Super Mario Bros. 2
| Super Mario Bros. 2 | |
|---|---|
| An image of a jumping man with red overalls and a red hat, a blue shirt, and a beet in his right hand North American box art, with Mario holding a beet. | |
| Developer(s) | Nintendo R&D4 |
| Director(s) | Kensuke Tanabe |
| Producer(s) | Shigeru Miyamoto |
| Composer(s) | Koji Kondo |
| Series | Super Mario |
| Platform(s) | Famicom Disk System, NES/Famicom, PlayChoice-10, SNES, Game Boy Advance, Virtual Console |
| Release | July 10, 1987
|
| Genre(s) | Platforming |
| Mode(s) | Single-player |
Super Mario Bros. 2, released in Japan as Super Mario USA (Japanese: スーパーマリオUSA, Sūpā Mario USA), is a 1988 platform game developed and published by Nintendo for the Nintendo Entertainment System as the North American/European sequel to the 1985 game Super Mario Bros. The game was first released in North America on October 10, 1988.[2] Super Mario Bros. 2 has been remade or re-released for several video game consoles.
The game that became Super Mario Bros. 2 started out as a prototype for a vertically scrolling, two-player, cooperative-action game. The prototype eventually evolved into Yume Kōjō: Doki Doki Panic, a Family Computer Disk System game meant to tie-in with Fuji Television's media technology expo, called Yume Kōjō (lit. Dream Factory).[3]
After Nintendo of America found the Japanese Super Mario Bros. 2 too difficult and similar to its predecessor, Yume Kōjō: Doki Doki Panic was developed into a separate Super Mario Bros. sequel for release outside of Japan.[4]: 2 The game became a commercial success, and eventually the game became well received enough that it was also released in Japan for the Family Computer itself as Super Mario USA.[3] Since its successful sales yield, Super Mario Bros. 2 has been considered a classic Super Mario Bros. game worldwide, including in Japan. It has since been rereleased in the Super Mario All-Stars collection, it has been remade as Super Mario Advance for the Game Boy Advance handheld system, and its design elements have been included in Super Mario 3D World for the Wii U system.
Gameplay
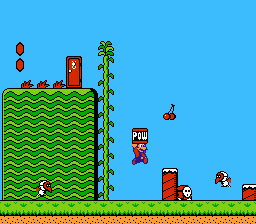
Super Mario Bros. 2 is a 2D side-scrolling platform game. The objective of the game is to navigate the player's character through the dream world Subcon and defeat the main antagonist Wart.[5]: 3–4 The player takes on the roles of the four protagonists of the game: Mario, Luigi, Toad, and Princess Toadstool. All four characters can run, jump, and climb ladders or vines, but each character possesses a unique strength that causes them to be controlled differently. For example, Luigi can jump the highest and Princess Peach can jump the farthest.[5]: 7–8 The player chooses the character to use before the start of each level. Unlike other Mario games, the characters cannot defeat enemies by jumping on them; but they can stand on, ride on, and jump from the enemies. Instead, the character picks up and throws objects at the enemies, or throws the enemies away, to defeat them. These objects include vegetables plucked from the ground, or other enemies.[5]: 13–16
The game consists of twenty different levels across the seven "worlds" comprising Subcon.[5]: 6 Each world has a particular theme that dictates the obstacles and enemies encountered in its levels, such as desert areas with dangerous quicksand and snowy areas with slippery surfaces. Levels contain multiple sections or rooms that are connected via doors or ladders. Some rooms are accessible by entering certain jars. Magic potions found in each level are used to temporarily access "Sub-space", an inverted area where the player can collect coins and Mushrooms that increase the character's maximum health. In addition, certain jars, when entered in Sub-space, will warp the player to later worlds, skipping levels altogether. Other items available include cherries, which are collected in order to acquire a Starman; and the POW block, which can be used to quickly destroy all enemies visible on the screen.[5]: 17–21
The player starts Super Mario Bros. 2 with three extra lives, which are lost each time the player's character loses all health from enemy or hazard damage or when the character falls off the screen. The player can replenish health by collecting floating hearts that appear upon defeating a certain number of enemies. The player will receive a game over upon losing all lives, though the player may continue up to twice in one game. Additional extra lives may be obtained by collecting hidden 1-Up Mushrooms or by using the coins collected from Sub-space to win the slot machine minigame played between levels.[5]: 9–10, 19, 22
Plot
Yume Kōjō: Doki Doki Panic
While two children are reading a story, a monstrous hand suddenly appears from inside the pages and kidnaps them. When the rest of the family hear their cries for help, they jump into the story and help save them.
