2016 United States presidential election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 53.8%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
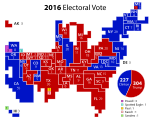
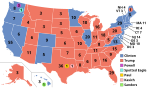
 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states projected for Trump/Pence; Blue denotes those projected for Clinton/Kaine; Numbers indicate electoral votes allotted to the winner of each state. The electoral college will vote on December 19, 2016. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Republican Party | |
|---|---|
| Democratic Party | |
| Third parties | |
| Related races | |
| |
The United States presidential election of 2016 was the 58th and most recent quadrennial American presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican Party nominee, businessman Donald Trump from New York, and his running mate, Governor Mike Pence of Indiana, defeated the Democratic Party nominee, former Secretary of State and former Senator Hillary Clinton from New York, and her running mate, Senator Tim Kaine from Virginia.
Voters selected presidential electors, who in turn will vote, based on the results of their jurisdiction, for a new president and vice president through the Electoral College on December 19, 2016.[3] Trump is expected to take office as the 45th President on January 20, 2017; Pence is expected to take office as the 48th Vice President. The 2016 election was the fifth in American history where the winner lost the popular vote nationwide.[a]
The series of presidential primary elections and caucuses took place between February and June 2016, staggered among the 50 states, the District of Columbia and U.S. territories. This nominating process was also an indirect election, where voters cast ballots for a slate of delegates to a political party's nominating convention, who in turn elected their party's presidential nominee. Businessman and reality television personality Donald Trump became the Republican Party's presidential nominee on July 19, 2016, after defeating Senator Ted Cruz of Texas, and 15 other major candidates in the Republican primary elections.[7] Former Secretary of State and Senator for New York Hillary Clinton became the Democratic Party's presidential nominee on July 26, 2016, after defeating Senator Bernie Sanders of Vermont.[8]
A total of 29 third party and independent presidential candidates appeared on the ballot in at least one state. Former Governor of New Mexico Gary Johnson and physician Jill Stein repeated their 2012 roles as the nominees for the Libertarian Party and Green Party, respectively.[9] With ballot access to the entire electoral college, Johnson acquired 4.3 million votes, the highest nationwide vote share for a third party candidate since Ross Perot in 1996.[10] Stein received 1.3 million votes, the most for a Green nominee since Ralph Nader in 2000. Independent Evan McMullin obtained 21% of the total votes in his home state of Utah.
By early morning November 9, 2016, initial vote counts indicated that Donald Trump was projected to obtain over 270 electoral votes, a majority of the 538 electors in the electoral college required to make him the president-elect of the United States.[11][12] The victory, considered unlikely by most pre-election forecasts,[13][14] was characterized by various news organizations as an "upset" and the most "shocking" U.S. presidential election result since Harry S. Truman's upset victory in 1948.[15][16]
Aside from Florida, the states which secured Trump's victory are situated in the Great Lakes/Rust Belt region. Wisconsin went Republican for the first time since 1984, while Pennsylvania and Michigan went Republican for the first time since 1988.[17][18][19] Maine split its electoral votes for the first time since 1828.[20] Despite winning the popular vote by more than 1.7 million votes,[21] Hillary Clinton is poised to lose the Electoral College by 74 votes,[22] with 30 states and Maine's 2nd congressional district going to Trump and 20 states plus DC to Clinton.
Both Clinton and Trump were seen unfavorably by the general public and caused major divides within their respective parties, due to the number of controversies surrounding them.[23]
Background

Article Two of the United States Constitution provides that the President and Vice President of the United States must be natural-born citizens of the United States, at least 35 years old, and a resident of the United States for a period of at least 14 years. Candidates for the presidency typically seek the nomination of one of the political parties of the United States, in which case each party devises a method (such as a primary election) to choose the candidate the party deems best suited to run for the position. Traditionally, the primary elections are indirect elections where voters cast ballots for a slate of party delegates pledged to a particular candidate. The party's delegates then officially nominate a candidate to run on the party's behalf. The general election in November is also an indirect election, where voters cast ballots for a slate of members of the Electoral College; these electors in turn directly elect the President and Vice President.
President Barack Obama, a Democrat and former U.S. Senator from Illinois, was ineligible to seek reelection to a third term due to restrictions of the Twenty-second Amendment; in accordance with Section I of the Twentieth Amendment, his term expires at 12 noon on January 20, 2017.
2008 presidential election
In the 2008 election, Obama was elected president, defeating the Republican nominee, Senator John McCain of Arizona, with 53% of the popular vote and 68% of the electoral vote,[24][25] succeeding two-term Republican President George W. Bush, the former Governor of Texas. Since the end of 2009, Obama's first year in office, polling companies such as Gallup have found Obama's approval ratings to be between 40–50%.[26][27]
2010 midterm elections
In the 2010 midterm elections, the Democratic Party suffered significant losses in Congress; the Republicans gained 63 seats in the House of Representatives – taking back control of the chamber in the process – and six seats in the Senate, though short of achieving a majority. As a result of the Republicans' recapture of the House after losing it to the Democrats in the 2006 midterm elections, John Boehner became the 53rd Speaker of the House of Representatives, making Obama the first President in 16 years to lose the House of Representatives in the first half of his first term, in an election that was characterized by the economy's slow recovery, and the rise of the Tea Party movement.[28]

2012 presidential election
In the 2012 presidential election, Obama defeated former Governor of Massachusetts Mitt Romney with 51% of the popular vote and 62% of the electoral vote.[29] Meanwhile, despite minor losses, Republicans retained their majority of seats in the House of Representatives while Democrats increased their majority in the Senate.[25]
Speculation about the 2016 campaign began almost immediately following the 2012 campaign, with New York magazine declaring the race had begun in an article published on November 8, two days after the 2012 election.[30] On the same day, Politico released an article predicting the 2016 general election would be between Clinton and former Governor of Florida Jeb Bush, while a The New York Times article named Governor of New Jersey Chris Christie and New Jersey Senator Cory Booker as potential candidates.[31][32]
2014 midterm elections
In the 2014 midterm elections, voter turnout was the lowest since 1942: 36% of eligible voters voted.[33] The Republicans retained control of the House of Representatives, increasing their majority to its largest since March 4, 1929,[34] and gained a majority in the Senate.[35]
Republican Party
Primaries
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Business and personal 45th & 47th President of the United States Tenure
Impeachments Civil and criminal prosecutions  |
||
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Vice President of the United States
U.S. Representative
for Indiana's 2nd and 6th districts Vice presidential campaigns
|
||
Seventeen major candidates entered the race starting March 23, 2015, when Senator Ted Cruz from Texas was the first to announce his candidacy: former Governor Jeb Bush of Florida, retired neurosurgeon Ben Carson from Maryland, Governor Chris Christie of New Jersey, businesswoman Carly Fiorina from California, former Governor Jim Gilmore of Virginia, Senator Lindsey Graham from South Carolina, former Governor Mike Huckabee of Arkansas, former Governor Bobby Jindal of Louisiana, Governor John Kasich of Ohio, former Governor George Pataki of New York, Senator Rand Paul from Kentucky, former Governor Rick Perry of Texas, Senator Marco Rubio from Florida, former Senator Rick Santorum from Pennsylvania, businessman Donald Trump from New York and Governor Scott Walker of Wisconsin. This was the largest presidential primary field for any political party in American history.[36]
Prior to the Iowa caucuses on February 1, 2016, Perry, Walker, Jindal, Graham and Pataki withdrew due to low polling numbers. Despite leading many polls in Iowa, Trump came in second to Cruz, after which Huckabee, Paul and Santorum withdrew due to poor performances at the ballot box. Following a sizable victory for Trump in the New Hampshire primary, Christie, Fiorina and Gilmore abandoned the race. Bush followed suit after scoring fourth place to Trump, Rubio and Cruz in South Carolina. On March 1, 2016, the first of four "Super Tuesday" primaries, Rubio won his first contest in Minnesota, Cruz won Alaska, Oklahoma and his home of Texas and Trump won the other seven states that voted. Failing to gain traction, Carson suspended his campaign a few days later.[37] On March 15, 2016, the second of four "Super Tuesday" primaries, Kasich won his only contest in his home state of Ohio and Trump won five primaries including Florida. Rubio suspended his campaign after losing his home state,[38] but retained a large share of his delegates for the national convention, which he released to Trump.[38]
Between March 16 and May 3, 2016, only three candidates remained in the race: Trump, Cruz and Kasich. Cruz won most delegates in four Western contests and in Wisconsin, keeping a credible path to denying Trump the nomination on first ballot with 1,237 delegates. Trump then augmented his lead by scoring landslide victories in New York and five Northeastern states in April and he grabbed all 57 delegates in the Indiana primary of May 3, 2016. Without any further chances of forcing a contested convention, both Cruz[39] and Kasich[40] suspended their campaigns. Trump remained the only active candidate and was declared the presumptive Republican nominee by Republican National Committee chairman Reince Priebus on the evening of May 3, 2016.[41]
Nominees
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Donald Trump | Mike Pence | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chairman of The Trump Organization (1971–present) |
50th Governor of Indiana (2013–present) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [42][43][44] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other major candidates
Major candidates were determined by the various media based on common consensus. The following were invited to sanctioned televised debates based on their poll ratings.
Trump received 14,010,177 total votes in the primary. Trump, Cruz, Rubio and Kasich each won at least one primary, with Trump receiving the highest number of votes and Ted Cruz receiving the second highest.
| Candidates in this section are sorted by reverse date of withdrawal from the primaries | |||||||
| John Kasich | Ted Cruz | Marco Rubio | Ben Carson | Jeb Bush | Jim Gilmore | Carly Fiorina | Chris Christie |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Governor of Ohio (2011–present) |
from Texas (2013–present) |
from Florida (2011–present) |
Johns Hopkins Hospital (1984–2013) |
Governor of Florida (1999–2007) |
Governor of Virginia (1998–2002) |
(1999–2005) |
Governor of New Jersey (2010–present) |
4,287,479 votes |
7,811,110 votes |
3,514,124 votes |
857,009 votes |
286,634 votes |
18,364 votes |
40,577 votes |
57,634 votes |
| Rand Paul | Rick Santorum | Mike Huckabee | George Pataki | Lindsey Graham | Bobby Jindal | Scott Walker | Rick Perry |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
from Kentucky (2011–present) |
from Pennsylvania (1995–2007) |
Governor of Arkansas (1996–2007) |
Governor of New York (1995–2006) |
from South Carolina (2003–present) |
Governor of Louisiana (2008–2016) |
Governor of Wisconsin (2011–present) |
Governor of Texas (2000–2015) |
66,781 votes |
16,622 votes |
51,436 votes |
2,036 votes |
5,666 votes |
222 votes |
1 write-in vote in New Hampshire |
1 write-in vote in New Hampshire |
Vice presidential selection
Donald Trump turned his attention towards selecting a running mate after he became the presumptive nominee on May 4, 2016.[80] In mid-June, Eli Stokols and Burgess Everett of Politico reported that the Trump campaign was considering New Jersey Governor Chris Christie, former Speaker of the House Newt Gingrich from Georgia, Alabama Senator Jeff Sessions, and Oklahoma Governor Mary Fallin.[81] A June 30 Washington Post report also included Senators Bob Corker from Tennessee, Richard Burr from North Carolina, Tom Cotton from Arkansas, Joni Ernst from Iowa, and Indiana Governor Mike Pence as individuals still being considered for the ticket.[82] Trump also stated that he was considering two military generals for the position, including retired Lieutenant General Michael Flynn.[83]
In July 2016, it was reported that Trump had narrowed his list of possible running mates down to three: Christie, Gingrich, and Pence.[84]
On July 14, 2016, several major media outlets reported that Trump had selected Pence as his running mate. Trump confirmed these reports in a message on Twitter on July 15, 2016, and formally made the announcement the following day in New York.[85][86] On July 19, the second night of the 2016 Republican National Convention, Pence won the Republican vice presidential nomination by acclamation.[87]
Democratic Party
Primaries
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
First Lady of the United States
U.S. Senator from New York
U.S. Secretary of State
2008 presidential campaign 2016 presidential campaign Organizations
|
||
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Mayor of Richmond
Lieutenant Governor of Virginia
Chair of the DNC
Governor of Virginia
U.S. Senator from Virginia
Vice presidential campaign
|
||
Former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who also served in the U.S. Senate and was the First Lady of the United States, became the first Democrat to formally launch a major candidacy for the presidency. Clinton made the announcement on April 12, 2015, via a video message.[88] While Nationwide opinion polls in 2015 indicated that Clinton was the front-runner for the 2016 Democratic presidential nomination, she faced challenges from Independent Vermont Senator Bernie Sanders,[89] who became the second major candidate when he formally announced on April 30, 2015, that he was running for the Democratic nomination.[90] September 2015 polling numbers indicated a narrowing gap between Clinton and Sanders.[89][91][92] On May 30, 2015, former Governor of Maryland Martin O'Malley was the third major candidate to enter the Democratic primary race.[93] On June 3, 2015, Lincoln Chafee, former Independent Governor and Republican Senator of Rhode Island, became the fourth major candidate to announce his candidacy for the Democratic nomination.[94][95] On July 2, 2015, former Virginia Senator Jim Webb became the fifth major Democratic candidate to announce his bid for the presidency.[96] On September 6, 2015, former Harvard law professor Lawrence Lessig became the sixth and final major Democratic candidate to enter the race.[97]
On October 20, 2015, Webb announced his withdrawal from the Democratic primaries, and explored a potential Independent run.[98] The next day Vice-President Joe Biden decided not to run, ending months of speculation, stating, "While I will not be a candidate, I will not be silent."[99][100] On October 23, Chafee withdrew, stating that he hoped for "an end to the endless wars and the beginning of a new era for the United States and humanity".[101] On November 2, after failing to qualify for the second DNC-sanctioned debate after adoption of a rule change negated polls which before might have necessitated his inclusion in the debate, Lessig withdrew as well, narrowing the field to Clinton, O'Malley, and Sanders.[102]
On February 1, 2016, in an extremely close contest, Clinton won the Iowa caucuses by a margin of 0.2 points over Sanders. After winning no delegates in Iowa, O'Malley withdrew from the presidential race that day. On February 9, Sanders bounced back to win the New Hampshire primary with 60% of the vote. In the remaining two February contests, Clinton won the Nevada caucuses with 53% of the vote and scored a decisive victory in the South Carolina primary with 73% of the vote.[103][104] On March 1, 11 states participated in the first of four "Super Tuesday" primaries. Clinton won Alabama, Arkansas, Georgia, Massachusetts, Tennessee, Texas, and Virginia and 504 pledged delegates, while Sanders won Colorado, Minnesota, Oklahoma and his home state of Vermont and 340 delegates. The following weekend, Sanders won victories in Kansas, Nebraska and Maine with 15–30-point margins, while Clinton won the Louisiana primary with 71% of the vote. On March 8, despite never having a lead in the Michigan primary, Sanders won by a small margin of 1.5 points and outperforming polls by over 19 points, while Clinton won 83% of the vote in Mississippi.[105] On March 15, the second of four "Super Tuesday" primaries, Clinton won in Florida, Illinois, Missouri, North Carolina and Ohio. Between March 22 and April 9, 2016, Sanders won six caucuses in Idaho, Utah, Alaska, Hawaii, Washington and Wyoming, as well as the Wisconsin primary, while Clinton won the Arizona primary. On April 19, Clinton won the New York primary with 58% of the vote. On April 26, in the third of four "Super Tuesday" primaries dubbed the "Acela primary", she won contests in Connecticut, Delaware, Maryland and Pennsylvania, while Sanders won in Rhode Island. Over the course of May, Sanders accomplished another surprise win in the Indiana primary[106] and also won in West Virginia and Oregon, while Clinton won the Guam caucus and Kentucky primary.
