Osaka
Osaka
大阪市 | |
|---|---|
| City of Osaka | |
 Night view from Umeda Sky Building Dōtonbori and Tsūtenkaku Shitennō-ji, Sumiyoshi taisha and Osaka Castle | |
 Location of Osaka in Osaka Prefecture | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kansai |
| Prefecture | Osaka Prefecture |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Hirofumi Yoshimura (ORA) |
| Area | |
| 223.00 km2 (86.10 sq mi) | |
| Population (January 1, 2012) | |
| 2,668,586 (3rd) | |
| • Metro | 19,341,976 (2nd) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| - Tree | Cherry |
| - Flower | Pansy |
| Phone number | 06-6208-8181 |
| Address | 1-3-20 Nakanoshima, Kita-ku, Ōsaka-shi, Ōsaka-fu 530-8201 |
| Website | www |


Osaka (大阪市, Ōsaka-shi) (Template:IPA-ja; ⓘ) is a designated city in the Kansai region of Japan. It is the capital city of Osaka Prefecture and the largest component of the Keihanshin Metropolitan Area, the second largest metropolitan area in Japan and among the largest in the world with over 19 million inhabitants (only after Tokyo). Situated at the mouth of the Yodo River on Osaka Bay, Osaka is the second largest city in Japan by daytime population after Tokyo's 23 wards and the third largest city by nighttime population after Tokyo's 23 wards and Yokohama, serving as a major economic hub for the country.
Historically a merchant city, Osaka has also been known as the "nation's kitchen" (天下の台所, tenka no daidokoro) and served as a center for the rice trade during the Edo period.[1][2][3][4]
History
Prehistory to the Kofun period
Some of the earliest signs of human habitation in the Osaka area at the Morinomiya ruins (森ノ宮遺跡, Morinomiya iseki) comprise shell mounds, sea oysters and buried human skeletons from the 5th–6th centuries BC. It is believed[by whom?] that what is today the Uehonmachi area consisted of a peninsular land with an inland sea in the east. During the Yayoi period, permanent habitation on the plains grew as rice farming became popular.[1]
By the Kofun period, Osaka developed into a hub port connecting the region to the western part of Japan. The large numbers of increasingly larger tomb mounds found in the plains of Osaka are seen as evidence of political-power concentration, leading to the formation of a state.[1][5]
Asuka and Nara period
The Kojiki records that during 390–430 AD there was an imperial palace located at Osumi, in what is present day Higashiyodogawa ward, but it may have been a secondary imperial residence rather than a capital.[6]
In 645, Emperor Kōtoku built his Naniwa Nagara-Toyosaki Palace in what is now Osaka,[7] making it the capital of Japan. The city now known as Osaka was at this time referred to as Naniwa, and this name and derivations of it are still in use for districts in central Osaka such as Naniwa (浪速) and Namba (難波).[8] Although the capital was moved to Asuka (in Nara Prefecture today) in 655, Naniwa remained a vital connection, by land and sea, between Yamato (modern day Nara Prefecture), Korea, and China.[1][9]
Naniwa was declared the capital again in 744 by order of Emperor Shōmu, and remained so until 745, when the Imperial Court moved back to Heijō-kyō (now Nara). By the end of the Nara period, Naniwa's seaport roles had been gradually taken over by neighboring areas, but it remained a lively center of river, channel, and land transportation between Heian-kyō (Kyoto today) and other destinations.
Heian to Edo period
In 1496, Jōdo Shinshū Buddhists established their headquarters in the heavily fortified Ishiyama Hongan-ji, located directly on the site of the old Naniwa Imperial Palace. Oda Nobunaga began a decade-long siege campaign on the temple in 1570 which ultimately resulted in the surrender of the monks and subsequent razing of the temple. Toyotomi Hideyoshi constructed Osaka Castle in its place in 1583.[10]
Osaka was long considered Japan's primary economic center,[11] with a large percentage of the population belonging to the merchant class (see Four divisions of society). Over the course of the Edo period (1603–1867), Osaka grew into one of Japan's major cities and returned to its ancient role as a lively and important port. Its popular culture[12] was closely related to ukiyo-e depictions of life in Edo. By 1780 Osaka had cultivated a vibrant arts culture, as typified by its famous Kabuki and Bunraku theaters.[13] In 1837 Ōshio Heihachirō, a low-ranking samurai, led a peasant insurrection in response to the city's unwillingness to support the many poor and suffering families in the area. Approximately one-quarter of the city was razed before shogunal officials put down the rebellion, after which Ōshio killed himself.[14] Osaka was opened to foreign trade by the government of the Bakufu at the same time as Hyōgo (modern Kobe) on 1 January 1868, just before the advent of the Boshin War and the Meiji Restoration.[15]
Osaka residents were stereotyped in Edo literature from at least the 18th century. Jippenisha Ikku in 1802 depicted Osakans as stingy almost beyond belief. In 1809 the derogatory term "Kamigata zeeroku" was used by Edo residents to characterize inhabitants of the Osaka region in terms of calculation, shrewdness, lack of civic spirit, and the vulgarity of Osaka dialect. Edo writers aspired to samurai culture, and saw themselves as poor but generous, chaste, and public spirited. Edo writers by contrast saw "zeeroku" as obsequious apprentices, stingy, greedy, gluttonous, and lewd. To some degree, Osaka residents are still stigmatized by Tokyo observers in the same way today, especially in terms of gluttony, evidenced in the phrase, "Residents of Osaka devour their food until they collapse" (大阪は食倒れ, "Ōsaka wa kuidaore").[16]
19th century to present