Super Mario Bros. 2
Mario, Luigi, Toad and Princess Toadstool must free the dreamland known as Subcon from a villainous frog known as Wart.[5]
Development
Nintendo originally released Super Mario Bros. 2 on Japan's Famicom Disk System in 1986. Its engine is that of an enhanced Super Mario Bros., with the same basic game format but adding more complex level designs, character features, and weather features. [citation needed] Some of the advanced level content had been culled from the American coin-operated arcade game Vs. Super Mario Bros.[4]: 2 All of these factors combined to yield an incremental game design with significantly higher difficulty.
Also in 1986, the young subsidiary, Nintendo of America, was just completing its test marketing of, and beginning its nationwide launch of, the new Nintendo Entertainment System and its flagship game, Super Mario Bros. This American adaptation of the Famicom platform had been altogether deliberately delayed in the wake of the video game crash of 1983, a regional market disaster which the Japanese market had not directly experienced. The subsidiary did not want the increasingly popular Mario series to be known for maximal frustration and thus inaccessible to a recovering, transfiguring, and expanding market — nor to be stylistically outdated by the time the Japanese Super Mario Bros. 2 could be eventually converted to the NES's cartridge format, localized, and mass-produced for America. Utilizing considerable regional autonomy in order to avoid risking the franchise's popularity in this burgeoning market, they declined this game's American release and instead requested a newer and more friendly Super Mario Bros. sequel for the non-Japanese world.[4]: 3
What was to eventually become this new game had originated as a prototype, which was developed and directed by Kensuke Tanabe[6][7] and implemented by Nintendo's frequent programming partner, SRD.[3] This gameplay model emphasized vertically scrolling levels with two players cooperatively tossing each other, and ascending by way of throwing and stacking blocks. However, the prototypical implementation of this scrolling and multi-player action was deemed to exceed the physical capability of Nintendo's consumer hardware at the time, and the gameplay was ultimately deemed to be lacking.[3]
The idea was that you would have people vertically ascending, and you would have items and blocks that you could pile up to go higher, or you could grab your friend that you were playing with and throw them to try and continue to ascend ... the vertical-scrolling gimmick wasn’t enough to get us interesting gameplay.
— Nintendo game Director, Kensuke Tanabe[3]
Unwilling to compromise on gameplay, Tanabe suspended development of the prototype until eventually receiving instruction to use the Yume Kōjō mascots in a game. In collaboration with Shigeru Miyamoto's team, they greatly expanded the gameplay and developed Yume Kōjō: Doki Doki Panic for the Family Computer Disk System,[3] released in Japan on July 10, 1987.
The title Yume Kōjō: Doki Doki Panic (夢工場ドキドキパニック, Yume Kōjo Doki Doki Panikku, lit. "Dream Factory: Heart-Pounding Panic") is derived from "doki doki", a Japanese onomatopoeia for the sound of a quickly-beating heart. The game's title and character concept were inspired by a license cooperation between Nintendo and Fuji Television to promote the broadcaster's Yume Kōjō '87 event, which showcased several of their latest TV shows and other products at the time. The Yume Kōjō festival's mascots became the game's protagonists, a family consisting of siblings Imajin and Lina and their parents, Papa and Mama. The rest of the game's characters, including the main villain named Mamu, were created by Nintendo for the project. Yume Kōjō: Doki Doki Panic takes place within a book with an Arabian setting. All four characters are optionally playable, though the game is not fully completed until the player clears all levels using each protagonist.
