Russian ruble
| Российский рубль Template:Ru icon[1] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| ISO 4217 | |||||
| Code | RUB (numeric: 643) | ||||
| Subunit | 0.01 | ||||
| Unit | |||||
| Plural | The language(s) of this currency belong(s) to the Slavic languages. There is more than one way to construct plural forms. | ||||
| Symbol | ₽ ( | ||||
| Denominations | |||||
| Subunit | |||||
| 1/100 | kopeyka (копейка[2]) | ||||
| Symbol | |||||
| kopeyka (копейка[2]) | коп. / к. | ||||
| Banknotes | |||||
| Freq. used | 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000, 5000 rubles | ||||
| Rarely used | 5 rubles | ||||
| Coins | |||||
| Freq. used | 10, 50 kopeks, 1, 2, 5, 10 rubles | ||||
| Rarely used | 1, 5 kopeks | ||||
| Demographics | |||||
| User(s) | |||||
| Issuance | |||||
| Central bank | Bank of Russia | ||||
| Website | www | ||||
| Printer | Goznak | ||||
| Website | www | ||||
| Mint | Moscow Mint and Saint Petersburg Mint | ||||
| Valuation | |||||
| Inflation | 9.1%, November 2014 | ||||
| Source | [1] | ||||
| Method | CPI | ||||
The ruble or rouble (Template:Lang-ru, rublʹ, plural рубли́, rubli; see note on English spelling) (code: RUB) is the currency of Russia and the two partially recognized republics of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Formerly, the ruble was also the currency of the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union before their dissolution. Belarus and Transnistria use currencies with the same name. The ruble is subdivided into 100 kopeks (sometimes written as kopecks or copecks; Template:Lang-ru, kopeyka; plural: копе́йки, kopeyki). The ISO 4217 code is RUB or 643; the former code, RUR or 810, refers to the Russian ruble before the 1998 redenomination (1 RUB = 1000 RUR).
History
Etymology
According to the most popular version, the word "ruble" is derived from the Russian verb руби́ть (rubit'), meaning "to chop".
Names of different denominations
In the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries, several coins had individual names:
- ¼ kopek – polushka
- ½ kopek – denga or dénezhka
- 2 kopek – semishnik (mostly disappeared by 20th century), dvúshka (20th century) or grosh
- 3 kopek – altyn (not in use anymore by the 1960s)
- 5 kopek – pyaták
- 10 kopek – grívennik
- 15 kopek – pyatialtýnny (5 altyn; the usage lived longer than altyn)
- 20 kopek – dvugrívenny (2 grivenniks)
- 25 kopek – polupoltínnik (half poltínnik) or chetverták (from the Russian for ¼)
- 50 kopek – poltína or poltínnik
The amount of 10 rubles (in either bill or coin) is sometimes informally referred to as a chervonets. Historically, it was the name for the first Russian three-ruble gold coin issued for general circulation in 1701. The current meaning comes from the Soviet golden chervonets (сове́тский золото́й черво́нец), issued in 1923. It was equivalent to the pre-revolution 10 gold rubles. All these names are no longer in use, however. The practice of using the old kopek coin names for amounts in rubles is not very common today. In modern Russian slang only these names are used:
- 1 ruble – tselkóvy (целко́вый), meaning "entire" or "whole" (це́лый)
- 5 rubles – pyatyórka (пятёрка), pyaták (пята́к), pyatachyók (пятачо́к)
- 10 rubles – chírik (чи́рик), chervónets (черво́нец) or desyátka (деся́тка)
- 50 rubles – poltínnik (полти́нник) with some variants like poltishók (полтишо́к), pyótr (Пётр) from picture of monument to the Peter I shown on a bill
- 100 rubles – stólnik (сто́льник), sótka (сотка)
- 500 rubles – pyatikhátka (пятиха́тка), originally pyatikátka (пятика́тка)
- 1,000 rubles – kosár (коса́рь), shtúka (шту́ка) or a hybrid shtukár (штукарь), tónna (то́нна), ruble (mostly in St. Petersburg)
- 1,000,000 rubles – limón (лимо́н), lyam (лям)
- 1,000,000,000 rubles lyard (лярд).
The term for 500 rubles derives from "пять кать" (five Catherines). Katya (Катя, Catherina), having been a slang name for the 100 ruble note in tsarist Russia, was used as the note had a picture of Catherine II on it.
