SAP HANA
 | |
| Developer(s) | SAP SE |
|---|---|
| Stable release | SPS12 Revision 120[1]
/ May 11, 2016 |
| Written in | C, C++ |
| Available in | Multi-lingual |
| Type | In-memory RDBMS |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | SAP HANA DB |
SAP HANA is an in-memory, column-oriented, relational database management system developed and marketed by SAP SE.[2][3] SAP HANA was previously called "SAP High-Performance Analytic Appliance".[4]
History
To create SAP HANA, SAP SE developed or acquired technologies, including TREX search engine (in-memory column-oriented search engine), P*TIME (in-memory OLTP Platform acquired by SAP in 2005), and MaxDB with its in-memory liveCache engine.[5][6] In 2008, teams from SAP SE, working with Hasso Plattner Institute and Stanford University, demonstrated an application architecture for real-time analytics and aggregation, mentioned as "Hasso's New Architecture" in former SAP executive Vishal Sikka's blog. Before the name "HANA" stabilised, people referred to this product as "New Database".[7]
The first product shipped in late November 2010.[6][8] By mid-2011, the technology had attracted interest but the experienced business customers still considered it "in early days".[9] HANA support for SAP NetWeaver Business Warehouse was announced in September 2011 for availability by November.[10]
In 2012, SAP promoted aspects of cloud computing.[11] In October 2012, SAP announced a variant called HANA One that used a smaller amount of memory. It is available on IBM Cloud[12] and on Amazon Web Services for a monthly and an hourly fee respectively.[13]
In January 2013, SAP enterprise resource planning software from its Business Suite was announced for HANA, and became available by May.[14][15] In May 2013, a software as a service offering called the HANA Enterprise Cloud service was announced.[16]
In May 2014 SAP and VMWare announced SAP HANA for production use on VMware vSphere 5.5 [17]
Rather than versioning, the software utilizes service packs.[18]
Architecture
The main process, called the index server, has a structure shown in the diagram to the right.[19]
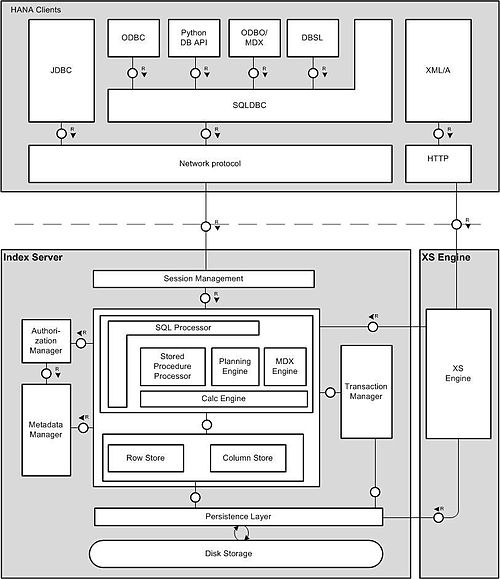
The indexer performs session management, authorization, transaction management and command processing. Note that HANA has both a row store and a column store. Users can create tables using either store, but the column store has more capabilities. The index server also manages persistence between cached memory images of database objects, log files and permanent storage files.
Features
Major Features as available in HANA SPS12:
- Triggers
- Cursors
- Query caching
- Sub-SELECTs (i.e. nested SELECTs)
- Full-text indexing and searching
- Unicode support
- Shared-nothing clustering (Scale-Out)
- ACID compliance[20][21]
- MVCC support[22]
- Multitenancy[23][24]
- Built in application server with Java, JavaScript, Node.JS, C++ runtime support and works with Git/GitHub and Maven.[25] Applications can use SQL, JDBC, ODBC, ADO.NET, ODATA XML/A and MDX to access data.[26]
- Text analytics: Supports text analysis, mining, natural language processing capabilities such as linguistic analysis, stemming, tokenization, tagging, entity extract and sentiment analysis from unstructured data from 32 languages[27][28]
- Predictive analytics[29]
- Spatial processing[30]
- Graph[31]
- Data Streaming[31]
- Time Series Data Processing[32]
- Text Search
Supported platforms
- Linux on x86-64 (Red Hat Enterprise Linux, and SUSE distributions are supported[33])
- Linux on POWER Systems[34]
Deployment
SAP HANA can be deployed on-premises as an appliance from a certified hardware vendor or on certified hardware with tailored data center integration (TDI). HANA is also available in the cloud as a Database as a Service on Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or the SAP HANA Cloud Platform.
