Paramesonephric duct
| Paramesonephric duct | |
|---|---|
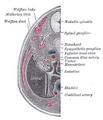
 Urogenital sinus of female human embryo of eight and a half to nine weeks old. | |
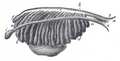
 Tail end of human embryo, from eight and a half to nine weeks old. | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 17 |
| Precursor | Intermediate mesoderm |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ductus paramesonephricus |
| MeSH | D009095 |
| TE | duct_by_E5.7.2.3.0.0.3 E5.7.2.3.0.0.3 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Paramesonephric ducts (or Müllerian ducts) are paired ducts of the embryo that run down the lateral sides of the urogenital ridge and terminate at the sinus tubercle in the primitive urogenital sinus. In the female, they will develop to form the uterine tubes, uterus, cervix, and the upper one-third of the vagina;[1] in the male, they are lost. These ducts are made of tissue of mesodermal origin.[2]
Development

The female reproductive system is composed of two embryological segments: the urogenital sinus and the paramesonephric ducts. The two are conjoined at the sinus tubercle.[3][4] Paramesonephric ducts are present on the embryo of both sexes.[4][5] Only in females do they develop into reproductive organs. They degenerate in males of certain species, but the adjoining mesonephric ducts develop into male reproductive organs. The sex based differences in the contributions of the paramesonephric ducts to reproductive organs is based on the presence, and degree of presence, of Müllerian inhibiting factor.
During the formation of the reproductive system, the paramesonephric ducts are formed just lateral to the mesonephric ducts in both female and male embryos 6 weeks after fertilization. During this time primordial germ cells migrate from the yolk sac to the gonadal ridge; a region of mesenchyme arising from, and running parallel with, the mesonephros. The paramesonephric ducts are formed by the craniocaudal invagination of a ribbon of thickened coelomic epithelium that extends from the third thoracic segment caudally to the posterior wall of the urogenital sinus. The caudal parts of the paramesonephric ducts fuse into a single tube, known as the uterovaginal primordium, before flowing into the dorsal aspect of the urogenital sinus at the sinus tubercle directly medial to the mesonephric ducts.
Anti-Müllerian hormone
The development of the paramesonephric (Müllerian) ducts is controlled by the presence or absence of "AMH", or Anti-Müllerian hormone (also known as "MIF" for "Müllerian-inhibiting factor", or "MIH" for "Müllerian-inhibiting hormone", or "APH" for Anti-Paramesonephric Hormone).[6][7]
| Male embryogenesis | The developing testes produce AMH causing regression of the paramesonphric ducts. | Disturbances can lead to persistent Müllerian duct syndrome. | The ducts disappear except for the vestigial vagina masculina and the appendix testis. |
| Female embryogenesis | The absence of AMH results in the development of the paramesonephric ducts into the uterine tubes, uterus, and the upper 2/3 of the vagina. | Disturbance in the development may result in uterine absence (Müllerian agenesis) or uterine malformations. | The ducts develop into the upper vagina, uterus, and uterine tubes. |
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), or Müllerian-inhibiting substance, is a glycoprotein hormone that is secreted by sustentacular cells (Sertoli cells) in males as they begin their morphologic differentiation in response to SRY expression. AMH begins to be secreted around week 8, which in turn causes the paramesonephric ducts to regress very rapidly between the 8th and 10th weeks. However, small paramesonephric ducts can still be identified, and the remnants can be detected in the adult male, located in the appendix testis, a small cap of tissue associated with the testis. Remnants of the paramesonephric ducts can also be found in the prostatic utricle, an expansion of the prostatic urethra at the center of the seminal colliculus.
AMH receptor-type II (AMHR-II), also known as Misr-II, causes AMH to act indirectly on mesenchymal cells surrounding the paramesonephric ducts rather than acting directly on the epithelium of the duct.[8] This receptor activation induces the ducts to regress. The importance of mesenchyme-to-epithelial signaling is to maintain AMHR-II expression in the mesenchyme. In the absence of the Wnta7a within the duct epithelium as the ducts regress, ductal AMHR-II expression is lost, and residual paramesonephric ducts would be retained in males, throwing off the urogenital system.
Cryptorchidism (undescended testis) or ectopic testis with inguinal hernias, have been identified in human males due to AMH and AMHR-II gene mutations. Recent studies have revealed another AMH receptor group, AMH receptor-type I (AMHR-I), based on the AMH being a TgfB/Bmp family member. Recent studies have shown that ALK2, Alk3 (or Bmpr 1a) and Alk6 all serve as AMHR-I receptors. When these receptors are blocked or knocked out in mice within the paramesonephric duct mesenchyme, AMH-induced paramesonephric duct regression is lost.