On June 4 and 5, Clinton won two victories in the Virgin Islands caucus and Puerto Rico primary. On June 6, 2016, the Associated Press and NBC News reported that Clinton had become the presumptive nominee after reaching the required number of delegates, including pledged delegates and superdelegates, to secure the nomination, becoming the first woman to ever clinch the presidential nomination of a major United States political party.[107] On June 7, Clinton secured a majority of pledged delegates after winning primaries in California, New Jersey, New Mexico and South Dakota, while Sanders only won in Montana and North Dakota. Clinton also won the final primary in Washington, DC on June 14. At the conclusion of the primary process, Clinton had won 2,204 pledged delegates (54% of the total) awarded by the primary elections and caucuses, while Sanders had won 1,847 (46%). Out of the 714 unpledged delegates or "superdelegates" who were set to vote in the convention in July, Clinton received endorsements from 560 (78%), while Sanders received 47 (7%).[108]
Although Sanders had not formally dropped out of the race, he announced on June 16, 2016, that his main goal in the coming months would be to work with Clinton to defeat Trump in the general election.[109] On July 8, appointees from the Clinton campaign, the Sanders campaign, and the Democratic National Committee negotiated a draft of the party's platform.[110] On July 12, Sanders formally endorsed Clinton at a rally in New Hampshire in which he appeared with Clinton.[111] On July 22, three days before the start of the Democratic National Convention, the Clinton campaign announced that Virginia Senator Tim Kaine had been selected as her running mate.
Nominees
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hillary Clinton | Tim Kaine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 67th U.S. Secretary of State (2009–2013) |
U.S. Senator from Virginia (2013–present) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [112][113][114] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other major candidates
The following candidates were frequently interviewed by major broadcast networks and cable news channels, or were listed in publicly published national polls. Lessig was invited to one forum, but withdrew when rules were changed which prevented him from participating in officially sanctioned debates.
Clinton received 16,849,779 votes in the primary.
| Candidates in this section are sorted by date of withdrawal from the primaries | ||||||||
| Bernie Sanders | Rocky De La Fuente | Martin O'Malley | Lawrence Lessig | Lincoln Chafee | Jim Webb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||
(1984 to present) |
Governor of Maryland (2007–2015) |
(2009–2016) |
Governor of Rhode Island (2011–2015) |
from Virginia (2007–2013) | ||||
13,167,848 primary votes and 1,846 delegates |
67,457 primary votes and 0 delegates |
110,423 votes |
4 write-in votes in New Hampshire |
0 votes |
2 write-in votes in New Hampshire | |||
| [120] | ||||||||
Vice presidential selection
In April 2016, the Clinton campaign began to compile a list of 15 to 20 individuals to vet for the position of running mate, even though Sanders continued to challenge Clinton in the Democratic primaries.[121] In mid-June, the The Wall Street Journal reported that Clinton's shortlist included Representative Xavier Becerra from California, Senator Cory Booker from New Jersey, Senator Sherrod Brown from Ohio, Housing and Urban Development Secretary Julián Castro from Texas, Mayor of Los Angeles Eric Garcetti from California, Senator Tim Kaine from Virginia, Labor Secretary Tom Perez from Maryland, Representative Tim Ryan from Ohio, and Senator Elizabeth Warren from Massachusetts.[122] Subsequent reports stated that Clinton was also considering Secretary of Agriculture Tom Vilsack, retired Admiral James Stavridis, and Governor John Hickenlooper of Colorado.[123] In discussing her potential vice presidential choice, Clinton stated that the most important attribute she looked for was the ability and experience to immediately step into the role of president.[123]
On July 22, Clinton announced that she had chosen Senator Tim Kaine from Virginia as her running mate.[124] The delegates at the 2016 Democratic National Convention, which took place July 25–28, formally nominated the Democratic ticket.
Third parties and independents
Third party and independent candidates that have obtained more than 100,000 votes nationally and one percent of the vote in at least one state, are stated separately.
Libertarian Party
- Gary Johnson, 29th Governor of New Mexico. Vice-presidential nominee: Bill Weld, 68th Governor of Massachusetts
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Governor of New Mexico
Presidential campaigns
|
||
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Pre-governorship
Governor of Massachusetts
|
||
- Additional Party Endorsements: Independence Party of New York
Ballot access to all 538 electoral votes
Nominees
| Libertarian Party ticket, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gary Johnson | William Weld | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29th Governor of New Mexico (1995–2003) |
68th Governor of Massachusetts (1991–1997) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Green Party
- Jill Stein, Physician from Lexington, Massachusetts. Vice-presidential nominee: Ajamu Baraka, Activist from Washington, D.C.
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Massachusetts campaigns
Presidential campaigns
Political party affiliations
|
||
Ballot access to 480 electoral votes (522 with write-in):[127] - map
- As write-in: Georgia, Indiana, North Carolina[128][129]
- Ballot access lawsuit pending: Oklahoma[130]
- No ballot access: Nevada, South Dakota[128][131]
Nominees
| Jill Stein | Ajamu Baraka | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physician from Lexington, Massachusetts |
Activist from Washington, D.C. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [132][133] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Independents
- Evan McMullin, Chief policy director for the House Republican Conference. Vice-presidential nominee: Mindy Finn, President of Empowered Women
- Additional Party Endorsement: Independence Party of Minnesota
Ballot access to 84 electoral votes (451 with write-in):[134] - map
- As write-in: Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, California, Connecticut, Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Kansas, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Texas, Vermont, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin[134][135][136][137][138][139][140]
- No ballot access: District of Columbia, Florida, Hawaii, Indiana, Mississippi, Nevada, North Carolina, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Wyoming
In some states, Evan McMullin's running mate was listed as Nathan Johnson on the ballot rather than Mindy Finn, although Nathan Johnson was intended to only be a placeholder until an actual running mate was chosen.[141]
| Independent ticket, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Evan McMullin | Mindy Finn | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief policy director for the House Republican Conference (2015–2016) |
President of Empowered Women (2015–present) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [142] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Constitution Party
- Darrell Castle, Attorney from Memphis, Tennessee. Vice-presidential nominee: Scott Bradley, Businessman from Utah
Ballot access to 207 electoral votes (451 with write-in):[143][144] - map
- As write-in: Alabama, Arizona, Connecticut, Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Texas, Vermont, Virginia[143][145][146][147][148]
- No ballot access: California, District of Columbia, Massachusetts, North Carolina, Oklahoma[143]
Nominees
| Constitution Party ticket, 2016 | |
| Darrell Castle | Scott Bradley |
|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President |
 |
 |
| Attorney from Memphis, Tennessee |
Businessman from Utah |
| Campaign | |
| [149] | |
Other nominations
| Party | Presidential nominee | Vice presidential nominee | Attainable Electors (write-in) |
Popular Vote | States with ballot access (write-in) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| American Delta Party Reform Party |
Rocky De La Fuente Businessman from California |
Michael Steinberg Lawyer from Florida |
147 (305) map |
32,408 (0.02%) |
Alaska, Colorado, Florida, Idaho, Iowa, Kentucky, Minnesota, Mississippi, Montana, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, North Dakota, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Utah, Vermont, Wisconsin, Wyoming[144][150][151][152][153][154][155] (Alabama, Arizona, Connecticut, Delaware, Indiana, Kansas, Maryland, Missouri, Nebraska, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia)[135][136][137][139][145][147][156][157][158][159][160][161][148][162][163] |
| Party for Socialism and Liberation |
Gloria La Riva Newspaper printer and activist from California |
Eugene Puryear Activist from Washington, D.C. |
112 (226) map |
50,672 (0.04%) |
California, Colorado, Iowa, Louisiana, New Jersey, New Mexico, Vermont, Washington[166][167] (Alabama, Connecticut, Delaware, Kansas, Maryland, Minnesota, New Hampshire, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, West Virginia)[136][137][139][147][156][157][161][163][168] |
| Socialist Workers Party | Alyson Kennedy Mineworker and Labor Leader from Illinois |
Osborne Hart of Pennsylvania |
70 (123) map |
11,667 (0.01%) |
Colorado, Louisiana, Minnesota, New Jersey, Tennessee, Utah, Washington[166] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[156][161] |
| Workers World Party | Monica Moorehead perennial candidate and political activist from Alabama[169] |
Lamont Lilly of North Carolina[170] |
30 (235) map |
4,003 (0.00%) |
New Jersey, Utah, Wisconsin[166] (Alabama, Indiana, Idaho, Iowa, Kansas, Massachusetts, Michigan, Montana, New Hampshire, New, York, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Vermont, Washington, West Virginia)[137][139][156][158][162][163][171][172][173][174][175][176] |
| Socialist Party USA |
Mimi Soltysik former National Co-Chair of the Socialist Party USA from California[178] Campaign |
Angela Nicole Walker of Wisconsin |
25 (209) map |
2,579 (0.00%) |
Colorado, Michigan, Guam[166][167][179] (Alabama, Indiana, Iowa, Maryland, Minnesota, Montana, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Wisconsin)[139][147][156][158][161][162][168][174][176][180][181] |
| Prohibition Party | James Hedges former Tax Assessor for Thompson Township, Fulton County, Pennsylvania[182][183] |
Bill Bayes of Mississippi[182] |
21 (116) map |
5,550 (0.00%) |
Arkansas, Colorado, Mississippi[166] (Alabama, Idaho, Iowa, Kansas, Maryland, Montana, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia)[137][147][156][161][163][171][174] |
| Independent | Mike Smith Lawyer, Colorado |
Daniel White | 20 (222) |
9,049 (0.01%) |
Colorado, Tennessee[166] (Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Connecticut, Delaware, Georgia, Idaho, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Minnesota, Montana, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington. West Virginia)[136][137][145][147][148][156][157][161][162][163][168][171][174][175][180][184][185] |
| Independent | Richard Duncan of Ohio |
Ricky Johnson | 18 (173) |
23,778 (0.02%) |
Ohio[186] (Alabama, Alaska, Delaware, Florida, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Maryland, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia)[147][156][157][158][160][161][163][167][168][171][174][184][185] |
| Independent | Laurence Kotlikoff Economics Professor at Boston University, Massachusetts |
Edward E. Leamer Economics Professor at UCLA, California |
17 (428) map |
2,371 (0.00%) |
Colorado, Louisiana[166] (Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, California, Connecticut, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, New Hampshire, New Jersey, North Dakota, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin)[135][136][138][140][145][147][148][156][158][161][162][163][167][168][171][172][173][174][175][176][180][181][184][185][187][188][189][190] |
| America's Party | Tom Hoefling activist from Iowa[191] |
Steve Schulin of South Carolina |
17 (369) map |
3,203 (0.00%) |
Colorado, Louisiana[166][192] (Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Connecticut, Delaware, Georgia, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin)[136][137][138][139][145][146][147][148][156][157][158][160][161][162][163][168][171][173][174][175][176][180][181][184][185][188][190] |
| Veterans Party of America | Chris Keniston reliability engineer from Texas[193] |
Deacon Taylor of Nevada[194] |
17 (196) map |
6,826 (0.01%) |
Colorado, Louisiana[166] (Alabama, Alaska, Idaho, Iowa, Kentucky, Minnesota, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, Wisconsin)[139][148][156][160][161][162][168][171][175][181][184][185] |
| Legal Marijuana Now Party | Dan Vacek of Minnesota |
Mark Elworth Jr. of Nebraska |
16 (77) |
13,530 (0.01%) |
Iowa, Minnesota[166] (Alabama, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[156][161] |
| Independent | Lynn Kahn Doctor of Clinical Psychology from Maryland |
Kathleen Monahan of Florida |
12 (160) |
5,614 (0.00%) |
Arkansas, Iowa[153][166] (Alabama, Delaware, Idaho, Kansas, Maryland, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, Washington, West Virginia)[137][139][147][156][157][160][161][162][163][168][171][174] |
| American Solidarity Party | Mike Maturen sales professional and magician from Michigan |
Juan Muñoz of Texas |
9 (332) map |
2,136 (0.00%) |
Colorado[195] (Alabama, Alaska, California, Georgia, Idaho, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, Wisconsin)[135][137][139][140][146][147][148][156][160][161][162][168][171][173][175][176][181][184][185] |
| Independent | Joseph Allen Maldonado of Oklahoma |
Douglas K. Terranova | 9 (212) |
868 (0.00%) |
Colorado[195] (Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Maryland, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin)[136][145][147][156][157][158][160][161][162][163][168][174][175][181][184][185][188] |
| Independent | Ryan Alan Scott | Bruce Kendall Barnard | 9 (108) |
741 (0.00%) |
Colorado[195] (Alabama, Delaware, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[139][156][157][161] |
| American Party (South Carolina) | Peter Skewes Animal Science Professor at Clemson University, South Carolina |
Michael Lacy | 9 (83) |
3,246 (0.00%) |
South Carolina[196] (Alabama, Connecticut, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[136][156][161] |
| Approval Voting Party | Frank Atwood of Colorado |
Blake Huber of Colorado |
9 (76) |
334 (0.00%) |
Colorado[195] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[156][161] |
| Independent American Party | Kyle Kenley Kopitke of Michigan |
Narthan R. Sorenson | 9 (76) |
1,073 (0.00%) |
Colorado[195] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[156][161] |
| Nutrition Party | Rod Silva restaurateur from New Jersey[197][198] |
Richard Silva | 9 (76) |
727 (0.00%) |
Colorado[195] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[156][161] |
| United States Pacifist Party | Bradford Lyttle peace activist from Illinois |
Hannah Walsh | 9 (76) |
372 (0.00%) |
Colorado[195] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[156][161] |
| Socialist Equality Party | Jerry White peace activist from Michigan |
Niles Niemuth journalist from Wisconsin |
8 (166) |
369 (0.00%) |
Louisiana[199] (Alabama, California, Delaware, Iowa, Kentucky, Maryland, Minnesota, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia)[135][147][156][157][161][163][168][185] |
| Independent | Princess Khadijah Jacob-Fambro of California |
Milton Fambro of California |
8 (75) |
748 (0.00%) |
Louisiana[199] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[156][161] |
| Independent American Party | Rocky Giordani from California |
Farley Anderson activist from Utah |
6 (79) |
2,177 (0.00%) |
Utah[180] (Alabama, Iowa, Kansas, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[137][156][161] |
| Constitution Party of Idaho | Scott Copeland of Texas |
J.R. Meyers | 4 (71) |
2,368 (0.00%) |
Idaho[200] (Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont)[156][161] |
Candidates gallery
Campaigns
Ballot access
| Presidential ticket | Party | Ballot access | Votes[2] | Percentage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| States | Electors | % of voters | ||||
| Trump / Pence | Republican | 50 + DC | 538 | 100% | 62,001,293 | 46.55% |
| Clinton / Kaine | Democratic | 50 + DC | 538 | 100% | 63,715,574 | 47.83% |
| Johnson / Weld | Libertarian | 50 + DC | 538 | 100% | 4,373,733 | 3.28% |
| Stein / Baraka | Green | 44 + DC | 480 | 89% | 1,364,411 | 1.02% |
| McMullin / Finn | Independent | 11 | 84 | 15% | 545,212 | 0.41% |
| Castle / Bradley | Constitution | 24 | 207 | 39% | 191,098 | 0.14% |
- Candidates in bold were on ballots representing 270 electoral votes, without needing write-in states.