The largest denomination note, as of September 2009, is 5000 rubles, so all the higher amount nicknames refer to amounts and not the coin or banknote.
Some of these definitions (chirik, poltos, pyatikatka, kosar) come from Russian jail slang (Fenya), and are considered vulgar in daily speech.[citation needed]
Currency symbol
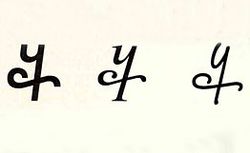
A currency symbol was used for the ruble between the 16th century and the 18th century. The symbol consisted of the Russian letters "Р" (rotated 90° counter-clockwise) and "У" (written on top of it). The symbol was placed over the amount number it belonged to.[3] This symbol, however, fell into disuse during the 19th century and onward.[citation needed]

No official symbol was used during the final years of the Empire, nor was one introduced in the Soviet Union. The characters R[4][5] and руб. were used and remain in use today, though they are not official.[6]
In July 2007, the Central Bank of Russia announced that it would decide on a symbol for the ruble and would test 13 symbols. This included the symbol РР (the initials of Российский Рубль "Russian ruble"), which has received preliminary approval from the Central Bank.[7] However, one more symbol, a Р with a horizontal stroke below the top similar to the Philippine peso sign, was proposed unofficially.[7] Proponents of the new sign claim that it is simple, recognizable and similar to other currency signs.[8][9][10] This symbol is also similar to the Armenian letter ք and Latin letter Ꝑ.
On 11 December 2013, the official symbol for the ruble became ![]() , a Cyrillic letter Er with a single added horizontal stroke,[11][12] though the abbreviation руб. is in wide use. In Unicode version 7.0 it was assigned the encoding U+20BD ₽ RUBLE SIGN.[13][14]
, a Cyrillic letter Er with a single added horizontal stroke,[11][12] though the abbreviation руб. is in wide use. In Unicode version 7.0 it was assigned the encoding U+20BD ₽ RUBLE SIGN.[13][14]
On 4 February 2014, the Unicode Technical Committee during its 138th meeting in San Jose accepted U+20BD ₽ RUBLE SIGN symbol for the Unicode version 7.0;[15] the symbol was then included into Unicode 7.0 released on 16 June 2014.[16] In August 2014, Microsoft issued updates for all of its mainstream versions of Microsoft Windows that enabled support for the new ruble sign.[17]
First ruble (antiquity–31 December 1921)

This section needs additional citations for verification. (January 2015) |

The ruble has been the Russian unit of currency for about 500 years. From 1710, the ruble was divided into 100 kopeks.
The amount of precious metal in a ruble varied over time. In a 1704 currency reform, Peter the Great standardized the ruble to 28 grams of silver. While ruble coins were silver, there were higher denominations minted of gold and platinum. By the end of the 18th century, the ruble was set to 4 zolotnik 21 dolya (almost exactly equal to 18 grams) of pure silver or 27 dolya (almost exactly equal to 1.2 grams) of pure gold, with a ratio of 15:1 for the values of the two metals. In 1828, platinum coins were introduced with 1 ruble equal to 77⅔ dolya (3.451 grams).
On 17 December 1885, a new standard was adopted which did not change the silver ruble but reduced the gold content to 1.161 grams, pegging the gold ruble to the French franc at a rate of 1 ruble = 4 francs. This rate was revised in 1897 to 1 ruble = 2⅔ francs (0.774 grams gold).
The ruble was worth about .50 USD in 1914.[18][19]
With the outbreak of World War I, the gold standard peg was dropped and the ruble fell in value, suffering from hyperinflation in the early 1920s. With the founding of the Soviet Union in 1922, the Russian ruble was replaced by the Soviet ruble. The pre-revolutionary Chervonetz was temporarily brought back into circulation from 1922-1925.[20]
Coins
At the beginning of the 19th century, copper coins were issued for ¼, ½, 1, 2 and 5 kopeks, with silver 5, 10, 25 and 50 kopeks and 1 ruble and gold 5 although production of the 10 ruble coin ceased in 1806. Silver 20 kopeks were introduced in 1820, followed by copper 10 kopeks minted between 1830 and 1839, and copper 3 kopeks introduced in 1840. Between 1828 and 1845, platinum 3, 6 and 12 rubles were issued. In 1860, silver 15 kopeks were introduced, due to the use of this denomination (equal to 1 złoty) in Poland, whilst, in 1869, gold 3 rubles were introduced.[21] In 1886, a new gold coinage was introduced consisting of 5 and 10 ruble coins. This was followed by another in 1897. In addition to smaller 5 and 10 ruble coins, 7½ and 15 ruble coins were issued for a single year, as these were equal in size to the previous 5 and 10 ruble coins. The gold coinage was suspended in 1911, with the other denominations produced until the First World War.