For the American conversion into Super Mario Bros. 2, many graphical changes were made to the look, animation, and identity of the scenery and characters.[8][9] The character likenesses of Mario, Luigi, Princess Peach, and Toad were built upon their respective counterpart models of Imajin, Mama, Lina, and Papa. This marked the first time that Mario and Luigi had noticeably different heights,[4] and Miyamoto originated the "fluttering" animation of Luigi's legs, to justify the enhanced jumping ability seen in the corresponding Mama character.[10] Yume Kōjō: Doki Doki Panic needed only a few alterations for its conversion into the Mario series, because it had already contained familiar features: Starmen, sound effects for coins and jumping, POW blocks, warp zones, and a soundtrack composed by original Super Mario Bros. composer Koji Kondo.[11][12] To reduce the game's overall difficulty, the designers made minor technical changes. They opted not to retain Yume Kōjō: Doki Doki Panic's ultimate requirement to complete each level using each protagonist; therefore, this new Super Mario Bros. 2 can be completed in only one pass by any combination of characters. And in the tradition of the Mario series, they added the ability to run, using the B button.
This Western version of Super Mario Bros. 2 was such a success that it was eventually released in Japan in 1992 under the title Super Mario USA. Likewise, Nintendo later released the Japanese Super Mario Bros. 2 in America in the form of Super Mario Bros.: The Lost Levels, a part of the re-release compilation Super Mario All Stars on the Super NES. Nintendo has continued to release both games, each with the title of Super Mario Bros 2. in their respective regions, including a Virtual Console release and a Wii re-release of Super Mario All Stars.
Re-releases
In 1993,[13] Nintendo released an enhanced Super Famicom/SNES compilation titled Super Mario All-Stars. It includes all of the Super Mario Bros. games released for the Nintendo Family Computer/Disk System and Nintendo Entertainment System. The version of Super Mario Bros. 2 included in the compilation has improved graphics and sound to match the Super Family Computer's and SNES's 16-bit capabilities, as well as minor alterations in some collision mechanics. It is possible to change the character after losing a single life, while the original version allows changing it only after completing a level or when the player loses all their lives and chooses "Continue", making the game much more forgiving when choosing a character not adept at some specific level. The player begins with 5 lives instead of 3, and the slot game gains an additional bonus; if the player obtains three "7"'s, the player wins ten lives.
In March–April 1996, Nintendo collaborated with the St.GIGA satellite radio station to release an ura or gaiden version of the game for the Satellaview system, featuring 16-bit audiovisual enhancements similar to that of Super Mario All-Stars. This new game is titled BS Super Mario USA Power Challenge (BSスーパーマリオUSA パワーチャレンジ, Bī Essu Sūpā Mario USA Pawā Charenji), and like all Satellaview titles it was released episodically in a number of weekly volumes.[14] BS Super Mario USA Power Challenge was never released outside of Japan and as with all other Satellaview titles it has never been rereleased as a stand-alone title. The game exists today solely in ROM format and is traded online by Satellaview emulation enthusiasts.[14]
Super Mario Advance
In 2001, Super Mario Bros. 2 received another release, this time based on the All-Stars remake, as part of Super Mario Advance, which also contains a remake of Mario Bros. Super Mario Advance was developed by Nintendo Entertainment Analysis and Development,[15] and was a launch title for the Game Boy Advance. The Super Mario Advance version of Super Mario Bros. 2 includes several new features such the addition of the enemy Robirdo, a robotic Birdo acting as the boss of World 3, replacing Mouser; the addition of the Yoshi Challenge, in which players may revisit stages to search for Yoshi Eggs; and an all-new point-scoring system, similar to that used in the aforementioned BS Super Mario USA Power Challenge. Graphical and audio enhancements appear in the form of enlarged sprites, multiple hit combos, digital voice acting, and such minor stylistic and aesthetic changes as an altered default health-meter level, boss-order, backgrounds, the size of hearts, Princess Toadstool being renamed to the now-standard "Princess Peach", and the inclusion of a chime to announce Stars.[16] The game was released for the Wii U Virtual Console in Japan on July 16, 2014 and later in North America on November 6, 2014.[17]
Reception
