Arab–Israeli conflict
| Arab–Israeli conflict | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
|
Suez Crisis: (1956) |
War of Attrition: (1967–70) | ||||||||
|
Supported by:
| |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
≈22,570 military deaths[7] ≈1,723 civilian deaths[8] ≈1,050 SLA militiamen deaths[9] | 91,105 total Arab deaths[10] | ||||||||
|
Both sides: 74,000 military deaths 18,000 civilian deaths (1945–1995)[11] | |||||||||
The Arab–Israeli conflict (Template:Lang-ar Al-Sira'a Al'Arabi A'Israili; Template:Lang-he Ha'Sikhsukh Ha'Yisraeli-Aravi) refers to the political tension and military conflicts between a number of Arab countries and Israel. The roots of the modern Arab–Israeli conflict are bound in the rise of Zionism and Arab nationalism towards the end of the 19th century. Territory regarded by the Jewish people as their historical homeland is also regarded by the Pan-Arab movement as historically and currently belonging to the Palestinians,[12] and in the Pan-Islamic context, as Muslim lands. The sectarian conflict between Palestinian Jews and Arabs emerged in the early 20th century, peaking into a full-scale civil war in 1947 and transforming into the First Arab-Israeli War in May 1948 following the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel.
The nature of the conflict has shifted over the years from the large scale regional Arab–Israeli conflict to a more local Israeli–Palestinian conflict, as large-scale hostilities mostly ended with the cease-fire agreements that followed the 1973 Yom Kippur War. Attempts have been made to resolve the conflict, but without success. Peace agreements were signed between Israel and Egypt in 1979, and Israel and Jordan in 1994. The interim Oslo Accords led to the creation of the Palestinian National Authority in 1994, though a final peace agreement has yet to be reached. An Israeli–Palestinian peace process is ongoing. A cease-fire currently stands between Israel and Syria, as well as more recently with Lebanon (since 2006). The conflict between Israel and Hamas-ruled Gaza, which resulted in the 2009 cease-fire (although fighting has continued since then) is usually also included as part of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict and hence the Arab–Israeli conflict. Despite the peace agreements with Egypt and Jordan and the generally existing cease-fire, the Arab world and Israel generally remain at odds with each other over many issues.
Background
Religious aspects of the conflict
Some groups opposed to the peace process invoke religious arguments for their uncompromising positions.[13] The contemporary history of the Arab–Israeli conflict is very much affected by the religious beliefs of the various sides and their views of the idea of the chosen people in their policies with regard to the "Promised Land" and the "Chosen City" of Jerusalem.[14]
The Land of Canaan or Eretz Yisrael (Land of Israel) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, promised by God to the Children of Israel. This is also mentioned in the Qur'an. In his 1896 manifesto, The Jewish State, Theodor Herzl repeatedly refers to the Biblical Promised Land concept.[15] Likud is currently the most prominent Israeli political party to include the Biblical claim to the Land of Israel in its platform.[16]
Muslims also claim rights to that land in accordance with the Quran.[17] Contrary to the Jewish claim that this land was promised only to the descendants of Abraham's younger son Isaac, they argue that the Land of Canaan was promised to what they consider the elder son, Ishmael, from whom Arabs claim descent.[17] Additionally, Muslims also revere many sites holy for Biblical Israelites, such as the Cave of the Patriarchs and the Temple Mount. In the past 1,400 years, Muslims have constructed Islamic landmarks on these ancient Israelite sites, such as the Dome of the Rock and the Al-Aqsa Mosque on the Temple Mount, the holiest site in Judaism. This has brought the two groups into conflict over the rightful possession of Jerusalem. Muslim teaching is that Muhammad passed through Jerusalem on his first journey to heaven. Hamas, which governs the Gaza Strip, claims that all of the land of Palestine (the current Israeli and Palestinian territories) is an Islamic waqf that must be governed by Muslims.[18]
Christian Zionists often support the State of Israel because of the ancestral right[clarification needed] of the Jews to the Holy Land, as suggested, for instance, by Paul in Romans 11. Christian Zionism teaches that the return of Jews in Israel is a prerequisite for the Second Coming of Christ.[19][20]
National movements
The roots of the modern Arab–Israeli conflict lie in the rise of Zionism and the reactionary Arab nationalism that arose in response to Zionism towards the end of the 19th century. Territory regarded by the Jewish people as their historical homeland is also regarded by the Pan-Arab movement as historically and presently belonging to the Palestinian Arabs. Before World War I, the Middle East, including Palestine (later Mandatory Palestine), had been under the control of the Ottoman Empire for nearly 400 years. During the closing years of their empire, the Ottomans began to espouse their Turkish ethnic identity, asserting the primacy of Turks within the empire, leading to discrimination against the Arabs.[21] The promise of liberation from the Ottomans led many Jews and Arabs to support the allied powers during World War I, leading to the emergence of widespread Arab nationalism. Both Arab nationalism and Zionism had their formulative beginning in Europe. The Zionist Congress was established in Basel in 1897, while the "Arab Club" was established in Paris in 1906.
In the late 19th century European and Middle Eastern Jewish communities began to increasingly immigrate to Palestine and purchase land from the local Ottoman landlords. The population of the late 19th century in Palestine reached 600,000 – mostly Muslim Arabs, but also significant minorities of Jews, Christians, Druze and some Samaritans and Bahai's. At that time, Jerusalem did not extend beyond the walled area and had a population of only a few tens of thousands. Collective farms, known as kibbutzim, were established, as was the first entirely Jewish city in modern times, Tel Aviv.
During 1915–16, as World War I was underway, the British High Commissioner in Egypt, Sir Henry McMahon, secretly corresponded with Husayn ibn 'Ali, the patriarch of the Hashemite family and Ottoman governor of Mecca and Medina. McMahon convinced Husayn to lead an Arab revolt against the Ottoman Empire, which was aligned with Germany against Britain and France in the war. McMahon promised that if the Arabs supported Britain in the war, the British government would support the establishment of an independent Arab state under Hashemite rule in the Arab provinces of the Ottoman Empire, including Palestine. The Arab revolt, led by T. E. Lawrence ("Lawrence of Arabia") and Husayn's son Faysal, was successful in defeating the Ottomans, and Britain took control over much of this area.
Sectarian conflict in Mandatory Palestine
First mandate years and the Franco-Syrian war
In 1917, Palestine was conquered by the British forces (including the Jewish Legion). The British government issued the Balfour Declaration, which stated that the government viewed favorably "the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people" but "that nothing shall be done which may prejudice the civil and religious rights of existing non-Jewish communities in Palestine". The Declaration was issued as a result of the belief of key members of the government, including Prime Minister David Lloyd George, that Jewish support was essential to winning the war; however, the declaration caused great disquiet in the Arab world.[22] After the war, the area came under British rule as the British Mandate of Palestine. The area mandated to the British in 1923 included what is today Israel, the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Transjordan eventually was carved into a separate British protectorate – the Emirate of Transjordan, which gained an autonomous status in 1928 and achieved complete independence in 1946 with the approval by the United Nations of the end of the British Mandate.
A major crisis among the Arab nationalists took place with the failed establishment of the Arab Kingdom of Syria in 1920. With the disastrous outcome of the Franco-Syrian War, the self-proclaimed Hashemite kingdom with its capital in Damascus was defeated and the Hashemite ruler took refuge in Mandatory Iraq. The crisis saw the first confrontation of nationalist Arab and Jewish forces, taking place in the Battle of Tel Hai in March 1920, but more importantly the collapse of the pan-Arabist kingdom led to the establishment of the local Palestinian version of Arab nationalism, with the return of Haj Amin al-Husseini from Damascus to Jerusalem in late 1920.
