Extensor digiti minimi muscle
| Extensor digiti minimi | |
|---|---|
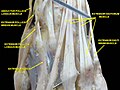
 The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the back of the wrist. (Extensor digiti quinti proprius labeled at center left.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | the anterior portion of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus (common extensor tendon) |
| Insertion | at the extensor expansion, located at the base of the proximal phalanx of digit V on the dorsal side |
| Artery | posterior interosseous artery |
| Nerve | posterior interosseous nerve (C7, 8) |
| Actions | extends the wrist and the little finger at all joints |
| Antagonist | Flexor digiti minimi brevis |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus extensor digiti minimi |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.044 |
| TA2 | 2506 |
| FMA | 38503 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The extensor digiti minimi (extensor digiti quinti proprius) is a slender muscle of the forearm, placed on the ulnar side of the Extensor digitorum communis, with which it is generally connected.
It arises from the common Extensor tendon by a thin tendinous slip, from the intermuscular septa between it and the adjacent muscles.
Its tendon runs through a compartment of the dorsal carpal ligament behind the distal radio-ulnar joint, then divides into two as it crosses the hand, and finally joins the expansion of the Extensor digitorum communis tendon on the dorsum of the first phalanx of the little finger.
Origin and Insertion
The extensor digiti minimi originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, or the outer edge of the elbow if the palm is facing up, in the anatomical position. It runs along the back of the back of the arm to the wrist and past the wrist to the proximal phalanx V, or the bone between the knuckle and first bend of the finger of the little finger.
Actions
The extensor digiti minimi is a two joint muscle. It acts as an extensor in both joints. It extends the wrist, which means it moves the back of the hand toward the back of the forarm. It also extends the little finger, which means it straightens the little finger from a fist.
Variations
An additional fibrous slip from the lateral epicondyle; the tendon of insertion may not divide or may send a slip to the ring finger.
Absence of muscle rare; fusion of the belly with the Extensor digitorum communis not uncommon.
Variations to the 5th extensor compartment, which the extensor digiti minimi runs through, may cause tenosynovitis and can limit the use of the extensor digiti minimi.
Extensor digiti minimi can also be bifurcated, which means split, at many different points in the muscle.
Additional images
-
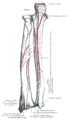
Bones of left forearm. Posterior aspect.
-
Posterior surface of the forearm. Superficial muscles.
-
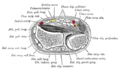
Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna.
-
Transverse section across the wrist and digits.
-
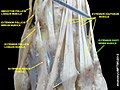
Extensor digiti minimi muscle
-
Extensor digiti minimi muscle '
-
Extensor digiti minimi muscle
-
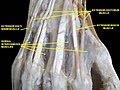
Muscles of hand. Posterior view.
-
Muscles of hand. Posterior view.
References
- Saladin, Kenneth S (2012). Anatomy & Physiology: the Unity of Form and Function (6th ed.). The McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-337825-1.
- Tanaka, T; Moran; Zhao, C; Zobitz, ME (Aug 2007). "Anatomic variation of the 5th extensor tendon compartment and extensor digiti minimi tendon". Clin Anat. 20 (6): 677–82. doi:10.1002/ca.20480. PMID 17352412.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|furst2=ignored (help) - Yoo, Moon-Jib; Chung, Kyung-Tae (December 2011). "Tendon impingement of the extensor digiti minimi: clinical cases series and cadaveric study". Clinical Anatomy. 5 (6). Wiley Periodicals. doi:10.1002/ca.22017. PMID 22162183.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 451 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 451 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)