Peter, Travels in Mauritania (Flamingo, 1991).
- Murphy, Joseph E, Mauritania in Photographs (Crossgar Press, 1998).
- Pazzanita, Anthony G, Historical Dictionary of Mauritania (Scarecrow Press, 2008).
- Ruf, Urs, Ending Slavery: Hierarchy, Dependency and Gender in Central Mauritania (Transcript Verlag, 2001).
- Sene, Sidi, The Ignored Cries of Pain and Injustice from Mauritania (Trafford Publishing, 2011).
External links
- Template:Ar icon République Islamique de Mauritanie (official government site).
- Template:Fr icon République Islamique de Mauritanie (official government site).
- "Mauritania". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Mauritania web resources provided by GovPubs at the University of Colorado Boulder Libraries
- Template:Dmoz
- Mauritania profile from the BBC News.
 Wikimedia Atlas of Mauritania
Wikimedia Atlas of Mauritania Mauritania travel guide from Wikivoyage
Mauritania travel guide from Wikivoyage- Forecasts for Mauritania Development
- Use dmy dates from November 2012
- Mauritania
- Arabic-speaking countries and territories
- Countries bordering the Atlantic Ocean
- Countries in Africa
- French-speaking countries and territories
- Islamic republics
- Islamic states
- Least developed countries
- Member states of La Francophonie
- Member states of the African Union
- Member states of the Arab League
- Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
- Member states of the United Nations
- Military dictatorship
- Political engineering by coup
- States and territories established in 1960
- West African countries