Constantine ruble
The Constantine ruble (Russian: константиновский рубль, pronounced "konstantinovsky rubl'") is a rare silver coin of the Russian Empire bearing the profile of Constantine, the brother of emperors Alexander I and Nicholas I. Its manufacture was being prepared at the Saint Petersburg Mint during the brief Interregnum of 1825, but it was never minted in numbers, and never circulated in public. The fact of its existence became known in 1857 in foreign publications.[22]
Banknotes
For banknotes issued between 1918 and 1992 see: Soviet ruble
Imperial issues


In 1768, during the reign of Catherine the Great, the Assignation Bank was instituted to issue the government paper money. It opened in St. Petersburg and in Moscow in 1769.
In 1769, Assignation rubles were introduced for 25, 50, 75 and 100 rubles, with 5 and 10 rubles added in 1787 and 200 ruble in 1819. The value of the Assignation rubles fell relative to the coins until, in 1839, the relationship was fixed at 1 coin ruble = 3½ assignat rubles. In 1840, the State Commercial Bank issued 3, 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 rubles notes, followed by 50 ruble credit notes of the Custody Treasury and State Loan Bank.
In 1843, the Assignation Bank ceased operations, and state credit notes (Russian: государственные кредитные билеты) were introduced in denominations of 1, 3, 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 rubles. These circulated, in various types, until the revolution, with 500 rubles notes added in 1898 and 250 and 1000 rubles notes added in 1917. In 1915, two kinds of small change notes were issued. One, issued by the Treasury, consisted of regular style (if small) notes for 1, 2, 3, 5 and 50 kopeks. The other consisted of the designs of stamps printed onto card with text and the imperial eagle printed on the reverse. These were in denominations of 1, 2, 3, 10, 15 and 20 kopeks.
Provisional Government issues
In 1917, the Provisional Government issued treasury notes for 20 and 40 rubles. These notes are known as "Kerenski" or "Kerensky rubles". The provisional government also had 25 and 1000 rubles state credit notes printed in the U.S.A. but most were not issued.
Post-Soviet ruble (1993–1998)
Following the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991, the ruble remained the currency of the Russian Federation. A new set of banknotes was issued in the name of Bank of Russia in 1993. During the period of hyperinflation of the early 1990s, the ruble was significantly devalued.
Coins
After the fall of the Soviet Union, the Russian Federation introduced new coins in 1992 in denominations of 1, 5, 10, 20, 50 and 100 rubles. The coins depict the double headed eagle above the legend "Банк России." The 1 and 5 rubles were minted in brass-clad steel, the 10 and 20 rubles in cupro-nickel and the 50 and 100 rubles were bimetallic (aluminium-bronze and cupro-nickel-zinc). In 1993, aluminium-bronze 50 rubles and cupro-nickel-zinc 100 rubles were issued, and the material of 10 and 20 rubles was changed to nickel-plated steel. In 1995 the material of 50 rubles was changed to brass-plated steel, but the coins were minted with the old date 1993. As high inflation persisted, the lowest denominations disappeared from circulation and the other denominations became rarely used.
During this period the commemorative one-ruble coin was regularly issued. It was practically identical in size and weight to a 5 Swiss franc coin (worth approx. €3 / US$4). For this reason, there have been several instances of (now worthless) ruble coins being used on a large scale to defraud automated vending machines in Switzerland.[23]
Banknotes
In 1961, new State Treasury notes were introduced for 1, 3 and 5 rubles, along with new State Bank notes for 10, 25, 50 and 100 rubles. In 1991, the State Bank took over production of 1, 3 and 5 ruble notes and also introduced 200, 500 and 1,000 ruble notes, although the 25 ruble note was no longer issued. In 1992, a final issue of notes was made bearing the name of the U.S.S.R. before the Russian Federation introduced notes for 5,000 and 10,000 rubles. These were followed by 50,000 ruble notes in 1993, 100,000 rubles in 1995 and finally 500,000 rubles in 1997 (dated 1995). Since the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991, Russian ruble banknotes and coins have been notable for their lack of portraits, which traditionally were included under both the Tsarist and Communist regimes. With the issue of the 500 ruble note depicting a statue of Peter I and then the 1000 ruble note depicting a statue of Yaroslav, the lack of recognizable faces on the currency has been partially alleviated.