The modern municipality was established[17] in 1889 by government ordinance, with an initial area of 15 square kilometres (6 sq mi), overlapping today's Chūō and Nishi wards. Later, the city went through three major expansions to reach its current size of 223 square kilometres (86 sq mi). Osaka was the industrial center most clearly defined in the development of capitalism in Japan. It became known as the "Manchester of the Orient."[10]
The rapid industrialization attracted many Korean immigrants, who set up a life apart for themselves.[18] The political system was pluralistic, with a strong emphasis on promoting industrialization and modernization.[19] Literacy was high and the educational system expanded rapidly, producing a middle class with a taste for literature and a willingness to support the arts.[20] In 1927, General Motors operated a factory called Osaka Assembly until 1941, manufacturing Chevrolet, Pontiac, Oldsmobile, and Buick vehicles, operated and staffed by Japanese workers and managers.[21] In the nearby city of Ikeda in Osaka Prefecture is the headquarters office of Daihatsu, Japan's oldest automobile manufacturer.
Like its European and American counterparts, Osaka displayed slums, unemployment, and poverty. In Japan it was here that municipal government first introduced a comprehensive system of poverty relief, copied in part from British models. Osaka policymakers stressed the importance of family formation and mutual assistance as the best way to combat poverty. This minimized the cost of welfare programs.[22]
During World War II, Osaka came under air attacks in 1945 by the United States Army Air Forces as part of the air raids on Japan. On March 13, 1945, a total of 329 Boeing B-29 Superfortress heavy bombers took part in the raid against Osaka. According to an American prisoner of war who was held in the city, the air raid took almost the entire night and destroyed 25 square miles (65 km2) of the city. The U.S. bombed the city again twice in June 1945 and again on August 14, a day before Japan's surrender.[23]
Etymology
"Osaka" literally means "large hill" or "large slope". It is unclear when this name gained prominence over Naniwa, but the oldest written evidence for the name dates back to 1496.
The name is now written 大阪 in kanji, but it was written 大坂 until 1870, when the partisans for the Meiji Restoration changed it, apparently to avoid the second kanji being misinterpreted as 士反, meaning "samurai rebellion". The older kanji is still in very limited use, usually in historical contexts, but in Japanese the kanji 阪—pronounced han when standing alone—now refers exclusively to Osaka City or Osaka Prefecture.
Geography and climate
Geography
The city's west side is open to Osaka Bay, and is otherwise completely surrounded by more than ten satellite cities, all of them in Osaka Prefecture, with one exception: the city of Amagasaki, belonging to Hyōgo Prefecture, in the northwest. The city occupies a larger area (about 13%) than any other city or village within Osaka Prefecture. When the city was established in 1889, it occupied roughly the area known today as the Chuo and Nishi wards, only 15.27 square kilometres (3,773 acres) that would eventually grow into today's 222.30 square kilometres (54,932 acres) via incremental expansions, the largest of which being a single 126.01 square kilometres (31,138 acres) expansion in 1925. Osaka's highest point is 37.5 metres (123.0 ft) Tokyo Peil in Tsurumi-ku, and the lowest point is in Nishiyodogawa-ku at −2.2 metres (−7.2 ft) Tokyo Peil.[24]
Climate
Osaka is located in the humid subtropical climate zone (Köppen Cfa), with four distinct seasons. Its winters are generally mild, with January being the coldest month having an average high of 9.3 °C (49 °F). The city rarely sees snowfall during the winter. Spring in Osaka starts off mild, but ends up being hot and humid. It also tends to be Osaka's wettest season, with the tsuyu (梅雨, tsuyu, "plum rain")—the rainy season—occurring between early June(average:Jun.7) to late July(average:Jul.21).[25] Summers are very hot and humid. In the months of July and August, the average daily high temperature approaches 35 °C (95 °F), while average nighttime temperatures typically hover around 25 °C (77 °F). Fall in Osaka sees a cooling trend, with the early part of the season resembling summer while the latter part of fall resembles winter.
| Climate data for Osaka, Osaka (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.5 (49.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13.7 (56.7) |
19.9 (67.8) |
24.5 (76.1) |
27.8 (82.0) |
31.6 (88.9) |
33.4 (92.1) |
29.3 (84.7) |
23.3 (73.9) |
17.6 (63.7) |
12.3 (54.1) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) |
6.3 (43.3) |
9.4 (48.9) |
15.1 (59.2) |
19.7 (67.5) |
23.5 (74.3) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.8 (83.8) |
25.0 (77.0) |
19.0 (66.2) |
13.6 (56.5) |
8.6 (47.5) |
16.9 (62.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 2.8 (37.0) |
2.9 (37.2) |
5.6 (42.1) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.6 (60.1) |
20.0 (68.0) |
24.3 (75.7) |
25.4 (77.7) |
21.7 (71.1) |
15.5 (59.9) |
9.9 (49.8) |
5.1 (41.2) |
13.3 (55.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 45.4 (1.79) |
61.7 (2.43) |
104.2 (4.10) |
103.8 (4.09) |
145.5 (5.73) |
184.5 (7.26) |
157.0 (6.18) |
90.9 (3.58) |
160.7 (6.33) |
112.3 (4.42) |
69.3 (2.73) |
43.8 (1.72) |
1,279 (50.35) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 1 (0.4) |
1 (0.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
3 (1.2) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 5.6 | 6.3 | 9.9 | 9.3 | 10.0 | 11.2 | 9.9 | 6.9 | 9.4 | 7.9 | 6.2 | 5.5 | 98.1 |
| Average snowy days | 5.0 | 6.3 | 2.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.9 | 15.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 61 | 60 | 59 | 59 | 62 | 68 | 70 | 66 | 67 | 65 | 64 | 62 | 64 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 142.6 | 135.4 | 159.5 | 188.6 | 194.3 | 156.2 | 182.1 | 216.9 | 156.7 | 163.9 | 148.5 | 151.6 | 1,996.4 |
| Source 1: Japan Meteorological Agency[26] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: World Meteorological Organization (rainy days)[27] | |||||||||||||
Cityscape
Osaka's sprawling cityscape has been described as "only surpassed by Tokyo as a showcase of the Japanese urban phenomenon."[28]

