Flag of Peru
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2013) |
 | |
| Other names | El Pendón Bicolor (The Bicolor Banner), La Enseña Nacional (The National Ensign) |
|---|---|
| Use | Civil flag and ensign |
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | February 25, 1824 (current triband version). |
| Design | A vertical bicolour triband of red, white and red |
| National flag of Peru. (Pabellón nacional) | |
 | |
| Use | State flag, state and naval ensign |
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Design | A vertical bicolour triband of red, white and red; charged with the Coat of arms in the center. |
| War flag of Peru (Bandera de guerra) | |
 | |
| Use | War flag |
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Design | A vertical bicolour triband of red, white and red; charged with the National Coat of Arms in the center. |
| Naval jack of Peru (Bara de proa) | |
 | |
| Proportion | 1:1 |
| Design | A white square with the Coat of arms on a red field. |
The flag of Peru was adopted by the government of Peru in 1824. It is a vertical triband with red outer bands and a single white middle band. Depending on its use, it may be defaced with different emblems, and has different names. Flag day in Peru is celebrated on June 7, the anniversary of the Battle of Arica.
Design and symbolism
Coat of arms
The Peruvian coat of arms includes the vicuña (a relative of the llama and alpaca), the quina (cinchona) tree, and a cornucopia of gold.
Meaning of the colors
Red represents the blood that was spilled for the fight for independence, and white represents peace and bravery.
Variants
National flag (civil flag)
The national or civil flag (Template:Lang-es) is used by citizens. It has no additions to the common form. It was changed several times; before 1950 it looked like the current national flag and was used as both the civil and state flag, when General Manuel A. Odría removed the coat of arms from the national flag and created the state and war flags.
National ensign (state flag)
The national ensign or state flag (pabellón nacional), used by state institutions, is marked with the coat of arms of Peru (escudo de armas). It is used during ceremonies in which the flag is hoisted in the presence of spectators (as opposed to a static, permanent flag). A form of this flag, the national standard (estandarte nacional) is used indoors by official and private institutions.
War flag
The war flag (Bandera de Guerra), similar to the state flag, is marked with the national shield (Escudo Nacional). It is flown by the Peruvian military and national police, and is typically inscribed with the service, name and number of the unit flying it.
Naval jack
The naval jack (bandera de proa) is not based on the triband; it is a square flag, consisting of a white square with the coat of arms (Escudo de Armas) on a red field. It is used on battleships, usually with the ensign of the highest-rank officer on board above it.
History
Proposed flag of 1820

 Flag hoisted by Admiral Miller in October 1820.
Flag hoisted by Admiral Miller in October 1820.During the Viceroyalty of Peru, the colonial-era Spanish flag flew over Peru. In 1820, during the struggle for independence, British-born General William Miller hoisted in Tacna the first flag that represented the emerging country. Though the original flag itself is now lost, it was described as navy blue, defaced with a golden sun (possibly representing Inti).
Flag of 1820

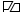 First republican flag, created by General José de San Martín.
First republican flag, created by General José de San Martín.The first flag of the Republic of Peru was created by General José de San Martín, and officially decreed on 21 October 1820. It is diagonally quartered, with white upper and lower fields, and the others red. The flag was defaced with an oval-shaped laurel crown in the center, surrounding a sun rising behind mountains by the sea. The symbolism of the flag's colors is uncertain, but according to Peruvian author Abraham Valdelomar, San Martín, having arrived on the coast of southern Pisco, was inspired by the colors of parihuanas, red-and-white flamingos. Historians of the early Peruvian Republic, such as Leguía y Martínez and Pareja Paz Soldán,[1] give a different explanation, suggesting that San Martín took the red from the flag of Chile and the white from the flag of Argentina, recognizing the provenance of the men of the liberation army. Historian Jorge Fernández Stoll thinks in 1820 San Martin was in favor of a constitutional monarchy, and he chose to use monarchical symbols and colors: Castile used the red and white colors for many years, the old flag of the viceroyalty the cross of Burgundy was red and white and the flag's diagonal lines mimicked the cross shape, the red color was the royal symbol of the mascaipacha of Inca kings and of the ensign of the King of Spain at that time.[2] The flag proved difficult to adopt due to its complex construction; without standardized measurements in place at the time, a triangular flag proved difficult to build.
Flag of March 1822

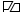 Second design, by Torre Tagle.
Second design, by Torre Tagle.In March 1822, José Bernardo de Tagle, Marquis of Torre Tagle and Supreme Delegate of the Republic, who replaced San Martín provisionally when the latter traveled to Guayaquil, decreed a new design for the flag. This consisted of a horizontal triband, with a white band between two red ones, and a golden sun at the center, similar to the flag of Argentina. This modification was justified, according to Torre Tagle, by the inconvenience in the construction of the previous version, among other issues.
A problem came up on the battlefields: the resemblance with the Spanish flag, especially from far away, made the distinction between the armies difficult, which led to a new change to the flag.
Flag of May 1822

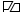 Third design.
Third design.On 31 May 1822, Torre Tagle changed the flag's design again. The new version was a vertical triband, with red outer bands and a white middle band, with a golden sun representing Inti at the center.
Flag of 1825

 Fourth flag, created in 1825.
Fourth flag, created in 1825.This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2013) |
On February 25, 1825, during Simón Bolívar's administration, the Constituent Congress changed Cortés.[clarification needed]
Flags of the Peru-Bolivian Confederation era, 1836-1839

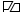 Flag of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, 1836-9.
Flag of the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, 1836-9.
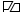 Flag of the Republic of South Peru, 1836-9.
Flag of the Republic of South Peru, 1836-9.From 1836 to 1839, Peru was temporarily dissolved into the Republics of South Peru and North Peru, which joined Bolivia to form the Peru–Bolivian Confederation.
The South was formed first, thus adopting a new flag: a red vertical band on the left, with a golden sun and four small stars above (representing Arequipa, Ayacucho, Cuzco and Puno, the four groups of the republic), and the right side divided into an upper green band and a lower white one. The North kept the currency and all ---- of the dissolved Peru, including its flag.
The flag of the Peru-Bolivian Confederation showed the coats of arms of Bolivia, South and North Peru, from left to right and slanted at different angles, on a red field, adorned by a laurel crown.
After the dissolution of the Confederation, the old Republic of Peru was restored to its 1836 composition, as were its national symbols.
Flag of 1950
In 1950, General Odría modified the national flag to its current form, removing the coat of arms from the civil flag, since it was used de facto, being easier to make. The national ensign and war flag were created for exclusive uses, each with a variant of the coat of arms, which was also changed slightly. These remain as the official flags today.
Similar flags
-
Flag of Peru
-
Flag of Saint Tropez, France
-
Flag of Canada
The Marcha de Banderas
The Marcha de Banderas (Spanish: March of Flags) is a military march sung during the flag raising. It was created in 1897 by SM Jose Salas Libornio who said President Nicolás de Piérola, he disagreed with the indiscriminate interpretation of the National Anthem at all official events that were derived from civic events. In December of that year was officially recognized to be executed in any official act.
|
Arriba, arriba, arriba el Perú |
Long live, long live, long live Peru |
In all occasions today only 3 out of 4 verses of this flag anthem are sung instead.
See also
References
- ^ Mariano Felipe Paz Soldán (1868). Historia del Perú independiente. pp. 75–. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- ^ Jorge Fernández Stoll. "Los orígenes de la bandera", Lima, Sociedad Bolivariana de Lima, 1953