| Banknote Series of the Sixth Ruble | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Series | Value | Obverse | Reverse | Issuer | Languages |
| 1961 | 1, 3, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 rubles | Vladimir Lenin or views of the Moscow Kremlin | Value, and views of the Moscow Kremlin for 50 rubles or higher | USSR | 15 |
| 1991 | 1, 3, 5, 10, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000 rubles | Russian3 | |||
| 1992 | 50, 200, 500, 1,000, 5,000, 10,000 rubles | USSR for 1000 rubles and lower Bank of Russia for 5000 and 10,000 rubles |
Russian | ||
| 1993 | 100, 200, 500, 1,000, 5,000, 10,000, 50,000 rubles | Moscow Kremlin with the tri-color Russian flag | Bank of Russia | ||
| 1995 | 1,000, 5,000, 10,000, 50,000, 100,000, 500,000 rubles | Same design as today's banknotes, where 1 new ruble = 1000 old rubles. See below.4, 5 | |||
The 1000 ruble note did not continue as a 1 new ruble note.
New ruble (1 January 1998-present)

The ruble was redenominated on 1 January 1998, with one new ruble equaling 1,000 old rubles. The redenomination was a purely psychological step that did not solve the fundamental economic problems faced by the Russian economy at the time, and the currency was devalued in August 1998 following the 1998 Russian financial crisis. The ruble lost 70% of its value against the U.S. dollar in the six months following this financial crisis.
In November 2004, the authorities of Dimitrovgrad (Ulyanovsk Oblast) erected a five-meter monument to the ruble.
On 23 November 2010, at a meeting of the Russian President Vladimir Putin and the Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao, it was announced that Russia and China have decided to use their own national currencies for bilateral trade, instead of the U.S. dollar. The move is aimed to further improve relations between Beijing and Moscow and to protect their domestic economies during the Great Recession. The trading of the Chinese yuan against the ruble has started in the Chinese interbank market, while the yuan's trading against the ruble was set to start on the Russian foreign exchange market in December 2010.[24][25]
Coins
In 1998, the ruble was once again revalued and the following coins were introduced:
| Currently circulating coins[26] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Technical parameters | Description | Date of first minting | ||||
| Diameter | Mass | Composition | Edge | Obverse | Reverse | ||
| 1 kopek | 15.5 mm | 1.5 g[27] | Cupronickel-steel | Plain | Saint George | Value | 1997 |
| 5 kopeks | 18.5 mm | 2.6 g[28] | |||||
| 10 kopeks | 17.5 mm | 1,95 g[29] | Brass 1997–2006 Brass plated steel 2006– |
Milled for brass and plain for plated | Saint George | Value | 1997 |
| 50 kopeks | 19.5 mm | 2.9 g[30] | |||||
| 1 ruble | 20.5 mm | 3.25 g | Cupronickel 1997–2009 Nickel plated steel 2009– |
Milled | 2-headed eagle emblem of the Bank of Russia | Value | 1997 |
| 2 rubles | 23 mm | 5.1~5.2 g | Broken reeding | ||||
| 5 rubles | 25 mm | 6.45 g | Cupronickelclad-copper 1997–2009 Nickel plated steel 2009– |
1997 | |||
| 10 rubles | 22 mm | 5.63 g | Brass plated steel | Broken reeding | 2-headed eagle emblem of the Bank of Russia | Value | 2009 |
| 1 ruble 1998 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Value | Emblem of the Bank of Russia |
1 and 5 kopek coins are rarely used (especially the 1 kopek coin) due to their low value and in some cases may not be accepted by stores or individuals. In some cases, the 10 kopek coin is disregarded (refused by individuals but is accepted by vendors and is mandatory for offer in exchange).[citation needed]
All these coins began being issued in 1998, despite the fact that some of them bear the year 1997. Kopek denominations all depict St. George and the Dragon, and all ruble denominations (with the exception of bimetallic commemorative pieces) depict the double headed eagle. Mint marks are denoted by "Л" or "M" on kopeks and the logo of either the Leningrad or Moscow mint on rubles. Since 2000, many bimetallic 10 ruble circulating commemorative coins have been issued. These coins have a unique holographic security feature inside the "0" of the denomination 10.[citation needed]
In 2008, it was proposed by the Bank of Russia to withdraw 1 and 5 kopek coins from circulation and to round all the prices to multiples of 10 kopeks, although the proposal hasn't been realized yet (though characteristic "x.99" prices are treated as rounded in exchange).[citation needed]
The material of 1, 2 and 5 ruble coins was switched from copper-nickel-zinc and copper nickel clad to nickel plated steel in the second quarter of 2009. 10 and 50 kopeks were also changed from aluminum-bronze to brass steel clad.[citation needed]
In October 2009, a new 10 ruble coin made of brass plated steel was issued, featuring optical security features.[31] The 10 ruble banknote would have been withdrawn in 2012, but a shortage of 10-ruble coins prompted the Central Bank to delay this and put new ones in circulation.[32] Bimetallic commemorative 10 ruble coins will continue to be issued.[citation needed]
A series of circulating Olympic commemorative 25 ruble coins will start in 2011. The new coins will be made of cupronickel.[citation needed] A number of commemorative smaller denominations of these coins exist in circulation as well, depicting national historic events and anniversaries.
