Geography of Slovenia
link title

 Slovenia is situated in Central Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean . The Alps — including the Julian Alps, the Kamnik-Savinja Alps and the Karavanke chain, as well as the Pohorje — dominate Northern Slovenia along its long border to Austria. Slovenia's Adriatic coastline streches approximately 50 kilometers (39 mi.) from Italy to Croatia.
Slovenia is situated in Central Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean . The Alps — including the Julian Alps, the Kamnik-Savinja Alps and the Karavanke chain, as well as the Pohorje — dominate Northern Slovenia along its long border to Austria. Slovenia's Adriatic coastline streches approximately 50 kilometers (39 mi.) from Italy to Croatia.
The term "Karst" originated in Southern Slovenia's Kras Plateau (German Karst Plateau), a limestone region of underground rivers, gorges, and caves, between Ljubljana and Mediterranean.
On the Pannonian plain to the East and Northeast, toward the Croatian and Hungarian borders, the landscape is essentially flat. However, the majority of Slovenian terrain is hilly or mountainous, with around 90% of the surface 200 meters or more above sea level.

Location
Southeastern or Central Europe, Eastern Alps bordering the Adriatic Sea, between Austria and Croatia
Extreme geographical points of Slovenia:
- North: 46°53′N 16°14′E / 46.883°N 16.233°E, municipality Šalovci,
- South: 45°25′N 15°10′E / 45.417°N 15.167°E, municipality Črnomelj,
- East: 46°28′N 16°36′E / 46.467°N 16.600°E, municipality Lendava,
- West: 46°17′N 13°23′E / 46.283°N 13.383°E, municipality Kobarid.
Maximum distance North - South is 1°28' or 163 km (101 miles).
Maximum distance East - West is 3°13' or 248 km (154 miles).
Map references
Area
- Total: 20,273 km²
- Land: 20,273 km²
- Water: 0 km²
- Comparison: slightly smaller than New Jersey
Borders
- Land boundaries
- Coastline: 46.6 km
Regions
Historical Regions
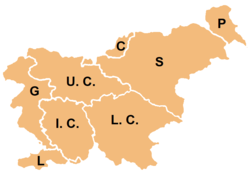
As given by Enciklopedija Slovenije (Encyclopedia of Slovenia), traditional Slovenian regions, based on the former division of Slovenia into four Habsburg crown lands (Carniola, Carinthia, Styria, and the Littoral) and their parts, are:
- Upper Carniola (Gorenjska) (denoted on the map by U.C.)
- Styria (Štajerska) (S)
- Prekmurje (T)
- Carinthia (Koroška) (C)
- Inner Carniola (Notranjska) (I.C.)
- Lower Carniola (Dolenjska) (L.C.)
- Goriška (G)
- Slovenian Istria (Slovenska Istra) (L)
The last two are usually considered together as the Littoral Region (Primorska). White Carniola (Bela krajina), otherwise part of Lower Carniola, is usually considered a separate region, as is Zasavje, which is otherwise a part of Upper and Lower Carniola and Styria.
Climate
Mediterranean climate on the coast, continental climate with mild to hot summers and cold winters in the plateaus and valleys to the east
Terrain
a short coastal strip on the Adriatic, an alpine mountain region adjacent to Italy and Austria, mixed mountain and valleys with numerous rivers to the east
Elevation extremes
- Lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 m
- Highest point: Triglav 2,864 m (9,396 feet)
Natural resources
lignite coal, lead, zinc, mercury, uranium, silver, hydropower
Land use
- Arable land: 12%
- Permanent crops: 3%
- Permanent pastures: 24%
- Forests and woodland: 54%
- Other: 7% (1996 est.)
- Irrigated land: 20 km² (1993 est.)
- Natural hazards: flooding and earthquakes
Environment
Current issues
The Sava River polluted with domestic and industrial waste; pollution of coastal waters with heavy metals and toxic chemicals; forest damage near Koper from air pollution (originating at metallurgical and chemical plants) and resulting acid rain
International agreements
- Party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78), Wetlands
- Signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
