User:Charco0917/sandbox
In polymer chemistry, living polymerization is a form of addition polymerization where the ability of a growing polymer chain to terminate has been removed.[1][2] This can be accomplished in a variety of ways. Chain termination and chain transfer reactions are absent and the rate of chain initiation is also much larger than the rate of chain propagation. The result is that the polymer chains grow at a more constant rate than seen in traditional chain polymerization and their lengths remain very similar (i.e. they have a very low polydispersity index). Living polymerization is a popular method for synthesizing block copolymers since the polymer can be synthesized in stages, each stage containing a different monomer. Additional advantages are predetermined molar mass and control over end-groups.
Living polymerization is desirable because it offers precision and control in macromolecular synthesis which is important since many of the novel/useful properties of polymers result from their microstructure and molecular weight (add ref?).
A chain polymerization from which chain transfer and chain termination are absent.
Note: In many cases, the rate of chain initiation is fast compared with the rate of chain
propagation, so that the number of kinetic-chain carriers is essentially constant throughout
the polymerization.[3]
The main living polymerization techniques are:
- Living anionic polymerization
- Living cationic polymerization
- Living free radical polymerization
- Living chain-growth polycondensations
History
Living polymerization was demonstrated by Michael Szwarc in 1956 in the anionic polymerization of styrene with an alkali metal / naphthalene system in tetrahydrofuran (THF). He found that after addition of monomer to the initiator system that the increase in viscosity would eventually cease but that after addition of a new amount of monomer after some time the viscosity would start to increase again.[4] {{Quote boxSeveral reported methods exist that introduce livingness in Ziegler-Natta polymerization.[5] The monomer in this type of polymerization (a subset of coordination polymerization) is an alpha-olefin and the active site contains an alkyl to metal bond. Chain growth is based on the Cossee-Arlman mechanism. An early method (Doi, 1979) describes propene polymerization in toluene at −50°C using diethylaluminium chloride and a vanadium catalyst for example V(acac)3 to syndiotactic polypropylene with a polydispersity index of 1.05 to 1.4.[6][7] Another living system as described by McConville in 1996 is based on titanium using 1-hexene, [RN(CH2)3NR]TiMe2 and tris(pentafluorophenyl)boron[8]
Characteristics
Characteristics of Living Polymerization
One of the key characteristics of a living polymerization is that the chain termination and transfer reactions are essentially eliminated from the four elementary reactions of Chain-growth polymerization leaving only initiation and (chain) propagation reactions.
Rate of Initiation
Another key characteristic is that the rate of initiation (meaning the dormant chemical species generates the active chain propagating species) must be much faster than the rate of chain propagation. This would allow all of the active species to form before chain propagation begins so all of the chains grow at the same rate (the rate of propagation). Conversely, if initiation is much slower than chain propagation (i.e. initiation is the rate determining step) then the active species will form at different points during the reaction leading to wider distribution between the individual polymer chains degree of polymerization (or chain length) and molecular weight (figure 1).
Dispersity
Dispersity (Đ) or polydispersity index (PDI) is an indication of the broadness in the distribution of polymer chains living polymers tend to have low Đ due to the absence of chain termination pathways as well as the rate of initiation being much faster than the rate of propagation. If chain termination are present then chains will "die" or become inactive at various times during the polymerization which leads to polymer chains with varying xn. As stated in the previous section, if the rate of propagation is much slower than the rate of initiation then all of the initiators will form the active species before the onset of propagation (see figure 1 and 2). When both of these characteristics are considered it becomes apparent that the concentration of active chains, that is those undergoing polymerization, becomes essentially constant. Both of these characteristics extend the lifetime of the propagating chain allowing for synthetic manipulation, co-block polymer formation and end group functionalization to be performed on the living chain. Increasing the lifetime of the propagating polymer chain allows for more control of the resulting polymers structure and properties since there is an inherent structure-property relationship in polymers.


Predictable xn Since termination and chain transfer are absent in living polymerization then each initiator that generates an active species will be responsible for one chain. This offers control over the average degree of polymerization, which is related to Mn (number average molecular weight), in living polymerizations by controlling the monomer ([M]o) to initiator ([I]o) ratio. For an idea living system, assuming efficiency for generating active species is 100% , where each initiator generates only one active species the chain length at a given time can be estimated by knowing the concentration of monomer remaining.
