Kuwait
State of Kuwait دولة الكويت Dawlat al Kuwayt | |
|---|---|
| Motto: For Kuwait | |
| Anthem: Al-Nasheed Al-Watani | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Kuwait City |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Government | nominal constitutional monarchy |
• Emir | Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah |
| Nawaf Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah | |
| Nasser Al-Mohammed Al-Ahmed Al-Sabah | |
| Independence | |
• From the UK | June 19, 1961 |
• Water (%) | Negligible |
| Population | |
• 2005 estimate | 2,687,0001 (137th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate |
• Total | $53.31 billion (77th) |
• Per capita | $22,800 (29th) |
| HDI (2003) | 0.844 very high (44th) |
| Currency | Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 |
| Calling code | 965 |
| ISO 3166 code | KW |
| Internet TLD | .kw |
1Figure includes 1.999 million non-nationals (End of 2005 est.) | |
The State of Kuwait (Template:Lang-ar) is a small oil-rich constitutional monarchy on the coast of the Persian Gulf, enclosed by Saudi Arabia in the south and Iraq in the north. The name is a diminutive of an Arabic word meaning "fortress built near water."
History
Kuwait was established in the 16th century when several clans (bedouins) from the "Al Aniza" tribe migrated to the northern shore of the Persian Gulf from the Najd, their famine-stricken homeland in central Arabia. They settled in what now is known as Qatar for more than 60 years before migrating over sea to settle in the Isle De Chader, where they built a small fort, or “kut”. The current rulers of the country are descended from Sabah I, who was chosen by the community, which was composed mainly of traders. They were tasked with administering the affairs of the State, including foreign affairs and taxation/duties. This is unlike most other Arab emirates of the Persian Gulf, where the rulers seized and maintained authority by force.
The 17th century saw the Arabian Peninsula experience some tumultuous times. The area that is now Kuwait was occupied by tribes and used for spice trading from India. By the 18th century, most of the local people made a living selling pearls. But as pearl farming developed in Japan during the 1930s, Kuwait became impoverished. In 1899, growing British influence led to Kuwait becoming a British protectorate. Oil transformed Kuwait into one of the richest countries in the Arab peninsula; in 1953 the country became the largest exporter of oil in the Persian Gulf. This massive growth attracted many immigrant laborers who were rarely granted citizenship. Kuwait, having amassed great wealth, was the first of the Persian Gulf-Arab states to declare independence, on June 19, 1961. Iraq challenged this declaration, claiming Kuwait was part of its territory. It threatened to invade Kuwait but was deterred by the British, who flew in troops.
An important period in Kuwait's political, social and economic development was the Souk Al-Manakh stock market crash of 1982. This was a major crash that had widespread consequences and has endured in the public memory even decades later.

After being allied with Iraq during the Iran-Iraq War until its end in 1988 (Kuwait paid Iraq to protect it from what it perceived as a threat posed by Iran), Kuwait was invaded and annexed by Iraq (under Saddam Hussein) on August 2, 1990. Hussein's primary justifications included a charge that Kuwaiti territory was in fact an Iraqi province, and that annexation was retaliation for "economic warfare" Kuwait allegedly had waged through slant drilling into oil supplies on Iraqi territories. Hussein deposed the monarchy after the annexation and installed a new Kuwaiti governor.
Authorized by the UN Security Council, an American-led coalition of 34 nations fought the Persian Gulf War to liberate Kuwait. After six weeks of fierce fighting in early 1991, the coalition forced Iraq to withdraw its troops from Kuwait on February 26, 1991; during retreat, the Iraqi Armed Forces exacted a scorched earth policy by setting fire to Kuwaiti oil wells. The fires took more than nine months to fully extinguish, and the cost of repairs to oil infrastructure exceeded $5 billion. Certain buildings and infrastructural facilities (including Kuwait International Airport) also were severely damaged during the war. Kuwait remains under the governance of the Emir, Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jabir Al-Sabah (since 29 January, 2006) as an independent state and is of strategic importance to the United States.
Politics
Kuwait is a constitutional monarchy and has the oldest directly elected parliament of the Persian Gulf Arab countries. Chief of state is the Emir, a hereditary title. The Emir appoints the prime minister, who until recently was also the crown prince. A council of ministers aids the prime minister in his task as head of government which must contain at least one of elected members of the parliament. The number of minister must not exceed ⅓ of the elected members of the parliament.
The parliament has the power to dismiss the prime minister or anyone of his cabinet through a series of constitutional procedures. According to the constitution, nomination of a new crown prince by the ruling family has to be confirmed by the National Assembly. If he does not win the votes of an absolute majority of the assembly, the Emir must submit the names of three candidates to the National Assembly, and the Assembly must select one of these to be the new crown prince. The parliament known as the Majlis Al-Umma (National Assembly), consists of elected 50 members, who are chosen in elections held every four years. Government ministers, according to the Constitution of the State, are given automatic membership in the parliament, and can number up to 15.