- All other candidates were on the ballots of fewer than 25 states, but had write-in access greater than 270.
-
Jill Stein
ballot access -
Evan McMullin
ballot access -
Darrell Castle
ballot access
Party conventions
- Democratic Party
- July 25–28, 2016: Democratic National Convention was held in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.[201]
- Republican Party
- Libertarian Party
- Green Party
- Constitution Party
- April 13–16, 2016: Constitution Party National Convention was held in Salt Lake City, Utah.[208]
Campaign finance
This is an overview of the money used in the campaign as it is reported to Federal Election Commission (FEC) and released in September 2016. Outside groups are independent expenditure only committees—also called PACs and SuperPACs. The sources of the numbers are the FEC and Center for Responsive Politics.[209] Some spending totals are not available, due to withdrawals before the FEC deadline. As of September 2016, ten candidates with ballot access have filed financial reports with the FEC.
| Candidate | Campaign committee (as of September 30) | Outside groups (as of October 16) | Total spent | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Money raised | Money spent | Cash on hand | Debt | Money raised | Money spent | Cash on hand | ||
| Hillary Clinton[210][211] | $460,168,401 | $400,504,099 | $59,664,302 | $626,094 | $171,240,103 | $148,604,471 | $22,635,633 | $534,352,332 |
| Donald Trump[212][213] | $224,449,710 | $189,673,422 | $34,776,287 | $0 | $214,496,514 | $183,418,431 | $31,078,083 | $367,405,384 |
| Gary Johnson[214][215] | $10,573,731 | $9,463,272 | $1,217,539 | $1,538,118 | $1,378,510 | $917,521 | $460,988 | $10,349,663 |
| Rocky De La Fuente[216] | $7,351,270 | $7,354,663 | -$3,392 | $7,334,250 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $7,354,663 |
| Jill Stein[217][218] | $3,218,525 | $3,144,843 | $73,681 | $87,740 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $3,144,843 |
| Evan McMullin[219] | $501,093 | $496,776 | $4,316 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $496,776 |
| Darrell Castle[220] | $52,234 | $51,365 | $869 | $2,500 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $51,365 |
| Gloria La Riva[221] | $29,243 | $24,207 | $5,034 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $24,207 |
| Monica Moorehead[222] | $11,547 | $9,127 | $2,419 | $4,500 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $9,127 |
| Peter Skewes[223] | $7,966 | $4,238 | $7,454 | $8,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $4,238 |
Newspaper endorsements
Clinton was endorsed by The New York Times,[224] Los Angeles Times,[225] Houston Chronicle,[226] San Jose Mercury News,[227] Chicago Sun-Times[228] and the New York Daily News[229] editorial boards. Trump, who has frequently criticized the mainstream media, was not endorsed by a major newspaper,[230][231] with the tabloid National Enquirer[232] and the Las Vegas Review-Journal his highest profile supporters.[233] Several papers which endorsed Clinton, such as the Houston Chronicle,[226] The Dallas Morning News,[234] The San Diego Union-Tribune[235] The Columbus Dispatch[236] and the The Arizona Republic,[237] endorsed their first Democratic candidate for many decades. USA Today, which had not endorsed any candidate since it was founded 34 years ago, broke tradition by giving an anti-endorsement against Trump, declaring him "unfit for the presidency".[238][239] The Atlantic, which has been in circulation since 1857, gave Clinton its third-ever endorsement (after Abraham Lincoln and Lyndon Johnson).[240]
Other traditionally-Republican papers, including The New Hampshire Union Leader, which had endorsed the Republican in every election for the last 100 years,[241] the Detroit News, which had not endorsed a non-Republican in its 143 years,[242] and the Chicago Tribune,[243] endorsed Gary Johnson. Trump received favorable coverage, but no explicit endorsement, from Breitbart, an alt-right news and opinion website.[244]
Forecasting
There were many ways to try to predict the outcome of the 2016 (or any other) election.[245] Since the advent of scientific polling in 1936, opinion polls have been a nearly universally accepted method to predict the outcome of elections throughout the world. More recently, prediction markets have been formed, starting in 1988 with Iowa Electronic Markets.
Academic scholars have constructed models of voting behavior to forecast the outcomes of elections. An early successful model which is still being used is The Keys to the White House by Allan Lichtman.[246] PollyVote takes a simple average of six types of inputs: Prediction markets, index models, expert judgment, citizen forecasts, poll aggregators and econometric models.
For the 2016 election, there were many competing election forecast approaches including Nate Silver's FiveThirtyEight, The Upshot at The New York Times, Daily Kos, Princeton Election Consortium, Cook Political Report, Rothenberg and Gonzales, PollyVote, Sabato and Electoral-Vote.[247]
These models mostly showed a Democratic advantage since the nominees were confirmed. Pollsters were puzzled by the failure of mainstream forecasting models to predict the 2016 election outcome.[248][249] Further confusion was attributed to The New York Times' live presidential election forecast website for misleading graphing after analyst Alp Toker identified the use of pseudorandom jitter to give the impression of live fluctuations in its outcome predictions.[250][251]
Debates
Primary election debates
General election debates
The Commission on Presidential Debates (CPD), a non-profit organization, hosted debates between qualifying presidential and vice-presidential candidates. According to the commission's website, to be eligible to opt to participate in the anticipated debates, "... in addition to being Constitutionally eligible, candidates must appear on a sufficient number of state ballots to have a mathematical chance of winning a majority vote in the Electoral College, and have a level of support of at least 15 percent of the national electorate as determined by five selected national public opinion polling organizations, using the average of those organizations' most recently publicly-reported results at the time of the determination."[252]
The three locations chosen to host the presidential debates, and the one location selected to host the vice presidential debate, were announced on September 23, 2015. The site of the first debate was originally designated as Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio; however, due to rising costs and security concerns, the debate was moved to Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York.[253]
On August 19, Trump's campaign manager confirmed that he would participate in a series of three debates.[254][255][256][257] Trump had complained that two of the scheduled debates, one on September 26 and the other October 9, will have to compete for viewers with National Football League games, referencing the similar complaints made regarding the dates with low expected ratings during the Democratic Party presidential debates.[258] According to a survey by Rasmussen Reports, the majority of American voters believe that the debate moderators at the presidential debates will be helping Hillary Clinton.[259]
The Free & Equal Elections Foundation announced plans to host an open debate among all presidential candidates who had ballot access sufficient to represent a majority of electoral votes.[260] In October 2016 Free and Equal extended the invitation to all candidates with ballot lines representing at least 15% of the electoral vote. The nominees of the Democratic, Republican, Libertarian, Green, Constitution, Reform, and Socialism and Liberation parties, as well as independent candidate Evan McMullin, were invited to participate.[261] The debate was held at the University of Colorado Boulder's Macky Auditorium on October 25, 2016. It was moderated by Ed Asner and Christina Tobin, with Darrell Castle, Rocky De La Fuente, and Gloria La Riva participating.[262]
PBS hosted a debate moderated by Tavis Smiley between Libertarian candidate Gary Johnson and Green Party candidate Jill Stein.[263]
| No. | Date | Time | Host | City | Moderator(s) | Participants | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | September 26, 2016 | 9 p.m. EDT | Hofstra University | Hempstead, New York | Lester Holt | Hillary Clinton Donald Trump | |||||||||||||||
| VP | October 4, 2016 | 9 p.m. EDT | Longwood University | Farmville, Virginia | Elaine Quijano | Tim Kaine Mike Pence | |||||||||||||||
| P2 | October 9, 2016 | 8 p.m. CDT | Washington University in St. Louis | St. Louis, Missouri | Anderson Cooper Martha Raddatz |
Hillary Clinton Donald Trump | |||||||||||||||
| P3 | October 19, 2016 | 6 p.m. PDT | University of Nevada, Las Vegas | Las Vegas, Nevada | Chris Wallace | Hillary Clinton Donald Trump | |||||||||||||||
| P4 | October 25, 2016 | 7 p.m. MDT | University of Colorado Boulder | Boulder, Colorado | Ed Asner Christina Tobin |
Darrell Castle Rocky De La Fuente Gloria La Riva | |||||||||||||||
| = Sponsored by the CPD; = Sponsored by Free & Equal | |||||||||||||||||||||
Results
The election was held on November 8, 2016. Hillary Clinton cast her vote in the New York City suburb of Chappaqua, while Donald Trump voted in a Manhattan public school.[264] Throughout the day, the election process went more smoothly than many had expected, with only a few reports of long lines and equipment issues.