Living Polymerization Techniques
Living anionic polymerization
As early as 1936, Karl Ziegler proposed that anionic polymerization of styrene and butadiene by consecutive addition of monomer to an alkyl lithium initiator occurred without chain transfer or termination. Twenty years later, living polymerization was demonstrated by Szwarc through the anionic polymerization of styrene in THF using sodium naphthalenide as celerator.[9][10][11]
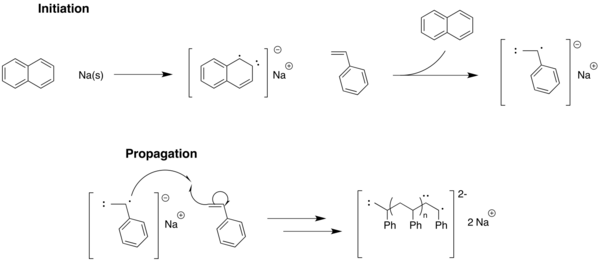
Here, the naphthalene anion acts as the initiator of the polymerization by activating the styrene. However, note that (with no impurities present for quenching and no solvent for chain transfer) there is no route for termination to occur. Therefore, these terminal anions will stay on the ends of the polymer until a quenching agent is introduced.
It is believed that the dianion of the polymer shown above is formed for this reaction, allowing the propagation to occur at either end of the chain. However, notice that there is no termination step (given impurities are not present to quench). This is the basis for anionic living polymerizations, where the terminal radical will exist until free monomer is available for additional propagation, or is quenched from an outside source.
Living α-olefin polymerization
α-olefins can be polymerized through an anionic coordination polymerization in which the metal center of the catalyst is considered the counter cation for the anionic end of the alkyl chain (through a M-R coordination). Ziegler-Natta initiators were developed in the mid-1950’s and are heterogeneous initiators used in the polymerization of alpha-olefins. Not only were these initiators the first to achieve relatively high molecular weight poly(1-alkenes) (currently the most widely produced thermoplastic in the world PE and PP) but the initiators were also capable of stereoselctive polymerizations which is attributed to the chiral crystal structure of the heterogeneous initiator (Odian). Due to the importance of this discovery Ziegler and Natta were presented with the 1963 Nobel Prize in chemistry (look up Nobel prize website for source). Although the active species formed from the Ziegler-Natta initiator generally have long lifetimes (on the scale of hours or longer) the lifetimes of the propagating chains are shortened due to several chain transfer pathways (Beta-hydride transfer, transfer to the co-initiator and transfer to H2 if present) and as a result are not considered living (Odian).
Metallocene initiators are considered as a type of Ziegler-Natta initiators due to the use of the two-component system consisting of a transition metal and a group I-III metal co-initiator (for example methylalumoxane (MAO) or other alkyl aluminum compounds). The metallocene initiators form homogenous single site catalysts that were initially developed to study the impact that the catalyst structure had on the resulting polymers structure/properties; which was difficult for multi-site heterogenous Ziegler-Natta initiators (2). Due to the discrete single site on the metallocene catalyst researchers were able to tune and relate how the ancillary ligand (those not directly involved in the chemical transformations) structure and the symmetry about the chiral metal center affect the microstructure of the polymer (3). However, do to chain breaking reactions (mainly Beta-Hydride elimination) very few metallocene based polymerizations are known (4) (Odian).
By tuning the steric bulk and electronic properties of the ancillary ligands and their substituents a class of initiators known as chelate initiators (or post-metallocene initiators) have been successfully used for stereospecific living polymerizations of alpha-olefins. The chelate initiators have a high potential for living polymerizations and can be further broken down based on the ancillary ligands; ansa-cyclopentyadienyl-amido initiators (figure_), alpha-diimine chelates (figure__) and phenoxy-imine chelates (fig_). When the term "living Zeigler-Natta polymerization" is generally refers to on the these types of initiators.
- Ansa-cyclopentadienyl-amido (CpA) initiators

CpA initiators have one cyclopentadienyl substituent and one or more nitrogen substituents coordinated to the metal center (generally a Zr or Ti) (Odian). The dimethyl(pentamethylcyclopentyl)zirconium acetamidinate in figure___ has been used for a stereospecific living polymerization of 1-hexene at -10 deg C. The resulting poly(1-hexene) was isotactic (stereohemistry is the same between adjacent repeat units)confirmed by 13C-NMR. The multiple trials demonstrated a controllable and predictable (from catalyst to monomer ratio) Mn with low Đ. The polymerization was further confirmed to be living by sequentially adding 2 portions of the monomer, the second portion was added after the first portion was already polymerized, and monitoring the Đ and Mn of the chain. The resulting polymer chains complied with the predicted Mn (with monomer concentration = portion 1 +2)and showed low Đ suggesting the chains were still active, or living, as the second portion of monomer was added (5).
