Bangor, Gwynedd
| Bangor | |
|---|---|
 The City of Bangor | |
| Population | 16,358 (2011 census) |
| Demonym | Bangorian |
| OS grid reference | SH580722 |
| • Cardiff | 184 miles (296 km) |
| • London | 258 miles (415 km) |
| Principal area | |
| Preserved county |
|
| Country | Wales |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | BANGOR |
| Postcode district | LL57 |
| Dialling code | 01248 |
| Police | North Wales |
| Fire | North Wales |
| Ambulance | Welsh |
| UK Parliament | |
| Senedd Cymru – Welsh Parliament | |
Bangor (/ˈbæŋɡər/ Template:IPA-cy) is a city in Gwynedd unitary authority, north west Wales, and one of the smallest cities in Britain. Historically in Caernarfonshire, it is a university city with a population of 16,358 at the 2011 census,[1] not including around 10,000 students at Bangor University. It is one of only six places classed as a city in Wales, although it is only the 36th-largest urban area by population. According to the 2001 census, 46.6% of the non-student resident population speak Welsh, which is low for Gwynedd but despite this, the language keeps a high profile in town.[2]
History
The origins of the city date back to the founding of a monastic establishment on the site of Bangor Cathedral by the Celtic saint Deiniol in the early 6th century AD. Bangor itself is an old Welsh word for a wattled enclosure,[3] such as the one that originally surrounded the cathedral site. The present cathedral is a somewhat more recent building and has been extensively modified throughout the centuries.

While the building itself is not the oldest, and certainly not the biggest, the bishopric of Bangor is one of the oldest in Britain. Another claim to fame is that Bangor allegedly has the longest High Street in Wales and the United Kingdom. Friars School was founded as a free grammar school in 1557, and Bangor University was founded in 1884.
In 1877, the former HMS Clio became a school ship, moored on the Menai Strait at Bangor, and had 260 pupils. Closed after the end of hostilities of World War I, she was sold for scrap and broken up in 1919.
During World War II, parts of the BBC evacuated to Bangor during the worst of the Blitz.
Geography
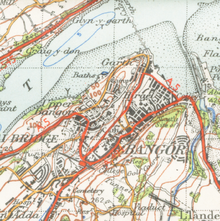
Bangor lies on the coast of North Wales near the Menai Strait which separates the island of Anglesey from Gwynedd unitary authority, the town of Menai Bridge lying just over the strait. Bangor Mountain lies to the east of the main part of the city, but the large housing estate of Maesgeirchen, originally built as council housing, is to the east of the mountain near Port Penrhyn. Bangor Mountain casts a shadow across the High Street, Glan Adda and Hirael areas, so that from November to March some parts of the High Street in particular receive no direct sunlight[citation needed]. Another ridge rises to the north of the High Street, dividing the city centre from the south shore of the Menai Strait; this area is known as Upper Bangor (Bangor Uchaf). Bangor has two rivers within its boundaries. The River Adda is a largely culverted watercourse which only appears above ground at its western extremities near the Faenol estate, whilst the River Cegin enters Port Penrhyn at the eastern edge of the city. Port Penrhyn was an important port in the 19th century, exporting the slates produced at the Penrhyn Quarry.
Transport
Bangor lies at the western end of the North Wales Path, a 60-mile (100 km) long-distance coastal walking route to Prestatyn. It is also on routes 5, 8 and 85 of the National Cycle Network.
Bangor railway station, which serves the city, is located on the North Wales Coast Line from Crewe to Holyhead.
Culture
Music
Classical music is performed regularly in Bangor, with concerts given in the Powis and Prichard-Jones Halls as part of the university's Music at Bangor concert series. The city is also home to the Gwynedd Museum and Art Gallery. A new arts centre, the Pontio arts complex, is earmarked for completion in the summer of 2014.[4]
Bangor hosted the National Eisteddfod in 1890, 1902, 1915, 1931, 1940 (through the medium of radio), 1943, 1971 and 2005, as well as an unofficial National Eisteddfod event in 1874.
Garth Pier
Garth Pier is the second longest pier in Wales, and the ninth longest in the British Isles, at 1,500 feet (460 m) in length. Almost demolished in 1974 due to the poor condition, local support ensured that it survived and gained a Grade II listed status, as it was considered one of the three finest surviving piers at the time. Restoration work took place between 1982 and 1988, and the pier was re-opened on 7 May 1988.
Retail trade
Bangor has a central shopping area around the High Street, and retail outlets on Caernarfon Road, on the outskirts of the city. One of these is St. David's Retail Park, built on the site of the demolished St David's maternity hospital.