Early exit polls favored the Democratic candidate Hillary Clinton.[265] However, as polls closed and the results came in throughout the night, those exit polls and forecasts proved inaccurate as the Republican candidate performed surprisingly well in all battleground states, especially Florida, Ohio and North Carolina. Even Wisconsin and Michigan, states that were predicted to swing blue, were won by Donald Trump.[266]
On November 9, 2016, at 3:00 AM Eastern Time, Donald Trump secured over 270 electoral votes, the majority of the 538 electors in the Electoral College, enough to make him the President-elect of the United States.[11][12] Clinton called Trump early on Wednesday morning, conceding defeat.[267] Clinton asked her supporters to accept the result and hoped that Trump would be "a successful president for all Americans".[268] In his victory speech Trump appealed for unity saying "it is time for us to come together as one united people" and praised Clinton who was owed "a major debt of gratitude for her service to our country".[269]
Six states plus a portion of Maine that Obama won in 2012 switched to Trump. These are (with Electoral College votes in parentheses): Florida (29), Pennsylvania (20), Ohio (18), Michigan (16), Wisconsin (10), Iowa (6), and Maine's second congressional district (1). Trump won exactly 100 more Electoral College votes than Mitt Romney in 2012. Forty-one states swung more Republican compared to the previous Presidential election, while nine states and the District of Columbia swung more Democratic.[270]
It is estimated that 134.5 million Americans cast a ballot in 2016. Considering a voting age population (VAP) of 251.1 million people and voting eligible population (VEP) of 231.5 million people, this a turnout rate of 53.7% VAP and 58.1% VEP.[271] Voting turnout percentage was down compared to 2008 (58.2% VAP) and 2012 (54.9% VAP), but more votes were cast in the 2016 election than any prior election due to an increase in the voting population.[271]
| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote | Electoral vote |
Running mate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | Vice-presidential candidate | Home state | Electoral vote | ||||
| Donald Trump | Republican | New York | 61,958,044[2] | 46.56% | 306 | Mike Pence | Indiana | 306 |
| Hillary Clinton | Democratic | New York | 63,640,193[2] | 47.83% | 232 | Tim Kaine | Virginia | 232 |
| Gary Johnson | Libertarian | New Mexico | 4,368,411[2] | 3.28% | 0 | William Weld | Massachusetts | 0 |
| Jill Stein | Green | Massachusetts | 1,360,952[2] | 1.02% | 0 | Ajamu Baraka | Illinois | 0 |
| Evan McMullin | Independent | Utah | 545,104[2] | 0.41% | 0 | Mindy Finn | District of Columbia | 0 |
| Darrell Castle | Constitution | Tennessee | 190,723[2] | 0.14% | 0 | Scott Bradley | Utah | 0 |
| Other | 996,775[2] | 0.76% | — | Other | — | |||
| Total | 133,060,202[2] | 100% | 538 | 538 | ||||
| Needed to win | 270 | 270 | ||||||
Note: Popular vote count is preliminary until all states have certified their results.
So far, Trump has received more votes than any Republican except George W. Bush in 2004, and Clinton more votes than any Democrat except Barack Obama in 2008 and 2012. Electoral vote figures are only projected, with the Electoral College voting on December 19, 2016.[272]
The Trump victory, considered unlikely by most forecasts,[273] was characterized as an 'upset' and as 'shocking' by the media.[274][275][276] This might be due to mainstream media's tendency to favor Clinton according to a poll by Media Research Center and YouGov showing 59% of respondents felt news outlets favored Clinton over Trump while only 3% said media's bias would influence their vote.[277]
Both major-party candidates were unusually old. At 70 years of age, Trump became the oldest person ever to be elected to a first term as president, surpassing Ronald Reagan, who was 69 years of age upon winning the 1980 election. Hillary Clinton would have been the second oldest after Ronald Reagan.
Along with Bill Clinton and George W. Bush, Trump was born in 1946; this is the first time a single birth year has produced three presidents. (1946 was a year of unusually numerous births, marking the first year of the post–World War II baby boom.) Trump will become the fifth president to be born in the state of New York, after Martin Van Buren, Millard Fillmore, Theodore Roosevelt, and Franklin D. Roosevelt; he will be the second president born in New York City after Theodore Roosevelt.
Trump will also become the fourth president, after James K. Polk in 1844, Woodrow Wilson in 1916 and Richard Nixon in 1968, to win an election despite losing his home state.
Trump became the first person since Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1952 to be elected president without having been elected to any other previous office, and the only individual to be elected president without any prior political or military experience. Among other presidents with limited political experience, William Howard Taft never served in the military and had only been elected to political office once as an Ohio state judge, although he later held a number of appointed federal government positions, including in the Cabinet of a president before being elected president himself. Herbert Hoover did not serve in the military and never held elected office, but he led two important federal government agencies during and after World War I and served in the Cabinets of two other presidents. However, Trump is unique in never having served in any state or federal government position: military, appointed or elected.
Results by state
This section's factual accuracy is disputed. (November 2016) |
| States won by Clinton/Kaine |
| States won by Trump/Pence |
Electoral methods
- WTA – Winner-takes-all
- CD – Congressional district★
| Hillary Clinton Democratic |
Donald Trump Republican |
Gary Johnson Libertarian |
Jill Stein Green |
Evan McMullin Independent |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State or district |
Electoral method |
# | % | Electoral votes |
# | % | Electoral votes |
# | % | Electoral votes |
# | % | Electoral votes |
# | % | Electoral votes |
# |
| Alabama | WTA | 718,084 | 34.55% | – | 1,306,925 | 62.89% | 9 | 44,211 | 2.09% | – | 9,341 | 0.44% | – | AL | |||
| Alaska | WTA | 93,007 | 37.72% | – | 130,415 | 52.89% | 3 | 15,396 | 5.92% | – | 4,699 | 1.80% | – | AK | |||
| Arizona | WTA | 1,161,167 | 45.46% | – | 1,252,401 | 49.03% | 11 | 106,327 | 4.16% | – | 34,345 | 1.34% | – | AZ | |||
| Arkansas | WTA | 378,632 | 33.65% | – | 681,765 | 60.59% | 6 | 29,662 | 2.63% | – | 9,413 | 0.84% | – | 13,187 | 1.17% | – | AR |
| California | WTA | 6,191,799 | 61.78% | 55 | 3,287,273 | 32.80% | – | 402,452 | 3.36% | – | 191,754 | 1.78% | – | CA | |||
| Colorado | WTA | 1,331,675 | 48.15% | 9 | 1,196,662 | 43.27% | – | 143,069 | 5.17% | – | 38,073 | 1.38% | – | 28,765 | 1.04% | – | CO |
| Connecticut | WTA | 823,360 | 53.86% | 7 | 637,919 | 41.73% | – | 48,691 | 3.01% | – | 22,810 | 1.41% | – | 1,481 | 0.10% | – | CT |
| Delaware | WTA | 235,581 | 53.35% | 3 | 185,103 | 41.92% | – | 14,757 | 3.34% | – | 6,100 | 1.38% | – | DE | |||
| Washington, D.C. | WTA | 260,223 | 90.54% | 3 | 11,553 | 4.02% | – | 4,906 | 1.58% | – | 4,258 | 1.39% | – | DC | |||
| Florida | WTA | 4,501,455 | 47.81% | – | 4,615,910 | 49.02% | 29 | 206,799 | 2.20% | – | 64,309 | 0.68% | – | FL | |||
| Georgia | WTA | 1,856,509 | 45.74% | – | 2,078,064 | 51.20% | 16 | 125,293 | 3.06% | – | – | GA | |||||
| Hawaii | WTA | 266,827 | 60.98% | 4 | 128,815 | 29.44% | – | 15,949 | 3.70% | – | 12,727 | 2.91% | – | HI | |||
| Idaho | WTA | 190,971 | 27.46% | – | 412,525 | 59.32% | 4 | 28,369 | 4.10% | – | 8,524 | 1.23% | – | 46,702 | 6.72% | – | ID |
| Illinois | WTA | 2,982,415 | 55.41% | 20 | 2,121,573 | 39.41% | – | 206,351 | 3.75% | – | 74,994 | 1.36% | – | IL | |||
| Indiana | WTA | 1,024,180 | 37.87% | – | 1,544,609 | 57.12% | 11 | 134,124 | 4.91% | – | 1,829 | 0.07% | – | IN | |||
| Iowa | WTA | 650,780 | 41.71% | – | 798,923 | 51.21% | 6 | 59,106 | 3.78% | – | 11,459 | 0.73% | – | 12,331 | 0.79% | – | IA |
| Kansas | WTA | 414,572 | 36.13% | – | 656,470 | 57.22% | 6 | 53,648 | 4.70% | – | 22,717 | 1.98% | – | KS | |||
| Kentucky | WTA | 628,834 | 32.69% | – | 1,202,942 | 62.54% | 8 | 53,749 | 2.79% | – | 13,913 | 0.72% | – | 22,780 | 1.18% | – | KY |
| Louisiana | WTA | 779,535 | 38.44% | – | 1,178,004 | 58.09% | 8 | 37,978 | 1.87% | – | 14,020 | 0.69% | – | 8,546 | 0.42% | – | LA |
| Maine (at-large) | CD | 352,156 | 47.84% | 2 | 332,418 | 45.16% | – | 37,764 | 5.10% | – | 13,995 | 1.90% | – | ME–a/l | |||
| Maine, 1st | CD | 210,921 | 53.95% | 1 | 154,173 | 39.43% | – | 18,429 | 4.71% | – | 7,446 | 1.90% | – | ME-1 | |||
| Maine, 2nd | CD | 143,952 | 41.06% | – | 180,665 | 51.53% | 1 | 19,335 | 5.52% | – | 6,629 | 1.89% | – | ME-2 | |||
| Maryland | WTA | 1,502,820 | 59.50% | 10 | 878,615 | 34.79% | – | 76,400 | 2.85% | – | 33,380 | 1.27% | – | MD | |||
| Massachusetts | WTA | 1,967,667 | 60.81% | 11 | 1,084,400 | 33.52% | – | 136,784 | 4.22% | – | 46,931 | 1.45% | – | MA | |||
| Michigan | WTA | 2,264,807 | 47.33% | – | 2,277,914 | 47.60% | 16 | 173,021 | 3.61% | – | 51,434 | 1.07% | – | MI | |||
| Minnesota | WTA | 1,367,705 | 46.45% | 10 | 1,322,949 | 44.93% | – | 112,972 | 3.84% | – | 36,986 | 1.26% | – | 53,075 | 1.80% | – | MN |
| Mississippi | WTA | 462,127 | 39.74% | – | 678,284 | 58.32% | 6 | 13,817 | 1.19% | – | 3,595 | 0.31% | – | MS | |||
| Missouri | WTA | 1,054,889 | 37.84% | – | 1,585,753 | 56.88% | 10 | 96,404 | 3.46% | – | 25,086 | 0.90% | – | 1,372 | 0.05% | – | MO |
| Montana | WTA | 174,281 | 35.97% | – | 273,879 | 56.52% | 3 | 28,036 | 5.67% | – | 7,868 | 1.60% | – | MT | |||
| Nebraska (at-large) | CD | 273,185 | 33.96% | – | 485,372 | 60.33% | 2 | 37,577 | 4.67% | – | 8,337 | 1.04% | – | NE–a/l | |||
| Nebraska, 1st | CD | 98,694 | 36.11% | – | 157,571 | 57.65% | 1 | 13,791 | 5.05% | – | 3,271 | 1.20% | – | NE-1 | |||
| Nebraska, 2nd | CD | 122,253 | 45.44% | – | 131,338 | 48.82% | 1 | 12,379 | 4.60% | – | 3,056 | 1.14% | – | NE-2 | |||
| Nebraska, 3rd | CD | 52,562 | 19.95% | – | 197,411 | 74.94% | 1 | 11,447 | 4.35% | – | 2,013 | 0.76% | – | NE-3 | |||
| Nevada | WTA | 539,260 | 47.92% | 6 | 512,045 | 45.50% | – | 37,382 | 3.32% | – | – | NV | |||||
| New Hampshire | WTA | 348,497 | 47.62% | 4 | 345,810 | 47.25% | – | 30,694 | 4.12% | – | 6,395 | 0.87% | – | NH | |||
| New Jersey | WTA | 1,967,444 | 54.77% | 14 | 1,509,688 | 42.03% | – | 71,474 | 1.86% | – | 37,131 | 0.98% | – | NJ | |||
| New Mexico | WTA | 380,923 | 48.26% | 5 | 316,134 | 40.05% | – | 74,031 | 9.34% | – | 9,797 | 1.24% | – | 5,722 | 0.72% | – | NM |
| New York | WTA | 4,145,376 | 57.89% | 29 | 2,638,135 | 36.84% | – | 162,273 | 2.28% | – | 100,110 | 1.41% | – | NY | |||
| North Carolina | WTA | 2,169,496 | 46.14% | – | 2,345,235 | 49.88% | 15 | 128,469 | 2.73% | – | 1,038 | 0.02% | – | NC | |||
| North Dakota | WTA | 93,526 | 27.24% | – | 216,133 | 62.95% | 3 | 21,351 | 6.22% | – | 3,779 | 1.10% | – | ND | |||
| Ohio | WTA | 2,320,596 | 43.51% | – | 2,776,683 | 52.06% | 18 | 168,599 | 3.16% | – | 44,310 | 0.82% | – | OH | |||
| Oklahoma | WTA | 419,788 | 28.93% | – | 947,934 | 65.33% | 7 | 83,481 | 5.75% | – | – | OK | |||||
| Oregon | WTA | 949,319 | 49.89% | 7 | 751,438 | 39.49% | – | 92,844 | 4.80% | – | 48,363 | 2.48% | – | OR | |||
| Pennsylvania | WTA | 2,843,707 | 47.74% | – | 2,901,295 | 48.70% | 20 | 142,407 | 2.39% | – | 48,880 | 0.82% | – | PA | |||
| Rhode Island | WTA | 227,062 | 53.83% | 4 | 166,454 | 39.46% | – | 14,685 | 3.21% | – | 6,171 | 1.37% | – | RI | |||
| South Carolina | WTA | 850,629 | 40.71% | – | 1,147,045 | 54.90% | 9 | 49,204 | 2.34% | – | 13,034 | 0.62% | – | 21,016 | 1.00% | – | SC |
| South Dakota | WTA | 117,442 | 31.74% | – | 227,701 | 61.53% | 3 | 20,845 | 5.63% | – | – | SD | |||||
| Tennessee | WTA | 868,853 | 34.90% | – | 1,519,926 | 61.06% | 11 | 70,286 | 2.82% | – | 15,952 | 0.64% | – | TN | |||
| Texas | WTA | 3,867,816 | 43.32% | – | 4,681,590 | 52.43% | 38 | 282,655 | 3.16% | – | 71,327 | 0.80% | – | 20,227 | 0.23% | – | TX |
| Utah | WTA | 222,858 | 27.81% | – | 375,006 | 46.80% | 6 | 37,896 | 3.48% | – | 7,695 | 0.78% | – | 207,288 | 21.05% | – | UT |
| Vermont | WTA | 178,082 | 61.12% | 3 | 95,114 | 32.64% | – | 10,077 | 3.44% | – | 6,755 | 2.31% | – | VT | |||
| Virginia | WTA | 1,981,473 | 49.75% | 13 | 1,769,443 | 44.43% | – | 118,274 | 2.97% | – | 27,638 | 0.69% | – | 54,054 | 1.36% | – | VA |
| Washington | WTA | 1,210,824 | 55.57% | 12 | 831,631 | 38.17% | – | 156,621 | 4.85% | – | 66,802 | 1.69% | – | WA | |||
| West Virginia | WTA | 187,519 | 26.47% | – | 486,304 | 68.65% | 5 | 22,798 | 3.22% | – | 8,016 | 1.13% | – | WV | |||
| Wisconsin | WTA | 1,383,926 | 46.94% | – | 1,411,432 | 47.87% | 10 | 106,470 | 3.58% | – | 31,016 | 1.04% | – | WI | |||
| Wyoming | WTA | 55,964 | 21.63% | – | 174,383 | 67.40% | 3 | 13,287 | 5.3% | – | 2,482 | 0.96% | – | WY | |||
| U.S. Total | – | 63,600,447 | 232 | 61,934,411 | 306 | 4,360,873 | – | 1,357,013 | – | 545,048 | – | US | |||||
★Two states (Maine and Nebraska) allow for their electoral votes to be split between candidates. The winner within each congressional district gets one electoral vote for the district. The winner of the statewide vote gets two additional electoral votes.[278][279] Results are from the Associated Press.[280]
Swing states
Presidential campaigns focus their resources on a relatively small number of competitive states, referred to as swing or battleground states.[281] Some potential swing states are: Florida, Iowa, Nevada, North Carolina, and Ohio.[282][283] Florida is the largest swing state and has been won by the overall winner every election since 1996. Ohio is another large swing state and has had a perfect bellwether record since 1964. The states regarded as competitive can fluctuate, as the polls fluctuate.