References
- ^ Support Package Stack 12 (Last Update: May 11, 2016, Revision 120)
- ^ Jeff Kelly (July 12, 2013). "Primer on SAP HANA". Wikibon. Retrieved October 9, 2013.
- ^ SAP HANA - The Column Oriented (Based) Database on YouTube (December 8, 2012)
- ^ http://www.computerworld.com/article/2514617/business-intelligence/sap-s-hana-will-speed-real-time-data-analytics.html
- ^ Vey, Gereon; Krutov, Ilya (January 2012). "SAP In-Memory Computing on IBM eX5 Systems" (PDF). Retrieved 22 October 2013.
- ^ a b SAP SE (June 17, 2012). "SAP HANA Timeline". SlideShare. Retrieved October 9, 2013.
- ^ "What is SAP HANA Database". Gucons web site. 2011. Retrieved October 9, 2013.
- ^ Chris Kanaracus (December 1, 2010). "SAP launches HANA for in-memory analytics: The in-memory analytic appliance will compete with next-generation data-processing platforms such as Oracle's Exadata machines". Info World. Retrieved September 24, 2013.
- ^ Chris Kanaracus (September 15, 2011). "SAP's HANA is hot, but still in early days". Network World. Retrieved October 15, 2013.
- ^ Courtney Bjorlin (November 9, 2011). "SAP Begins BW on HANA Ramp-Up, First Big Test for the HANA Database". ASUG News. Retrieved October 15, 2013.
- ^ Trevis Team (April 30, 2012). "SAP Headed For $71 On Cloud, Mobile And HANA Growth". Forbes. Retrieved October 9, 2013.
- ^ IBM Cloud AMM for SAP HANA One
- ^ Doug Henschen (October 17, 2012). "SAP Launches Cloud Platform Built On Hana". Information Week. Archived from the original on October 19, 2012. Retrieved October 15, 2013.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Brian McKenna (January 11, 2013). "SAP puts Business Suite on HANA, joins transactional to analytical". Computer Weekly. Retrieved October 15, 2013.
- ^ "Sapphire 2013: Business Suite on HANA goes to general availability". Computer Weekly. May 15, 2013. Retrieved October 15, 2013.
- ^ Chris Kanaracus (May 7, 2013). "SAP unveils HANA Enterprise Cloud service: Customers will be able to run their applications on the HANA-powered cloud". Network World. Retrieved October 15, 2013.
- ^ http://www.vmware.com/company/news/releases/vmw-newsfeed/SAP-and-VMware-Announce-SAP-HANA%C2%AE-for-Production-Use-on-VMware-vSphere-5.5/1837460#sthash.SJsM5ITw.dpuf
- ^ John Appleby (May 28, 2012). "Update III: The SAP HANA FAQ - answering key SAP In-Memory questions". Bluefin Solutions. Retrieved October 9, 2013.
- ^ http://www.saphana.com/community/blogs/blog/2012/12
- ^ "What is HANA (SAP HANA)? - Definition from WhatIs.com". SearchSAP. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ "SAP HANA System Properties". db-engines.com. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ "SAP HANA Course" (PDF).
- ^ "SAP Unleashes Major Hana Upgrade - InformationWeek". InformationWeek. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ Dignan, Larry. "SAP outlines HANA updates | ZDNet". ZDNet. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ SE, SAP. "Customers Choose SAP HANA® to Run Their Business". www.prnewswire.com. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ "SAP HANA and the MDX Query Language - Simba Technologies". Simba Technologies. 2014-02-17. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ "SAP Releases Sentiment Analysis Solution". CRM Magazine. 2012-08-02. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ Miller, Ron. "NBA Bolsters Partnership With SAP To Bring Natural Language Queries To Stats Site". TechCrunch. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ Groenhof, Dick. "Predictive Analytics on SAP HANA". www.thenextview.nl. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ "SAP Accelerates Geo-Enabled Access to Enterprise Data : Geospatial Solutions". geospatial-solutions.com. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ a b "SAP Unleashes Major Hana Upgrade - InformationWeek". InformationWeek. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ "SAP HANA in-memory DBMS overview". SearchDataManagement. Retrieved 2016-05-26.
- ^ "SAP HANA Hardware and Software Requirements".
- ^ "SAP HANA on Power with SUSE Linux Enterprise Server for SAP Applications".