Neighborhoods



Central Osaka is roughly divided into downtown and uptown areas known as Kita (北, "north") and Minami (南, "south").[29][30]
Kita is home to the Umeda district and its immediate surrounding neighborhoods, a major business and retail hub that plays host to Osaka Station City and a large subterranean network of shopping arcades.[29] Kita and nearby Nakanoshima contain a prominent portion of the city's skyscrapers and are often featured in photographs of Osaka's skyline.
Minami, though meaning "south", is essentially in Chūō Ward (中央区, Chūō-ku) and geographically central within the city.[30] Well known districts here include Namba and Shinsaibashi shopping areas, the Dōtonbori canal entertainment area, Nipponbashi Den Den Town, as well as arts and fashion culture-oriented areas such as Amerikamura and Horie.
The business districts between Kita and Minami such as Honmachi and Yodoyabashi, called Semba (船場), house the regional headquarters of many large-scale banks and corporations. The Midōsuji boulevard runs through Semba and connects Kita and Minami.
Further south of Minami are neighborhoods such as Shinsekai (with its Tsūtenkaku tower), Tennoji and Abeno (with Tennoji Zoo, Shitennō-ji and Abeno Harukas), and the Kamagasaki slum, the largest slum in Japan.[31]
The city's west side is a prominent bay area[32] which serves as its main port as well as a tourist destination with attractions such as Kyocera Dome, Universal Studios Japan and the Tempozan Harbour Village. East Osaka is zoned as a separate city, although the east side of Osaka city proper contains numerous residential neighborhoods including Tsuruhashi Korea Town, as well as the Osaka Castle Park, Osaka Business Park and the hub Kyōbashi Station.
Osaka contains numerous urban canals and bridges, many of which serve as the namesake for their surrounding neighbourhoods.[33] The phrase "808 bridges of Naniwa" was an expression in old Japan used to indicate impressiveness and the "uncountable". Osaka numbered roughly 200 bridges by the Edo period [34] and 1629 bridges by 1925. As many of the city's canals were gradually filled in, the number dropped to 872, of which 760 are currently managed by Osaka City.[33]
Wards
Osaka has 24 wards (区, ku):
| Map of Osaka | ||
|---|---|---|
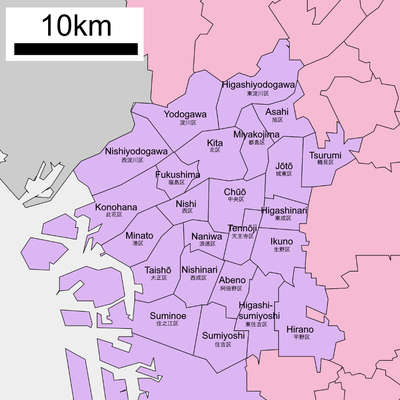 | ||
| Place Name | ||
| Rōmaji | Kanji | |
| 1 | Abeno-ku | 阿倍野区 |
| 2 | Asahi-ku | 旭区 |
| 3 | Chūō-ku | 中央区 |
| 4 | Fukushima-ku | 福島区 |
| 5 | Higashinari-ku | 東成区 |
| 6 | Higashisumiyoshi-ku | 東住吉区 |
| 7 | Higashiyodogawa-ku | 東淀川区 |
| 8 | Hirano-ku | 平野区 |
| 9 | Ikuno-ku | 生野区 |
| 10 | Jōtō-ku | 城東区 |
| 11 | Kita-ku (administrative center) | 北区 |
| 12 | Konohana-ku | 此花区 |
| 13 | Minato-ku | 港区 |
| 14 | Miyakojima-ku | 都島区 |
| 15 | Naniwa-ku | 浪速区 |
| 16 | Nishi-ku | 西区 |
| 17 | Nishinari-ku | 西成区 |
| 18 | Nishiyodogawa-ku | 西淀川区 |
| 19 | Suminoe-ku | 住之江区 |
| 20 | Sumiyoshi-ku | 住吉区 |
| 21 | Taishō-ku | 大正区 |
| 22 | Tennōji-ku | 天王寺区 |
| 23 | Tsurumi-ku | 鶴見区 |
| 24 | Yodogawa-ku | 淀川区 |
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1900 | 881,344 | — |
| 1910 | 1,239,373 | +40.6% |
| 1920 | 1,798,295 | +45.1% |
| 1930 | 2,453,573 | +36.4% |
| 1940 | 3,252,340 | +32.6% |
| 1965 | 3,156,222 | −3.0% |
| 1970 | 2,980,487 | −5.6% |
| 1975 | 2,778,987 | −6.8% |
| 1980 | 2,648,180 | −4.7% |
| 1985 | 2,636,249 | −0.5% |
| 1990 | 2,623,801 | −0.5% |
| 1995 | 2,602,421 | −0.8% |
| 2000 | 2,598,774 | −0.1% |
| 2005 | 2,628,811 | +1.2% |
| 2010 | 2,666,371 | +1.4% |
According to the census in 2005, there were 2,628,811 residents in Osaka, an increase of 30,037 or 1.2% from 2000.[35] There were 1,280,325 households with approximately 2.1 persons per household. The population density was 11,836 persons per km². The Great Kantō earthquake caused a mass migration to Osaka between 1920 and 1930, and the city became Japan's largest city in 1930 with 2,453,573 people, outnumbering even Tokyo, which had a population of 2,070,913. The population peaked at 3,252,340 in 1940, and had a post-war peak of 3,156,222 in 1965, but continued to decrease since, as the residents moved out to the suburbs.[36]
There were 99,775.5 registered foreigners, the two largest groups being Korean (71,015) and Chinese (11,848). Ikuno, with its Tsuruhashi district, is the home to one of the largest population of Korean residents in Japan, with 27,466 registered Zainichi Koreans.[37][38]
Dialect
The commonly spoken dialect of this area is Osaka-ben, a typical sub-dialect of Kansai-ben. Of the many other particularities that characterize Osaka-ben, examples include using the copula ya instead of da, and the suffix -hen instead of -nai in the negative of verbs.
Politics
| Local administration | |
|---|---|
| The Mayor and the Council | |
 Osaka City Hall | |
| Mayor: | Toru Hashimoto |
| Vice Mayors: | Akira Morishita, Takashi Kashiwagi |
| City Council | |
| President: | Toshifumi Tagaya (LDP) |
| Members: | 89 councilors (1 vacant) |
| Factions: | Liberal Democratic Party and Citizen's Club (33), Komei Party (20), Democratic Party of Japan and Citizens' Coalition (19), Japanese Communist Party (16) |
| Seats by districts: | Ward (no. of seats)
|
| Website | Osaka City Council |
| Note: As of March 10, 2009 | |
The Osaka City Council is the city's local government formed under the Local Autonomy Law. The Council has eighty-nine seats, allocated to the twenty-four wards proportional to their population and re-elected by the citizens every four years. The Council elects its President and Vice President. Toshifumi Tagaya (LDP) is the current and 104th President since May 2008. The Mayor of the city is directly elected by the citizens every four years as well, in accordance with the Local Autonomy Law. Tōru Hashimoto, former governor of Osaka Prefecture is the 19th mayor of Osaka since 2011. The mayor is supported by two Vice Mayors, currently Akira Morishita and Takashi Kashiwagi, who are appointed by him in accordance with the city bylaw.[39]
Osaka also houses several agencies of the Japanese Government. Below is a list of Governmental Offices housed in Osaka.
|
|
In July 2012, a joint multi-party bill was submitted to the Diet that would allow for implementation of the Osaka Metropolis plan as pursued by the mayor of Osaka city, the governor of Osaka and their party. If implemented, Osaka City, neighbouring Sakai City and possibly other surrounding municipalities would dissolve and be reorganized as special wards of Osaka prefecture – similar to former Tokyo City's successor wards within Tokyo prefecture. Special wards are municipal-level administrative units that leave some otherwise municipal administrative responsibilities and revenues to the prefectural administration.[40]
Politics regarding the use of nuclear energy
On February 27, 2012 three Kansai cities, Kyoto, Osaka and Kobe, jointly asked Kansai Electric Power Company to break its dependence on nuclear power. In a letter to KEPCO they also requested to disclose information on the demand and supply of electricity, and for lower and stable prices. The three cities were stockholders of the plant: Osaka owned 9% of the shares, while Kobe had 3% and Kyoto 0.45%. Toru Hashimoto, the mayor of Osaka, announced a proposal to minimize the dependence on nuclear power for the shareholders meeting in June 2012.[41]
On March 18, 2012 the city of Osaka decided as largest shareholder of Kansai Electric Power Co, that at the next shareholders-meeting in June 2012 it would demand a series of changes:
- that Kansai Electric would be split into two companies, separating power generation from power transmission
- a reduction of the number of the utility's executives and employees.
- the implementation of absolutely secure measurements to ensuring the safety of the nuclear facilities.
- the disposing of spent fuel.
- the installation of new kind of thermal power generation to secure non-nuclear supply of energy.
- selling all unnecessary assets including the stock holdings of KEPCO.
In this action Osaka had secured the support of two other cities and shareholders: Kyoto and Kobe, but with their combined voting-rights of 12.5 percent they were not certain of the ultimate outcome, because for this two-thirds of the shareholders would be needed to agree to revise the corporate charter.[42]
At a meeting held on April 10, 2012 by the "energy strategy council", formed by the city of Osaka and the governments of the prefectures, it became clear that at the end of the fiscal year 2011 some 69 employees of Kansai Electric Power Company were former public servants. "Amakudari" was the Japanese name for this practice of rewarding by hiring officials that formerly controlled and supervised the firm. Such people included the following:
- 13 ex-officials of the: Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
- 3 ex-officials of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry,
- 2 ex-officials of the Ministry of the Environment,
- 16 former policemen,
- 10 former fire-fighters,
- 13 former civil engineers.
Besides this, it became known that Kansai Electric had done about 600 external financial donations, to a total sum of about 1.695 billion yen:
- 70 donations were paid to local governments: to a total of 699 million yen
- 100 donations to public-service organizations: 443 million yen,
- 430 donations to various organizations and foundations: a total of 553 million yen
During this meeting some 8 conditions were compiled, that needed to be fulfilled before a restart of the No.3 and No.4 reactors Oi Nuclear Power Plant:
- the consent of the local people and government within 100 kilometer from the plant
- the installation of a new independent regulatory agency
- a nuclear safety agreement
- the establishment of new nuclear safety standards
- stress tests and evaluations based on these new safety rules [43]
Economy

The gross city product of Osaka in fiscal year 2004 was ¥21.3 trillion, an increase of 1.2% over the previous year. The figure accounts for about 55% of the total output in the Osaka Prefecture and 26.5% in the Kinki region. In 2004, commerce, services, and manufacturing have been the three major industries, accounting for 30%, 26%, and 11% of the total, respectively. The per capita income in the city was about ¥3.3 million, 10% higher than that of the Osaka Prefecture.[44] MasterCard Worldwide reported that Osaka ranks 19th among the world's leading cities and plays an important role in the global economy.[45]


The GDP in the greater Osaka area (Osaka and Kobe) is $341 billion. Osaka, along with Paris and London, has one of the most productive hinterlands in the world.[46]
Historically, Osaka was the center of commerce in Japan, especially in the middle and pre-modern ages. Nomura Securities, the first brokerage firm in Japan, was founded in the city in 1925, and Osaka still houses a leading futures exchange. Many major companies have since moved their main offices to Tokyo. However, several major companies, such as Panasonic, Sharp, and Sanyo, are still headquartered in Osaka. Recently, the city began a program, headed by mayor Junichi Seki, to attract domestic and foreign investment.[47]
The Osaka Securities Exchange, specializing in derivatives such as Nikkei 225 futures, is based in Osaka. The merger with JASDAQ will help the Osaka Securities Exchange become the largest exchange in Japan for start-up companies.[48]
According to global consulting firm Mercer, Osaka was the second most expensive city for expatriate employees in the world in 2009. It jumped up nine places from 11th place in 2008 and was the eighth most expensive city in 2007. However, it was not ranked in the top ten places of the list in 2013.[49][50] The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) ranked Osaka as the second most expensive city in the world in its 2013 Cost of Living study.[51]
Transportation

Greater Osaka has an extensive network of railway lines, comparable to that of Greater Tokyo. Major stations within the city include Umeda (梅田), Namba (難波), Shinsaibashi (心斎橋), Tennōji (天王寺), Kyōbashi (京橋), and Yodoyabashi (淀屋橋).
Osaka connects to its surrounding cities and suburbs via the JR West Urban Network as well as numerous private lines such as Keihan Electric Railway, Hankyu Railway, Hanshin Electric Railway, Kintetsu Railway, and Nankai Electric Railway.
The Osaka Municipal Subway system alone ranks 8th in the world by annual passenger ridership, serving over 912 million people annually (a quarter of Greater Osaka Rail System's 4 billion annual riders), despite being only 8 of more than 70 lines in the metro area.
All Shinkansen trains including Nozomi stop at Shin-Osaka Station and provide access to other major cities in Japan, such as Kobe, Kyoto, Nagoya, Yokohama, and Tokyo.
Regular bus services are provided by Osaka Municipal Transportation Bureau (the City Bus), as well Hankyu, Hanshin and Kintetsu, providing a dense network covering most parts of the city.
Osaka is served by two airports outside of the city, Kansai International Airport (IATA: KIX) which handles primarily international passenger flights and Osaka International Airport (IATA:ITM) which handles mostly domestic services and some international cargo flights.
Due to its geographical position, Osaka's international ferry connections are far greater than that of Tokyo, with international service to Shanghai, Tianjin, Korea along with domestic routes to Kitakyushu, Kagoshima, Miyazaki and Okinawa.
Culture and lifestyle




Shopping and culinary
Osaka has a large number of wholesalers and retail shops: 25,228 and 34,707 respectively in 2004, according to the city statistics.[52] Many of them are concentrated in the wards of Chuō (10,468 shops) and Kita (6,335 shops). Types of shops vary from malls to conventional shōtengai shopping arcades, built both above- and underground.[53] Shōtengai are seen across Japan, and Osaka has the longest one in the country.[54] The Tenjinbashi-suji arcade stretches from the road approaching the Tenmangū shrine and continues for 2.6 km (1.6 miles) going north to south. The stores along the arcade include commodities, clothing, and catering outlets.
Other shopping areas include Den Den Town, the electronic and manga/anime district, which is comparable to Akihabara; the Umeda district, which has the Hankyu Sanbangai shopping mall and Yodobashi Camera, a huge electrical appliance store that offers a vast range of fashion stores, restaurants, and a Shonen Jump store.
Osaka is known for its food, in Japan and abroad. Author Michael Booth and food critic François Simon of Le Figaro have suggested that Osaka is the food capital of the world.[55] Osakans' love for the culinary is made apparent in the old saying "Kyotoites are financially ruined by overspending on clothing, Osakans are ruined by spending on food."[56] Regional cuisine includes okonomiyaki (お好み焼き, pan-fried batter cake), takoyaki (たこ焼き, octopus in fried batter), udon (うどん, a noodle dish), as well as the traditional oshizushi (押し寿司, pressed sushi), particularly battera (バッテラ, pressed mackerel sushi).
Osaka is known for its fine sake, which is made with fresh water from the prefecture's mountains.[57] Osaka's culinary prevalence is the result of a location that has provided access to high quality ingredients, a high population of merchants, and proximity to the ocean and waterway trade.[58] In recent years, Osaka has started to garner more attention from foreigners with the increased popularity of cooking and dining in popular culture.[59]
Other shopping districts include:
- American Village (Amerika-mura or "Ame-mura") – fashion for young people
- Dōtonbori – part of Namba district and considered heart of the city
- Namba – main shopping, sightseeing, and restaurant area
- Shinsaibashi – luxury goods and department stores
- Umeda – theaters, boutiques, and department stores near the train station
Entertainment and performing arts

- Osaka is home to the National Bunraku Theatre,[60] where traditional puppet plays, bunraku, are performed.
- At Osaka Shochiku-za, close to Namba station, kabuki can be enjoyed as well as manzai.
- At Shin-kabuki-za, formerly near Namba and now near Uehommachi area, enka concerts and Japanese dramas are performed.
- Yoshimoto Kogyo, a Japanese entertainment conglomarate operates a hall in the city for manzai and other comedy shows: the Namba Grand Kagetsu hall.
- The Hanjō-tei opened in 2006, dedicated to rakugo. The theatre is in the Ōsaka Tenman-gū area.
- Umeda Arts Theater opened in 2005 after relocating from its former 46-year-old Umeda Koma Theater. The theater has a main hall with 1,905 seats and a smaller theater-drama hall with 898 seats. Umeda Arts Theatre stages various type of performances including musicals, music concerts, dramas, rakugo, and others.
- The Symphony Hall, built in 1982, is the first hall in Japan designed specially for classical music concerts. The Hall was opened with a concert by the Osaka Philharmonic Orchestra, which is based in the city. Orchestras such as the Berlin Philharmonic and Vienna Philharmonic have played here during their world tours as well.
- Osaka-jō Hall is a multi-purpose arena in Osaka-jō park with a capacity for up to 16,000 people. The hall has hosted numerous events and concerts including both Japanese and international artists.
- Near City Hall in Nakanoshima Park, is Osaka Central Public Hall, a Neo-Renaissance-style building first opened in 1918. Re-opened in 2002 after major restoration, it serves as a multi-purpose rental facility for citizen events.
- The Osaka Shiki Theatre[61] is one of the nine private halls operated nationwide by the Shiki Theatre, staging straight plays and musicals.
- Festival Hall was a hall hosting various performances including noh, kyōgen, kabuki, ballets as well as classic concerts. The Bolshoi Ballet and the Philharmonia are among the many that were welcomed on stage in the past. The hall has closed at the end of 2008, planned to re-open in 2013 in a new facility.
Annual festivals


One of the most famous festivals held in Osaka, the Tenjin Matsuri, is held on July 24 and 25 (Ikukunitama Shrine). Other festivals in Osaka include the Aizen Matsuri (June 30–July 2, Shouman'in Temple), the Sumiyoshi Matsuri (July 30–August 1, Sumiyoshi Taisha), Shōryō-e (April 22, Shitennō-ji) and Tōka-Ebisu (January 9–10, Imamiya Ebisu Jinja). The annual Osaka Asian Film Festival takes place in Osaka every March.
Museum and galleries
The National Museum of Art (NMAO) is a subterranean Japanese and international art museum, housing mainly collections from the post-war era and regularly welcoming temporary exhibitions. Osaka Science Museum is in a five storied building next to the National Museum of Art, with a planetarium and an OMNIMAX theatre. The Museum of Oriental Ceramics holds more than 2,000 pieces of ceramics, from China, Korea, Japan and Vietnam, featuring displays of some of their Korean celadon under natural light. Osaka Municipal Museum of Art is inside Tennōji park, housing over 8,000 pieces of Japanese and Chinese paintings and sculptures. The Osaka Museum of History, opened in 2001, is located in a 13-story modern building providing a view of Osaka Castle. Its exhibits cover the history of Osaka from pre-history to the present day. Osaka Museum of Natural History houses a collection related to natural history and life.
Sports

Osaka hosts four professional sport teams: one of them is the Orix Buffaloes, a Nippon Professional Baseball team, playing its home games at Kyocera Dome Osaka. Another baseball team, the Hanshin Tigers, although based in Nishinomiya, Hyōgo, plays a part of its home games in Kyocera Dome Osaka as well, when their homeground Koshien Stadium is occupied with the annual National High School Baseball Championship games during summer season. There are two J.League clubs, Gamba Osaka, plays its home games at Suita City Football Stadium. Another club Cerezo Osaka, plays its home games at Kincho Stadium. The city is home to Osaka Evessa, a basketball team that plays in the bj league. Evessa has won the first three championships of the league since its establishment. Kintetsu Liners, a rugby union team, play in the Top League. After winning promotion in 2008-09, they will again remain in the competition for the 2009-10 season. Their base is the Hanazono Rugby Stadium.
The Haru Basho (春場所, "Spring Tournament"), one of the six regular tournaments of professional sumo, is held annually in Osaka at Osaka Prefectural Gymnasium.
Another major annual sporting event that takes place is Osaka is Osaka International Ladies Marathon. Held usually at the end of January every year, the 42.195 km (26.219 miles) race starts from Nagai Stadium, runs through Nakanoshima, Midōsuji and Osaka castle park, and returns to the stadium. Another yearly event held at Nagai Stadium is the Osaka Gran Prix Athletics games operated by the International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF) in May. The Osaka GP is the only IAAF games annually held in Japan.
Osaka is the home of the 2011 created Japan Bandy Federation and the introduction of bandy, in the form of rink bandy, was made in the city.[62] In July 2012 the first Japan Bandy Festival was organised.[63]
Media

Osaka serves as one of the media hubs for Japan, housing headquarters of many media-related companies. Abundant television production takes place in the city and every nationwide TV network (with the exception of TXN network) registers its secondary-key station in Osaka. All five nationwide newspaper majors also house their regional headquarters, and most local newspapers nationwide have branches in Osaka. However major film productions are uncommon in the city. Most major films are produced in nearby Kyoto or in Tokyo. The Ad Council Japan is based in Osaka.
Newspapers
All the five nationwide newspaper majors of Japan, the Asahi Shimbun, Mainichi Shimbun, Nihon Keizai Shimbun, Sankei Shimbun and Yomiuri Shimbun,[64] have their regional headquarters in Osaka and issue their regional editions. Furthermore, Osaka houses Osaka Nichi-nichi Shimbun, its newspaper press. Other newspaper related companies located in Osaka include, the regional headquarters of FujiSankei Business i.;Houchi Shimbunsha; Nikkan Sports; Sports Nippon, and offices of Kyodo News Jiji Press; Reuters; Bloomberg L.P..
Television and radio
The five TV networks are represented by Asahi Broadcasting Corporation (ANN), Kansai Telecasting Corporation (FNN), Mainichi Broadcasting System, Inc. (JNN), Television Osaka, Inc. (TXN) and Yomiuri Telecasting Corporation (NNN), headquartered in Osaka. NHK has also its regional station based in the city. AM Radio services are provided by NHK as well as the ABC Radio (Asahi Broadcasting Corporation), MBS Radio (Mainichi Broadcasting System, Inc.) and Radio Osaka (Osaka Broadcasting Corporation) and headquartered in the city. FM services are available from NHK, FM OSAKA, FM802 and FM Cocolo, the last providing programs in multiple languages including English.
As of February 2009, the city is fully covered by terrestrial digital TV broadcasts[65]
Publishing companies
Osaka is home to many publishing companies including: Examina, Izumi Shoin, Kaihou Shuppansha, Keihanshin Elmagazine, Seibundo Shuppan, Sougensha, and Toho Shuppan.
Places of interest
Tourist attractions include:



Amusement parks
- Osaka Aquarium Kaiyukan – An aquarium located in Osaka Bay, containing 35,000 aquatic animals in 14 tanks, the largest of which holds 5,400 tons of water and houses a variety of sea animals including whale sharks. This tank is the world's second-largest aquarium tank, behind the Georgia Aquarium, whose largest tank holds approximately 29,000 tons of water.
- Tempozan Ferris Wheel - A 112m tall Ferris wheel located next to the aquarium in the bay area.
- Tennōji Zoo
- Universal Studios Japan
- HEP Five - A shopping/amusement plaza in Umeda featuring a Sega Joypolis and rooftop Ferris wheel offering views of the city.
- Umeda Sky Building – Twin 173 m skyscrapers bridged by a rooftop "Floating Garden" observatory presenting a 360-degree panoramic view of Osaka. Popular for photographs, the structure also houses an underground mall with restaurants styled after the early Showa period of the 1920s.
Parks
- Nakanoshima Park: About 10.6 ha. In the vicinity of the City Hall
- Osaka Castle Park: About 106 ha. Includes Osaka-jō Hall, a Japanese plum blossom (Ume) garden, a Cherry Blossom garden, and more. It is a hotspot for migrating birds in the spring and autumn.
- Sumiyoshi Park
- Tennōji Park: About 28 ha. Includes Tennōji Zoo; an art museum (established by contribution from Sumitomo family in 1936); and a Japanese garden, Keitaku-en (慶沢園). Keitaku-en was constructed in 1908 by Jihei Ogawa (小川治兵衛, Hiragana: おがわ じへえ), an illustrious gardener in Japan. This was originally one of Sumitomo family's gardens until 1921.
- Utsubo Park
- Nagai Park: The 2007 IAAF World Championships in Athletics were held at the Nagai Stadium, located in this park.
- Tsurumi-Ryokuchi Park with the Sakuya Konohana Kan was the site of the flower expo in 1990.
Temples, shrines, and other historical sites


- Osaka Castle
- Sankō Shrine
- Shitennō-ji – The oldest buddhist temple in Japan, established in 593 AD by Prince Shōtoku
- Sumiyoshi taisha One of the oldest Shinto shrines, built in 211 AD.[66]
- Tamatsukuri Inari Shrine
- Ōsaka Tenmangū Shrine
- Osaka Peace Pagoda, built by Nipponzan Myohoji in 1963.
- Imamiya Ebisu
Entertainment
- Dōtonbori - Osaka's primary tourist and nightlife area
- Namba and Shinsaibashi districts - Located side by side in Minami, offering shopping, restaurants, bars and nightclubs running 24/7
- Higashi-Dori area - A network of shōtengai in Umeda with numerous restaurants, bars, and nightlife options
- Shin-michi/Kitashinchi district - Well known for its upscale dining and hostess clubs, also offers more reasonably priced izakaya as well as bars and nightclubs that cater to tourists and foreigners
- Shinsekai - Earthy eating/drinking district, built around the Tsūtenkaku Tower and famous for cheap kushikatsu
- Den Den Town - An electronics/anime district analogous to Tokyo's Akihabara, Den Den Town also features maid cafes, bars, and other venues of entertainment
- Sankaku Koen (Triangle Park) - A popular youth meeting spot in Amerika-mura. Eccentric fashions and local skateboarders abound
- Jūsō - Popular working class bar/nightlife district
- Kyobashi - A commercial area and shotengai with a diverse variety of izakaya
- Zepp Osaka - A live stage venue in the Osaka Bay area that hosts many big-name musical acts and events
- Doyama - Considered a hub for Osaka's LGBT community
- Tobita - A red-light district
Education


Public elementary and junior high schools in Osaka are operated by the city of Osaka. Its supervisory organization on educational matters is Osaka City Board of Education.[67] Likewise, public high schools are operated by the Osaka Prefectural Board of Education.
Osaka city once had a large number of universities and high schools, but because of growing campuses and the need for larger area, many chose to move to the suburbs, including Osaka University.[68]
Historically foreign expatriates in the Kansai region preferred to live in Kobe rather than Osaka. As a result, until 1991 the Osaka area has no schools catering to expatriate children.[69] Osaka International School of Kwansei Gakuin, founded in 1991, is located in nearby Minoh,[70] and it was the first international school in the Osaka area.[69] The Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake of 1995 caused a decline in demand for international schools, as there were about 2,500 U.S. nationals resident in Osaka after the earthquake while the pre-earthquake number was about 5,000. American Chamber of Commerce in Japan (ACCJ) Kansai chapter president Norman Solberg stated that since 2002 the numbers of expatriates in Kansai were recovering "but the fact is there is still a persistent exodus to Tokyo."[71] In 2001 the city of Osaka and YMCA established the Osaka YMCA International School.[69]
Colleges and universities include:
- Kansai University
- Morinomiya University of Medical Sciences
- Osaka City University
- Osaka University of Economics
- Osaka Institute of Technology
- Osaka Jogakuin College
- Osaka Seikei University
- Osaka University of Arts, Minamikawachi District, Osaka
- Osaka University of Comprehensive Children education
- Osaka University of Education
- Soai University
- Tokiwakai Gakuen University
Libraries
- International Institute for Children's Literature, Osaka[72]
- Osaka Prefectural Nakanoshima Library
- Osaka Municipal Central Library
Learned society
- The Japanese Academy of Family Medicine
International relations