At this point in time Jewish immigration to Mandatory Palestine continued, while to some opinions a similar, but less documented, immigration also took place in the Arab sector, bringing workers from Syria and other neighbouring areas. Palestinian Arabs saw this rapid influx of Jewish immigrants as a threat to their homeland and their identity as a people. Moreover, Jewish policies of purchasing land and prohibiting the employment of Arabs in Jewish-owned industries and farms greatly angered the Palestinian Arab communities.[23][verification needed] Demonstrations were held as early as 1920, protesting what the Arabs felt were unfair preferences for the Jewish immigrants set forth by the British mandate that governed Palestine at the time. This resentment led to outbreaks of violence later that year, as the al-Husseini incited riots broke out in Jerusalem. Winston Churchill's 1922 White Paper tried to reassure the Arab population, denying that the creation of a Jewish state was the intention of the Balfour Declaration.
1929 events
In 1929, after a demonstration by Vladimir Jabotinsky's political group Betar at the Western Wall, riots started in Jerusalem and expanded throughout Mandatory Palestine; Arabs murdered 67 Jews in the city of Hebron, in what became known as the Hebron massacre.

During the week of the 1929 riots, at least 116 Arabs and 133 Jews[24] were killed and 339 wounded.[25]
1930s and 1940s
By 1931, 17 percent of the population of Mandatory Palestine were Jews, an increase of six percent since 1922.[26] Jewish immigration peaked soon after the Nazis came to power in Germany, causing the Jewish population in British Palestine to double.[27]
In the mid-1930s Izz ad-Din al-Qassam arrived from Syria and established the Black Hand, an anti-Zionist and anti-British militant organization. He recruited and arranged military training for peasants and by 1935 he had enlisted between 200 and 800 men. The cells were equipped with bombs and firearms, which they used to kill Jewish settlers in the area, as well as engaging in a campaign of vandalism of Jewish settler plantations.[28] By 1936, escalating tensions led to the 1936–39 Arab revolt in Palestine.[29]
In response to Arab pressure,[30] the British Mandate authorities greatly reduced the number of Jewish immigrants to Palestine (see White Paper of 1939 and the SS Exodus). These restrictions remained in place until the end of the mandate, a period which coincided with the Nazi Holocaust and the flight of Jewish refugees from Europe. As a consequence, most Jewish entrants to Mandatory Palestine were considered illegal (see Aliyah Bet), causing further tensions in the region. Following several failed attempts to solve the problem diplomatically, the British asked the newly formed United Nations for help. On May 15, 1947, the General Assembly appointed a committee, the UNSCOP, composed of representatives from eleven states.[31] To make the committee more neutral, none of the Great Powers were represented.[32] After five weeks of in-country study, the Committee reported to the General Assembly on September 3, 1947.[33] The Report contained a majority and a minority plan. The majority proposed a Plan of Partition with Economic Union. The minority proposed The Independent State of Palestine. With only slight modifications, the Plan of Partition with Economic Union was the one the adoption and implementation of which was recommended in resolution 181(II) of November 29, 1947.[34] The Resolution was adopted by 33 votes to 13 with 10 abstentions. All six Arab states who were UN-members voted against it. On the ground, Arab and Jewish Palestinians were fighting openly to control strategic positions in the region. Several major atrocities were committed by both sides.[35]
Civil War in Mandatory Palestine
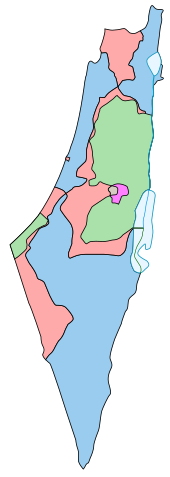
Boundaries defined in the 1947 UN Partition Plan for Palestine:
Armistice Demarcation Lines of 1949 (Green Line):
In the weeks prior to the end of the Mandate the Haganah launched a number of offensives in which they gained control over all the territory allocated by the UN to the Jewish State, creating a large number of refugees and capturing the towns of Tiberias, Haifa, Safad, Beisan and, in effect, Jaffa.
Early in 1948, the United Kingdom announced its firm intention to terminate its mandate in Palestine on May 14.[36] In response, U.S. President Harry S. Truman made a statement on March 25 proposing UN trusteeship rather than partition, stating that "unfortunately, it has become clear that the partition plan cannot be carried out at this time by peaceful means. ... unless emergency action is taken, there will be no public authority in Palestine on that date capable of preserving law and order. Violence and bloodshed will descend upon the Holy Land. Large-scale fighting among the people of that country will be the inevitable result."[37]
History
1948 Arab–Israeli War
On May 14, 1948, the day on which the British Mandate over Palestine expired, the Jewish People's Council gathered at the Tel Aviv Museum, and approved a proclamation which declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz Israel, to be known as the State of Israel. The declaration was made by David Ben-Gurion, the Executive Head of the World Zionist Organization.[38]
There were no mention of the borders of the new state other than that it was in Eretz Israel. In an official cablegram from the Secretary-General of the League of Arab States to the UN Secretary-General on May 15, 1948, the Arab stated publicly that Arab Governments found "themselves compelled to intervene for the sole purpose of restoring peace and security and establishing law and order in Palestine." (Clause 10(e)). Further in Clause 10(e) – "The Governments of the Arab States hereby confirm at this stage the view that had been repeatedly declared by them on previous occasions, such as the London Conference and before the United Nations mainly, the only fair and just solution to the problem of Palestine is the creation of United State of Palestine based upon the democratic principles ..."
That day, the armies of Egypt, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Iraq invaded/intervened in what had just ceased to be the British Mandate, marking the beginning of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. The nascent Israeli Defense Force repulsed the Arab nations from part of the occupied territories, thus extending its borders beyond the original UNSCOP partition.[39] By December 1948, Israel controlled most of the portion of Mandate Palestine west of the Jordan River. The remainder of the Mandate consisted of Jordan, the area that came to be called the West Bank (controlled by Jordan), and the Gaza Strip (controlled by Egypt). Prior to and during this conflict, 713,000[40] Palestinian Arabs fled their original lands to become Palestinian refugees, in part, due to a promise from Arab leaders that they would be able to return when the war had been won, and also in part due to attacks on Palestinian villages and towns by Israeli forces and Jewish militant groups.[41] Many Palestinians fled from the areas that are now present-day Israel as a response to massacres of Arab towns by militant Jewish organizations like the Irgun and the Stern Gang (See Deir Yassin massacre). The War came to an end with the signing of the 1949 Armistice Agreements between Israel and each of its Arab neighbours.