- α-diimine chelate initiators
- Phenoxy-imine chelates
Living ring-opening metathesis polymerization
Given the right reaction conditions ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) can be rendered living. The first such systems were described by Robert H. Grubbs in 1986 based on norbornene and Tebbe's reagent and in 1978 Grubbs together with Richard R. Schrock describing living polymerization with a tungsten carbene complex.[12]
Generally, ROMP reactions involve the conversion of a cyclic olefin with significant ring-strain (>5 kcal/mol), such as cyclobutene, norbornene, cyclopentene, etc., to a polymer that also contains double bonds. The important thing to note about ring-opening metathesis polymerizations is that the double bond is usually maintained in the backbone, which can allow it to be considered “living” under the right conditions.[13]
For a ROMP reaction to be considered “living”, several guidelines must be met [13]:
- Fast and complete initiation of the monomer. This means that the rate at which an initiating agent activates the monomer for polymerization, must happen very quickly.
- How many monomers make up each polymer (the degree of polymerization) must be related linearly to the amount of monomer you started with.
- The dispersity of the polymer must be < 1.5. In other words, the distribution of how long your polymer chains are in your reaction must be very low.
With these guidelines in mind, it allows you to create a polymer that is well controlled both in content (what monomer you use) and properties of the polymer (which can be largely attributed to polymer chain length).

Because living polymers have had their termination ability removed, this means that once your monomer has been consumed, the addition of more monomer will result in the polymer chains continuing to grow until all of the additional monomer is consumed. This will continue until the metal catalyst at the end of the chain is intentionally removed by the addition of a quenching agent. As a result, it may potentially allow one to create a block or gradient copolymer fairly easily and accurately. This can lead to a high ability to tune the properties of the polymer to a desired application (electrical/ionic conduction, etc.) [13] [14]
Living cationic polymerization
Monomers for living cationic polymerization are electron-rich alkenes such as vinyl ethers, isobutylene, styrene, and N-vinylcarbazole. The initiators are binary systems consisting of an electrophile and a Lewis acid. The method was developed around 1980 with contributions from Higashimura, Sawamoto and Kennedy. Typically, generating a stable carbocation for a prolonged period of time is difficult, due to the possibility for the cation to be quenched by a β-protons attached to another monomer in the backbone, or in a free monomer. Therefore a different approach is taken[15] [14] [16]
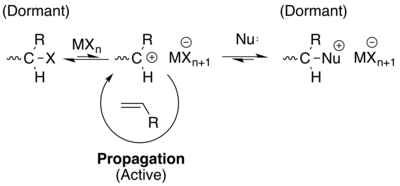
In this example, the carbocation is generated by the addition of a Lewis acid (co-initiator, along with the halogen "X" already on the polymer - see figure), which ultimately generates the carbocation in a weak equilibrium. This equilibrium heavily favors the dormant state, thus leaving little time for permanent quenching or termination by other pathways. In addition, a weak nucleophile (Nu:) can also added to reduce the concentration of active species even further, thus keeping the polymer "living"[14] [16][15] . However, it is important to note that by definition, these polymers are not technically living due to the introduction of a dormant state (though this topic is still up for debate). But, they do operate similarly, and are used in similar applications to those of true living polymerizations.
Living free radical polymerization
Starting in the 1970s several new methods were discovered which allowed the development of living polymerization using free radical chemistry. These techniques involved catalytic chain transfer polymerization, iniferter mediated polymerization, stable free radical mediated polymerization (SFRP), atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization, and iodine-transfer polymerization.
Living chain-growth polycondensations
Chain growth polycondensation polymerizations were initially developed under the premise that a change in substituent effects of the polymer, relative to the monomer, causes the polymers end group to be more reactive this has been referred to as “reactive intermediate polycondensation”. The essential result is monomers preferentially react with the activated polymer end groups over reactions with other monomers. This preferred reactivity is the fundamental difference when categorizing a polymerization mechanism as chain-growth as opposed to step-growth in which the monomer and polymer chain end group have equal reactivity (the reactivity is uncontrolled). Several strategies were employed to minimize monomer-monomer reactions (or self-condensation) and polymerizations with low D and controllable Mn have been attained by this mechanism for small molecular weight polymers (ref’s). However, for high molecular weight polymer chains (i.e. small initiator to monomer ratio) the Mn is not easily to controlled, for some monomers, since self-condensation between monomers occurred more frequently due to the low propagating species conc (1).
Catalyst-transfer Polycondensation
Catalyst transfer polycondensation (CTP) is an alternative chain-growth mechanism in which the monomers do not directly react with one another and instead the monomer will only react with the polymer end group through a catalyst-mediated mechanism (1). The general process consists of the catalyst activating the polymer end group followed by a reaction of the end group with a 2nd monomer. The catalyst is then transferred to the elongated chain while activating the chains end group (as shown below) (2).
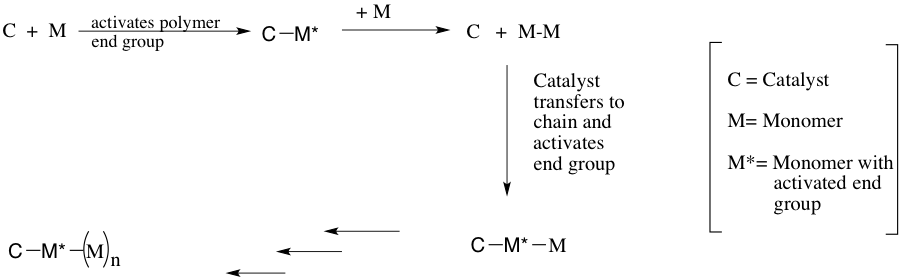
Catalyst transfer polycondensation allows for the living polymerization of pi-conjugated polymers using either a Kumada Cross Coupling or a Negishi cross coupling.
Living group-transfer polymerization?
Group-transfer polymerization also has characteristics of living polymerization.[17] It is applied to alkylated methacrylate monomers and the initiator is a silyl ketene acetal. New monomer adds to the initiator and to the active growing chain in a Michael reaction. With each addition of a monomer group the trimethylsilyl group is transferred to the end of the chain. The active chain-end is not ionic as in anionic or cationic polymeriation but is covalent. The reaction can be catalysed by bifluorides and bioxyanions such as tris(dialkylamino)sulfonium bifluoride or tetrabutyl ammonium bibenzoate. The method was discovered in 1983 by O.W. Webster[18] and the name first suggested by Barry Trost.
Several reported methods exist that introduce livingness in Ziegler-Natta polymerization.[19] The monomer in this type of polymerization (a subset of coordination polymerization) is an alpha-olefin and the active site contains an alkyl to metal bond. Chain growth is based on the Cossee-Arlman mechanism. An early method (Doi, 1979) describes propene polymerization in toluene at −50°C using diethylaluminium chloride and a vanadium catalyst for example V(acac)3 to syndiotactic polypropylene with a polydispersity index of 1.05 to 1.4.[20][21] Another living system as described by McConville in 1996 is based on titanium using 1-hexene, [RN(CH2)3NR]TiMe2 and tris(pentafluorophenyl)boron[22]
Applications
Living polymerizations can be (and in some cases are) used industrially for many different applications. They can range from self-healing materials for space equipment to the easy design of copolymers for ion-exchange membranes in fuel cells. While living polymerizations are still not widely used industrially, the field is rapidly growing, as well as the list of practical applications.
Self-healing materials
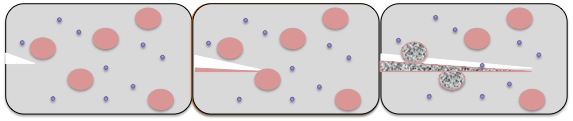
Self-healing materials are materials in which repair, or “heal”, themselves upon damage from an external force[23] . For example, if a crack forms in the material, it proceeds to repair the crack and restore itself to its original, undamaged form. This has been achieved recently[1] using a polyurethane derivative, with beads of monomer embedded in the material that become opened upon cracking of the material[24] .
The polymer that makes up the material is designed as a living polymer, with reactive terminal end-groups that bind to the freshly provided monomer upon damage to the microbeads. This addition of monomer to the polymer chain increases the polymer chain to a length that fills the once open crack, in essence reconnecting all of the pieces back into one. According to Odriozola and coworkers, this application is originally designed for space equipment (in the event of debris damaging the equipment).
