Heart valve
| Heart valves | |
|---|---|
 Valve positions in heart | |
| Details | |
| System | Cardiovascular |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D006351 |
| FMA | 7110 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A heart valve normally allows blood to flow in only one direction through the heart. The four valves commonly represented in a mammalian heart determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart valve opens or closes incumbent on differential blood pressure on each side.[1][2][3]
The four main valves in the heart are:
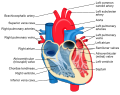
- The two atrioventricular (AV) valves, the mitral valve (bicuspid valve), and the tricuspid valve, which are between the upper atria and the lower ventricles.
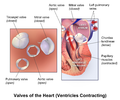
- The two semilunar (SL) valves, the aortic valve and the pulmonary valve, which are in the arteries leaving the heart.
The mitral valve and the aortic valve are in the left heart; the tricuspid valve and the pulmonary valve are in the right heart.
There are also the coronary sinus and the inferior vena cava valves.
Structure

The heart valves and the chambers are lined with endocardium. Heart valves separate the atria from the ventricles, or the ventricles from a blood vessel. Heart valves are situated around the fibrous rings of the cardiac skeleton. The valves incorporate leaflets or cusps, which are pushed open to allow blood flow and which then close together to seal and prevent backflow. The mitral valve has two cusps, whereas the others have three. There are nodules at the tips of the cusps that make the seal tighter.
The pulmonary valve has left, right, and anterior cusps.[4] The aortic valve has left, right, and posterior cusps.[5] The tricuspid valve has anterior, posterior, and septal cusps; and the mitral valve has just anterior and posterior cusps.
Atrioventricular valves

These are the mitral and tricuspid valves, which are situated between the atria and the ventricles and prevent backflow from the ventricles into the atria during systole. They are anchored to the walls of the ventricles by chordae tendineae, which prevent the valves from inverting.
The chordae tendineae are attached to papillary muscles that cause tension to better hold the valve. Together, the papillary muscles and the chordae tendineae are known as the subvalvular apparatus. The function of the subvalvular apparatus is to keep the valves from prolapsing into the atria when they close. The subvalvular apparatus has no effect on the opening and closure of the valves, however, which is caused entirely by the pressure gradient across the valve. The peculiar insertion of chords on the leaflet free margin, however, provides systolic stress sharing between chords according to their different thickness.[6]
The closure of the AV valves is heard as lub, the first heart sound (S1). The closure of the SL valves is heard as dub, the second heart sound (S2).
The mitral valve is also called the bicuspid valve because it contains two leaflets or cusps. The mitral valve gets its name from the resemblance to a bishop's mitre (a type of hat). It is on the left side of the heart and allows the blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle.
During diastole, a normally-functioning mitral valve opens as a result of increased pressure from the left atrium as it fills with blood (preloading). As atrial pressure increases above that of the left ventricle, the mitral valve opens. Opening facilitates the passive flow of blood into the left ventricle. Diastole ends with atrial contraction, which ejects the final 20% of blood that is transferred from the left atrium to the left ventricle. This amount of blood is known as the end diastolic volume (EDV), and the mitral valve closes at the end of atrial contraction to prevent a reversal of blood flow.
The tricuspid valve has three leaflets or cusps and is on the right side of the heart. It is between the right atrium and the right ventricle, and stops the backflow of blood between the two.
Semilunar valves
The aortic and pulmonary valves are located at the base of the aorta and the pulmonary trunk respecively. These are also called the "semilunar valves". These two arteries receive blood from the ventricles and their semilunar valves permit blood to be forced into the arteries, and prevent backflow from the arteries into the ventricles. These valves do not have chordae tendineae, and are more similar to the valves in veins than they are to the atrioventricular valves. The closure of the semilunar valves causes the second heart sound.
The aortic valve, which has three cusps, lies between the left ventricle and the aorta. During ventricular systole, pressure rises in the left ventricle and when it is greater than the pressure in the aorta, the aortic valve opens, allowing blood to exit the left ventricle into the aorta. When ventricular systole ends, pressure in the left ventricle rapidly drops and the pressure in the aorta forces aortic valve to close. The closure of the aortic valve contributes the A2 component of the second heart sound.
