Kabachnik–Fields reaction
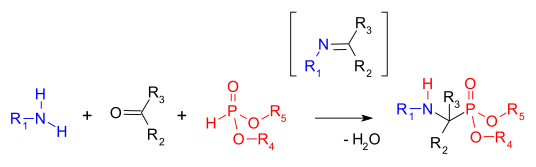
The Kabachnik–Fields reaction is an organic reaction forming an α-amino phosphonate from an amine, a carbonyl compound and a dialkyl phosphonate. Aminophosphonates are synthetic targets of some importance as phosphorus analogues of α-amino acids (a bioisosteric). This multicomponent reaction was independently discovered by Martin Izrailevich Kabachnik[1] and Ellis K. Fields[2] in 1952.
The first step in this reaction is the formation of an imine followed by an addition reaction of the phosphonate P-H bond into the C=N double bond (a Pudovik reaction).[3] A related reaction is the Mannich reaction.
The reaction is accelerated with a combination of dehydrating reagent and Lewis acid. The carbonyl component in the reaction is usually an aldehyde and sometimes a ketone.
References
- ^ Kabachnik, Martin I. (1952). "Новый метод синтеза сс-аминофосфиновых кислот". Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR. 83: 689.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|trans_title=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Fields, Ellis K. (1952). "The synthesis of esters of substituted amino phosphonic acids". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 74 (6): 1528–1531. doi:10.1021/ja01126a054.
- ^ Zefirov, Nikolay S. (2008-01-18). "Catalytic Kabachnik-Fields reaction: New horizons for old reaction" (PDF). ARKIVOC. 2008 (i): 1–17. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)