Copolymer Synthesis and Application
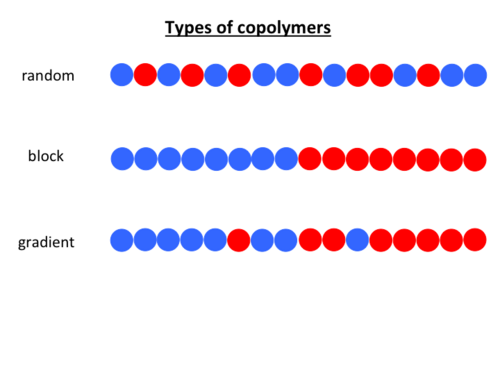
External links
- IUPAC Gold Book Definition
- Living Ziegler-Natta Polymerization Article
- Living polymers 50 years of evolution Article
References
- ^ Halasa, A. F. Rubber Chem. Technol., 1981, 54, 627.
- ^ (2006) The Chemistry of Radical Polymerization - Second fully revised edition (Graeme Moad & David H. Solomon). Elsevier. ISBN 0-08-044286-2
- ^ "Glossary of basic terms in polymer science (IUPAC Recommendations 1996)" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 68 (12): 2287–2311. 1996. doi:10.1351/pac199668122287.
- ^ Webster, O. W. Science, 1991, 251, 8877.
- ^ organicdivision.org Essay: Living Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 2002 Richard J. Keaton PDF
- ^ "'Living' Coordination Polymerization of Propene Initiated by the Soluble V(acac)3-Al(C2H5)2Cl System" Yoshiharu Doi, Satoshi Ueki, Tominaga Keii Macromolecules, 1979, 12 (5), pp. 814–819 doi:10.1021/ma60071a004
- ^ "Living coordination polymerization of propene with a highly active vanadium-based catalyst" Yoshiharu Doi, Shigeo Suzuki, Kazuo Soga Macromolecules, 1986, 19 (12), pp. 2896–2900 doi:10.1021/ma00166a002
- ^ "Living Polymerization of α-Olefins by Chelating Diamide Complexes of Titanium" John D. Scollard and David H. McConville J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118 (41), pp. 10008–10009 doi:10.1021/ja9618964
- ^ M. Szwarc, Nature 1956, 178, 1168.
- ^ Szwarc, M.; Levy, M.; Milkovich, R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1956, 78, 2656.
- ^ US 4 158 678 (priority date 30 June 1976).
- ^ "Ring-opening polymerization of norbornene by a living tungsten alkylidene complex" R. R. Schrock, J. Feldman, L. F. Cannizzo, R. H. Grubbs Macromolecules; 1987; 20(5); 1169–1172. doi:10.1021/ma00171a053
- ^ a b c Bielawski, Christopher W. (January 2007). "Living ring-opening metathesis polymerization". Progress in Polymer Science. 32 (1): 1–29. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2006.08.006.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Odian, George (2004). Principles of polymerization (4. ed. ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 0471274003.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Cowiewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Goethals, E (February 2007). "Carbocationic polymerizations". Progress in Polymer Science. 32 (2): 220–246. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.01.001.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Polymer chemistry: a practical approach 2004 Fred J. Davis
- ^ "Group-transfer polymerization. 1. A new concept for addition polymerization with organosilicon initiators" O. W. Webster, W. R. Hertler, D. Y. Sogah, W. B. Farnham, T. V. RajanBabu J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1983, 105 (17), pp. 5706–5708 doi:10.1021/ja00355a039
- ^ organicdivision.org Essay: Living Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 2002 Richard J. Keaton PDF
- ^ "'Living' Coordination Polymerization of Propene Initiated by the Soluble V(acac)3-Al(C2H5)2Cl System" Yoshiharu Doi, Satoshi Ueki, Tominaga Keii Macromolecules, 1979, 12 (5), pp. 814–819 doi:10.1021/ma60071a004
- ^ "Living coordination polymerization of propene with a highly active vanadium-based catalyst" Yoshiharu Doi, Shigeo Suzuki, Kazuo Soga Macromolecules, 1986, 19 (12), pp. 2896–2900 doi:10.1021/ma00166a002
- ^ "Living Polymerization of α-Olefins by Chelating Diamide Complexes of Titanium" John D. Scollard and David H. McConville J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118 (41), pp. 10008–10009 doi:10.1021/ja9618964
- ^ Wu, Dong Yang (May 2008). "Self-healing polymeric materials: A review of recent developments". Progress in Polymer Science. 33 (5): 479–522. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2008.02.001.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Rekondo, Alaitz (2014). "Catalyst-free room-temperature self-healing elastomers based on aromatic disulfide metathesis". Materials Horizons. 1 (2): 237. doi:10.1039/c3mh00061c.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)


![{\displaystyle \ v={\frac {[M]_{0}-[M]}{[I]_{0}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/enwiki/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/db304320640f163330c3130db03ff9691e1a8ffa)