The status of Jewish citizens in Arab states worsened during the 1948 Israeli-Arab war. Anti-Jewish riots erupted throughout the Arab World in December 1947, and Jewish communities were hit particularly hard in Aleppo and British-controlled Aden, with hundreds of dead and injured. In Libya, Jews were deprived of citizenship, and in Iraq, their property was seized.[needs context][42] Egypt expelled most of its foreign community, including Jews, after the Suez War 1956,[43] while Algeria denied its French citizens, including Jews, of citizenship upon its independence in 1962. Over the course of twenty years, some 850,000 Jews from Arab countries immigrated to Israel and other countries.[44]
1949–67
As a result of Israel's victory in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, any Arabs caught on the wrong side of the ceasefire line were unable to return to their homes in what became Israel. Likewise, any Jews on the West Bank or in Gaza were exiled from their property and homes to Israel. Today's Palestinian refugees are the descendants of those who left, the responsibility for their exodus being a matter of dispute between the Israeli and the Palestinian side.[45][46]: 114 Morris concluded that the "decisive cause" for the abandonment by Palestinian Arabs of their settlements was predominantly related to, or caused by, actions of the Jewish forces (citing actual physical expulsions, military assaults on settlements, fear of being caught up in fighting, the fall of nearby settlements, and propaganda inciting flight), while abandonment due to orders by the Arab leadership was decisive in only six out of the 392 depopulated Arab settlements analysed by him.[46]: xiv–xviii Over 700,000 Jews emigrated to Israel between 1948 and 1952, with approximately 285,000 of them from Arab countries.[47][48]
In 1956, Egypt closed the Straits of Tiran to Israeli shipping, and blockaded the Gulf of Aqaba, in contravention of the Constantinople Convention of 1888. Many argued that this was also a violation of the 1949 Armistice Agreements.[49][50][failed verification] On July 26, 1956, Egypt nationalized the Suez Canal Company, and closed the canal to Israeli shipping.[51] Israel responded on October 29, 1956, by invading the Sinai Peninsula with British and French support. During the Suez Crisis, Israel captured the Gaza Strip and Sinai Peninsula. The United States and the United Nations soon pressured it into a ceasefire.[51][52] Israel agreed to withdraw from Egyptian territory. Egypt agreed to freedom of navigation in the region and the demilitarization of the Sinai. The United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) was created and deployed to oversee the demilitarization.[53] The UNEF was only deployed on the Egyptian side of the border, as Israel refused to allow them on its territory.[54]
Israel completed work on a national water carrier, a huge engineering project designed to transfer Israel's allocation of the Jordan river's waters towards the south of the country in realization of Ben-Gurion's dream of mass Jewish settlement of the Negev desert. The Arabs responded by trying to divert the headwaters of the Jordan, leading to growing conflict between Israel and Syria.[55]
The PLO (Palestinian Liberation Organization) was first established in 1964, under a charter including a commitment to "[t]he liberation of Palestine [which] will destroy the Zionist and imperialist presence..." (PLO Charter, Article 22, 1968).
On May 19, 1967, Egypt expelled UNEF observers,[56] and deployed 100,000 soldiers in the Sinai Peninsula.[57] It again closed the Straits of Tiran to Israeli shipping,[58][59] returning the region to the way it was in 1956 when Israel was blockaded.
On May 30, 1967, Jordan signed a mutual defense pact with Egypt. Egypt mobilized Sinai units, crossing UN lines (after having expelled the UN border monitors) and mobilized and massed on Israel's southern border. On June 5, Israel launched an attack on Egypt. The Israeli Air Force (IAF) destroyed most of the Egyptian Air Force in a surprise attack, then turned east to destroy the Jordanian, Syrian and Iraqi air forces.[60] This strike was the crucial element in Israel's victory in the Six-Day War.[57][59] At the war's end, Israel had gained control of the Sinai Peninsula, the Gaza Strip, the West Bank (including East Jerusalem), Shebaa farms, and the Golan Heights. The results of the war affect the geopolitics of the region to this day.
1967–73

At the end of August 1967, Arab leaders met in Khartoum in response to the war, to discuss the Arab position toward Israel. They reached consensus that there should be no recognition, no peace, and no negotiations with the State of Israel, the so-called "three no's".[61]
In 1969, Egypt initiated the War of Attrition, with the goal of exhausting Israel into surrendering the Sinai Peninsula.[62] The war ended following Gamal Abdel Nasser's death in 1970. Once Sadat took over, he tried to forge positive relations with the USA, hoping they would put pressure on Israel to return the land, by expelling 15,000 Russian advisors from Egypt.[63]
On October 6, 1973, Syria and Egypt staged a surprise attack on Israel on Yom Kippur, the holiest day of the Jewish calendar. The Israeli military were caught off guard and unprepared, and took about three days to fully mobilize.[64][65] This led other Arab states to send troops to reinforce the Egyptians and Syrians. In addition, these Arab countries agreed to enforce an oil embargo on industrial nations including the U.S, Japan and Western European Countries. These OPEC countries increased the price of oil fourfold, and used it as a political weapon to gain support against Israel.[66] The Yom Kippur War accommodated indirect confrontation between the US and the Soviet Union. When Israel had turned the tide of war, the USSR threatened military intervention. The United States, wary of nuclear war, secured a ceasefire on October 25.[64][65]
1974–2000
Egypt

Following the Camp David Accords of the late 1970s, Israel and Egypt signed a peace treaty in March 1979. Under its terms, the Sinai Peninsula returned to Egyptian hands, and the Gaza Strip remained under Israeli control, to be included in a future Palestinian state. The agreement also provided for the free passage of Israeli ships through the Suez Canal and recognition of the Straits of Tiran and the Gulf of Aqaba as international waterways.
Jordan
In October 1994, Israel and Jordan signed a peace agreement, which stipulated mutual cooperation, an end of hostilities, the fixing of the Israel-Jordan border, and a resolution of other issues. The conflict between them had cost roughly 18.3 billion dollars. Its signing is also closely linked with the efforts to create peace between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) representing the Palestinian National Authority (PNA). It was signed at the southern border crossing of Arabah on October 26, 1994 and made Jordan only the second Arab country (after Egypt) to sign a peace accord with Israel.
Iraq
Israel and Iraq have been implacable foes since 1948. Iraq sent its troops to participate in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, and later backed Egypt and Syria in the 1967 Six-Day War and in the 1973 Yom Kippur War.
In June 1981, Israel attacked and destroyed newly built Iraqi nuclear facilities in Operation Opera.
During the Gulf War in 1991, Iraq fired 39 Scud missiles into Israel, in the hopes of uniting the Arab world against the coalition which sought to liberate Kuwait. At the behest of the United States, Israel did not respond to this attack in order to prevent a greater outbreak of war.
Lebanon
In 1970, following an extended civil war, King Hussein expelled the Palestine Liberation Organization from Jordan. September 1970 is known as the Black September in Arab history and sometimes is referred to as the "era of regrettable events". It was a month when Hashemite King Hussein of Jordan moved to quash the autonomy of Palestinian organisations and restore his monarchy's rule over the country.[67] The violence resulted in the deaths of tens of thousands of people, the vast majority Palestinians.[68] Armed conflict lasted until July 1971 with the expulsion of the PLO and thousands of Palestinian fighters to Lebanon. The PLO resettled in Lebanon, from which it staged raids into Israel. In 1978, Israel launched Operation Litani, in which it together with the South Lebanon Army forced the PLO to retreat north of the Litani river. In 1981 another conflict between Israel and the PLO broke out, which ended with a ceasefire agreement that did not solve the core of the conflict. In June 1982, Israel invaded Lebanon. Within two months the PLO agreed to withdraw thence.
In March 1983, Israel and Lebanon signed a ceasefire agreement. However, Syria pressured President Amine Gemayel into nullifying the truce in March 1984. By 1985, Israeli forces withdrew to a 15 km wide southern strip of Lebanon, following which the conflict continued on a lower scale, with relatively low casualties on both sides. In 1993 and 1996, Israel launched major operations against the Shiite militia of Hezbollah, which had become an emergent threat. In May 2000, the newly elected government of Ehud Barak authorized a withdrawal from Southern Lebanon, fulfilling an election promise to do so well ahead of a declared deadline. The hasty withdrawal lead to the immediate collapse of the South Lebanon Army, and many members either got arrested or fled to Israel.
In 2006, as a response to a Hezbollah cross-border raid, Israel launched air strikes on Hezbollah strongholds in Southern Lebanon, starting the 2006 Lebanon War. The inconclusive war lasted for 34 days, and resulted in the creation of a buffer zone in Southern Lebanon and the deployment of Lebanese troops south of the Litani river for the first time since the 1960s. The Israeli government under Ehud Olmert was harshly criticized for its handling of the war in the Winograd Commission.