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, and has three cusps. Similar to the aortic valve, the pulmonary valve opens in ventricular systole, when the pressure in the right ventricle rises above the pressure in the pulmonary artery. At the end of ventricular systole, when the pressure in the right ventricle falls rapidly, the pressure in the pulmonary artery will close the pulmonary valve. The closure of the pulmonary valve contributes the P2 component of the second heart sound. The right heart is a low-pressure system, so the P2 component of the second heart sound is usually softer than the A2 component of the second heart sound. However, it is physiologically normal in some young people to hear both components separated during inhalation.
Development
In the developing heart, the valves between the atria and ventricles, the bicuspid and the tricuspid valves, develop on either side of the atrioventricular canals.[7] The upward extension of the bases of the ventricles causes the canal to become invaginated into the ventricle cavities. The invaginated margins form the rudiments of the lateral cusps of the AV valves. The middle and septal cusps develop from the downward extension of the septum intermedium.
The semilunar valves (the pulmonary and aortic valves) are formed from four thickenings at the cardiac end of the truncus arteriosus.[7] These thickenings are called called endocardial cushions.[citation needed] The truncus arteriosus is originally a single outflow tract from the embryonic heart that will later split to become the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk. Before it has split, four thickenings occur. There are anterior, posterior, and two lateral thickenings. A septum begins to form between what will later become the ascending aorta and pulmonary tract. As the septum forms, the two lateral thickenings are split, so that the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk have three thickenings each (an anterior or posterior, and half of each of the lateral thickenings). The thickenings are the origins of the three custs of the semilunar valves. The valves are visible as unique structures by the ninth week. As they mature, they rotate slightly as the outward vessels spiral, and move slightly closer to the heart.[7]
Physiology
In general, the motion of the heart valves is determined using the Navier–Stokes equation; using boundary conditions of the blood pressures, pericardial fluid, and external loading as the constraints. The motion of the heart valves is used as a boundary condition in the Navier–Stokes equation in determining the fluid dynamics of blood ejection from the left and right ventricles into the aorta and the lung.


- Relationship between pressure and flow in open valves
The pressure drop, , across an open heart valve relates to the flow rate, Q, through the valve:
If:
- Inflow energy conserved
- Stagnant region behind leaflets
- Outflow momentum conserved
- Flat velocity profile
- Valves with a single degree of freedom
Usually, the aortic and mitral valves are incorporated in valve studies within a single degree of freedom. These relationships are based on the idea of the valve being a structure with a single degree of freedom. These relationships are based on the Euler equations.
Equations for the aortic valve in this case:
where:
- u = axial velocity
- p = pressure
- A = cross sectional area of valve
- L = axial length of valve
- Λ(t) = single degree of freedom; when
Atrioventricular valve
Clinical significance
Valvular heart disease is a general term referring to dysfunction of the valves, and is primarily in two forms, either regurgitation, where a dysfunctional valve lets blood flow in the wrong direction, or stenosis, when a valve is narrow.[8]
Regurgitation occurs when a valve becomes insufficient and malfunctions, allowing some blood to flow in the wrong direction. This insufficiency can affect any of the valves as in aortic insufficiency, mitral insufficiency, pulmonary insufficiency and tricuspid insufficiency. The other form of valvular heart disease is stenosis, a narrowing of the valve. This is a result of the valve becoming thickened and any of the heart valves can be affected, as in mitral valve stenosis, tricuspid valve stenosis, pulmonary valve stenosis and aortic valve stenosis. Stenosis of the mitral valve is a common complication of rheumatic fever. Inflammation of the valves can be caused by infective endocarditis , usually a bacterial infection but can sometimes be caused by other organisms. Bacteria can more readily attach to damaged valves.[9] Another type of endocarditis which doesn't provoke an inflammatory response, is nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis. This is commonly found on previously undamaged valves.[9] A major valvular heart disease is mitral valve prolapse, which is a weakening of connective tissue called myxomatous degeneration of the valve. This sees the displacement of a thickened mitral valve cusp into the left atrium during systole.[8]
