Piroxicam
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Feldene, "Arantil", "Brexidol", "Brexin", "Erazon", "Exipan", "Faxiden", "Felden", "Feldoral", "Flamexin", "Hawksone", "Hotemin", "Lubor", "Mobilis", "Pirox von ct", "Proponol", "Reumador", "Remox", "Roxam", "Sinartrol", "Toricam", "Tracam", "Ugesic", "Veral" and "Vurdon" |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a684045 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | PO |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | 4 to 10% renal |
| Elimination half-life | 30 to 86 hours |
| Excretion | 4 to 10% renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.144 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
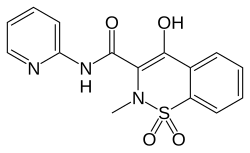
| Formula | C15H13N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 331.348 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Piroxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug of the oxicam class used to relieve the symptoms of rheumatoid and osteoarthritis, primary dysmenorrhoea, postoperative pain; and act as an analgesic, especially where there is an inflammatory component. It is manufactured by Pfizer under the tradename Feldene, and is available in the UK, Spain, Portugal, Belgium, Australia, Italy, Brazil and the United States. It is also manufactured by Bosnalijek under the tradename Roxam, and is available in Eastern Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. In India, it is available by the tradename Dolonex. In Thailand it is available by the tradename Fasden. It is manufactured as a patch by SK Chemicals Co., Ltd. in Korea (www.skchemicals.com.cn) for use in China under the trade name "Trast"; the Chinese name (in Pinyin) is Biluoxikang Tiepian". In Pakistan it is available by the trade name Feldene.
The first study of theraputic use in humans was reported in 1977 [2]
It is also used in veterinary medicine to treat certain neoplasias expressing cyclooxygenase (COX) receptors, such as bladder, colon, and prostate cancers.
Other brand names for Piroxicam include "Arantil", "Brexidol", "Brexin", "Erazon", "Exipan", "Faxiden", "Felden", "Feldoral", "Flamexin", "Hawksone", "Hotemin", "Lubor", "Mobilis", "Pirox von ct", "Proponol", "Reumador", "Remox", "Roxam", "Sinartrol", "Toricam", "Tracam", "Ugesic", "Veral" and "Vurdon".
Mechanism of action
Piroxicam is an NSAID and, as such, is a non-selective COX inhibitor possessing both analgesic and antipyretic properties. It undergoes enterohepatic circulation.
Adverse effects
Piroxicam use can result in gastrointestinal toxicity, tinnitus, dizziness, headache, rash, and pruritus. The most severe adverse reactions are peptic ulceration, gastrointestinal bleeding, and severe skin reactions including Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Approximately 30% of all patients receiving daily doses of 20 mg of piroxicam experience side effects.[3]
In rare cases, piroxicam may cause skin to become more sensitive to sunlight.[4]
References
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ Weintraub M, Jacox RF, Angevine CD, Atwater EC (1977). "Piroxicam (CP 16171) in rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled clinical trial with novel assessment techniques". Journal of Rheumatology. 4 (4): 393–404.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority. "Candyl Medicines datasheet". Retrieved 2006-09-10.
- ^ Mammen L, Schmidt CP (1995). "Photosensitivity reactions: a case report involving NSAIDs". Am Fam Physician. 52 (2): 575–9. PMID 7625330.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