Some consensus among political pundits developed throughout the primary election season regarding swing states.[284] From the results of presidential elections from 2004 through to 2012, generally the Democratic and Republican parties start with a safe electoral vote count of about 150 to 200.[285][286] The margins required to constitute a swing state are vague, however, and local factors can come into play.[287][288] It was thought that left-leaning states in the Rust Belt could become more conservative, as Trump mostly appealed to blue-collar workers.[289] They represent a large portion of the American populace and were a major factor in Trump's eventual nomination. Trump's primary campaign was propelled by victories in Democratic states, and his supporters often did not identify as Republican.
In Maine and Nebraska, two electors are given to whoever has the most overall votes, and the winner of each congressional district receives one electoral vote.[290] Every other state awards all of its electoral votes to the candidate with the highest vote percentage.[291] Media reports indicated that both candidates planned to concentrate on Florida, Pennsylvania, Wisconsin, Ohio and North Carolina.[292][293]
Among the Republican-leaning states, potential Democratic targets included Nebraska's second congressional district, Georgia, and Arizona.[294] Trump's relatively poor polling in some traditionally Republican states, such as Utah, raised the possibility they could vote for Clinton, despite easy wins there by recent Republican nominees.[295] Many analysts asserted that Utah is not a viable Democratic destination.[296][297]
Sites and individuals publish electoral predictions. These generally rate the race by the probability either of the two main parties wins each state. "Tossup" is generally used to indicate that neither party has an advantage, "lean" to indicate a party has a slight edge, "likely" to indicate a party has a clear advantage, and "safe" to indicate a party is heavily favored. Ratings from the Cook Political Report, Sabato's Crystal Ball, or the Rothenberg-Gonzales Political Report are included in the table below. The state's 2014 Cook PVI and the latest swing for each state are also listed.
| State | Electoral votes |
2012 margin |
Cook PVI |
Cook Nov. 7 2016[298] |
RCP Nov. 6 2016[299] |
Roth. Nov. 7 2016[300] |
Sabato Nov. 7 2016[301] |
Last swing |
2016 margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | 11 | 9.1 R | R+7 | Lean R | Tossup | Tilt R | Lean R | 2000 | 3.6 R |
| Colorado | 9 | 5.4 D | D+1 | Lean D | Tossup | Likely D | Likely D | 2008 | 4.9 D |
| Florida | 29 | 0.9 D | R+2 | Tossup | Tossup | Tilt D | Lean D | 1.2 R | |
| Georgia | 16 | 7.8 R | R+6 | Lean R | Tossup | Lean R | Likely R | 1996 | 5.7 R |
| Iowa | 6 | 5.8 D | D+1 | Lean R | Tossup | Tilt R | Lean R | 9.6 R | |
| Maine (statewide) | 2 | 15.3 D | D+6 | Likely D | Tossup | Likely D | Likely D | 1992 | 2.7 D |
| Maine (CD-2) | 1 | 8.6 D | D+2 | Tossup | Tossup | No rating | Lean R | TBD | |
| Michigan | 16 | 9.5 D | D+4 | Lean D | Tossup | Lean D | Lean D | 0.3 R | |
| Minnesota | 10 | 7.7 D | D+2 | Likely D | Lean D | Likely D | Likely D | 1976 | 1.5 D |
| Nebraska (CD-2) | 1 | 7.2 R | R+4 | Tossup | Likely R | No rating[b] | Lean R | 2012 | TBD |
| New Mexico | 5 | 10.2 D | D+4 | Likely D | Tossup | Safe D | Likely D | 2008 | 8.3 D |
| Nevada | 6 | 6.7 D | D+2 | Lean D | Tossup | Tilt D | Lean D | 2008 | 2.4 D |
| New Hampshire | 4 | 5.6 D | D+1 | Lean D | Tossup | Lean D | Lean D | 2004 | 0.2 D |
| North Carolina | 15 | 2.0 R | R+3 | Tossup | Tossup | Tilt D | Lean D | 2012 | 3.7 R |
| Ohio | 18 | 3.0 D | R+1 | Lean R | Tossup | Tossup | Lean R | 8.6 R | |
| Pennsylvania | 20 | 5.4 D | D+1 | Lean D | Tossup | Lean D | Lean D | 1.0 R | |
| Virginia | 13 | 3.9 D | EVEN | Likely D | Tossup | Likely D | Likely D | 2008 | 5.3 D |
| Wisconsin | 10 | 6.9 D | D+2 | Lean D | Lean D | Tilt D | Likely D | 1.0 R |
- ^ In early elections, beginning with the election of George Washington, many electors were chosen by state legislatures instead of public balloting and, in those states which practiced public balloting, votes were cast for undifferentiated lists of candidates, leaving no or only partial vote totals. Some states continued to allocate electors by legislative vote as late as 1860.[4][5][6]
- ^ Statewide Nebraska race rated as Likely R
Close races
Red denotes states (or congressional districts that contribute an electoral vote) won by Republican Donald Trump; blue denotes those won by Democrat Hillary Clinton.
States where the margin of victory was under 1% (50 electoral votes; 46 won by Trump, 4 by Clinton):
- Michigan, 0.27%
- New Hampshire, 0.37%
- Wisconsin, 0.81%
- Pennsylvania, 0.96%
States where the margin of victory was between 1% and 5% (84 electoral votes; 56 won by Trump, 28 by Clinton):
- Florida, 1.21%
- Minnesota, 1.52%
- Nevada, 2.42%
- Maine, 2.68%
- Nebraska's 2nd Congressional District, 3.38%
- Arizona, 3.57%
- North Carolina, 3.74%
- Colorado, 4.88%
States/districts where the margin of victory was between 5% and 10% (96 electoral votes; 78 won by Trump, 18 by Clinton):
- Virginia, 5.32%
- Georgia, 5.46%
- New Mexico, 8.21%
- Ohio, 8.55%
- Texas, 9.11%
- Iowa, 9.50%
Reactions
Protests were held in many cities across the nation for several days after the election.[302][303][304] Furthermore, suicide crisis hotlines reported a major increase in calls.[305][306] Intense lobbying (some amounting to harassment) and grass-roots campaigns been directed at various GOP electors of the United States Electoral College[307] to convince a sufficient number of them (37) to not vote for Trump, thus precluding a Trump presidency.[308]
- Layne Bangerter
Maps
-
Results by state, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
-
Results by Vote Distribution Among States. Each state's pie chart is proportional to the number of electoral votes they have.
-
Results by county. Red denotes counties that went to Trump; blue denotes counties that went to Clinton.
-
Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote.
-
Results by congressional district
-
Results by county, shaded according to percentage of the vote for Trump
-
Results by county, shaded according to percentage of the vote for Clinton
-
Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote (Red-Purple-Blue view)
-
County swing from 2012 to 2016
-
County swing from 2012 to 2016, relative to national swing
-
Electoral vote cartogram
Voter demographics
Voter demographic data for 2016 were collected by Edison Research for the National Election Pool, a consortium of ABC News, The Associated Press, CBS News, CNN, Fox News and NBC News. The voter survey is based on questionnaires completed by 24,537 voters leaving 350 voting places throughout the United States on Election Day including 4,398 telephone interviews with early and absentee voters.[309][310][311]
| 2016 Presidential vote by demographic subgroup | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic subgroup | Clinton | Trump | Other | % of total vote | |||
| Total vote | 47.8 | 46.6 | 5.6 | 100 | |||
| Ideology | |||||||
| Liberals | 84 | 10 | 6 | 26 | |||
| Moderates | 52 | 41 | 7 | 39 | |||
| Conservatives | 15 | 81 | 4 | 35 | |||
| Party | |||||||
| Democrats | 89 | 9 | 2 | 37 | |||
| Republicans | 7 | 90 | 3 | 33 | |||
| Independents | 42 | 48 | 10 | 31 | |||
| Party by gender | |||||||
| Democratic men | 87 | 10 | 3 | 14 | |||
| Democratic women | 90 | 8 | 2 | 23 | |||
| Republican men | 6 | 90 | 2 | 17 | |||
| Republican women | 8 | 89 | 2 | 16 | |||
| Independent men | 37 | 51 | 10 | 17 | |||
| Independent women | 47 | 43 | 7 | 14 | |||
| Gender | |||||||
| Men | 41 | 53 | 6 | 48 | |||
| Women | 54 | 42 | 4 | 52 | |||
| Gender by marital status | |||||||
| Married men | 37 | 58 | 5 | 29 | |||
| Married women | 49 | 47 | 4 | 30 | |||
| Non-married men | 46 | 45 | 9 | 19 | |||
| Non-married women | 62 | 33 | 5 | 23 | |||
| Race/ethnicity | |||||||
| White | 37 | 58 | 5 | 70 | |||
| Black | 88 | 8 | 4 | 12 | |||
| Asian | 65 | 29 | 6 | 4 | |||
| Other | 56 | 37 | 7 | 3 | |||
| Hispanic (of any race) | 65 | 29 | 6 | 11 | |||
| Gender by race/ethnicity | |||||||
| White men | 31 | 63 | 5 | 34 | |||
| White women | 43 | 53 | 3 | 37 | |||
| Black men | 80 | 13 | 6 | 5 | |||
| Black women | 94 | 4 | 2 | 7 | |||
| Latino men (of any race) | 62 | 33 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Latino women (of any race) | 68 | 26 | 5 | 6 | |||
| All other races | 61 | 32 | 5 | 6 | |||
| Religion | |||||||
| Protestant | 37 | 60 | 3 | 27 | |||
| Catholic | 45 | 52 | 3 | 23 | |||
| Mormon | 25 | 61 | 14 | 1 | |||
| Other Christian | 43 | 55 | 2 | 24 | |||
| Jewish | 71 | 24 | 5 | 3 | |||
| Other religion | 58 | 33 | 9 | 7 | |||
| None | 68 | 26 | 6 | 15 | |||
| Religious service attendance | |||||||
| Weekly or more | 40 | 56 | 4 | 33 | |||
| Monthly | 46 | 49 | 5 | 16 | |||
| A few times a year | 48 | 47 | 5 | 29 | |||
| Never | 62 | 31 | 7 | 22 | |||
| White evangelical or born-again Christian | |||||||
| White evangelical or born-again Christian | 16 | 81 | 3 | 26 | |||
| Everyone else | 59 | 35 | 6 | 74 | |||
| Age | |||||||
| 18–24 years old | 56 | 35 | 9 | 10 | |||
| 25–29 years old | 53 | 39 | 8 | 9 | |||
| 30–39 years old | 51 | 40 | 9 | 17 | |||
| 40–49 years old | 46 | 50 | 4 | 19 | |||
| 50–64 years old | 44 | 53 | 3 | 30 | |||
| 65 and older | 45 | 53 | 2 | 15 | |||
| Sexual orientation | |||||||
| LGBT | 78 | 14 | 8 | 5 | |||
| Heterosexual | 47 | 48 | 5 | 95 | |||
| First time voter | |||||||
| First time voter | 56 | 40 | 4 | 10 | |||
| Everyone else | 47 | 47 | 6 | 90 | |||
| Education | |||||||
| High school or less | 45 | 51 | 4 | 18 | |||
| Some college education | 43 | 52 | 5 | 32 | |||
| College graduate | 49 | 45 | 6 | 32 | |||
| Postgraduate education | 58 | 37 | 5 | 18 | |||
| Education by race/ethnicity | |||||||
| White college graduates | 45 | 49 | 4 | 37 | |||
| White no college degree | 28 | 67 | 4 | 34 | |||
| Non-white college graduates | 71 | 23 | 5 | 13 | |||
| Non-white no college degree | 75 | 20 | 3 | 16 | |||
| Family income | |||||||
| Under $30,000 | 53 | 41 | 6 | 17 | |||
| $30,000–49,999 | 51 | 42 | 7 | 19 | |||
| $50,000–99,999 | 46 | 50 | 4 | 31 | |||
| $100,000–199,999 | 47 | 48 | 5 | 24 | |||
| $200,000–249,999 | 48 | 49 | 3 | 4 | |||
| Over $250,000 | 46 | 48 | 6 | 6 | |||
| Issue regarded as most important | |||||||
| Foreign policy | 60 | 34 | 6 | 13 | |||
| Immigration | 32 | 64 | 4 | 13 | |||
| Economy | 52 | 42 | 6 | 52 | |||
| Terrorism | 39 | 57 | 4 | 18 | |||
| Community size | |||||||
| Cities (population 50,000 and above) | 59 | 35 | 6 | 34 | |||
| Suburbs | 45 | 50 | 5 | 49 | |||
| Rural areas | 34 | 62 | 4 | 17 | |||
See also
- History of the United States (1991–present)
- List of United States presidential elections where winner lost popular vote
References
- ^ Estimate of 134.5 million votes cast and 251.1 million people of voting age. This represents an increase in total votes cast from the 2012 election (130,292,355 votes cast and 241 million people of voting age) but a decrease in percentage of voter turn out."2016 November General Election Turnout Rates". www.electproject.org. Retrieved November 22, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Leip, David (November 21, 2016). "2016 Presidential General Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Massachusetts. Retrieved November 21, 2016.