Twin towns and sister cities
Osaka is twinned with the following cities around the world.[73]
 San Francisco, United States (since 1957)
San Francisco, United States (since 1957) São Paulo, Brazil (since 1969)[74][75]
São Paulo, Brazil (since 1969)[74][75] Chicago, United States (since 1973)
Chicago, United States (since 1973) Shanghai, China (since 1974)
Shanghai, China (since 1974) Melbourne, Australia (since 1978)
Melbourne, Australia (since 1978) Saint Petersburg, Russia (since 1979)[76]
Saint Petersburg, Russia (since 1979)[76] Milan, Italy (since 1981)[77]
Milan, Italy (since 1981)[77] Hamburg, Germany (since 1989)
Hamburg, Germany (since 1989) Kanpur, India (since 1998)[citation needed]
Kanpur, India (since 1998)[citation needed]
Osaka also has the following friendship and cooperation cities.[78]
 Buenos Aires, Argentina (since 1998)
Buenos Aires, Argentina (since 1998) Budapest, Hungary (since 1998)[79]
Budapest, Hungary (since 1998)[79] Busan, South Korea (since 2008)[80]
Busan, South Korea (since 2008)[80]
Business partner cities
Osaka's business partnerships are:[81]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d "Historical Overview, the City of Osaka official homepage". Archived from the original on March 22, 2009. Retrieved 2009-03-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) Navigate to the equivalent Japanese page (大阪市の歴史 タイムトリップ20,000年 (History of Osaka, A timetrip back 20,000 years))[1] for additional information. - ^ Aprodicio A. Laquian (2005). Beyond metropolis: the planning and governance of Asia's mega-urban regions. Washington, D.C: Woodrow Wilson Center Press. p. 27. ISBN 0-8018-8176-5.
- ^ edited by James L. McClain and Wakita Osamu (1999). Osaka, the merchants' capital of early modern Japan. Ithaca, N.Y: Cornell University Press. p. 67. ISBN 0-8014-3630-3.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Robert C. Hsu (1999). The MIT encyclopedia of the Japanese economy. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press. p. 327. ISBN 0-262-08280-2.
- ^ Wada, Stephanie (2003). Tsuneko S. Sadao, Stephanie Wada, Discovering the Arts of Japan: A Historical Overview. ISBN 978-4-7700-2939-3. Retrieved 2007-03-25.
- ^ 大石慎三郎「日本の遷都の系譜」、『學習院大學經濟論集』第28巻第3号、学習院大学、1991年10月、 31-41頁、 NAID 110007523974。P.31
- ^ "史跡 難波宮跡, 財団法人 大阪都市協会 (Naniwa Palace Site, by Osaka Toshi Kyokai)" (in Japanese). Retrieved 2007-03-25.
- ^ This name was historically written as 浪華 or 浪花, with the same pronunciation, though these renderings are uncommon today.
- ^ edited by Peter G. Stone and Philippe G. Planel (1999). The constructed past: experimental archaeology, education, and the public. London: Routledge in association with English Heritage. p. 68. ISBN 0-415-11768-2.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ a b "HISTORICAL OVERVIEW - DISCOVER - OSAKA INFO -Osaka Visitors' Guide".
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on March 22, 2009. Retrieved March 21, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "A Guide to the Ukiyo-e Sites of the Internet".
- ^ C. Andrew Gerstle, Kabuki Heroes on the Osaka Stage 1780-1830 (2005)
- ^ Ebrey, Patricia Buckley; Walthall, Anne; Palais, James B. (2006). East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. 400. ISBN 0-618-13384-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Jansen, Marius B; Hall, John Whitney (1989). ''The Cambridge History of Japan'' p.304. Books.google.com. ISBN 978-0-521-22356-0. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ Richard Torrance, "Literacy and Literature in Osaka, 1890-1940," The Journal of Japanese Studies 31#1 (Winter 2005), pp. 27-60
- ^ "Osaka city". Osaka-info.jp. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ Chisato Hotta, "The Construction of the Korean Community in Osaka between 1920 and 1945: A Cross-Cultural Perspective." PhD dissertation U. of Chicago 2005. 498 pp. DAI 2005 65(12): 4680-A. DA3158708 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
- ^ Blair A. Ruble, Second Metropolis: Pragmatic Pluralism in Gilded Age Chicago, Silver Age Moscow, and Meiji Osaka. (2001)
- ^ Richard Torrance, "Literacy and Literature in Osaka, 1890-1940," Journal of Japanese Studies 31#1 (Winter 2005), p.27-60 in Project MUSE
- ^ "GM had early start in Japan but was hobbled by nationalism".
- ^ Kingo Tamai, "Images of the Poor in an Official Survey of Osaka, 1923-1926." Continuity and Change 2000 15(1): 99-116. ISSN 0268-4160 Fulltext: Cambridge UP
- ^ Andy Raskin, "The Ramen King and I: How the Inventor of Instant Noodles Fixed My Love Life".
- ^ http://www.city.osaka.jp/keikakuchousei/toukei/G000/Gyh19/Gb00/Gb00.html
- ^ Agency, 気象庁 Japan Meteorological. "気象庁 - 過去の梅雨入りと梅雨明け(近畿)".
- ^ "平年値(年・月ごとの値)". Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved June 28, 2013.
- ^ "World Weather Information Service - Osaka". World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved June 28, 2013.
- ^ Discover Japan. Lonely Planet. 2010. pp. 146–. ISBN 9781741799965.
- ^ a b "Osaka Travel: Kita (Umeda)".
- ^ a b "Osaka Travel: Minami (Namba)".
- ^ "Kamagasaki: Japan's biggest slum". 8 April 2014.
- ^ "Osaka Travel: Osaka Bay Area".
- ^ a b Eiichi Watanabe, Dan M. Frangopol, Tomoaki Utsunomiya (2004). Bridge Maintenance, Safety, Management and Cost: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Bridge Maintenance, Safety and Management. Kyoto, Japan: Taylor & Francis. p. 195. ISBN 978-90-5809-680-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "More About Osaka, Osaka City Government".
- ^ "2005 Population Census". Statistics Bureau, Director-General for Policy Planning (Statistical Standards) and Statistical Research and Training Institute, Japan. Retrieved 2009-02-18.
- ^ Prasad Karan, Pradyumna; Kristin Eileen Stapleton (1997). The Japanese City. University Press of Kentucky. pp. 79–81. ISBN 0-8131-2035-7.
- ^ JOHNSTON, ERIC (June 29, 2002). "Tsuruhashi, home of 'exotic' Korea in Osaka". The Japan Times Online. The Japan Times. Retrieved 2009-02-18.
- ^ Karan, Pradyumna Prasad; Kristin Eileen Stapleton. The Japanese City. University Press of Kentucky. p. 124. ISBN 0-8131-2035-7.
- ^ "Osaka City Council homepage". City.osaka.lg.jp. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ The Japan Times, July 31, 2012: Bill to transform Osaka government jointly submitted to Diet
- ^ The Mainichi Shimbun (27 February 2012)3 major Kansai cities aim to break dependence on nuclear power