Palestinians
The 1970s were marked by a large number of major, international terrorist attacks, including the Lod Airport massacre and the Munich Olympics Massacre in 1972, and the Entebbe Hostage Taking in 1976, with over 100 Jewish hostages of different nationalities kidnapped and held in Uganda.
In December 1987, the First Intifada began. The First Intifada was a mass Palestinian uprising against Israeli rule in the Palestinian territories.[69] The rebellion began in the Jabalia refugee camp and quickly spread throughout Gaza and the West Bank. Palestinian actions ranged from civil disobedience to violence. In addition to general strikes, boycotts on Israeli products, graffiti and barricades, Palestinian demonstrations that included stone-throwing by youths against the Israel Defense Forces brought the Intifada international attention. The Israeli army's heavy handed response to the demonstrations, with live ammunition, beatings and mass arrests, brought international condemnation. The PLO, which until then had never been recognised as the leaders of the Palestinian people by Israel, was invited to peace negotiations the following year, after it recognized Israel and renounced terrorism.

In mid-1993, Israeli and Palestinian representatives engaged in peace talks in Oslo, Norway. As a result, in September 1993, Israel and the PLO signed the Oslo Accords, known as the Declaration of Principles or Oslo I; in side letters, Israel recognized the PLO as the legitimate representative of the Palestinian people while the PLO recognized the right of the state of Israel to exist and renounced terrorism, violence and its desire for the destruction of Israel.
The Oslo II agreement was signed in 1995 and detailed the division of the West Bank into Areas A, B, and C. Area A was land under full Palestinian civilian control. In Area A, Palestinians were also responsible for internal security. The Oslo agreements remain important documents in Israeli-Palestinian relations.
2000–09
The Second Intifada forced Israel to rethink its relationship and policies towards the Palestinians. Following a series of suicide bombings and attacks, the Israeli army launched Operation Defensive Shield. It was the largest military operation conducted by Israel since the Six-Day War.[70]
As violence between the Israeli army and Palestinian militants intensified, Israel expanded its security apparatus around the West Bank by re-taking many parts of land in Area A. Israel established a complicated system of roadblocks and checkpoints around major Palestinian areas to deter violence and protect Israeli settlements. However, since 2008, the IDF has slowly transferred authority to Palestinian security forces.[71][72][73]
Israel's then prime minister Ariel Sharon began a policy of disengagement from Gaza from the Gaza Strip in 2003. This policy was fully implemented in August 2005.[74] Sharon's announcement to disengage from Gaza came as a tremendous shock to his critics both on the left and on the right. A year previously, he had commented that the fate of the most far-flung settlements in Gaza, Netzararem and Kfar Darom, was regarded in the same light as that of Tel Aviv.[75] The formal announcements to evacuate seventeen Gaza settlements and another four in the West Bank in February 2004 represented the first reversal for the settler movement since 1968. It divided his party. It was strongly supported by Trade and Industry Minister Ehud Olmert and Tzipi Livni, the Minister for Immigration and Absorption, but Foreign Minister Silvan Shalom and Finance Minister Benjamin Netanyahu strongly condemned it. It was also uncertain whether this was simply the beginning of further evacuation.[76]
On March 16, 2003, Rachel Corrie, an American peace activist was crushed to death by an Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) bulldozer in Rafah, Gaza, during a non-violent protest of the Israeli demolition of Palestinian homes.[77] Corrie stood in confrontation with the bulldozers for three hours wearing a bright orange jacket and carrying a megaphone.[77] Although the Israeli government has denied responsibility in the incident and ruled her death as an accident, several eye-witness reports say that the Israeli soldier operating the bulldozer deliberately ran her over.[77][78]
In June 2006, Hamas militants infiltrated an army post near the Israeli side of the Gaza Strip and abducted Israeli soldier Gilad Shalit. Two IDF soldiers were killed in the attack, while Shalit was wounded after his tank was hit with an RPG. Three days later Israel launched Operation Summer Rains to secure the release of Shalit.[79] He was held hostage by Hamas, who barred the International Red Cross from seeing him, until October 18, 2011, when he was exchanged for 1,027 Palestinian prisoners.[80][81]
In July 2006, Hezbollah fighters crossed the border from Lebanon into Israel, attacked and killed eight Israeli soldiers, and abducted two others as hostages, setting off the 2006 Lebanon War which caused much destruction in Lebanon.[82] A UN-sponsored ceasefire went into effect on August 14, 2006, officially ending the conflict.[83] The conflict killed over a thousand Lebanese and over 150 Israelis,[84][85][86][87][88][89][90] severely damaged Lebanese civil infrastructure, and displaced approximately one million Lebanese[91] and 300,000–500,000 Israelis, although most were able to return to their homes.[92][93][94] After the ceasefire, some parts of Southern Lebanon remained uninhabitable due to Israeli unexploded cluster bomblets.[95]
In the aftermath of the Battle of Gaza, where Hamas seized control of the Gaza Strip in a violent civil war with rival Fatah, Israel placed restrictions on its border with Gaza borders and ended economic cooperation with the Palestinian leadership based there. Israel and Egypt have imposed a blockade of the Gaza Strip since 2007. Israel maintains the blockade is necessary to limit Palestinian rocket attacks from Gaza and to prevent Hamas from smuggling advanced rockets and weapons capable of hitting its cities.[77]
On September 6, 2007, in Operation Orchard, Israel bombed an eastern Syrian complex which was allegedly a nuclear reactor being built with assistance from North Korea.[96] Israel had also bombed Syria in 2003.