- ^ "U. S. Electoral College: 2016 Key Dates". www.archives.gov. Office of the Federal Register, National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Electoral College Box Scores 1789-1996". archives.gov. National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ Austin, Erik (1986). Political Facts of the United States Since 1789. Columbia University Press. p. 92. ISBN 0231060947.
- ^ Duignan, Brian (2009). The Executive Branch of the Federal Government: Purpose, Process, and People. Rosen Publishing. p. 366. ISBN 1615300236.
- ^ Collinson, Stephen; Kopan, Tal (July 19, 2016). "It's official: Trump is Republican nominee". CNN. Retrieved July 19, 2016.
- ^ Dann, Carrie (July 27, 2016). "Hillary Clinton Becomes First Female Nominee of Major U.S. Political Party". NBC News. Retrieved September 25, 2016.
- ^ Geier, Ben (June 27, 2016). "The 2016 Presidential Election Could Have Two Spoiler Candidates". Fortune. Retrieved September 25, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Presidential Ballot Access Map".
- ^ a b "Presidential Election Results: Donald J. Trump Wins". The New York Times. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ a b Pace, Julie; Furlow, Robert (November 9, 2016). "Trump claims astounding victory as America's 45th president". Associated Press. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ Lohr, Steve; Singer, Natasha. "How Data Failed Us in Calling an Election". The New York Times. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ D.R. (November 9, 2016). "How did the polls get it wrong?". The Economist. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ Healy, Patrick; Peters, Jeremy W. (November 9, 2016). "Donald Trump's Victory Is Met With Shock Across a Wide Political Divide". The New York Times. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ Arkin, Daniel; Siemaszko, Corky (November 9, 2016). "2016 Election: Donald Trump Wins the White House in Upset". NBC News. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ Trump stomps all over the Democrats' Blue Wall, CNN, November 9, 2016.
- ^ Angst over the economy helps Trump flip Great Lakes states, Chicago Tribune, November 9, 2016.
- ^ Donald Trump’s Promise of Bringing Back Jobs Worked With Many Michigan Voters, The Wall Street Journal, November 9, 2016.
- ^ "Maine Splits its Electoral Votes for First Time Since 1828". ballot-access.org.
- ^ News, A.B.C. (November 20, 2016). "Clinton Popular Vote Lead Over Trump Now Exceeds 1.5 Million". ABC News. Retrieved November 21, 2016.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Hillary Clinton's Popular-Vote Victory Is Unprecedented—and Still Growing". Retrieved November 17, 2016 – via The Nation.
- ^ "RealClearPolitics - Clinton & Trump: Favorability Ratings". www.realclearpolitics.com. Retrieved November 16, 2016.
- ^ "United States House of Representatives floor summary for Jan 8, 2009". Clerk.house.gov. Retrieved January 30, 2009.
- ^ a b "Federal elections 2008" (PDF). Federal Election Commission. Retrieved May 11, 2015.
- ^ "Presidential Approval Ratings – Barack Obama". Gallup. Retrieved January 19, 2016.
- ^ "Election Other – President Obama Job Approval". RealClearPolitics. Retrieved December 24, 2015.
- ^ "Mid-term Elections 2010: Democrats lose the House in Republican tsunami". Daily Mail.
- ^ "President Map". The New York Times. November 29, 2012. Retrieved May 11, 2015.
- ^ Amira, Dan (November 8, 2012). "Let the 2016 Campaign Season Begin!". New York. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ Martin, Johnathon; Haberman, Maggie (November 8, 2012). "2016 election: Hillary Clinton vs. Jeb Bush?". Politico. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ Barbaro, Micharl (November 8, 2012). "After Obama, Christie Wants a G.O.P. Hug". The New York Times. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ "2014 midterm election turnout lowest in 70 years | PBS NewsHour". PBS NewsHour. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Sullivan, Sean (December 17, 2014). "McSally win gives GOP historic majority in House". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ^ Collinson, Stephen (November 5, 2014). "Republicans seize Senate, gaining full control of Congress". CNN. Retrieved August 25, 2016.
- ^ Linshi, Jack (July 7, 2015). "More People Are Running for Presidential Nomination Than Ever". Time. Retrieved February 14, 2016.
- ^ Rafferty, Andrew (March 4, 2016). "Ben Carson Suspends 2016 Campaign at CPAC". NBC News. Retrieved March 9, 2016.
- ^ a b Peters, Jeremy; Barbaro, Michael (March 16, 2016). "Marco Rubio Suspends His Presidential Campaign". The New York Times. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Rosenfeld, Everett (May 3, 2016). "Ted Cruz suspends presidential campaign". CNBC. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ^ Kaplan, Thomas (May 4, 2016). "John Kasich Drops Out of Presidential Race". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ^ "Reince Priebus on Twitter". Twitter. May 3, 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
.@realDonaldTrump will be presumptive @GOP nominee, we all need to unite...
- ^ "Donald Trump is running for president". Business Insider. June 16, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2015.
- ^ "Donald Trump announces presidential bid". The Washington Post. June 16, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2015.
- ^ "Donald Trump FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 22, 2015. Retrieved June 24, 2015.
- ^ "John Kasich FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. July 23, 2015. Retrieved July 28, 2015.
- ^ Mascaro, Lisa; Lauter, David (March 22, 2015). "Texas Republican Sen. Ted Cruz Launches Presidential Bid". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved March 23, 2015.
- ^ Zezima, Katie (March 23, 2015). "Ted Cruz Announces He's Running for President". The Washington Post. Retrieved March 23, 2015.
- ^ "Ted Cruz FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. March 23, 2015. Retrieved April 1, 2015.
- ^ Parker, Ashley (April 13, 2015). "Marco Rubio Announces 2016 Presidential Bid". The New York Times. Retrieved April 13, 2015.
- ^ Nelson, Rebecca (April 13, 2015). "Marco Rubio Makes His Pitch as the Fresh Face of the GOP in 2016". National Journal. Retrieved April 14, 2015.
- ^ "Marco Rubio FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. April 13, 2015. Retrieved May 7, 2015.
- ^ Terris, Ben (May 3, 2015). "Ben Carson announces presidential campaign". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 4, 2015.
- ^ Rafferty , Andrew (May 4, 2015). "Ben Carson Announces 2016 Run". NBCNews.com. Retrieved May 4, 2015.
- ^ "Ben Carson FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. May 4, 2015. Retrieved May 7, 2015.
- ^ Rafferty, Andrew (June 15, 2015). "Jeb Bush Makes 2016 Run Official". NBC News. Retrieved June 15, 2015.
- ^ "Jeb Bush FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 15, 2015. Retrieved June 16, 2015.
- ^ Allen, Cooper (July 30, 2015). "Jim Gilmore formally joins GOP presidential race". USA Today. Retrieved July 30, 2015.
- ^ "Jim Gilmore FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. July 29, 2015. Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ^ Gass, Nick (May 4, 2015). "Carly Fiorina: 'Yes, I am running for president'". Politico. Retrieved May 4, 2015.
- ^ "Carly Fiorina FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. May 4, 2015. Retrieved May 7, 2015.
- ^ Barbaro, Michael (June 30, 2015). "Chris Christie Announces Run, Pledging 'Truth' About Nation's Woes". The New York Times. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- ^ "Christopher J. Christie FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. July 1, 2015. Retrieved July 6, 2015.
- ^ Lambert, Lisa (April 7, 2015). "Republican Rand Paul announces 2016 presidential run on website". Reuters. Retrieved April 7, 2015.
- ^ Killough, Ashley (April 7, 2015). "Rand Paul: 'I am running for president'". CNN. Retrieved April 7, 2015.
- ^ "Rand Paul FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. April 8, 2015. Retrieved April 9, 2015.
- ^ Jackson, David (May 27, 2015). "Santorum officially begins 2016 presidential campaign". USA Today. Retrieved May 28, 2015.
- ^ "Rick Santorum FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. May 27, 2015. Retrieved June 1, 2015.
- ^ Trip, Gabriel (May 5, 2015). "Mike Huckabee Joins Republican Presidential Race". The New York Times. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ "Mike Huckabee FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. Retrieved May 10, 2015.
- ^ "George Pataki FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 2, 2015. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- ^ Jaffe, Alexandra (June 1, 2015) "Graham bets on foreign experience in White House bid announcement", CNN. Retrieved June 1, 2015.
- ^ "Lindsey Graham FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 1, 2015. Retrieved June 2, 2015.
- ^ Fahrenthold, David A.; Hohmann, James (June 24, 2015). "Bobby Jindal announces entry into 2016 presidential race". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 24, 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Bobby Jindal FEC Filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 29, 2015. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- ^ Burlij, Terence; Lee, MJ; LoBianco, Tom (July 13, 2015). "Wisconsin Gov. Scott Walker officially enters 2016 presidential race". CNN. Retrieved July 13, 2015.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Scott Walker FEC filing". FEC. FEC.gov. Retrieved July 13, 2015.
- ^ a b "2016 Presidential Primary - Republican President - NHSOS". sos.nh.gov. Retrieved October 9, 2016.
- ^ Beckwith , Ryan Teague; Rhodan, Maya (June 4, 2015). "Rick Perry Announces Presidential Bid". Time. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Rick Perry FEC filing" (PDF). FEC.gov. June 19, 2015. Retrieved June 22, 2015.
- ^ Keneally, Meghan (May 4, 2016). "Donald Trump Teases Possible VP Requirements". ABC News. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ^ Stokols, Eli; Everett, Burgess (June 17, 2016). "Trump's performance raises hard question: Who'd want to be his VP?". Politico. Retrieved June 21, 2016.
- ^ Costa, Robert (June 30, 2016). "Gingrich, Christie are the leading candidates to be Trump's running mate". Washington Post. Retrieved July 1, 2016.
- ^ Zurcher, Anthony (July 8, 2016). "US election: Who will Trump pick as his vice-president?". BBC. Retrieved July 8, 2016.
- ^ O'Donnell, Kelly (July 12, 2016). "Team Trump Plans Public Event Friday With VP Pick". NBC News. Retrieved July 12, 2016.
- ^ Bash, Dana; Acosta, Jim; Lee, MJ (July 14, 2016). "Donald Trump selects Mike Pence as VP". CNN. Retrieved July 14, 2016.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Levingston, Ivan (July 15, 2016). "Donald Trump officially names Mike Pence as his VP". CNBC. Retrieved July 16, 2016.
- ^ Cook, Tony (July 19, 2016). "Gov. Mike Pence formally nominated as the Republican Party's vice presidential candidate". The Indianapolis Star. Retrieved July 20, 2016.
- ^ Keith, Tamara; Montanar, Domenico (April 10, 2015). "Hillary Clinton Expected To Go Small With Big Announcement". NPR. Retrieved April 12, 2015.
- ^ a b "Second straight poll shows Bernie Sanders leading in New Hampshire". Boston Globe. Retrieved August 26, 2015.
- ^ Merica, Dan (April 30, 2015). "Bernie Sanders is running for president". CNN. Retrieved July 6, 2015.
- ^ "Bernie Sanders surpasses Hillary Clinton in New Hampshire polls". The Huffington Post. August 25, 2015. Retrieved August 25, 2015.
- ^ "Huffpost Pollster". The Huffington Post. October 1, 2015. Retrieved October 1, 2015.
- ^ Jackson, David; Cooper, Allen (May 30, 2015). "Martin O'Malley jumps into presidential race". USA Today. Retrieved May 30, 2015.
- ^ DelReal, Jose A. (June 3, 2015). "Lincoln Chafee announces long-shot presidential bid". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 3, 2015.
- ^ "Rhode Island's Chafee enters 2016 Democratic contest". Boston Herald. Associated Press. June 3, 2015. Retrieved June 3, 2015.
- ^ Catanese, David (July 2, 2015). "Jim Webb Announces For President". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved July 2, 2015.
- ^ Meyer, Theodoric (September 6, 2015). "Lessig: I'm running for president". Slate. Retrieved September 7, 2015.
- ^ "Jim Webb to consider running as an independent". POLITICO. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ "Biden says he's not running in 2016". OnPolitics. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ "Joe Biden Not Running for President". ABC News. October 21, 2015. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ Wagner, John; Weigel, David (October 23, 2015). "Lincoln Chafee ends Democratic bid for president". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ a b Strauss, Daniel (November 2, 2015). "Lessig drops out of presidential race". Politico. Retrieved November 2, 2015.