Prior to 2005, only 15% of the Kuwaiti citizen population was allowed to vote, with all women, "recently naturalised" citizens (less than 30 years of citizenship), and members of the armed forces excluded. On May 16, 2005, Parliament permitted women's suffrage by a 35-23 vote, subject to Islamic law and effective for the 2006 Parliamentary Election. The decision could raise Kuwait's voter rolls from 139,000 to as many as 339,000 if all eligible women register; the total number of Kuwaitis is estimated at more than 960,000. Recently, the former Prime Minister Sheikh Sabah al-Ahmad al-Sabah announced the appointment of Dr Massouma Mubarak as planning minister and minister of state for administrative development affairs. The appointment of a woman as a cabinet minister was a major breakthrough in Kuwaiti political system and it makes Kuwait the third country in the conservative Persian Gulf Arab monarchies to have a woman cabinet minister.
See also: al-Sabah Ruling Family
See also: Elections in Kuwait
Administrative Divisions
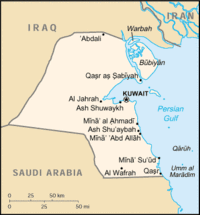
Kuwait is divided into 6 governorates (muhafazat, sing. - muhafadhah). The governorates include:
The major cities are the capital Kuwait, and Jahrah (further in the north-west, 30-minute drive from the capital). The main residential and business areas are Salmiya and Hawalli. The main industrial area is Shuwaikh which resides within the Al Asimah Governorate.
Geography and climate
Kuwait consists mostly of desert, with little altitude difference. Kuwait is the only country in the world with no natural lake or water reservoir. It has nine islands, the largest one being Bubiyan, which is linked to the mainland by a concrete bridge (after the liberation in 1991 the island was converted into a military base and currently no civilians are allowed in). The islands are:

- Auhah Island
- Bubiyan Island
- Failaka Island
- Kubbar Island
- Miskan Island
- Qaruh Island
- Umm al Maradim Island
- Umm an Namil Island
- Warbah Island
Kuwait enjoys a variable continental climate. Summers (April to October) are extremely hot and dry with temperatures reaching above 51 °C (124 °F) in Kuwait City. Winters (November to February) are cool with limited precipitation and temperature level dropping below 21 °C (70 °F). The spring season is cool and pleasant.
Economy
Kuwait is a small, rich, relatively open economy with proven crude oil reserves of 96 billion barrels (15 km³) - 10% of world reserves. Petroleum accounts for nearly half of GDP, 95% of export revenues, and 80% of government income. Kuwait's climate limits agricultural development. Consequently, with the exception of fish, it depends almost wholly on food imports. About 75% of potable water must be distilled or imported. Higher oil prices put the FY99/00 budget into a €1.7 billion ($2 billion) surplus. The FY00/01 budget covers only nine months because of a change in the fiscal year. The budget for FY01/02 envisioned higher expenditures for salaries, construction, and other general categories. Kuwait continues its discussions with foreign oil companies to develop fields in the northern part of the country. By 1990 the country earned more from foreign investment than from oil exports. The expenses of the Iraqi invasion and postwar reconstruction placed a heavy economic burden on the country, but by the mid-1990s Kuwait had resumed its preinvasion prosperity. Gross domestic product (GDP) for 2005 was $53.31 billion, giving Kuwait a per capita GDP of $22,800. The labor force totals 1,670,000 people,only about one fifth of whom are Kuwaiti citizens.
The Central Bank of Kuwait in the capital city issues Kuwait’s currency, the Kuwaiti dinar. The dinar is currently valued at 0.351676 KWD per 1EUR and at 0.292010 KWD per 1USD, making it the highest-valued currency in the world.
Oil Industry
Because the government owns the oil industry, it controls most of the economy—in all, about 75 percent of the GDP. Kuwait’s oil exports vary depending on internal needs (almost all of Kuwait’s energy is derived from oil), international demand and prices, and production quotas fixed by the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), of which Kuwait is a member. OPEC’s quotas, however, are difficult to enforce, and Kuwait and other countries have been accused of violating them. In 2002 oil production was 692 million barrels.
The chief oil companies are -
- Kuwait Petroleum Corporation (KPC) - International Marketing and Mother Company
- Kuwait Oil Company (KOC) - A crude oil exploration and development company
- Kuwait National Petroleum Company (KNPC) - Runs Oil Refineries across Kuwait
- Petrochemicals Industries Company (PIC) - Petrochemical & Fertilizers manufacturer
- Kuwait Petroleum International (KPI - Q8) - Runs refining and marketing business overseas
- Kuwait Foreign Petroleum Exploraton Company (KUFPEC) - Intl. Oil Exploration Company
- Equate (EQUATE) - A Petrochemical company formed by (PIC) and (Dow Chemical)
- Kuwait Oil Tanker Company (KOTC) - Crude Oil Shipping
- Kuwait Aviation Fueling Company (KAFCO) - Aircraft Fueling
- Kuwait Gulf Oil Company (KGOC) -Oil & Gas exploration and production in the divided zone. A shared joint venture with Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Oil Sector Services Company (OSSC) - Handles all construction projects , maintenance , security , fire fighting , and medical services to all oil sector employees and their families.