The Bank of Russia issues other commemorative non-circulating coins ranging from 1–50,000 rubles. See[33] for listing.
Banknotes
On 1 January 1998 a new series of notes dated 1997 was released. Modifications to the series were made in 2001, 2004, 2010 and 2014.
| 1997 Series[34] | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | Value | Dimensions | Description | Date of | ||||||
| Obverse | Reverse | Obverse | Reverse | Watermark | printing* | issue | withdrawal | lapse | ||
| 5 rubles | 137 × 61 mm | The Millennium of Russia monument on background of Saint Sophia Cathedral in Veliky Novgorod | Fortress wall of the Novgorod Kremlin | "5", Saint Sophia Cathedral in Novgorod | 1997 | 1 January 1998 | Current, but no longer issued since 2001 and very rarely seen in ciruculation. | |||
| 10 rubles | 150 × 65 mm | Kommunalny Bridge across the Yenisei River in Krasnoyarsk and Paraskeva Pyatnitsa Chapel | Krasnoyarsk hydroelectric plant | "10", Paraskeva Pyatnitsa Chapel | 1997 2001 2004 |
Current, but no longer issued since January 2010. Still in use, but less common than the 10 ruble coin. | ||||
| 50 rubles | A Rostral Column sculpture on background of Petropavlosk Fortress in Saint Petersburg | Old Saint Petersburg Stock Exchange and Rostral Columns | "50", Peter and Paul Cathedral | Current | ||||||
| 100 rubles | Quadriga on the portico of the Bolshoi Theatre in Moscow | The Bolshoi Theatre | "100", The Bolshoi Theatre | 1997 2001 2004 2014 | ||||||
| 500 rubles | Monument to Peter the Great, Sedov sailing ship and sea terminal in Arkhangelsk | Solovetsky Monastery | "500", Monument to Peter the Great | 1997 2001 2004 2010 | ||||||
| 1,000 rubles | 157 × 69 mm | Monument to Yaroslav I the Wise and the Lady of Kazan Chapel in Yaroslavl | John the Baptist Church in Yaroslavl | "1000", Monument to Yaroslav I the Wise | 1997 2004 2010 |
1 January 2001 | ||||
| 5,000 rubles | Monument to Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky in Khabarovsk | Khabarovsk Bridge over the Amur | "5000", Head of the monument to Muravyov-Amursky | 1997 2010 |
31 July 2006 | |||||
These images are to scale at 0.7 pixel per millimetre. For table standards, see the banknote specification table.
| ||||||||||
Commemorative banknotes
In 2013 a special banknote in honor of the Olympic Games in Sochi was issued.

Printing
All Russian ruble banknotes are currently printed at the state-owned factory Goznak in Moscow, which was organized on 6 June 1919 and has continued to operate ever since. Coins are minted in Moscow and at the Saint Petersburg Mint, which has been operating since 1724.
Controversy
On 8 July 2014 State Duma deputy and Vice-Chairman of the Duma Regional Political Committee Roman Khudyakov declared that the image of Apollo driving Quadriga on the portico of the Bolshoi Theatre in Moscow on the 100 ruble banknote constitutes pornography that should only be available to persons over the age of 18. Since it is impractical to limit the access of minors to banknotes, he requested in his letter to the Governor of the Bank of Russia Elvira Nabiullina to urgently change the design of the banknote.[36]
Khudyakov, a member of parliament for the LDPR party stated, "You can clearly see that Apollo is naked, you can see his genitalia. I submitted a parliamentary request and forwarded it directly to the head of the central bank asking for the banknote to be brought into line with the law protecting children and to remove this Apollo."[37][38]
Exchange rates

In January 2014, President Putin said there should be a sound balance on the ruble exchange rate; that the Central Bank only regulated the national currency exchange rate when it went beyond the upper or lower limits of the floating exchange rate; and that the freer the Russian national currency is, the better it is, adding that this would make the economy react more effectively and timely to processes taking place in it.[39]
From early 2014 to December 2014 the ruble fell more than 50 percent against the dollar. A 6.5 percentage point interest rate rise to 17 percent[40] failed to prevent the currency hitting record lows in a "perfect storm" of low oil prices, looming recession and Western sanctions over the Ukraine crisis.[41]
| Year | Lowest ↓ | Highest ↑ | Average | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Rate | Date | Rate | Rate | ||||
| 1998 | 1 January | 5.9600 | 29 December | 20.9900 | 9.7945 | |||
| 1999 | 1 January | 20.6500 | 29 December | 27.0000 | 24.6489 | |||
| 2000 | 6 January | 26.9000 | 23 February | 28.8700 | 28.1287 | |||
| 2001 | 4 January | 28.1600 | 18 December | 30.3000 | 29.1753 | |||
| 2002 | 1 January | 30.1372 | 7 December | 31.8600 | 31.3608 | |||
| 2003 | 20 December | 29.2450 | 9 January | 31.8846 | 30.6719 | |||
| 2004 | 30 December | 27.7487 | 1 January | 29.4545 | 28.8080 | |||
| 2005 | 18 March | 27.4611 | 6 December | 28.9978 | 27.1910 | |||
| 2006 | 6 December | 26.1840 | 12 January | 28.4834 | 27.1355 | |||
| 2007 | 24 November | 24.2649 | 13 January | 26.5770 | 25.5808 | |||
| 2008 | 16 July | 23.1255 | 31 December | 29.3804 | 24.8529 | |||
| 2009 | 13 November | 28.6701 | 19 February | 36.4267 | 31.7403 | |||
| 2010 | 16 April | 28.9310 | 8 June | 31.7798 | 30.3679 | |||
| 2011 | 6 May | 27.2625 | 5 October | 32.6799 | 29.3823 | |||
| 2012 | 28 March | 28.9468 | 5 June | 34.0395 | 31.0661 | |||
| 2013 | 5 February | 29.9251 | 5 September | 33.4656 | 31.9063 | |||
| 2014 | 1 January | 32.6587 | 18 December | 67.7851 | 38.6025 | |||
| 2015 | 1 January | 56.2376 | 3 February | 69.6640 | NA | |||
| Source: USD exchange rates in RUB, Bank of Russia[42]
XE Currency US Dollar to Russian Ruble[43] | ||||||||
| Current RUB exchange rates | |
|---|---|
| From Google Finance: | AUD CAD CHF CNY EUR GBP HKD JPY USD CNY INR |
| From Yahoo! Finance: | AUD CAD CHF CNY EUR GBP HKD JPY USD CNY INR |
| From XE.com: | AUD CAD CHF CNY EUR GBP HKD JPY USD CNY INR |
| From OANDA: | AUD CAD CHF CNY EUR GBP HKD JPY USD CNY INR |
References
- ^ Template:Lang-ab; Template:Lang-ba; Template:Lang-cv; Template:Lang-kv; Lak: къуруш; Mari: теҥге; Template:Lang-os; Template:Lang-tt; Template:Lang-udm; Template:Lang-sah
- ^ Template:Lang-tt; Template:Lang-ba; Template:Lang-cv; Template:Lang-os; Template:Lang-udm; Mari: ыр; Template:Lang-sah
- ^ Забытый знак российского рубля (in Russian). RIA Novosti. Retrieved 6 May 2006.
- ^ "Currencies of the World". The University of British Columbia Sauder School of Business. Retrieved 28 June 2007.
- ^ "Russia". Lonely Planet. Retrieved 28 June 2007.
- ^ Valeria Korchagina (15 June 2006). "'R' for Ruble Is Symbol of Pride". The Moscow Times. Retrieved 28 June 2007.
- ^ a b Peter Finn (28 June 2006). "Russians Bet Ruble Will Rise To Status of Dollar, Euro, Yen". The Washington Post. Retrieved 28 June 2007.
- ^ "О знаке рубля". 1 August 2007. Retrieved 11 April 2008.
- ^ "Знак рубля. Попытка анализа". Imadesign.ru. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Оюпюрюио Мнбнярх – Хмтнплюжхъ Н Мнбшу Цюпмхрспюу Х Н Пюгкхвмшу Ьпхтрнбшу Янашрхъу". Fonts.ru. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Экономика: Деньги: Банк России утвердил символ рубля". Lenta.ru. 25 November 2013. Retrieved 11 December 2013.
- ^ 2013-12-11, Russian ruble gets graphic symbol, RT.com
- ^ The UTC just accepted the Russian ruble currency symbol
- ^ Proposal to add the currency sign for the Russian Ruble to the UCS (PDF), 11 February 2014, retrieved 16 June 2014
- ^ "UTC 138 Draft Minutes". The Unicode Consortium. 10 February 2014.
- ^ "Announcing The Unicode Standard, Version 7.0". The Unicode Consortium. 16 June 2014.
- ^ "Update to support the new currency symbol for the Russian ruble in Windows". Microsoft. August 2014.
- ^ http://www.cyberussr.com/hcunn/gold-std.html
- ^ http://www.dollartimes.com/inflation/inflation.php?amount=100000&year=1914
- ^ La Crise de la Monnaie Anglaise (1931), Catiforis S.J. Receuil Sirey, 1934, Paris
- ^ http://www.pjsymes.com.au/articles/three.htm
- ^ By 1880 Russian numismatists were well aware of the existence of Constantine rubles, but their first printed description was published only in 1886 – Kalinin, p.1.
- ^ "Mit alten Rubelmünzen Automaten am Zürcher HB geplündert" (in German). Swissinfo. 15 November 2006.
- ^ China, Russia quit dollar China Daily
- ^ Chinese minister says China-Russia economic, trade co-op at new starting point Xinhua News
- ^ "Coins, Bank of Russia". Cbr.ru. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Монеты, Банк России". Cbr.ru. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Монеты , Банк России". Cbr.ru. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Монеты, Банк России". Cbr.ru. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Монеты, Банк России". Cbr.ru. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "News article about new 10-ruble coins being issued". Altapress.Ru. 22 September 2009. Retrieved 10 December 2012.
- ^ "ЦБ возвращает в оборот 10-рублевые банкноты". Rbc.Ru. 22 December 2011. Retrieved 6 January 2013.
- ^ "Commemorative and Investment Coins database, Bank of Russia". Cbr.ru. 22 March 2011. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Banknotes and Coins". Cbr.ru. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ Video Demonstration of Olympic One Hundred-Ruble Banknote on YouTube
- ^ "На 100-рублевой купюре в Госдуме разглядели "порнографию"". Izvestia. 8 July 2014.
- ^ Baczynska, Gabriela (9 July 2014). "No more naked Apollos on Russian banknotes, lawmaker says". Reuters. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- ^ Wong, Curtis (9 July 2014). "Russia's 100-Ruble Banknote With Naked Apollo Image Is Pornographic, Politician Argues". Huffington Post. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- ^ "Putin hopes Central Bank and government find balance in ruble exchange rate dynamics". ITAR-TASS. 22 January 2014. Retrieved 22 January 2014.
- ^ "Russian Ruble Meltdown in Full Force". PrimePair.com. 17 December 2014.
- ^ "Rouble crisis could shake Putin's grip on power". Investing.com. 17 December 2014.
- ^ USD exchange rates in RUB, Bank of Russia
- ^ http://www.xe.com/
- Krause, Chester L.; Clifford Mishler (1991). Standard Catalog of World Coins: 1801–1991 (18th ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0873411501.
- Pick, Albert (1994). Standard Catalog of World Paper Money: General Issues. Colin R. Bruce II and Neil Shafer (editors) (7th ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0-87341-207-9.
External links
- Goznak official site
- Foreign Currency Market | Bank of Russia
- Russian Currency Exchange Rate History
- LIVE Russian Ruble eXchange Rates : RUB
- History of the Russian paper money
- Russian Banknotes from 1898 to 1917
- Images of historic and modern Russian bank notes
- All of Russian coins
- Coins of Russia at CISCoins.net
- Shishanov V. The Assignats of 1802–1803.[dead link]