- ^ "Nevada Caucus Results". The New York Times. Retrieved February 28, 2016.
- ^ "South Carolina Primary Results". The New York Times. Retrieved February 28, 2016.
- ^ "Why The Polls Missed Bernie Sanders's Michigan Upset". FiveThirtyEight. March 9, 2016. Retrieved May 1, 2016.
- ^ Roberts, Dan; Jacobs, Ben (May 4, 2016). "Bernie Sanders pulls off shock victory over Hillary Clinton in Indiana". The Guardian. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ^ Dann, Carrie (June 6, 2016). "Clinton hits 'magic number' of delegates to clinch nomination". NBC News. Retrieved June 7, 2016.
- ^ "Democratic Convention 2016". thegreenpapers.com. Retrieved May 14, 2016.
- ^ "Sanders vows to help Clinton beat Trump, but keeps campaign alive". Reuters. June 17, 2016. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- ^ Sentinel, Orlando. "Sanders backers frustrated by defeats at Orlando platform meeting". Retrieved July 25, 2016.
- ^ Reily, Molly (July 12, 2016). "Bernie Sanders Endorses Hillary Clinton For President". Huffington Post. Retrieved July 13, 2016.
- ^ Chozick, Amy. "Hillary Clinton Announces 2016 Presidential Bid". The New York Times. Retrieved April 12, 2015.
- ^ Karni, Annie (April 12, 2015). "Hillary Clinton formally announces 2016 run". Politico. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- ^ "Hillary Rodham Clinton FEC filing" (PDF). FEC. April 13, 2015. Retrieved April 13, 2015.
- ^ "Bernie Sanders endorses Hillary Clinton".
- ^ Berg-Andersson, Richard E. (2016). Tony Roza (ed.). "Democratic Delegation 2016". thegreenpapers.com. Retrieved September 24, 2016.
- ^ Yglesias, Matthew (February 1, 2016) "Iowa Results: Martin O'Malley drops out after third place finish", Vox.com. Retrieved February 1, 2016.
- ^ Fritze, John (June 9, 2016). "Martin O'Malley endorses Hillary Clinton". Baltimore Sun. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- ^ Merica, Dan; LoBianco, Tom (October 23, 2015) "Lincoln Chafee drops out of Democratic primary race", CNN.com. Retrieved October 23, 2015
- ^ Walsh, Michael (October 20, 2015) "Jim Webb drops out of Democratic primary race", Yahoo! Politics. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- ^ Healy, Patrick (April 23, 2016). "Hillary Clinton's Campaign, Cautious but Confident, Begins Considering Running Mates". The New York Times. Retrieved April 23, 2016.
- ^ Matthews, Dylan (June 16, 2016). "Hillary Clinton's VP shortlist has leaked. Here are the pros and cons of each". Vox. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- ^ a b Gearan, Anne (July 19, 2016). "Two names emerge from Clinton's VP deliberations: Kaine and Vilsack". Washington Post. Retrieved July 20, 2016.
- ^ Gearan, Anne; Wagner, John (July 22, 2016). "Sen. Timothy M. Kaine of Virginia chosen as Hillary Clinton's VP". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 23, 2016.
- ^ Collins, Eliza (January 6, 2016). "Libertarian Gary Johnson launches presidential bid". Politico. Retrieved January 6, 2016.
- ^ "Gary Johnson U.S. FEC filing" (PDF). Federal Election Commission. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "New Hampshire Secretary of State Says Jill Stein Petition is Valid". ballot-access.org. Retrieved September 2, 2016.
- ^ a b "Ballot Access". gp.org. Archived from the original on May 5, 2016. Retrieved June 19, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (August 11, 2016). "Jill Stein Qualifies for Write-in Status in North Carolina; No Other Write-in Presidential Candidate Does So". Ballot Access News. Retrieved August 20, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (August 10, 2016). "Rocky De La Fuente and Jill Stein File Oklahoma Ballot Access Case". Ballot Access News. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ "Nevada Green Party Loses Ballot Access Lawsuit". ballot-access.org. Retrieved September 2, 2016.
- ^ "Exclusive: Green Party's Jill Stein Announces She Is Running for President on Democracy Now!". Democracy Now!. June 22, 2015. Retrieved May 18, 2016.
- ^ "Green Party candidate Jill Stein announces VP running mate". August 1, 2016. Retrieved August 1, 2016.
- ^ a b McMullin, Evan. "34 States and Counting". Evan McMullin for President. Rumpf, Sarah. Retrieved October 2, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e "November 8, 2016, General Election Certified List of Write-In Candidates" (PDF). elections.cdn.sos.ca.gov. California Secretary of State. October 28, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "REGISTERED WRITE-IN CANDIDATES NOVEMBER 8, 2016" (PDF). sots.ct.gov. Connecticut Secretary of State. October 28, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "2016 General Election Write-In Presidential Candidates" (PDF). sos.ks.gov. Kansas Secretary of State. October 31, 2016. Retrieved November 2, 2016.
- ^ a b c Winger, Richard (October 31, 2016). "Missouri Secretary of State Releases List of Presidential Write-in Candidates". Ballot Access News. Retrieved November 2, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Official Write-In Candidates for President" (PDF). www.elections.ny.gov. New York State Board of Elections. October 24, 2016. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
- ^ a b c Winger, Richard (October 20, 2016). "Six Write-in Presidential Candidates File to Have North Dakota Write-ins Counted". ballot-access.org. Ballot Access News. Retrieved October 20, 2016.
- ^ Strauss, Daniel (September 7, 2016). "Whoops: Independent candidate appears to have accidentally picked a running mate". Politico. Retrieved November 16, 2016.
- ^ "Anti-Trump Republican Launching Independent Presidential Bid". BuzzFeed. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- ^ a b c "Ballot access | The Constitution Party". www.constitutionparty.com. Retrieved October 3, 2016.
- ^ a b Winger, Richard (September 7, 2016). "North Dakota Says All Three Independent Presidential Petitions are Valid". Ballot Access News.
- ^ a b c d e f "2016 Election Information". azsos.gov. Arizona Secretary of State. Retrieved September 28, 2016.
- ^ a b c Kemp, Brian (September 12, 2016). "Qualifying Candidate Information". sos.ga.gov. Georgia Secretary of State. Retrieved September 13, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "2016 Candidate Listing". elections.state.md.us. Maryland State Board of Elections. 2016. Retrieved September 21, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g "2016 Certification of Write-in Candidates - President and Vice President" (PDF). Virginia Department of Elections. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ "Constitution Party Nominates Darrell Castle and Scott Bradley". April 16, 2016. Retrieved August 23, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (September 1, 2016). "September 2016 Ballot Access News Print Edition". Ballot Access News. p. 5. Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ^ "Eight Presidential Candidates will be on Mississippi ballot". ballot-access.org. September 9, 2016.
- ^ "New Hampshire Says Rocky De La Fuente Has Enough Valid Signatures". ballot-access.org. Retrieved September 8, 2016.
- ^ a b "Federal Nominations filed for the 2016 General Election". elections.ny.gov. New York State Board of Elections. August 11, 2016. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- ^ "Rhode Island Secretary of State Says Three Independent Presidential Petitions Have Enough Valid Signatures". Ballot Access News. Retrieved September 9, 2016.
- ^ "Wyoming Says Jill Stein and Rocky De La Fuente Have Enough Valid Signatures". Ballot Access News. Retrieved September 8, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y Winger, Richard (July 1, 2016). "Ballot Access News". ballot-access.org. p. 4. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
States that allow write-ins in the general election, and don't have write-in filing laws, are legally obliged to count all write-ins: Alabama, Iowa, New Hampshire, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, and Vermont.... Only one state, South Carolina, has a law that says that although write-ins in general elections are permitted, they are not permitted for president.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Declared Write-In Candidates, November 8, 2016 General Election" (PDF). elections.delaware.gov. Delaware Department of Elections. 2016. Retrieved September 21, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g "2016 General Election Candidate Abbreviated List" (PDF). www.in.gov. Indiana Secretary of State Election Division. August 22, 2016. Retrieved October 11, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (November 1, 2016). "Missouri Secretary of State Adds Rocky De La Fuente to the List of Declared Write-in Presidential Candidates". ballot-access.org. Ballot Access News. Retrieved November 1, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g Roza, Tony (2016). "Nebraska 2016 General Election". thegreenpapers.com. Retrieved November 2, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x "Ballot access requirements for presidential candidates in Oregon". ballotpedia.org. Ballotpedia. Retrieved October 20, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Official List of Write-In Candidates for the 2016 General Election" (PDF). sos.wa.gov. Washington Secretary of State. Retrieved October 18, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Write-In Candidate Listing" (PDF). sos.wv.gov. West Virginia Secretary of State. 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (August 13, 2016). "Peace & Freedom Party Nominates Gloria LaRiva for President". Ballot Access News. Retrieved August 13, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (May 15, 2016). "Liberty Union Party of Vermont Nominates Gloria La Riva for President". Ballot Access News. Retrieved May 16, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Winger, Richard (September 1, 2016). "September 2016 Ballot Access News Print Edition". ballot-access.org. p. 6. Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ^ a b c d "Candidate Listing". elections.myflorida.com. Florida Department of State, Division of Elections. 2016. Retrieved September 13, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Tony Roza, ed. (2016). "Minnesota 2016 General Election". thegreenpapers.com. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- ^ "Workers World Party Nominates Monica Moorehead for President". November 9, 2015. Retrieved August 2, 2016.
- ^ Hudnall, David. "Durham's Lamont Lilly is Running for Vice President (of the United States)". Retrieved August 2, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "2016 November General Write-In List" (PDF). sos.idaho.gov. Idaho Secretary of State. October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 13, 2016.
- ^ a b Tony Roza, ed. (2016). "Massachusetts 2016 General Election". thegreenpapers.com. Retrieved October 20, 2016.
- ^ a b c d Winger, Richard (November 2, 2016). "Michigan List of Declared Write-in Presidential Candidates". ballot-access.org. Ballot Access News. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Jorden, Henry (October 5, 2016). "2016 General Election Official State-Filed Write-In Candidates" (PDF). sos.mt.gov. Montana Secretary of State. Retrieved October 20, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g Pietenpol, Laura (October 3, 2016). "Ohio 2016 General Election Candidates List". sos.state.oh.us. Ohio Secretary of State. Retrieved October 5, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e "2016 Write-in Certificate with New Presidential Write-in" (PDF). sos.state.tx.us. Texas Secretary of State. 2016. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
- ^ "Natural Law Party of Michigan Nominates Socialist Party National Ticket | Ballot Access News". Ballot-access.org. Retrieved August 2, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (October 17, 2015). "Socialist Party National Ticket Nominated". Ballot Access News. Retrieved October 17, 2015.
- ^ Winger, Richard (September 26, 2016). "Socialist Party is Only Party, Besides Republicans and Democrats, to File for Guam Advisory Presidential Vote". ballot-access.org. Ballot Access News. Retrieved September 26, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e "2016 Candidate Fillings". elections.utah.gov. Utah Lieutenant Governor. 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f "Registered Write-in Candidates for November 8, 2016" (PDF). elections.wi.gov. Wisconsin Elections Commission. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 23, 2016. Retrieved October 19, 2016.
- ^ a b "Prohibition Party Nominates National Ticket". Ballot Access News. July 31, 2015. Retrieved August 3, 2015.
- ^ "James Hedges FEC Filing" (PDF). Federal Election Commission. October 27, 2015. Retrieved October 30, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g "November 8, 2016 General Election Candidate List". elections.alaska.gov. State of Alaska Division of Elections. 2016. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Election Candidate Filings - President of the United States". apps.sos.ky.gov. Retrieved October 5, 2016.
- ^ Husted, Jon (August 24, 2016). "Husted Announces Independent Candidates for President and Vice President". sos.state.oh.us. Ohio Secretary of State. Retrieved September 12, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (September 19, 2016). "Georgia Secretary of State Now Says Laurence Kotlikoff May be a Declared Write-in Presidential Candidate". ballot-access.org. Ballot Access News. Retrieved September 21, 2016.
- ^ a b c "November 8, 2016 Write-in Candidates". cookcountyclerk.com. Cook County Clerk. 2016. Retrieved October 11, 2016.
- ^ "List of Declared Write-in Candidates for the General Election". maine.gov. Maine Bureau of Corporations, Elections & Commissions. September 9, 2016. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
- ^ a b Summers, Kathy (October 4, 2016), "Certified Write-In Candidates for United States President November 8, 2016", sos.tn.gov, Tennessee Secretary of State, retrieved October 4, 2016
- ^ Ziggler, Jed (January 1, 2016). "Tom Hoefling Announces 2016 Presidential Campaign". Independent Political Report. Retrieved January 15, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (September 26, 2016). "Arkansas Secretary of State Removes Tom Hoefling from Ballot for President". ballot-access.org. Ballot Access News. Retrieved September 26, 2016.
- ^ "Chris Keniston 2016". Chris Keniston 2016.
- ^ "Veterans Party of America". Veterans Party of America.
- ^ a b c d e f g Wayne Williams, ed. (August 31, 2016). "2016 General Election Candidate List". sos.state.co.us. Colorado Secretary of State. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (June 1, 2016). "American Party of South Carolina Nominates Peter Skewes for President". Ballot Access News. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- ^ Silva, Rod (October 20, 2015). "FEC Form 2: Statement of Candidacy" (PDF). fec.gov. Retrieved December 22, 2015.