In April 2008, Syrian President Bashar al-Assad told a Qatari newspaper that Syria and Israel had been discussing a peace treaty for a year, with Turkey as a go-between. This was confirmed in May 2008 by a spokesman for Prime Minister Ehud Olmert. As well as a peace treaty, the future of the Golan Heights is being discussed. President Assad said "there would be no direct negotiations with Israel until a new US president takes office."[97]
Speaking in Jerusalem on August 26, 2008, then United States Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice criticized Israel's increased settlement construction in the West Bank as detrimental to the peace process. Rice's comments came amid reports that Israeli construction in the disputed territory had increased by a factor of 1.8 over 2007 levels.[98]
A fragile six-month truce between Hamas and Israel expired on December 19, 2008;[99] attempts at extending the truce failed amid accusations of breaches from both sides.[100][101][102][103] Following the expiration, Israel launched a raid on a tunnel suspected of being used to kidnap Israeli soldiers which killed several Hamas fighters.[104] Following this, Hamas resumed rocket and mortar attacks on Israeli cities, most notably firing over 60 rockets on December 24. On December 27, 2008, Israel launched Operation Cast Lead against Hamas. Numerous human rights organizations accused Israel and Hamas of committing war crimes.[105]
In 2009 Israel placed a 10-month settlement freeze on the West Bank. Hillary Clinton praised the freeze as an "unprecedented" gesture that could "help revive Middle East talks."[106][107]
A raid was carried out by Israeli naval forces on six ships of the Gaza Freedom Flotilla in May 2010.[108] after the ships refused to dock at Port Ashdod. On the MV Mavi Marmara, activists clashed with the Israeli boarding party. During the fighting, nine activists were killed by Israeli special forces. Widespread international condemnation of and reaction to the raid followed, Israel–Turkey relations were strained, and Israel subsequently eased its blockade on the Gaza Strip.[109][110][111][112] Several dozen other passengers and seven Israeli soldiers were injured,[110] with some of the commandos suffering from gunshot wounds.[113][114]
2010–present
Following the latest round of peace talks between Israel and the Palestinian Authority, 13 Palestinian militant movements led by Hamas initiated a terror campaign designed to derail and disrupt the negotiations.[115] Attacks on Israelis have increased since August 2010, after 4 Israeli civilians were killed by Hamas militants. Palestinian militants have increased the frequency of rocket attacks aimed at Israelis. On August 2, Hamas militants launched seven Katyusha rockets at Eilat and Aqaba, killing one Jordanian civilian and wounding 4 others.[116]
Intermittent fighting continued since then, including 680 rocket attacks on Israel in 2011.[117] On November 14, 2012, Israel killed Ahmed Jabari, a leader of Hamas's military wing, launching Operation Pillar of Cloud.[118] Hamas and Israel agreed to an Egyptian-mediated ceasefire on November 21.[119]
The Palestinian Centre for Human Rights said that 158 Palestinians were killed during the operation, of which: 102 were civilians, 55 were militants and one was a policeman; 30 were children and 13 were women.[120][121] B'Tselem stated that according to its initial findings, which covered only the period between 14 and 19 November, 102 Palestinians were killed in the Gaza Strip, 40 of them civilians. According to Israeli figures, 120 combatants and 57 civilians were killed.[122] International outcry ensued, with many criticizing Israel for what much of the international community perceived as a disproportionately violent response.[123] Protests took place on hundreds of college campuses across the U.S., and in front of the Israeli consulate in New York.[124] Additional protests took place throughout the Middle East, throughout Europe, and in parts of South America.[124]
However, the governments of the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, France, Australia, Belgium, Bulgaria, Czech Republic and Netherlands expressed support for Israel's right to defend itself, and/or condemned the Hamas rocket attacks on Israel.[125][126][127][128][129][130][131][132][133][134][135]
Following an escalation of rocket attacks by Hamas, Israel started an operation in the Gaza Strip on July 8, 2014.[136]
Notable wars and violent events
| Time | Name |
|---|---|
| 1948–1949 | First Arab–Israeli War |
| 1951–1955 | Reprisal operations |
| 1956 | Suez War |
| 1967 | The Six-Day War |
| 1967–1970 | War of Attrition |
| 1971–1982 | Palestinian insurgency in South Lebanon |
| 1973 | Yom Kippur War |
| 1978 | First South Lebanon conflict |
| 1982 | First Lebanon War |
| 1985–2000 | Second South Lebanon conflict |
| 1987–1993 | First Intifada |
| 2000–2004 | Second Intifada |
| 2006 | Operation Summer Rains |
| Second Lebanon War | |
| 2008–2009 | Gaza War |
| 2012 | Operation Pillar of Defense |
| 2014 | 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict |
Cost of conflict
A report by Strategic Foresight Group has estimated the opportunity cost of conflict for the Middle East from 1991–2010 at $12 trillion. The report's opportunity cost calculates the peace GDP of countries in the Middle East by comparing the current GDP to the potential GDP in times of peace. Israel's share is almost $1 trillion, with Iraq and Saudi Arabia having approximately $2.2 and $4.5 trillion, respectively. In other words, had there been peace and cooperation between Israel and Arab League nations since 1991, the average Israeli citizen would be earning over $44,000 instead of $23,000 in 2010.[137]
In terms of the human cost, it is estimated that the conflict has taken 92,000 lives (74,000 military and 18,000 civilian from 1945 to 1995).[11]
See also
- Art of the Arab–Israeli conflict
- One-state solution
- Two-state solution
- International law and the Arab–Israeli conflict
- Media coverage of the Arab–Israeli conflict
- Arab League and the Arab–Israeli conflict
- Soviet Union and the Arab–Israeli conflict and Russia and the Arab–Israeli conflict
- Foreign relations of Israel
- Israel–European Union relations
- Timeline of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict
- Israeli–Lebanese conflict
- Occupation of the Gaza Strip by Egypt
- Jordanian occupation of the West Bank
- Policide
- Israel–Turkey relations
- Political status of the Palestinian territories
- Jewish-Islamic conflict in the days of Muhammad
- Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator
- Civil defense in Israel
- List of wars involving Israel
- Israeli casualties of war
- Palestinian casualties of war
- Palestinian political violence
- Zionist political violence
References
- ^ Olsen, John Andreas (2011). Global Air Power. Potomac. p. 561. ISBN 1597975559.
- ^ Pollack, Kenneth, M., Arabs at War: Military Effectiveness, University of Nebraska Press, (2002), pp. 93–94, 96.
- ^ Karsh, Efraim: The Cautious Bear: Soviet Military Engagement in Middle East Wars in the Post-1967 Era
- ^ Moshe Yegar, "Pakistan and Israel," Jewish Political Studies Review 19:3–4 (Fall 2007)
- ^ "Pakistani Pilots in Arab Israel War". Opinion Maker. Archived from the original on 2013-05-13. Retrieved 2013-05-13.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Remembering the past: Bangladeshi fighters for Palestine of the 1980s". Opinion Maker. Archived from the original on 2015-06-17. Retrieved 2015-06-17.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Memorial Day / 24,293 fallen soldiers, terror victims since Israel was born. Haaretz. Retrieved on 2014-07-28.
- ^ Memorial Day / 24,293 fallen soldiers, terror victims since Israel was born. Haaretz Retrieved on 2014-07-28.
- ^ https://books.google.no/books?id=HNyv0N8cVE0C&printsec=frontcover&dq=in+the+path+of+hezbollah&hl=no&sa=X&ei=NS2cVfnHHYG2-QHdjbWQAw&ved=0CB0Q6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=in%20the%20path%20of%20hezbollah&f=false
- ^ Total Casualties, Arab-Israeli Conflict. Jewish Virtual Library.
- ^ a b Buzan, Barry (2003). Regions and powers. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-89111-0. Retrieved April 21, 2009.
- ^ "The Palestinian National Charter – Article 6". Mfa.gov.il. Retrieved 2013-01-19.
- ^ Weinberger, Peter E. (May 2004). "Incorporating religion into israeli-palestinian peacemaking: recommendations for policymakers" (PDF). Center for World Religions, Diplomacy, and Conflict Resolution, Institute for Conflict Analysis and Resolution, George Mason University.
- ^ Avi Beker, The Chosen: The History of an Idea and the Anatomy of an Obsession, New York: Palgrave Mcmillan, 2008
- ^ The State of the Jews[dead link], Theodor Hertzl, 1896, Translated from the German by Sylvie D'Avigdor, published in 1946 by the American Zionist Emergency Council. The original German title, "Der Judenstaat", literally means "The Jews' State". Archived 2009-10-25.
- ^ "Likud – Platform". Knesset.gov.il. Archived from the original on October 6, 2008. Retrieved September 4, 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b 'Jerusalem in the Qur'an', Masjid Dar al-Qur'an, Long Island, New York. 2002
- ^ "The Avalon Project : Hamas Covenant 1988". Avalon.law.yale.edu. August 18, 1988. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ "Seven Major Prophetic Signs Of The Second Coming". Gracethrufaith.com. December 31, 2011.
- ^ Review of On the Road to Armageddon: How Evangelicals Became Israel's Best Friend
- ^ Fraser, T.G. The Middle East: 1914–1979. St. Martin's Press, New York. (1980) Pg. 2
- ^ Segev, Tom (2000): One Palestine, Complete, pp. 48–49, Abacus, ISBN 0-349-11286-X.
- ^ Lesch, Ann M. and Tschirgi, Dan. Origins and Development of the Arab-Israeli Conflict. Greenwood Press: West Port, Connecticut. (1998). Pg.47,51
- ^ San Francisco Chronicle, Aug. 9, 2005, "A Time of Change; Israelis, Palestinians and the Disengagement"
- ^ NA 59/8/353/84/867n, 404 Wailing Wall/279 and 280, Archdale Diary and Palestinian Police records.