Function
In females, the paramesonephric ducts give rise to the uterine tubes, uterus, and upper portion of the vagina, while the mesonephric ducts degenerate due to the absence of male androgens. In contrast, the paramesonephric ducts begin to proliferate and differentiate in a cranial-caudal progression to form the aforementioned structures. During this time, the single-layered paramesonephric duct epithelium differentiates into other structures, ranging from the ciliated columnar epithelium in the uterine tube to stratified squamous epithelium in the vagina.[8]
The paramesonephric ducts and the mesonephric ducts share a majority of the same mesenchyme due to Hox gene expression. The genes expressed play a critical role in mediating the regional characterization of structures found along the cranial-caudal axis of the female reproductive tract.
Clinical significance
Mutations in AMH
Individuals that are 46, XY and have been tested positive for mutations in their AMH or AMH receptor genes have been known to exhibit features typical of that which are exhibited in persistent müllerian duct syndrome due to the fact that the paramesonephric ducts fail to regress. When this happens the individuals develop structures that are derived from the paramesonephric duct, and also structures that are derived from the mesonephric duct. A male that has persistent müllerian duct syndrome may have an upper vagina, uterus, and uterine tubes as well as ductus deferens along with male external genitalia. The female organs are in the correct anatomical position but the position of the testis varies. 60% to 70% of detected cases, both testes will lie in the normal position for the ovaries; about 20% to 30% of the time, one of the testis will lie within the inguinal hernial sac while in other cases both testes will lie within the same inguinal hernia sac. However whenever an individual exhibits persistent müllerian duct syndrome, the ductus deferens will run along the lateral sides of the uterus.[8]
Paramesonephric duct anomalies
Anomalies that develop within the paramesonephric duct system continue to puzzle and fascinate obstetricians and gynecologist. The paramesonephric ducts play a critical role in the female reproductive tract and differentiate to form the uterine tubes, uterus, superior vagina as well as the uterine cervix. Many types of disorders can occur when this system is disrupted ranging from uterine and vagina agenises to the duplication of unwanted cells of the uterus and vagina. Paramesonephric malformations are usually related to abnormalities of the renal and axial skeletal system.[8] Malfunction in the ovaries and age onset abnormalaites can also be associated with most paramesonephric ducts. Most abnormalities are often recognized once the external genitalia is no longer masked and the internal reproductive organ abnormalities become revealed. Due to a very broad range of anomalies it is very difficult to diagnose paramesonephric duct anomalies.[9][9]
Due to improved surgical instruments and technique women with paramesonephric duct anomalies can have normal sexual relations. Through the use of Vecchietti and Mclndoe procedures women can carry out their sexual activity.[9] On another note, many other surgical advances have tremendously improved fertility chances as well as obstetric outcomes. Assisted reproductive technology makes it possible for some women that have paramesonephric duct anomalies to conceive and give birth to healthy babies.
History
They are named after Johannes Peter Müller, a physiologist who described these ducts in his text "Bildungsgeschichte der Genitalien" in 1830.
Additional images
-
Enlarged view from the front of the left mesonephros before the establishment of the distinction of sex.
-
Transverse section of human embryo eight and a half to nine weeks old.
See also
References
- ^ Sizonenko, P.C. "Human Sexual Differentiation". Retrieved 2008-09-04.
- ^ Hashimoto R (2011-07-27). "Development of the human Müllerian duct in the sexually undifferentiated stage". The Anatomical Record Part A: Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary Biology. 272 (2): 514–9. doi:10.1002/ar.a.10061. PMID 12740945.
- ^ Yasmin Sajjad (2011-07-27). "Development of the genital ducts and external genitalia in the early human embryo". The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research. 36 (5): 929–937. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0756.2010.01272.x.
- ^ a b Moore, Keith; Persaud, T; Torchia, Mark (2013). The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (9 ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 269–271. ISBN 978-1-4377-2002-0.
- ^ "Normal male sexual differentiation and aetiology of disorders of sex development". Male Reproductive Endocrinology. 25 (2): 221–238. 2011-07-27. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2010.08.013.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ "Expression of anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) in the equine testis". Theriogenology. 69 (5): 624–631. 2011-07-27. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2007.11.009.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Minkoff, Eli; Baker, Pamela (2004). Biology Today: An Issues Approach (Third Edition ed.). New York: Garland Science. p. 296. ISBN 1136838759.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - ^ a b c d Schoenwolf, Gary C. (2008). Larsen’s Human Embryology. Churchill Livingstone. pp. 509, 510504, 518, 520. ISBN 9780443068119.
- ^ a b c Amesse, Ibrahim. "Mullerian Duct Anomalies". Retrieved 2012-11-29.