Rhodium(III) oxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.666 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Rh2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 253.8092 g/mol |
| Appearance | dark grey odorless powder |
| Density | 8.20 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,100 °C (2,010 °F; 1,370 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Solubility | insoluble in aqua regia |
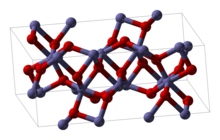
| Structure | |
| hexagonal (corundum) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Rhodium(III) oxide (or Rhodium sesquioxide) is the chemical compound with the formula Rh2O3.
Structure
Rh2O3 has been found in two major forms. The hexagonal form has the corundum structure. It transforms into an orthorhombic structure when heated above 750 °C.[1]
Production
Rhodium oxide can be produced via several routes:
- Rh metal powder is fused with potassium hydrogen sulfate. Adding sodium hydroxide results in hydrated rhodium oxide, which upon heating converts to Rh2O3.[2]
- Rhodium oxide thin films can be produced by exposing Rh layer to oxygen plasma.[3]
- Nanoparticles can be produced by the hydrothermal synthesis.[4]
Physical properties
Rhodium oxide films behave as a fast two-color electrochromic system: Reversible yellow ↔ dark green or yellow ↔ brown-purple color changes are obtained in KOH solutions by applying voltage ~1 V.[5]
Rhodium oxide films are transparent and conductive, like indium tin oxide (ITO) - the common transparent electrode, but Rh2O3 has 0.2 eV lower work function than ITO. Consequently, deposition of rhodium oxide on ITO improves the carrier injection from ITO thereby improving the electrical properties of organic light-emitting diodes.[3]
Applications
The major application of rhodium oxides is in catalysts, e.g. for the conversion of CO[6] or NO gases.[7]
Safety
Conditions/substances to avoid are: extreme heat, organic solvents, hydrochloric acid, hydrosulfuric acid and ammonia.
See also
References
- ^ J. M. D. Coey "The crystal structure of Rh2O3" Acta Cryst. (1970). B26, 1876
- ^ A. Wold et al. "The Reaction of Rare Earth Oxides with a High Temperature Form of Rhodium(III) Oxide" Inorg. Chem. 2 (1963) 972
- ^ a b S. Y. Kim et al. "Rhodium-oxide-coated indium tin oxide for enhancement of hole injection in organic light emitting diodes" Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 (2005) 072105
- ^ R. S. Mulukutla "Synthesis and characterization of rhodium oxide nanoparticles in mesoporous MCM-41" Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1 (1999) 2027
- ^ S. Gottesfeld "The Anodic Rhodium Oxide Film: A Two-Color Electrochromic System" J. Electrochem. Soc. 127 (1980) 272
- ^ P. R. Watson and G. A. Somorjai "The hydrogenation of carbon monoxide over rhodium oxide surfaces" Journal of Catalysis 72 (1981) 347
- ^ R. S. Mulukutla "Characterization of rhodium oxide nanoparticles in MCM-41 and their catalytic performances for NO–CO reactions in excess O2" Applied Catalysis A: 228 (2002) 305