- ^ Lesch, Ann M. and Tschirgi, Dan. Origins and Development of the Arab-Israeli Conflict. Greenwood Press: West Port, Connecticut. (1998). Pg. 47
- ^ Smith, Charles D. Palestine and the Arab Israeli Conflict: A History With Documents. Bedford/St. Martin's: Boston. (2004). Pg. 129
- ^ Segev, Tom (1999). One Palestine, Complete. Metropolitan Books. pp. 360–362. ISBN 0-8050-4848-0.
- ^ Lesch, Ann M. and Tschirgi, Dan. Origins and Development of the Arab-Israeli Conflict. Greenwood Press: West Port, Connecticut. (1998). Pg.
- ^ "The Struggle against Jewish Immigration to Palestine". Middle Eastern Studies. July 1, 1998. Retrieved April 20, 2010.[dead link]
- ^ A/RES/106 (S-1) of May 15, 1947 General Assembly Resolution 106 Constituting the UNSCOP: Retrieved12 May 2012
- ^ Smith, Charles D. Palestine and the Arab Israeli Conflict: A History With Documents. Bedford/St. Martin's: Boston. (2004). Pg. 186
- ^ "UNITED NATIONS: General Assembly: A/364: 3 September 1947: Retrieved 10 May 2012". United Nations.
- ^ "A/RES/181(II) of 29 November 1947". United Nations. 1947. Retrieved May 12, 2012.
- ^ Fraser, T.G. The Middle East: 1914–1979. St. Martin's Press, New York. (1980). Pg. 41
- ^ Stefan Brooks (2008). "Palestine, British Mandate for". In Spencer C. Tucker (ed.). The Encyclopedia of the Arab-Israeli Conflict. Vol. 3. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 770. ISBN 978-1-85109-842-2.
- ^ "United States Proposal for Temporary United Nations Trusteeship for Palestine Source: Department of State Bulletin, vol. 18, No. 457, April 4, 1948, p. 451". Mideastweb.org.
- ^ "Declaration of Establishment of State of Israel: May 14, 1948". Mfa.gov.il. Retrieved 2013-01-19.
- ^ Smith, Charles D. Palestine and the Arab Israeli Conflict: A History With Documents. Bedford/St. Martin's: Boston. (2004). Pg. 198
- ^ GENERAL PROGRESS REPORT AND SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT OF THE UNITED NATIONS CONCILIATION COMMISSION FOR PALESTINE, Covering the period from December 11, 1949 to October 23, 1950, GA A/1367/Rev.1 23 October 1950
- ^ "The Palestinian Diaspora". Global Exchange. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ^ Aharoni, Ada (March 2003). "The Forced Migration of Jews from Arab Countries". Vol. 15, no. 1. Routledge, part of the Taylor & Francis Group.[dead link]
- ^ Gorman, Anthony (2003). Historians, State and Politics in Twentieth Century Egypt: Contesting the Nation. Psychology Press. pp. 174–5. ISBN 9780415297530.
- ^ Hoge, Warren (5 November 2007). "Group seeks justice for 'forgotten' Jews". The New York Times. Retrieved 7 June 2015.
- ^ Erskine Childers, "The Other Exodus", The Spectator, May 12, 1961, reprinted in Walter Laqueur (ed.) The Israel-Arab Reader: A Documentary History of the Middle East Conflict,(1969) rev.ed. Pelican, 1970 pp. 179–188 p.183.
- ^ a b Morris, Benny (2004). The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-679-42120-3.
- ^ '1942–1951', Jewish Agency for Israel.
- During the first four years of statehood, the country had to struggle for its existence, while simultaneously absorbing over 700,000 immigrants. - ^ Aliyeh to Israel: Immigration under Conditions of Adversity[dead link] – Shoshana Neumann, Bar-Ilan University, page 10. Asia: Yemen – 45,127 (6.7), Turkey – 34,647 (5), Iraq – 124,225 (18), Iran – 25,971 (3.8), Syria and Lebanon – 3,162 (0.5), Eden – 3,320 (0.5); Africa: Morocco, Tunisia and Algeria – 52,565 (7.7), Libya – 32,130 (4.6) (Keren-Hayesod, 1953). Note: The numbers add up to 286,500 (without Turkey, see also: History of the Jews in Turkey).
- ^ Sachar, Howard M. (1976). A History of Israel: From the Rise of Zionism to Our Time. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. p. 455. ISBN 0-394-48564-5
- ^ "Background Note: Israel". US State Department. Archived from the original on March 13, 2007. Retrieved March 4, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "1956: Egypt Seizes Suez Canal". British Broadcasting Service. July 26, 1956. Archived from the original on March 17, 2007. Retrieved March 4, 2007.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "UN GA Resolution 997". Mideast Web. Archived from the original on February 7, 2007. Retrieved March 4, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Israel – MSN Encarta. Archived from the original on October 31, 2009.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "First United Nations Emergency Force (Unef I) – Background (Full Text)". United Nations.
- ^ "The Disaster of 1967". Retrieved 12 January 2013.
- ^ "UN: Middle East – UNEF I, Background". United Nations. Archived from the original on March 27, 2007. Retrieved March 4, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Lorch, Netanel (September 2, 2003). "The Arab-Israeli Wars". Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on March 9, 2007. Retrieved March 4, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ 'Egypt Closes Gulf Of Aqaba To Israel Ships: Defiant move by Nasser raises Middle East tension', The Times, Tuesday, May 23, 1967; pg. 1; Issue 56948; col A.
- ^ a b "The Disaster of 1967". The Jordanian Government. Archived from the original on February 19, 2007. Retrieved March 4, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Morris, Benny (2001). Righteous victims : a history of the Zionist-Arab conflict, 1881–2001 (1st Vintage Books ed.). New York: Vintage Books. pp. 316–318. ISBN 0-679-74475-4.
- ^ "President Mubarak Interview with Israeli TV". Egyptian State Information Service. February 15, 2006. Retrieved March 4, 2007.[dead link]
- ^ "Israel: The War of Attrition". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on February 22, 2007. Retrieved March 3, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ US Department of State. "1973 MILESTONES: 1969–1976", October 31, 2013. Retrieved on July 2, 2014.
- ^ a b "Israel: The Yom Kippur War". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved March 3, 2007.
- ^ a b Arab-Israeli War of 1973. Encarta Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on October 31, 2009. Retrieved March 4, 2007.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) Cite error: The named reference "Encarta: Arab-Israeli War of 1973" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ Smith, Charles D. (2006) Palestine and the Arab-Israeli Conflict, New York: Bedford, p. 329.
- ^ Shlaim. Avi. Lion of Jordan; The life of King Hussein in War in Peace, 2007, pg.301.
- ^ Massad, Joseph Andoni. "Colonial Effects: The Making of National Identity in Jordan", pg. 342.
- ^ "Uprising by Palestinians against Israeli rule in the West Bank and Gaza Strip territories", Intifada, Microsoft Encarta.
- ^ Harel, Amos; Avi Isacharoff (2004). The Seventh War. Tel-Aviv: Yedioth Aharonoth Books and Chemed Books and it had a very big conflict. pp. 274–275. ISBN 978-965-511-767-7.
- ^ "PA security forces seize 17 bombs, transfer them to IDF". The Jerusalem Post.
- ^ Press, Associated (June 16, 2010). "UN: Israel has dismantled 20 percent of West Bank checkpoint". The Jerusalem Post.
- ^ Katz, Yaakov. "Israel sets up trial program to expedite PA export process". The Jerusalem Post.