Super Mario Bros. 2 sold ten million copies, and was the third highest-selling game ever released on the Nintendo Entertainment System at that time.[21] Nintendo Power listed Super Mario Bros. 2 as the eighth best Nintendo Entertainment System video game, mentioning that regardless of not being originally released as a Mario game, it was able to stand on its own merits and its unique takes on the series' trademark format.[22] Super Mario Bros. 2 was ranked 108th out of 200 of the "Greatest Games of Their Time" by Electronic Gaming Monthly.[citation needed] GamesRadar ranked it the 6th best NES game ever made. The staff complimented it and other 8-bit games for being a greater improvement than sequels around 2012, which they thought had seen only small improvements.[23]
When it was rereleased in 2001 as Super Mario Advance it received generally positive reviews, garnering an aggregate score of 84% on Metacritic.[24] One reviewer concluded "all nostalgia and historical influence aside, Super Mario Bros. 2 is still a game worth playing on the merits of its gameplay alone", also saying that "the only reason you may not want to pick it up is if ... you already own it in another form."[25] However, GameSpot thought that Super Mario Bros. 3 or Super Mario World would have been a better choice for a launch game considering their respective popularity;[26] both titles were eventually also remade as part of the Super Mario Advance series. Conversely, IGN praised the choice, calling it "one of the most polished and creative platformers of the era".[16] The game was named one of the NES best games ever by IGN, saying that the game offers greater diversity in graphics and gameplay than the original, making it a great bridge game between the other NES Mario titles.[27] They also named the music played in the battle against the final boss Wart in the eight best 8-Bit Final Boss Themes.[28]
Legacy
Many elements in Super Mario Bros. 2 have endured in subsequent sequels and in related series. The game added the ability to pick up and toss enemies and objects. A defining feature of its earliest prototype,[3] this move has become part of Mario's permanent repertoire, appearing in other Mario games including Super Mario Bros. 3, Donkey Kong (Game Boy), Super Mario World, Super Mario Land 2: 6 Golden Coins, Super Mario 64, Super Mario Sunshine, Mario vs. Donkey Kong, New Super Mario Bros., Super Paper Mario, New Super Mario Bros. Wii, Super Mario Galaxy, Super Mario Galaxy 2, New Super Mario Bros. U, and Super Mario 3D World. The Wii U game Super Mario 3D World features the same playable characters with the same basic physical abilities from Super Mario Bros. 2.[25][29][30][31]
The New Super Mario Bros. series also includes elements and ideas originally proposed for the prototype of this game. The multi-player elements originally proposed, were finally realized in the Wii game, where up to four players can play competitively or co-operatively. This gameplay incorporates the competitive elements from the original Mario Bros., with the platforming of Super Mario Bros. Vertical scrolling multi-player levels are frequent in this game, and also the other games in the series that followed after the Wii release.
Many characters of Super Mario Bros. 2 have been assimilated into the greater Mario universe as well, such as Birdo, Pokeys, Bob-ombs, and Shy Guys.[25] This is the first game in which Princess Peach and Toad are featured as playable characters. Princess Peach herself has eventually starred in other Mario games such as Super Princess Peach[25] while Toad has received supporting roles in later Mario games and has starred in games like Wario's Woods and New Super Mario Bros. Wii. His first game as main character is Captain Toad: Treasure Tracker even though his ability to jump has been removed in this Puzzle game. Super Mario Bros. 2 is also the first game where Luigi received the appearance he has today; notably, he is taller than Mario.[4][25] In the Super Smash Bros. series, Peach not only has the ability to pluck and throw vegetables, but she can also float in mid-air both in the same fashion as in this game. Super Smash Bros. Melee has a stage called Mushroom Kingdom II, which is based on Super Mario Bros. 2, though the visuals are more similar to the version seen in Super Mario All-Stars. The stage also has characters in their 2D sprite form, including Pidgit and Birdo. The television series The Super Mario Bros. Super Show produced by DIC Entertainment features animated segments featuring characters from Super Mario Bros. 2.
References
- ^ "Super Mario Bros. 2". GameFAQs. Retrieved July 15, 2014.
- ^ Nintendo Power 2010 calendar. Nintendo. 2009.
{{cite book}}:|magazine=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f g "The Secret History of Super Mario Bros. 2". wired.com. 3 April 2011. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- ^ a b c d e McLaughlin, Rus (September 14, 2010). "IGN Presents The History of Super Mario Bros". IGN. Retrieved April 9, 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g Super Mario Bros. 2 (U) instruction manual (First ed.). America: Nintendo of America Inc. 1988.