Disease of the heart valves can be congenital, such as aortic regurgitation or acquired, for example infective endocarditis. Different forms are associated with cardiovascular disease, connective tissue disorders and hypertension. The symptoms of the disease will depend on the affected valve, the type of disease, and the severity of the disease. For example, valvular disease of the aortic valve, such as aortic stenosis or aortic regurgitation, may cause breathlessness, whereas valvular diseaes of the tricuspid valve may lead to dysfunction of the liver and jaundice. When valvular heart disease results from infectious causes, such as infective endocarditis, an affected person may have a fever and unique signs such as splinter haemorrhages of the nails, Janeway lesions, Osler nodes and Roth spots. A particularly feared complication of valvular disease is the creation of emboli because of turbulent blood flow, and the development of heart failure.[8]
Valvular heart disease is diagnosed by echocardiography, which is a form of ultrasound. Damaged and defective heart valves can be repaired, or replaced with artificial heart valves. Infectious causes may also require treatment with antibiotics.[8]
Congenital heart disease
The most common form of valvular anomaly is a congenital heart defect (CHD), called a bicuspid aortic valve. This results from the fusing of two of the cusps during embryonic development forming a bicuspid valve instead of a tricuspid valve. This condition is often undiagnosed until calcific aortic stenosis has developed, and this usually happens around ten years earlier than would otherwise develop.[10][11]
Less common CHD's are tricuspid and pulmonary atresia, and Ebstein's anomaly. Tricuspid atresia is the complete absence of the tricuspid valve which can lead to an underdeveloped or absent right ventricle. Pulmonary atresia is the complete closure of the pulmonary valve. Ebstein's anomaly is the displacement of the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve causing a larger atrium and a smaller ventricle than normal.
History
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (October 2014) |
Additional images
-
Illustration of heart valves (superior view)
-
Illustration of the valves of the heart when the ventricles are contracting
-
Base of ventricles exposed by removal of the atria. (Valves visible on top of heart.)
-
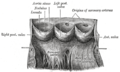
Blause 0469 Heart Valves.png. (Note that captions don't align with current terminology.)
-
Illustration showing the heart valves in situ
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ "Heart Valves". Heart and Stroke Encyclopedia. American Heart Association, Inc. Retrieved 2010-08-05.
{{cite web}}: External link in|work= - ^ Klabunde, RE (2009-07-02). "Pressure Gradients". Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts. Richard E. Klabunde. Retrieved 2010-08-06.
- ^ Klabunde, RE (2007-04-05). "Cardiac Valve Disease". Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts. Richard E. Klabunde. Retrieved 2010-08-06.
- ^ Anatomy photo:20:21-0102 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center – "Heart: The Pulmonic Valve"
- ^ Anatomy photo:20:29-0104 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center – "Heart: The Aortic Valve and Aortic Sinuses"
- ^ S Nazari et al.: Patterns Of Systolic Stress Distribution On Mitral Valve Anterior Leaflet Chordal Apparatus. A Structural Mechanical Theoretical Analysis. J Cardiovasc Surg (Turin) 2000 Apr;41(2):193–202 (video)
- ^ a b c Larsen's human embryology (4th ed., Thoroughly rev. and updated. ed.). Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. 2009. pp. 177–179. ISBN 9780443068119.
{{cite book}}:|first=missing|last=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help) - ^ a b c d Britton, the editors Nicki R. Colledge, Brian R. Walker, Stuart H. Ralston ; illustated by Robert (2010). Davidson's principles and practice of medicine (21st ed. ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. pp. 612–628. ISBN 978-0-7020-3085-7.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help);|first=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Mitchell RS, Kumar V, Robbins SL, Abbas AK, Fausto N (2007). Robbins Basic Pathology (8th ed.). Saunders/Elsevier. pp. 406–8. ISBN 1-4160-2973-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bertazzo, S. et al. Nano-analytical electron microscopy reveals fundamental insights into human cardiovascular tissue calcification. Nature Materials 12, 576–583 (2013).
- ^ Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. Nature Materials 12, 476–478 (2013).





![{\displaystyle A(x,t)=A_{0}\left(1-[1-{\Lambda }(t)]{x \over {L}}\right)^{2}}](https://wikimedia.org/enwiki/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d86e8a7cd26aac3833526c8a4a24ace993b9f68f)
![{\displaystyle \int _{0}^{L}p(x,t){{\partial }A \over {\partial }x}\,dx=[A_{0}-A(L,t)]\,p(L,t)}](https://wikimedia.org/enwiki/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cd1e3437e71128cc9a0e20f42e2ab4d7dbbc19d8)