- ^ "Special Update: Disengagement – August 2005", Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
- ^ Ma'ariv II December 2002
- ^ Shindler, Colin. A History of Modern Israel, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2008, pg. 314
- ^ a b c d "Profile: Rachel; Corrie:". BBC News. August 28, 2012. Cite error: The named reference "BBCProfile" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "Rachel Corrie's death: 'it's a no brainer that this was gross negligence'".
- ^ Ravid, Barak (2011-10-12). "Gilad Shalit to be returned to Israel within a week – Israel News | Haaretz Daily Newspaper". Haaretz. Retrieved 2013-01-19.
- ^ "Who are the deadly terrorists Israel refuses to release for Shalit?"
- ^ Ravid, Barak (2009-03-18). "Israel to publish Hamas prisoner list". Haaretz. Retrieved 2013-01-19.
- ^ Israel (country), Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia., 2007, p. 12. Archived 2009-10-31.
- ^ "Lebanon truce holds despite clashes", CNN
- ^ Lessons of the 2006 Israeli-Hezbollah War, By Anthony H. Cordesman, William D. Sullivan, CSIS, 2007, page 16
- ^ "Lebanon Sees More Than 1,000 War Deaths". AP via Usti.net. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ^ guardian.co.uk (September 14, 2006). "Amnesty report accuses Hizbullah of war crimes". Retrieved July 16, 2008.
- ^ Reuters via The Epoch Times (August 6, 2006). "No Let Up in Lebanon War". Retrieved July 16, 2008.
- ^ Associated Press via CHINAdaily (July 30, 2006). "Rice postpones trip to Beirut". Retrieved July 16, 2008.
- ^ Sarah Martin and Kristele Younes, Refugees International (August 28, 2006). "Lebanon: Refugees International's Statement for Donors' Conference"[dead link]. Retrieved July 16, 2008.
- ^ Human Rights Watch (August 2006). "Fatal Strikes: Israel's Indiscriminate Attacks Against Civilians in Lebanon". Retrieved 2007-04-05.
- ^ Lebanon Higher Relief Council (2007). "Lebanon Under Siege"[dead link]. Retrieved March 5, 2007.
- ^ Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs (July 12, 2006). "Hizbullah attacks northern Israel and Israel's response". Retrieved March 5, 2007.
- ^ "Middle East crisis: Facts and Figures". BBC News. August 31, 2006. Archived from the original on July 19, 2008. Retrieved July 13, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Israel says it will relinquish positions to Lebanese army". USA Today. August 15, 2006.
- ^ "'Million bomblets' in S Lebanon". BBC News. September 26, 2006. Retrieved July 13, 2008.
- ^ "Statement by the Press Secretary". The White House. April 24, 2008.[dead link]
- ^ Walker, Peter; News Agencies (May 21, 2008). "Olmert confirms peace talks with Syria". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2008.
Israel and Syria are holding indirect peace talks, with Turkey acting as a mediator...
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Sengupta, Kim (August 27, 2008). "Rice calls for Israel to stop building in West Bank". The Independent. London. Retrieved April 7, 2010.
- ^ "TIMELINE – Israeli-Hamas violence since truce ended". Reuters. January 5, 2009.
- ^ "Hamas 'might renew' truce in Gaza". BBC. December 23, 2008. Retrieved January 1, 2010.
- ^ "Israel Rejected Hamas Ceasefire Offer In December". Huffington Post. January 9, 2009.
- ^ Anthony H. Cordesman, 'THE "GAZA WAR": A Strategic Analysis,' Center for Strategic & International Studies, February 2009 p.9
- ^ "'Israeli Airstrike on Gaza Threatens Truce with Hamas,' Fox News, November 4, 2008". Fox News Channel. November 4, 2008.
- ^ Derfner, Larry (December 30, 2008). "Larry Derfner (US News): Why the Gaza War Between Israel and Hamas Broke Out Now". U.S. News & World Report.
- ^ "Demands grow for Gaza war crimes investigation" UK Guardian, Jan 13, 2009.
- ^ Rozen, Laura (November 25, 2009). "Clinton praises Netanyahu West Bank settlement moratorium (UPDATED) – Laura Rozen". Politico.Com. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ "Palestinians blast Clinton for Israel praise". CNN. November 1, 2009.
- ^ Black, Ian; Haroon Siddique (May 31, 2010). "Q&A: The Gaza Freedom flotilla". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on June 3, 2010. Retrieved June 2, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Flotilla activists 'shot 30 times'". Al Jazeera. June 5, 2010. Archived from the original on June 5, 2010. Retrieved June 6, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Edmund Sanders (June 1, 2010). "Israel criticized over raid on Gaza flotilla". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on June 2, 2010. Retrieved June 2, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ivan Watson; Talia Kayali (June 4, 2010). "Autopsies reveal 9 men on Gaza aid boat shot, 5 in head". CNN World. Archived from the original on June 4, 2010. Retrieved June 4, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Israeli assault on Gaza-bound flotilla leaves at least 9 dead". CNN. May 31, 2010. Archived from the original on June 3, 2010. Retrieved June 2, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Yaakov Katz (June 4, 2010). "We had no choice". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on June 7, 2010. Retrieved July 6, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Yaakov Katz (June 1, 2010). "Vicious conflict aboard 'Mavi Marmara'". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on June 3, 2010. Retrieved July 6, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Hamas targets Israeli-Palestinian talks by killing four Israelis". The Christian Science Monitor.
- ^ Blomfield, Adrian (August 2, 2010). "Jordanian national killed in multiple militant rocket strike". The Daily Telegraph. London.
- ^ "IDF Spokesperson". Idf.il. Retrieved 2013-01-19.
- ^ Henderson, Barney (14 November 2012). "Hamas military chief killed in Gaza air strike". The Daily Telegraph. UK.
- ^ "Full text: Terms of Israel-Palestinian cease-fire". The Washington Post. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^ [1][dead link][348] The UN has given a figure of 103 dead civilians.
- ^ "Israeli strikes kill 23 in bloodiest day for Gaza". The News International. 2012-11-19. Retrieved 2013-01-19.
- ^ "After eight days of fighting, ceasefire is put to the test". The Times of Israel. 21 November 2012. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^ "Gaza-Israel war rages amid international protests – video". The Guardian. London. November 21, 2012. Retrieved 2013-01-19.
- ^ a b "Global anti-Israel protests staged as fears of Gaza ground invasion escalate". RT. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ^ Lazaroff, Tovah (16 November 2012). "Ashton, Merkel say Israel has right to defend itself". The Jerusalem Post.
- ^ "Gaza Rocket Attacks" (Press release). US: Department of State. 14 November 2012. Retrieved 14 November 2012.
- ^ "Foreign Secretary statement on Gaza and southern Israel". UK: Foreign & Commonwealth Office. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
- ^ al-Mughrabi, Nidal (14 November 2012). "UPDATE 8-Rockets hits near Tel Aviv as Gaza death toll rises". Reuters. Retrieved 18 November 2012.
- ^ Hall, Bianca (16 November 2012). "Gillard condemns attacks on Israel" (Press release). Australia. Retrieved 16 November 2012.
- ^ "Les ministres européens mettent en garde Israël quant à l'escalade de la violence à Gaza" (in French). EurActiv. 16 November 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Foreign minister Nikolay Mladenov commenting on the situation in southern Israel and the Gaza Strip". Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Bulgaria). 15 November 2012. Retrieved 16 November 2012.
- ^ "Canada Condemns Hamas and Stands with Israel" (Press release). Canada: Foreign Affairs and International Trade. 14 November 2012. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
- ^ Statement of MFA on Israel and the Gaza Strip[dead link], Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic 15 November 2012
- ^ Timmermans condemns rocket attacks on Israel from Gaza, Government of the Netherlands 13 November 2012
- ^ "Russia condemns 'disproportionate' strikes on Gaza". The Daily Star. Lebanon. 15 November 2012. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
- ^ "Israel and Hamas Trade Attacks as Tension Rises". The New York Times. 8 July 2014.