- ^ Tanabe, Kensuke (18 May 2004). "Interview - Kensuke Tanabe Talks Metroid Prime 2: Echoes" (Interview). Interviewed by Jonathan Metts; Daniel Bloodworth; Matt Cassamassina. Nintendo World Report. Archived from the original on November 5, 2013. Retrieved January 11, 2014.
{{cite interview}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|subjectlink=ignored (|subject-link=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: interviewers list (link) - ^ "クリエイターズファイル 第101回". Gpara.com. 10 February 2003. Retrieved 11 January 2011.
- ^ "From Doki Doki Panic to Super Mario Bros. 2". The Mushroom Kingdom. Retrieved August 1, 2014.
- ^ Mike (January 24, 2003). "Doki Doki Panic: The strange truth behind Super Mario Bros. 2". Progressive Boink. Archived from the original on June 22, 2007. Retrieved February 8, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Konno discusses how Luigi got his infamous leg flutter jump". GoNintendo. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- ^ Nintendo Entertainment Analysis and Development (10 July 1987). Yume Kōjō: Doki Doki Panic. Nintendo Co., Ltd. Scene: staff credits.
- ^ Nintendo Sound Selection vol.3 Luigi: B-Side Music (Media notes). Scitron Digital Contents Inc. 2005.
- ^ "SNES: Super Mario All-Stars". GameSpot. Retrieved 2008-08-27.
- ^ a b Kameb (12 February 2008). スーパーファミコンアワー番組表 (in Japanese). The Satellaview History Museum. Retrieved 29 March 2009.
- ^ "Joining Nintendo After Super Mario". Iwata Asks: Super Mario Bros. 25th Anniversary. Nintendo of America, Inc. 13 September 2010. Retrieved 19 January 2011.
- ^ a b "Super Mario Bros. 2: Super Mario Advance - Game Boy Advance Review at IGN". IGN. Retrieved 2010-02-26.
- ^ "Super Mario Advance Wii U Virtual Console footage (Japan)". Nintendo Everything. July 15, 2014. Retrieved 2014-07-16.
- ^ Miller, Skyler. "Super Mario Bros 2 – Overview". Allgame. Archived from the original on November 14, 2014. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ "The Video Game Critic's NES Reviews". videogamecritic.net. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ^ Navarro, Alex. "Super Mario Bros 2 Review". Gamespot. Retrieved December 6, 2012.
- ^ "All Time Top 20 Best Selling Games". 2003-05-21. Archived from the original on 2006-02-21. Retrieved 2006-12-01.
- ^ "NP Top 200". 231. Nintendo Power. August 2008: 71.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Best NES Games of all time". GamesRadar. 2012-04-16. Retrieved 2013-12-05.
- ^ "Super Mario Advance (gba) reviews at". Metacritic.com. 11 June 2001. Retrieved 20 July 2009.
- ^ a b c d e "Super Mario Bros. 2 Review". IGN. IGN Entertainment, Inc. 5 July 2007. Retrieved 25 August 2009.
- ^ "Super Mario Advance for the Game Boy Advance review". GameSpot. Retrieved 2010-02-26.
- ^ "18. Super Mario Bros. 2". IGN. 11 June 2001. Retrieved 10 April 2010.
- ^ "ScrewAttack - Top Ten 8-Bit Boss Themes". ScrewAttack. Retrieved 2010-04-11.
- ^ "Mario's Basic Moves". Nintendo Power: Strategy Guide. SG1 (13). Nintendo: 4. 1990.
- ^ "Full Coverage — Super Mario 64". Nintendo Power (88). Nintendo: 14–23. September 1996.
- ^ Miller, Skyler. "Super Mario World - Review". Allgame. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
External links
- 1988 video games
- Advergames
- Dreams in fiction
- Famicom Disk System games
- Game Boy Advance games
- Mario platform games
- Mario Universe games
- Nintendo Entertainment Analysis and Development games
- Nintendo Entertainment System games
- PlayChoice-10 games
- Satellaview games
- Side-scrolling platform games
- Video game remakes
- Video game sequels
- Video games composed by Koji Kondo
- Video games featuring female protagonists
- Video games produced by Shigeru Miyamoto
- Virtual Console games
- Virtual Console games for Wii U