- ^ Silva, Rod. "My fellow Americans". Rod Silva for President 2016. Retrieved December 22, 2015.
- ^ a b Tom Schedler, ed. (2016). "Candidate Inquiry". sos.la.gov. Louisiana Department of State. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ "2016 November General Candidate List" (PDF). sos.idaho.gov. Idaho Secretary of State. September 1, 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ Camia, Catalina; Moore, Martha A. (February 12, 2015). "Democrats pick Philadelphia for 2016 convention". USA Today. Retrieved February 12, 2015.
- ^ "RNC officially approves Cleveland as 2016 convention host". CBS News. August 8, 2014. Retrieved August 14, 2014.
- ^ Isenstadt, Alex (January 14, 2014). "GOP convention set for July 18–21 in 2016". Politico. Retrieved January 15, 2015.
- ^ Winger, Richard (July 11, 2014). "Libertarian Party Moves into National Party Headquarters That it Owns". Ballot Access News. Retrieved July 11, 2014.
- ^ "Libertarian National Committee Minutes July 15–16, 2012". Libertarian National Committee. p. 4. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 2, 2016. Retrieved July 11, 2014.
- ^ Winger, Richard (August 2, 2015) "Green Party Will Hold Presidential Convention in Houston", Ballot Access News. Retrieved August 5, 2015.
- ^ "Houston, We Have a Solution – Vote Green 2016". Green Party of the United States. April 4, 2016. Archived from the original on May 10, 2016. Retrieved May 11, 2016.
- ^ Mills, Glen (April 14, 2016) "The Constitution Party hosts national convention in Salt Lake City", Good4Utah. Retrieved September 14, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Presidential Race". OpenSecrets.org. Center for Responsive Politics. Retrieved February 26, 2016.
- ^ "Summary data for Hillary Clinton, 2016 Cycle". opensecrets.org. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P00003392". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Summary data for Donald Trump, 2016 Cycle". opensecrets.org. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P80001571". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Summary data for Gary Johnson, 2016 Cycle". opensecrets.org. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P20002671". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P60016342". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Summary data for Jill Stein, 2016 Cycle". opensecrets.org. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Committee ID: C00581199". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P60022654". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P60021102". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P80005572". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Committee ID: C00607788". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ "Details for Candidate ID: P60012960". fec.gov. Federal Election Commission. 2016. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^ Editorial Board (September 24, 2016). "Hilary Clinton for President". The New York Times. Retrieved September 24, 2016.
- ^ Politico staff (September 23, 2016). "LA Times endorses Clinton, bashes Trump". Politico. Retrieved September 24, 2016.
- ^ a b Lim, Naomi (August 1, 2016). "Hillary Clinton endorsed by Houston Chronicle, Trump 'danger to the Republic'". CNN.
- ^ "Editorial: In battle for America's soul, Hillary Clinton is our pick". The San Jose Mercury News. October 21, 2016.
- ^ "Editorial: Vote for Clinton and avert a train wreck". Chicago Sun-Times. Retrieved September 30, 2016.
- ^ "Daily News Editorial Board says Vote Hillary Clinton: She's the best choice for President, while Donald Trump represents a clear and present danger to the republic". Daily News. New York. July 28, 2016.
- ^ Diaz, John (October 7, 2016). "Trump strikes out on newspaper endorsements". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- ^ Hod, Italy. "Donald Trump Makes History With Zero Major Newspaper Endorsements". Yahoo News. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- ^ Cannon, Carl (May 9, 2016). "Trump's tabloid". RealClearPolitics.com. Retrieved May 15, 2016.
- ^ "Editorial:Donald Trump for president". Las Vegas Journal-Review. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- ^ "We recommend Hillary Clinton for president". The Dallas Morning News. September 6, 2016.
- ^ "Endorsement Why Hillary Clinton is the safe choice for president". U-T San Diego. September 30, 2016.
- ^ "For president: Trump unfit, Clinton is qualified". The Columbus Dispatch. Retrieved October 9, 2016.
- ^ The Arizona Republic Editorial Board (September 27, 2016). "Endorsement: Hillary Clinton is the only choice to move America ahead".
- ^ "Campaign 2016 updates: Another newspaper that has long backed GOP candidates bucks Donald Trump" – via LA Times.
- ^ "USA TODAY's Editorial Board: Trump is 'unfit for the presidency'".
- ^ "The Case for Hillary Clinton And Against Donald Trump". October 5, 2016.
- ^ Diaz, Daniella; Spodak, Cassie (September 14, 2016). "Union Leader breaks with 100-year tradition, endorses Gary Johnson". CNN. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ^ "Endorsement: Libertarian Gary Johnson for president". Retrieved October 6, 2016.
- ^ "Editorial: A principled option for U.S. president: Endorsing Gary Johnson, Libertarian". Chicago Tribune. September 30, 2016. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- ^ Greenslade, Roy (October 26, 2016). "Breitbart takes centre stage as Donald Trump embraces the alt-right". The Guardian. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- ^ Stegmaier, Mary; Norpoth, Helmut (September 30, 2013). "Election forecasting". doi:10.1093/obo/9780199756223-0023. Retrieved September 26, 2016.
- ^ Lichtman, Allan (1996). The Keys to the White House. Madison Books. ISBN 1568330618.
- ^ "Who will be president? How Other Forecasts Compare". The New York Times. Retrieved September 26, 2016.
- ^ Skibba, Ramin. "Pollsters struggle to explain failures of US presidential forecasts". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2016.20968.
- ^ Graefe, Andreas (November 9, 2016). "A terrible day for election forecasters. Where are the winners?". pollyvote.com. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ Alp Toker [@atoker] (November 8, 2016). "Looking for trends in @nytimes's presidential forecast needle? Don't look too hard - the bounce is random jitter from your PC, not live data" (Tweet) – via Twitter. in McCormick, Rich (November 8, 2016). "The NYT's election forecast needle is stressing people out with fake jitter". The Verge. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ "The Fake Twitchy Hell Dials of the Times' Forecast Only Made Last Night Worse". New York Magazine. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ "The Commission on Presidential Debates: An Overview", Debates.org.
- ^ Hulsey, Lynn (July 19, 2016). "Hofstra University offers debate spots for WSU students". Dayton Daily News. Retrieved July 21, 2016.
- ^ Flores, Reena. "Campaign manager: Trump will attend all three presidential debates". CBS News. Retrieved August 19, 2016.
- ^ "CPD Announces 2016 Debate Host Applicants". Commission on Presidential Debates. Retrieved April 2, 2015.
- ^ Sanchez, Stephen M. "Three Texas Locations Vie For 2016 Presidential Debates". San Antonio Daily News. Archived from the original on April 3, 2015. Retrieved April 2, 2015.
- ^ "Commission on Presidential Debates announces sites and dates for 2016 general election debates". Commission on Presidential Debates. Retrieved September 23, 2015.
- ^ Lima, Cristiano (July 29, 2016). "Trump wants three presidential debates, accuses Clinton of rigging schedule". Politico. Retrieved July 30, 2016.
- ^ "Voters See Debate Moderators Giving Clinton A Helping Hand". Rasmussen Reports. September 26, 2016.
- ^ Winger, Richard (October 6, 2015). "Free and Equal Announces Date and Location for General Election Presidential Debate". Ballot Access News. Retrieved May 17, 2016.
- ^ "UWS Festival". freeandequal.org. Free & Equal Elections Foundation. 2016. Retrieved October 20, 2016.
- ^ "United We Stand Festival & People's Presidential Debate Live Now from Boulder, CO!". Free & Equal Elections Foundation. October 25, 2016. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- ^ "Gary Johnson, Jill Stein debate on Tavis Smiley show". Independent Political Report. Retrieved November 17, 2016.
- ^ "It's All Over But The Voting, As Trump And Clinton Cast Their Ballots". NPR.org. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ "Frank Luntz: Ban exit polls". Politico. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ "Live Coverage: Election Night 2016". Kansas Public Radio. November 8, 2016. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ Martosko, David (November 9, 2016). "Conway: Huma Abedin placed the call when Clinton conceded to Trump". Mail Online. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ Rappeport, Alan; Burns, Alexander (November 9, 2016). "Highlights of Hillary Clinton's Concession Speech and President Obama's Remarks". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ Flegenheimer, Matt; Barbaro, Michael (November 9, 2016). "Donald Trump Is Elected President in Stunning Repudiation of the Establishment". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved November 18, 2016.
- ^ a b "2016 November General Election Turnout Rates". www.electproject.org. Retrieved November 15, 2016.
- ^ "U.S. Electoral College: The 2016 Presidential Election". National Archives and Records Administration. 2016. Archived from the original on September 20, 2016. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "How did the polls get it wrong?". The Economist. November 9, 2016. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ "Donald Trump's Victory Is Met With Shock Across a Wide Political Divide". The New York Times. November 9, 2016. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ Arkin, Daniel; Siemaszko, Corky (November 9, 2016). "2016 Election: Donald Trump Wins the White House in Upset". NBC News. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ "How Donald Trump swept to an unreal, surreal presidential election win". Guardian. November 9, 2016. Retrieved November 9, 2016.
- ^ "Almost 80 per cent of voters believe the media's coverage of the election was biased". DailyMail. November 15, 2016.
- ^ "State of Maine Certificate of Ascertainment of Electors" (PDF). Retrieved December 18, 2012.
- ^ "Official Results of Nebraska General Election – November 6, 2012" (PDF). Retrieved December 26, 2012.
- ^ "2016 U.S. General Election". Associated Press. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ Abramowitz, Alan (August 2, 2012). "Do Presidential Campaigns Matter? Evidence From the 2008 Election". Sabato's Crystal Ball. Retrieved November 8, 2014.
- ^ Silver, Nate (June 29, 2016). "2016 Election Forecast - FiveThirtyEight".
- ^ "Who Will Be President?". The New York Times. August 30, 2016.
- ^ "The 2016 Results We Can Already Predict". POLITICO Magazine. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Presidential Election Interactive Map". 270toWin.com. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ "Larry J. Sabato's Crystal Ball » The Electoral College: The Only Thing That Matters". www.centerforpolitics.org. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ Levin, Sam (March 21, 2016). "Why Mormons in America's most conservative state could turn a Trump stronghold questionably Democratic". the Guardian. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ Roche, Lisa Riley (March 20, 2016). "Poll: Utah would vote for a Democrat for president over Trump". DeseretNews.com. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ Frum, David. "The Great Republican Revolt". Retrieved August 3, 2016.
- ^ Doherty, Brendan (July 31, 2012). "President Obama's Disproportionate Battleground State Focus Started Early, Echoed Predecessors' Actions". Monkey Cage. Retrieved November 4, 2014.
- ^ Yglesias, Matthew (November 8, 2014). "A totally legal, totally shady way that Republicans could ensure Hillary Clinton's defeat". Vox. Retrieved November 8, 2014.
- ^ Haberman, Maggie (July 30, 2016). "Electoral Map Gives Donald Trump Few Places to Go". The New York Times. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ^ Challan, David (July 20, 2016). "Road to 270: CNN's new electoral college map". CNN. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ^ Balz, Dan (January 18, 2014). "The Republican Party's uphill path to 270 electoral votes in 2016 elections". The Washington Post. Retrieved October 3, 2014.
- ^ Villa, Lissandra (July 10, 2016). "Why Utah Doesn't Like Donald Trump". Time. Retrieved July 18, 2016.
- ^ "Hillary Clinton's path to victory". Retrieved August 3, 2016.
- ^ Kondik, Kyle; Skelley, Geoffrey; Sabato, Larry (May 3, 2015). "The 2016 Results We Can Already Predict". Politico. Retrieved September 22, 2015.
- ^ Charles E. Cook, Jr, ed. (November 7, 2016). "2016 Electoral Vote Scorecard". cookpolitical.com. Cook Political Report. Retrieved November 7, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Battle for White House". realclearpolitics.com. RealClear Media Group. November 6, 2016. Retrieved November 7, 2016.
- ^ "Presidential Ratings". rothenberggonzales.com. The Rothenberg & Gonzales Political Report. November 7, 2016. Retrieved November 7, 2016.
- ^ "The Crystal Ball's 2016 Electoral College ratings". www.centerforpolitics.org. University of Virginia Center for Politics. November 7, 2016. Retrieved November 7, 2016.
- ^ "Across The Country, Thousands March In Protest Against Trump's Victory : The Two-Way". NPR. November 9, 2016. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ y Scott Calvert; Cameron McWhirter (November 11, 2016). "Anti-Trump Protests Likely to Continue Friday and Saturday". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Leah Sottile; Samantha Schmidt; Brian Murphy (November 11, 2016). "As anti-Trump anger feeds protests and violence, Obama echoes appeals for unity". The Washington Post.
- ^ Matesic, Emily (November 11, 2016). "Presidential politics leading some to seek mental health help". wbay.com. Retrieved November 16, 2016.
- ^ "At suicide hotlines, the first 24 hours of Trump's America have been full of fear". tampabay.com. Retrieved November 16, 2016.
- ^ Dentzer, Bill (November 15, 2016). "Electoral College: Are Idaho's 4 electors being pressured to dump Trump, or harassed?". The Idaho Statesman.
- ^ Kruesi, Kimberlee (November 21, 2016). "Trump opponents' campaign to beat him at the Electoral College is a long shot". Associated Press.
- ^ "exit polls". CNN. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ "Election 2016: Exit Polls". The New York Times. Retrieved November 10, 2016.
- ^ "Presidential Results". NBC News. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
External links
- Presidential election process from USA.gov, the official United States Federal Government web portal
- Template:Dmoz
- 2016 Presidential Form 2 Filers at the Federal Election Commission (FEC)
- Hillary Clinton's Concession Speech on YouTube