In 1865, Morris Wartski, a refugee from the Tsarist pogroms, first established a jewellery business on Bangor's High Street, and then a drapery store. His son, Isidore, went on to develop the drapery business and to create a large, fashionable, store. He also redeveloped the Castle Inn on High Street in Bangor, which then became the high-class Castle Hotel. He was a very popular mayor of the city and a great patron of local sports and charities. Wartski Fields were bequeathed to the city and people of Bangor by his widow, Winifred Marie, in memory of Isidore Wartski.
Education
Bangor University and Coleg Menai are located in the city. Secondary schools include Ysgol Friars, Ysgol Tryfan, Hillgrove School and St. Gerard's School. There are also a number of primary and infant schools.[5]
Hospital

Ysbyty Gwynedd is located in Bangor in the suburb of Penrhosgarnedd. It has 453.8 beds, making it slightly smaller than the other district general hospitals in Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board (after Wrexham Maelor Hospital with 581.3 beds and Ysbyty Glan Clwyd near Rhyl with 490.9 beds.[6] It houses the headquarters of the Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board.
Sport
Bangor has a long-established football team, Bangor City F.C. which competes in the national Welsh Premier League (formerly League of Wales). Bangor City have won the League of Wales on three occasions (1994, 1995, 2011) and been continuous members of the league since its inception. Bangor City have also won the Welsh Cup eight times, most recently in the 2010 competition. Before 1992 they were members of the English football pyramid, peaking with the Northern Premier League title in 1982 and being FA Trophy runners-up in 1984. They have also competed in the UEFA Cup Winners' Cup three times (including its final season, 1998-99, before being merged into the UEFA Cup), UEFA Champions League twice, and UEFA Cup five times, though they have not progressed far in any of the European competitions. Many Bangor fans have been seen to have anger towards the Welsh FA for forcing Bangor into the Welsh Premier League when there are other Welsh teams in the English pyramid system. Bangor is also home to rugby union team Bangor RFC who play in the WRU Division Two North league.
Media
Bangor is home to a small BBC broadcasting centre, producing a large amount of output for BBC Radio Cymru. The studios are also the main North-West Wales newsroom for television, radio and on-line. The BBC's Light Entertainment Department moved to Bangor during World War II and many classic programmes (like It's That Man Again) came from Bangor.
Bangor was also previously home to two commercial radio stations, Heart Cymru (serving Anglesey and Gwynedd) and the now-defunct Heart North Wales Coast (serving the North Wales Coast), which shared studio facilities on the Parc Menai office complex - the studios were closed in August 2010 after the stations were moved to Wrexham.
Bangor University also has its own student radio station called Storm FM, which broadcasts to the Ffriddoedd Site and from their website.
In 1967, The Beatles came to Bangor, staying in Dyfrdwy, one of the halls comprising Adeilad Hugh Owen (Hugh Owen Building), now part of the Management Centre, for their first encounter with Maharishi Mahesh Yogi, during which visit they learned of the death of their manager Brian Epstein.[7][8]
On 24 February 2010 BBC Radio 1's The Chris Moyles Show announced Bangor as the location for Radio 1's Big Weekend concert festival. The morning show was broadcast on location from Bangor, with the announcement as well as a portion of the lineup being revealed. Big international acts such as Rihanna, MGMT, Kesha and Alicia Keys played as well as British acts like Biffy Clyro, Pixie Lott, Cheryl Cole, Pendulum and Dizzee Rascal.
Notable people
- Cai Griffiths, rugby player playing for London Welsh.
- Duffy, singer and actress.
- Eddie Niedzwiecki goalkeeper and professional footballer.
- Errie Ball, golfer, played in first Masters Tournament in 1934.
- John Edward Daniel, theologian and Plaid Cymru political leader.
- Matthew Dent, graphic artist and designer of the redesigned 2008 British coinage.
- Owain Tudur Jones, professional footballer.
- Sasha, DJ and record producer.
- Wayne Hennessey, footballer (goalkeeper) playing for Wales & Crystal Palace FC.
- Joshua Nelson, magician, master of the moot, vice-president of the Legal Advocacy Society Bangor University
Twin towns
References
- ^ Office for National Statistics 2011 census - Bangor C
- ^ 6,199 out of 13,310 people aged 3 and older spoke Welsh in the following wards: Deiniol, Marchog, Hirael, Garth, Menai, Glyder, Hendre, Dewi. [1]
- ^ Wade-Evans, Arthur. Welsh Medieval Laws. Oxford Univ., 1909. Accessed 31 Jan 2013.
- ^ "Bryn Terfel: Pontio theatre named after opera star in Bangor". bbc.co.uk. 11 October 2013. Retrieved 28 November 2013.
- ^ "Schools – Gwynedd Council". gwynedd.gov.uk. Retrieved 18 July 2010.
- ^ https://statswales.wales.gov.uk/Catalogue/Health-and-Social-Care/NHS-Hospital-Activity/NHS-Beds/NHSBeds-by-Organisation-Site
- ^ "Bangor and the Beatles". Bangor University. Retrieved 2014-10-27.
- ^ "The Beatles in Bangor". BBC Wales. 2009-09-02. Retrieved 2014-10-27.