- ^ "''Cost of Conflict in the Middle East'', Strategic Foresight Group" (PDF).[dead link]
Further reading
- Associated Press, comp. (1996). Lightning Out of Israel: [The Six-Day War in the Middle East]: The Arab-Israeli Conflict. Commemorative Ed. Western Printing and Lithographing Company for the Associated Press. ASIN B000BGT89M.
- Bard, Mitchell (1999). Middle East Conflict. Indianapolis: Alpha Books. ISBN 0-02-863261-3.
- Barzilai, Gad (1996). Wars, Internal Conflicts and Political Order: A Jewish Democracy in the Middle East. Albany: State University of New York Press. ISBN 0-7914-2944-X
- Brown, Wesley H. & Peter F. Penner (ed.): Christian Perspectives on the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict. Neufeld Verlag, Schwarzenfeld 2008. ISBN 978-3-937896-57-1.
- Carter, Jimmy (2006). Palestine: Peace Not Apartheid. New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN 0-7432-8502-6.
- Casper, Lionel L. (2003). Rape of Palestine and the Struggle for Jerusalem. New York & Jerusalem: Gefen Publishing House. ISBN 965-229-297-4.
- Citron, Sabina (2006). The Indictment: The Arab-Israeli Conflict in Historical Perspective. New York & Jerusalem: Gefen Publishing House. ISBN 965-229-373-3.
- Cramer, Richard Ben (2004). How Israel Lost: The Four Questions. New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN 0-7432-5028-1.
- Dershowitz, Alan (2004). The Case for Israel. New York: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-67952-6.
- Falk, Avner (2004). Fratricide in the Holy Land: A Psychoanalytic View of the Arab-Israeli Conflict. Madison: U of Wisconsin P. ISBN 0-299-20250-X
- Gelvin, James L. (2005). The Israel-Palestine Conflict: 100 Years of War. New York & Cambridge, Eng.: Cambridge UP. ISBN 0-521-61804-5.
- Gold, Dore (2004). Tower of Babble: How the United Nations Has Fueled Global Chaos. New York: Crown Forum. ISBN 1-4000-5475-3.
- Finkelstein, Norman G. (2003). Image and Reality of the Israel-Palestine Conflict. Verso Books. ISBN 1-85984-442-1.
- Golani, Motti (2005). From Civil War to Interstate War and Back again. The War over Israel/Palestine, 1945–2000, in: Zeithistorische Forschungen/Studies in Contemporary History 2 (2005), pp. 54–70.
- Goldenberg, Doron (2003). State of Siege. Gefen Publishing House. ISBN 965-229-310-5.
- Gopin, Marc. (2002). Holy War, Holy Peace: How Religion Can Bring Peace to the Middle East. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-514650-6.
- Hamidullah, Muhammad (January 1986). "Relations of Muslims with non-Muslims". Journal of Muslim Minority Affairs. 7 (1): 9. doi:10.1080/13602008608715960.
- Howell, Mark (2007). What Did We Do to Deserve This? Palestinian Life under Occupation in the West Bank, Garnet Publishing. ISBN 1-85964-195-4
- Israeli, Raphael (2002). Dangers of a Palestinian State. New York & Jerusalem: Gefen Publishing House. ISBN 965-229-303-2.
- Katz, Shmuel (1973). Battleground: Fact and Fantasy in Palestine. Shapolsky Pub. ISBN 0-933503-03-2.
- Khouri, Fred J. (1985). The Arab-Israeli Dilemma (3rd ed.). Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press. ISBN 0-8156-2339-9.
- Lewis, Bernard (1984). The Jews of Islam. Princeton, NJ: Princeton UP. ISBN 0-691-05419-3.
- Lesch, David (2007). The Arab-Israeli Conflict A History. Oxford University Press, USA. ISBN 0-19-517230-2.
- –––. (September 1990). "The Roots of Muslim Rage." The Atlantic Monthly.
- Maoz, Zeev (2006). Defending the Holy Land. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan. ISBN 0-472-11540-5
- Morris, Benny (1999). Righteous Victims: A History of the Zionist-Arab Conflict, 1881–2001. New York: Knopf. ISBN 0-521-00967-7.
- Morris, Benny (2004). The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-679-42120-3.
- Morris, Benny (2009). 1948: A History of the First Arab-Israeli War, Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-15112-1
- Reiter, Yitzhak (2009). National Minority, Regional Majority: Palestinian Arabs Versus Jews in Israel (Syracuse Studies on Peace and Conflict Resolution), Syracuse University Press (Sd). ISBN 978-0-8156-3230-6
- Rogan, Eugene L., ed., and Avi Shlaim, ed. (2001). The War for Palestine: Rewriting the History of 1948. Cambridge: Cambridge UP. ISBN 978-0-521-79476-3.
- Segev, Tom (1999). One Palestine Complete: Jews and Arabs Under British Mandate. New York: Henry Holt & Co. ISBN 0-8050-6587-3.
External links
Government and official sources
- Israel's Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- League of Arab States
- Palestinian Authority Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- United Nations on the Question of Palestine
- Arab-Israeli Conflict from UCB Libraries GovPubs
Regional media
- Israeli
- Israel News – Yedioth Aharonoth Israel's largest newspaper, centrist (Hebrew)
- Jerusalem Post, Israel's oldest English newspaper, conservative
- Ha'aretz Israeli newspaper, liberal
- Jerusalem Newswire Christian-run Jerusalem-based news website, conservative
- Arab
- Lebanon Daily Star, largest English-circulation newspaper in the Arab world
- Al Ahram, Egypt's largest newspaper (see also Al Ahram)
- Palestine Chronicle, weekly electronic paper
Think tanks and strategic analysis
- Dean Peter Krogh Examines Prospects for Peace from the Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
- NGO Monitor, NGO watchdog group, highlighting perceived instances of anti-Israeli NGO bias
- Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs
- Palestinian Academic Society for the Study of International Affairs (PASSIA), Palestinian research organization
- Israel/Palestine Center for Research and Information Joint Israeli-Palestinian think tank
- Middle East Research and Information Project (see also Middle East Research and Information Project)
- Saban Center for Middle East Policy (see also Saban Center for Middle East Policy)
- Washington Institute for Near East Policy (see also Washington Institute for Near East Policy)
- Original analysis of current developments in the peace-process, from Middle East Media Research Institute
- The Ariel Center for Policy Research
- A Regional Perspective on the Arab-Israeli Conflict by Jay Shapiro
- Jerusalem Institute for Israel Studies
Peace proposals
Maps
- MideastWeb Middle East Map Collection
- FactsOfIsrael.com Maps, history, statistics, victims
- University of Texas Map Collection
General sources
- Crisis Guide: The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict from the Council on Foreign Relations
- The State of Israel The Jewish History Resource Center, Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
- Daily digest of commentary about the Arab-Israeli conflict from around the world
- Israel and the Palestinians
- Encarta Encyclopedia on the Arab-Israeli Conflict (Archived 2009-10-31)
- Guide to the Arab-Israeli Conflict, includes links to historical sources, as well as sources representing the Arab and Israeli sides of the conflict.
- The Guardian (UK) A Brief History of Arab-Israeli Conflict (flash)
- Template:Dmoz
- Diplomacy Monitor – Middle East[dead link]
- Information (articles, reports, maps, books, links, ...) on the israeli palestinian conflict (middle east conflict)
- Holy Land, Unholy War Independent coverage of the Middle East conflicts by the news agency Inter Press Service
- "A Brief History of the Arab-Israeli Conflict" by Jeremy Pressman