- ^ The Mainichi Shimbun (19 March 2012)Osaka aims to end Kansai Electric's nuclear power ops as shareholder
- ^ The Mainichi Shimbun (10 April 2012) Kansai Electric, affiliates had 69 ex-bureaucrats employed as execs as of end of fiscal 2011
- ^ "大阪市データネット 市民経済計算 (Osaka City Datanet: Osaka City Economy)" (in Japanese). Retrieved 2007-03-25.
- ^ "Mastercard - Global Leading Company in Payment Solutions Offering Credit, Debit, Prepaid Cards & More" (PDF).
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 9, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Osaka aims to stem exodus of firms to Tokyo". Retrieved June 1, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)[dead link] - ^ 経営に資する統合的内部監査. "大証との経営統合、ようやく決着 ジャスダック : J-CASTニュース". J-cast.com. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ "Worldwide Cost of Living survey 2009". Mercer.com. 2009-07-07. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ "2013 Cost of Living Rankings". Mercer. Mercer LLC. 2013. Retrieved 23 February 2014.
- ^ George Arnett; Chris Michael (14 February 2014). "The world's most expensive cities". The Guardian. Retrieved 23 February 2014.
- ^ http://www.city.osaka.jp/keikakuchousei/toukei/G000/Gyh17/Ga00/Ga00.html
- ^ Reiber, Beth; Janie Spencer (2008). Frommer's Japan. Frommer's. p. 388. ISBN 0-470-18100-1.
- ^ [2] Archived December 22, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Booth, Michael (2009-07-13). "Osaka - the world's greatest food city". The Guardian.
- ^ Shinbunsha, Asahi (1979). Japan Quarterly, Asahi Shinbunsha 1954. Retrieved 2007-03-25.
- ^ "Superior brand sake : Food Library - Kuidaore Osaka".
- ^ "The Roots : Food Library - Kuidaore Osaka".
- ^ Osaka Food Guide, The City Lane
- ^ "National Theatre of Japan". Ntj.jac.go.jp. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ "劇団四季 サイトインフォメーション Theatres". Shiki.gr.jp. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ Bandy came to Japan!
- ^ BANDY Festival 2012 in OSAKA
- ^ The five largest newspapers by number of circulation in Japan in alphabetical order. Mooney, Sean; ebrary, Inc (2000). 5,110 Days in Tokyo and Everything's Hunky-dory. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 99–104. ISBN 1-56720-361-2.
- ^ See the Association for Promotion of Digital Broadcasting web page for the coverage map.
- ^ Dodd, Jan; Simon Richmond (2001). The Rough Guide to Japan. Rough Guides. p. 446. ISBN 1-85828-699-9.
- ^ [3] Archived March 10, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "History of Education in Osaka 大阪市の教育史 osaka-shi no kyōikushi" (in Japanese). Archived from the original on April 6, 2009. Retrieved 2009-02-18.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Stewart, Alex. "educating kansai" (Archive). The Journal of the American Chamber of Commerce in Japan (Jānaru), Volume 40, Issues 7-12. The American Chamber of Commerce in Japan (ACCJ), 2003. p. 43.
- ^ "School Profile 2014-2015" (Archived March 6, 2016, at the Wayback Machine). Osaka International School of Kwansei Gakuin. Retrieved on November 1, 2015.
- ^ Stewart, Alex. "education kansai" (Archive). The Journal of the American Chamber of Commerce in Japan (Jānaru), Volume 40, Issues 7-12. The American Chamber of Commerce in Japan (ACCJ), 2003. p. 41.
- ^ [4] Archived February 14, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Sister Cities, the official website of the Osaka city". Archived from the original on March 23, 2009. Retrieved 2009-08-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Pesquisa de Legislação Municipal - No 14471". Prefeitura da Cidade de São Paulo [Municipality of the City of São Paulo] (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 2011-10-18. Retrieved 2013-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Lei Municipal de São Paulo 14471 de 2007 WikiSource Template:Pt icon
- ^ "Saint Petersburg in figures - International and Interregional Ties". Saint Petersburg City Government. Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- ^ "Milano - Città Gemellate". Municipality of Milan. Retrieved 2009-07-17.
- ^ "Friendship and Cooperation Cities, the official website of the Osaka city". Archived from the original on March 23, 2009. Retrieved 2009-08-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Sister cities of Budapest" (in Hungarian). Official Website of Budapest. Archived from the original on March 9, 2005. Retrieved 2009-07-01.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "大阪市市政 友好協力都市(釜山広域市)(Busan (Friendship Cooperation City), the official website of Osaka city)". Retrieved 2009-08-05.
- ^ "Business Partner Cities (BPC), the official website of Osaka city". Retrieved 2009-08-05.
Further reading
- Gerstle, C. Andrew. Kabuki Heroes on the Osaka Stage 1780-1830 (2005).
- Hanes, Jeffrey. The City as Subject: Seki Hajime and the Reinvention of Modern Osaka (2002) online edition
- Hauser, William B. "Osaka: a Commercial City in Tokugawa Japan." Urbanism past and Present 1977-1978 (5): 23-36.
- Hein, Carola, et al. Rebuilding Urban Japan after 1945. (2003). 274 pp.
- Hotta, Chisato. "The Construction of the Korean Community in Osaka between 1920 and 1945: A Cross-Cultural Perspective." PhD dissertation U. of Chicago 2005. 498 pp. DAI 2005 65(12): 4680-A. DA3158708 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
- Lockyer, Angus. "The Logic of Spectacle C. 1970," Art History, Sept 2007, Vol. 30 Issue 4, p571-589, on the international exposition held in 1970
- McClain, James L. and Wakita, Osamu, eds. Osaka: The Merchants' Capital of Early Modern Japan. (1999). 295 pp. online edition
- Michelin Red Guide Kyoto Osaka Kobe 2011 (2011)
- Najita, Tetsuo. Visions of Virtue in Tokugawa Japan: The Kaitokudo Merchant Academy of Osaka. (1987). 334 pp. online edition
- Rimmer, Peter J. "Japan's World Cities: Tokyo, Osaka, Nagoya or Tokaido Megalopolis?" Development and Change 1986 17(1): 121-157. ISSN 0012-155X
- Ropke, Ian Martin. Historical Dictionary of Osaka and Kyoto. (1999) 273pp
- Ruble, Blair A. Second Metropolis: Pragmatic Pluralism in Gilded Age Chicago, Silver Age Moscow, and Meiji Osaka. (2001). 464 pp.
- Torrance, Richard. "Literacy and Literature in Osaka, 1890-1940," The Journal of Japanese Studies 31#1 (Winter 2005), pp. 27–60 in Project Muse
External links
- Osaka City official website Template:En icon
- Official Osaka Tourist Guide
- . . 1914.
 Geographic data related to Osaka at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Osaka at OpenStreetMap


