Hurricane-proof building
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2008) |
Tornadoes, cyclones, and other storms with strong winds damage or destroy many buildings. However, with proper design and construction, the damage to buildings by these forces can be greatly reduced. A variety of methods can help a building survive strong winds and storm surge.
Storm surge considerations
Waves along coastal areas can destroy a building. Buildings should preferably be built on high ground in order to avoid waves. If waves can reach the building site, the building ought to be elevated on steel, concrete, or wooden pilings or anchored to solid rock. By Kyirannne-Kacey Martin-Guzman and Wilkeisi-Ann Martin-Guzman
Wind loading considerations
The foundation

Wind acting on the roof surfaces of a building can cause negative pressures that create a lifting force sufficient to lift the roof off the building. Once this occurs, the building is weakened considerably and the rest of the building will likely fail as well. To minimize this vulnerability, the upper structure ought to be anchored through the walls to the foundation.
Several methods can be used to anchor the roof. Typically, roof trusses are "toenailed" into the top of the walls, which provide insufficient force to resist high winds. Hurricane ties nail into the wall and wrap over the trusses provide higher force resistance.
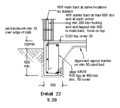
Mobile home tie down to the foundation
Interlocking metal pan roof systems installed on mobile homes can fail under the pressure differential (lift) created by the high velocity winds passing over the surface plane of the roof. This is compounded by the wind entering the building allowing the building interior to pressurize lifting the underside of the roof panels, resulting in destruction of the building. One example of pan roof systems can be found in this document from Structall Building Systems.
To mitigate this pressure differential, pre-installed aluminum tabular channels can permanently be fastened perpendicularly across the top of the interlocking ribs of the metal roof system without disturbing the flow of rainwater at the eaves, mid-span, and ridge locations of the building.
Earth sheltering
Earth sheltered construction is generally more resistant to strong winds and tornadoes than standard construction. Cellars and other earth sheltered components of other buildings, can provide safe refuge during tornadoes.
Dome homes
The physical geometry of a building affects its aerodynamic properties and how well it can withstand a storm. Geodesic dome roofs or buildings have low drag coefficients and can withstand higher wind forces than a square building of the same area.[1][2] Even stronger buildings result from monolithic dome construction.[3]
Building components
Building openings such as garage doors and windows are often weak points susceptible to failure by wind pressure and blowing debris. Once failure occurs, wind pressure builds up inside the building resulting in the roof lifting off the building. Hurricane shutters can provide protection.
Doors can be blown into the house by wind causing potential structural failure (see http://www.floridadisaster.org/hrg/content/openings/openings_index.asp#Hinged_Exterior_Doors). Some doors can resist high winds[citation needed]
Windows can be constructed with plastic panes, shatterproof glass, or glass with protective membranes. The panes are often more firmly attached than normal window panes, including using screws or bolts through the edges of larger panes. Tapcons are used to fasten windows with the concrete structure surrounding.
Wood has a relatively high degree of flexibility which can be beneficial under certain building stresses.
Reinforced concrete is a strong, dense material that, if used in a building that is designed properly, can withstand the destructive power of very high winds, and high-speed debris.
Regulation
After Hurricane Andrew in 1992 caused $16 billion in insured damage, the state of Florida established new building standards and enforcement. The state increased performance criteria for wind-load provisions and adopted new wind provisions from the American Society of Civil Engineers. One important addition included with the new code was the requirement of missile-impact resisting glass, which can withstand high velocity impact from wind-borne debris during a hurricane. Many houses built in South Florida since Hurricane Andrew are cinder block masonry construction reinforced with concrete pillars, hurricane-strapped roof tresses, and codes requirements for adhesives and types of roofing.[4][5] Florida also has a zone designed Florida HVHZ (High Velocity Hurricane Zone) with special requirements defined as Miami-Dade and Broward Counties.[6]
Hong Kong requires many structures to withstand winds from typhoons.[7]
Examples of cyclonic construction methods
Residential construction in Darwin Northern Australia
-
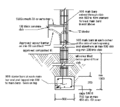
Starter bars cast into concrete slab for blockwork wall reinforcing,
-
Detail of reinforcing steel at edge of concrete raft slab
-
16mm Cast in hold down bolts. 150 to 300 long cast into blockwork bond beams
-
HD bolt to truss connection. also seen, metal roof batten fixing, speedbrace end fixing.
-
Typical roof member connector straps.
-
Internal mig welded shearwalls
-
Shearwall to slab connection, M12 chemsets through 6 plate washers, typ. at ends and 900ctrs.
-
Sketch of 200 series reinforced blockwork fence wall. Terrain category 3 (close to sea front)
-
Sketch of typical foundation layout for sloping ground.
See also
- Bubble Houses (Hobe Sound, Florida)
- Dymaxion house
- Hurricane preparedness
- HurriQuake nail (for resisting hurricanes and earthquakes)
- Structural design
- Structural engineering
- Windstorm inspection
- Hurricane shutter
References
Notes
- ^ http://www.stanford.edu/~scheulen/.../StructuralMechanicsFinalReport.pdf
- ^ http://www.ewb-uk.org/system/files/Marek+Kubik+report.pdf
- ^ http://www.monolithic.com/stories/building-survivability-the-strength-of-the-monolithic-dome
- ^ "Fla. Building Codes, Revamped Since Andrew, Still Being Worked". Insurance Journal. 2007-05-18. Retrieved 2016-10-09.
- ^ Tsikoudakis, Mike. "Hurricane Andrew prompted better building code requirements - Business Insurance". Business Insurance. Retrieved 2016-10-09.
- ^ "Changes to the Wind Speed Maps and Wind Design – 2010 Florida Building Codes" (PDF). Retrieved Oct 9, 2016.
- ^ Phil Muncaster (September 30, 2013). "Hong Kong's data centres stay high and dry amid Typhoon Usagi". The Register. Retrieved January 5, 2015.