- Oil Development Company (ODC) -
Demographics
As of the end of 2005, Kuwait had a total population of 2.992 million people which included 1.999 million non-nationals[1]. Kuwaiti citizens are a minority of those who reside in Kuwait. The government only rarely grants citizenship to non-citizens (who are generally referred to as expatriates). About 57% of the Kuwaiti population is Arab; Arab expatriates include a large group of stateless Arabs, locally known as Bidoon (an Arabic word meaning "without" and different from Bedouin), along with Egyptians, Lebanese and other Arabs. Other large groups of expatriates include Pakistanis, Indians, Bangladeshis and Filipinos. In 2003, more than 400,000 Indian nationals lived in Kuwait[2], making them the largest expatriate community in the oil-rich state[3]. Kuwait formerly had a large Palestinian population, though most of them were forced out of the country after PLO leader Yassir Arafat's support of Iraq during the Iraqi occupation of Kuwait.
The official language is Arabic, although English is generally understood. Hindi, Urdu, Punjabi Bengali, Tamil and other Indian languages are largely spoken by expatriates from the Indian subcontinent. About 85% of Kuwait's population are Muslims (45% Sunni and 40% Shia): Kuwait also has much smaller Christian and Hindu populations. About 55% of the overall population is Sunni, while approximately 45% is Shi'i.
Infrastructure

Kuwait's infrastructure took a considerable beating during the 1st Persian Gulf War. Hundreds of oil wells were set on fire and the country's oil production had come to standstill. Much has changed since the end of the Persian Gulf War. The Kuwaiti government has spent billions of dollars to construct an elaborate roadway system and in 2003, the telecommunication industry achieved an incredible growth rate. Kuwait City boasts more than a dozen 5-star hotels and resorts and several skyscrapers dominate the city's skyline. Kuwait Infrastructure Maintenance Management System overlooks the oil-rich country's infrastructure. Kuwait's energy sector is the main source for 47% of the country's annual income.
Kuwait has also planned one of the biggest sea front projects in the world, Madinat al-Hareer . If completed, this project would include the world's tallest tower, and numerous housing, health, education, environmental, business, and touristic centers.
Transportation
Kuwait’s transportation system is modern and efficient, with a road system that is well developed by regional standards. Roads total 4,450 kilometers (2,765 mi), of which 81 % are paved and 350 kilometers (217 mi) are freeways, with most people traveling by automobile. The network consists of over 250 bridges. Many of these bridges, however, are of surprisingly poor quality. There is no railway system in Kuwait although public and private bus systems are operated. An international airport is located in the southern outskirts of the Kuwait city metropolitan area and Kuwait Airways is the national airline owned by the government. There is a new airline company called Jazeera Airways. The country has three modern seaports, one of which specializes in oil exports.
Education
Oil revenues have allowed Kuwait to build an extensive educational system, yielding a literacy rate of 90 percent. Public school is free and compulsory from the age of 6 to 13, and several private schools also teach this age group. Kuwait University is Kuwait's only public university, but it is known as a very prestigious institution in the Middle East. Both the extensive library system at Kuwait University and the collection at Kuwait National Museum (1957) were heavily damaged and looted during the Iraqi occupation in the 1991 Persian Gulf War. Gulf University for Science and Technology is the first private university established in Kuwait. Other private universities are the American University of Kuwait and the Australian College of Kuwait.
Mass media
Kuwait has 10 TV channels (4 controlled by the Ministry of Information), 2 modern English FM stations, mostly targeting the Westerners residing in Kuwait (one playing latest Western pop music and hits, while the other one playing Jazz, Blues and other light music), a few Arabic radio stations, 5 daily newspapers published in Arabic, and 3 daily newspapers published in English (Arab Times & Kuwait Times). The newspapers exercise self-censorship. No newspaper is permitted to criticize the executive authority, however criticizing other members of the ruling family is permitted. All newspapers in Kuwait were established with a "princely decree". For the past 30 years there have been demands to allow the establishment of other newspapers, but with no response from government. Also there is one private radio station (Marina FM) named after the shopping complex of the same name, Marina World.
Culture
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Kuwait
- Foreign relations of Kuwait
- Geography of Kuwait
- Kuwaiti Architecture
- List of Kuwaiti companies
- Military of Kuwait
- Postage stamps and postal history of Kuwait
- Transportation in Kuwait
- Persian Gulf War
- Kuwait Boy Scouts Association
- Madinat al-Hareer
- World's Largest Kite
- Human rights in Kuwait
External links
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, Kuwait - Country Page
- Official site of Kuwait
- BBC News Country Profile - Kuwait
- CIA World Factbook - Kuwait
- Congressional Research Service (CRS) Reports regarding Kuwait
- Kuwait Information Guide
- Kuwait Yellow Pages
- Kuwait Shopping Malls
- Kuwait Web Site Design
- KuWiki wiki page
- Middle East Public Relations Association (MEPRA)
- Open Directory Project - Kuwait directory category
- The Persian Gulf - Kuwait information and history
- US State Department - Kuwait includes Background Notes, Country Study and major reports
- A brief history of the Souk AlManakh, Kuwait's modern depression
- Ministry of information
- The Silk City project - 1001m tall tower as a centerpiece
Template:Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf


